Abstract
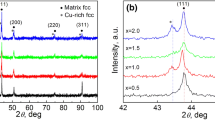
In this article, the microstructure, hardness, and corrosion resistance of the Al0.3CrFe1.5MnNi0.5Ti x and Al0.3CrFe1.5MnNi0.5Si x (x = 0, 0.2, 0.5, 1.0) high-entropy alloys were investigated via X-ray diffraction (XRD), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), digital display Vickers hardness tester, and electrochemical technique. These alloys are mainly composed of BCC solid-solution structure. When adding high content of Ti or Si element (x ≥ 0.5), some intermetallic compounds are found in the microstructure, which makes the alloys have a high hardness, high brittleness, and easy cracking. While the alloys with low content of Ti or Si (x = 0.2) have a hardness of HV 420–HV 430, and its hardness increases about 14 % compared with that of Al0.3CrFe1.5MnNi0.5. Electrochemical results in 3.5 % NaCl solution show that the alloying elements Ti and Si have a negative influence on the corrosion resistance of the Al0.3CrFe1.5MnNi0.5 alloys.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yeh JW. Recent progress in high-entropy alloys. Ann Chim Sci Mater. 2006;31(6):633.
Cantor B, Chang ITH, Knight P, Vincent AJB. Microstructural development in equiatomic multicomponent alloys. Mater Sci Eng A. 2004;375–377:213.
Zhu C, Lu ZP, Nieh TG. Incipient plasticity and dislocation nucleation of FeCoCrNiMn high-entropy alloy. Acta Mater. 2013;61(8):2993.
Tong CJ, Chen YL, Chen SK, Yeh JW, Shun TT, Tsau CH, Lin SJ, Chang SY. Microstructure characterization of Al x CoCrCuFeNi high-entropy alloy system with multiprincipal elements. Metall Mater Trans A. 2005;36(4):881.
Li C, Li JC, Zhao M, Jiang Q. Effect of alloying elements on microstructure and properties of multiprincipal elements high-entropy alloys. J Alloy Compd. 2009;475(1–2):752.
Chen TK, Wong MS, Shun TT, Yeh JW. Nanostructured nitride films of multi-element high-entropy alloys by reactive DC sputtering. Surf Coat Technol. 2005;200(5–6):1361.
Huang YS, Chen L, Lui HW, Cai MH, Yeh JW. Microstructure, hardness, resistivity and thermal stability of sputtered oxide films of AlCoCrCu0.5NiFe high-entropy alloy. Mater Sci Eng A. 2007;457(1–2):77.
Tong CJ, Chen MR, Chen SK, Yeh JW, Shun TT, Lin SJ, Chang SY. Mechanical performance of the Al x CoCrCuFeNi high-entropy alloy system with multiprincipal elements. Metall Mater Trans A. 2005;36(5):1263.
Zhou YJ, Zhang Y, Wang YL, Chen GL. Microstructure and compressive properties of multicomponent Al x (TiVCrMnFeCoNiCu)100−x high-entropy alloys. Mater Sci Eng A. 2007;454–455:260.
Wen LH, Kou HC, Li JS, Chang H, Xue XY, Zhou L. Effect of aging temperature on microstructure and properties of AlCoCrCuFeNi high-entropy alloy. Intermetallics. 2009;17(4):266.
Chen YY, Hong UT, Shih HC, Yeh JW, Duval T. Electrochemical kinetics of the high entropy alloys in aqueous environments: a comparison with type 304 stainless steel. Corros Sci. 2005;47(11):2679.
Tsai CW, Tsai MH, Yeh JW, Yang CC. Effect of temperature on mechanical properties of Al0.5CoCrCuFeNi wrought alloy. J Alloy Compd. 2010;490(1–2):160.
Chen ST, Tang WY, Kuo YF, Chen SY, Tsau CH, Shun TT, Yeh JW. Microstructure and properties of age-hardenable Al x CrFe1.5MnNi0.5 alloys. Mater Sci Eng A. 2010;527(21–22):5818.
Shun TT, Du YC. Age hardening of the Al0.3CoCrFeNiC0.1 high entropy alloy. J Alloy Compd. 2009;478(1–2):269.
Ranganathan S. Alloyed pleasures: multimetallic cocktails. Curr Sci. 2003;85(10):1404.
Lee CP, Chen YY, Hsu CY, Yeh JW, Shih HC. Enhancing pitting corrosion resistance of Al x CrFe1.5MnNi0.5 high-entropy alloys by anodic treatment in sulfuric acid. Thin Solid Films. 2008;517(3):1301.
Lee CP, Chang CC, Chen YY, Yeh JW, Shih HC. Effect of the aluminium content of Al x CrFe1.5MnNi0.5 high-entropy alloys on the corrosion behaviour in aqueous environments. Corros Sci. 2008;50(7):2053.
Tang WY, Chuang MH, Chen HY, Yeh JW. Microstructure and mechanical performance of new Al0.5CrFe1.5MnNi0.5 high-entropy alloys improved by plasma nitriding. Surf Coat Technol. 2010;204(20):3118.
Zhang Y, Yang X, Liaw KP. Alloy design and properties optimization of high-entropy alloys. JOM. 2012;64(7):830.
Kittel C. Introduction to Solid State Physics. 7th ed. New York: Wiley; 1996. 673.
Takeuchi A, Inoue A. Classification of bulk metallic glasses by atomic size difference, heat of mixing and period of constituent elements and its application to characterization of the main alloying element. Mater Trans. 2005;46(12):2817.
Ren B, Liu ZX, Li DM, Shi L, Cai B, Wang MX. Effect of elemental interaction on microstructure of CuCrFeNiMn high entropy alloy system. J Alloy Compd. 2010;493(1–2):148.
Zhang Y, Zhou YJ, Lin JP, Chen GL, Liaw PK. Solid-solution phase formation rules for multi-component alloys. Adv Eng Mater. 2008;10(6):534.
Zhang Y, Zhou YJ, Wang YL, Chen GL. Solid solution alloys of AlCoCrFeNiTi x with excellent room-temperature mechanical properties. Appl Phys Lett. 2007;90(18):181904.
Zhu JM, Fu HM, Zhang HF, Wang AM, Li H, Hu ZQ. Synthesis and properties of multiprincipal component AlCoCrFeNiSi x alloys. Mater Sci Eng A. 2010;527(27–28):7210.
Chen MR, Lin SJ, Yeh JW, Chen SK, Huang YS, Chuang MH. Effect of vanadium addition on the microstructure, hardness, and wear resistance of Al0.5CoCrCuFeNi high-entropy alloy. Metall Mater Trans A. 2006;37(5):1363.
Hsu YJ, Chiang WC, Wu JK. Corrosion behavior of FeCoNiCrCu x high-entropy alloys in 3.5 % sodium chloride solution. Mater Chem Phys. 2005;92(1):112.
Qiu XW. Microstructure and properties of AlCrFeNiCoCu high entropy alloy prepared by powder metallurgy. J Alloy Compd. 2013;555:246.
Acknowledgments
This work was financially supported by the Post-doctoral Scientific Research Foundation of Zhengzhou University and Post-doctoral Scientific Research Foundation of China (No. 2013M541986).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ren, B., Zhao, RF., Liu, ZX. et al. Microstructure and properties of Al0.3CrFe1.5MnNi0.5Ti x and Al0.3CrFe1.5MnNi0.5Si x high-entropy alloys. Rare Met. 33, 149–154 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12598-014-0224-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12598-014-0224-4