Abstract
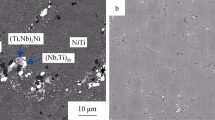
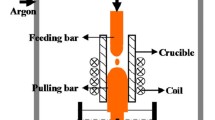
By liquid metal cooling (LMC) process, the Ni-43Ti-4Al-2Nb-2Hf (%, atomic fraction) alloy was directionally solidified (DS). The microstructure and tensile properties at room and elevated temperature were investigated. It was found that the DS process significantly improves the room temperature tensile strength, increasing by 70% compared with the as-cast alloy. After appropriate heat treatment (HT), the average tensile strength reaches above 1900 MPa, nearly twice of the as-cast one. At 800 and 900 °C, the tensile strengths are about 308 and 169 MPa, respectively.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Robert B., Shape-memory materials: a review of technology and applications, Assembly Automation, 2009, 29(3): 214.
Mehmet K., Nuri O., and Gül T., The effect of the combustion channels on the compressive strength of porous NiTi shape memory alloy fabricated by SHS as implant material, Current Opinion in Solid State and Materials Science, 2010 (14): 21.
Xu Z.Y., and Jiang B.H., Shape Memory Materials, Shanghai Jiaotong University Press, Shanghai, 2000: 75.
Yang Y.Z., Zhao X.Q., Meng L.J., Yang S.L., and Xu H.B., Microstructure and transformation behavior of Ni-Ti-Nb shape memory alloys with low Nb content, Acta Metall. Si., 2005, 41(6): 627.
Otsuka K., and Wayman C.M., Shape Memory Materials, Cambridge University Press, London, 1998: 51.
Koizumi Y., Ro Y., Nakazawa S., and Harada H., NiTi-base intermetallic alloys strengthened by Al substitution, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 1997, 223(2): 36.
Song X.Y., Li Y., Zhang F., and Li S.S., NiTiAl intermetallic alloys strengthened by Mo replacement, Chinese Journal of Aeronautics, 2010, 26(23): 715.
Zheng Y.R., Cai Y.L., and Ruan Z., Investigation of effect mechanism of hafnium and zirconium in high temperature materials, Journal of Aeronautical Materials, 2006, 26(3): 25.
Warren P., Murakami Y., and Koizumi Y., Phase separation in NiTi-Ni2TiAl alloy system, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 1997, 223A(12): 36.
Jung J., Ghosh G., and Olson G.B., A comparative study of precipitation behavior of Heusler phase (Ni2TiAl) from B2-TiNi in Ni-Ti-Al and Ni-Ti-AI-X (X= Hf, Pd, Pt, Zr) alloys, Acta Materialia, 2003, 51(20): 6341.
Xu J., Zhao X.Q., and Gong S.K., The influence of Nb diffusion on the oxidation behavior of TiNiAlNb alloys with different Ti/Ni ratio, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2007, 458(23): 381.
Meng L.J., Li Y., Zhao X.Q., and Xu H.B., Effect of Nb on strengthening mechanism of Ti-rich TiNiAl intermetallics, Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 2007, 28(5): 1206.
Meng L.J., Li Y., Zhao X.Q., and Xu H.B., The mechanical properties of intermetallic Ni50−x Ti50Alx alloys (x=6, 7, 8, 9), Intermetallics, 2007, 43(15): 814.
Xu H.B., Meng L.J., Xu J., Li Y., and Zhao X.Q., Mechanical properties and oxidation characteristics of TiNiAl(Nb) intermetallics, Intermetallics, 2007, 15(5): 778.
Zhao X.Q., Xu J., Tang L., and Gong S.K., High temperature oxidation behavior of NiTiNb intermetallic alloys, Intermetallics, 2007, 54(15): 1105.
Zhang H.R., Gao M., Tang X.X., and Zhang H., Interaction between Ti-47Al-2Cr-2Nb alloy and Y2O3 ceramic during directional solidification, Acta Metall. Sin., 2010, 46(7): 890.
Pan Q., Zheng L.J., Sang Y.R., Zhou L., Li Y., and Zhang H., Microstructural characteristics of directionally solidified alloys Ni-44Ti-5Al-2Nb-1Mo, Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 2011, 32(7): 1345.
Yang C.L., Zhang X.L., Zheng L.J., and Zhang H., Effect of heating temperature on microstructure of directionally solidified Ni-45Ti-5Al alloy, Hot Working Technology, 2011, 40(9): 71.
Pan Q., Zheng L.J., Sang Y.R., Li Y., Zhou L., and Zhang H., Effect of casting temperature on microstructure in a directionally solidified Ni-44Ti-5Al-2Nb-1Mo alloy, Rare Metals, 2011, 30(s): 349.
Sang Y.R., Zheng L.J., Pan Q., Zhou L., Li Y., and Zhang H., Microstructural characteristics of directionally solidified Ni-43Ti-4Al-2Nb-2Hf alloy, Rare Metals, 2011, 30(s): 340.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jiang, D., Zheng, L., Zhou, L. et al. High temperature tensile properties of directionally solidified Ni-43Ti-4Al-2Nb-2Hf alloy. Rare Metals 31, 328–331 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12598-012-0514-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12598-012-0514-7