Abstract
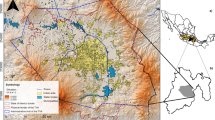
Groundwater (GW) contamination due to urbanization, industrialization and agriculture is a major environmental problem in India. The present case study aims to estimate the vulnerability of the aquifer with the help of GIS based DRASTIC method. A micro watershed, characterized by Granites and Gondwana Formation in the vicinity of Koradi, 15 km from Nagpur in Central India has been considered. The DRASTIC method accounts for hydrogeological parameters like depth to water, net recharge, aquifer media, soil media, impact of vadose zone and hydraulic conductivity. The DRASTIC index (DI) for GW vulnerability to pollution is calculated as the sum of the product of ratings and weights assigned to each of the parameter on the scale of 1 to 10 and 1 to 5 respectively. A Groundwater vulnerability map has been prepared using the Arc GIS software (Version 10.1) and it delineates the total study area into two vulnerable zones with vulnerability score ranging from 107 to 142 and indicates that 33% and 67% of the area lies in low and moderate vulnerability zones respectively. The vulnerability score as obtained is also verified with field data.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aller, L., Bennet, T., Lehr, J.H., Petty, R.J. and Hacket, G. (1985) DRASTIC: A standardized system for evaluating groundwater pollution using hydrological settings. Prepared by the National water Well Association for the US EPA Office of Research and Development, Ada.
Central Ground Water Board, (CGWB) (2015) Report on district groundwater management studies in parts of Nagpur districts, Maharashtra (Central region, Nagpur)
EPA, (2003) Contaminated sediment transport and fate methoding. Athens.
GEC, (1997) Report of the Groundwater Resource Estimation Committee.
Herlinger, J.R. and Viero, A.P. (2007) Groundwater vulnerability assessment in coastal plain of Rio Grande do Sul State, Brazil, using DRASTIC and adsorption capacity of soils. Environ. Geol., v.52, pp.819–829.
Khan, R. and Jhariya, D.C. (2019) Assessment of Groundwater Pollution Vulnerability Using GIS Based Modified DRASTIC Model in Raipur City, Chhattisgarh. Jour. Geol. Soc. India, v.93(3), pp.293–304. doi:https://doi.org/10.1007/s12594-019-1177-x
Prasad, K. and Shukla, J.P. (2014) Assessment of groundwater vulnerability using GIS-based DRASTIC technology for the basaltic aquifer of Burhner watershed, Mohgaon block, Mandla (India). Curr. Sci., v.107(10), pp.25.
Rahman, A. (2008) A GIS based DRASTIC method for assessing groundwater vulnerability in shallow aquifer in Aligarh, India. Appld. Geograp., v.28, pp.32–53.
Richards, R.P., Baker, D.B., Creamer, N.L., Kramer, J.W., Ewing, D.E., Merryfield, B.J. and Wallrabenstein, L.K. (1996) Wellwater quality, well vulnerability, and agricultural contamination in the midwestern United States. Jour. Environ. Qual., v.25, pp.389–402.
Singhal, D.C., Sharma, V.K., & Tungaria, M. (2016) Role of Groundwater Protection Planning in Groundwater Governance: A Case Study from North India. Jour. Geol. Soc. India, v.88(4), pp.449–463.
Sniffer, (2004) Development of a groundwater vulnerability screening methodology for the water framework directive. Project report code WFD 28, September 2004, Edinburgh
Suryanarayana, K. (1965) A new lower Gondwana basin between Nagpur and Kampee. Curr. Sci., v.34, pp.610–621.
Suryanarayana, K. (1968) The Nara-Pawangaon extension of the Bhokara basin between Nagpur and Kamptee. Indian Geological Science Association, Hyderabad, v.8, pp.67–78
Thirumalaivasan, D., Karmegam, M. and Venugopal, K. (2003) AHPDRASTIC: software for specific aquifer vulnerability assessment using DRASTIC method and GIS. Environ. Methodl. Softw., v.18, pp.645–656
Timmons, D.R. and Dylla, A.S. (1981) Nitrogen leaching as influenced by nitrogen management and supplemental irrigation level. Jour. Environ. Qual., v.10, pp.421–426
Umar, R., Ahmed, I. and Alam, F. (2009) Mapping Groundwater Vulnerable Zones Using Modified DRASTIC Approach of an Alluvial Aquifer in Parts of Central Ganga Plain, Western Uttar Pradesh. Jour. Geol. Soc. India, v.73(2), pp.193–201
USDA (1994) (United State Department of Agriculture), Permeability Key
Venkatesan, G., Pitchaikani, S. and Saravanan, S. (2019) Assessment of Groundwater Vulnerability Using GIS and DRASTIC for Upper Palar River Basin, Tamil Nadu. Jour. Geol. Soc. India, v.94(4), pp.387–394
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Janipella, R., Quamar, R., Sanam, R. et al. Evaluation of Groundwater Vulnerability to Pollution using GIS Based DRASTIC Method in Koradi, India — A Case Study. J Geol Soc India 96, 292–297 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12594-020-1549-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12594-020-1549-2