Abstract
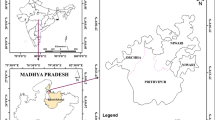
A detailed hydrogeological and hydrochemical study was carried out in Yamuna-Krishni sub-basin which is a part of the vast central Ganga plain. Groundwater is the major source of water supply for agricultural, domestic and industrial uses. The excess use of groundwater has resulted in depletion of water levels. The groundwater quality, too, has deteriorated in areas dominated by industrial activity. This has led to the preparation of a groundwater vulnerability map in relation to contamination. Groundwater vulnerability maps are valuable derivative maps that show, quantitatively or qualitatively, certain characteristics of the sub-surface environment that determine vulnerability of groundwater to contamination. The modified DRASTIC method was used to prepare vulnerability map. The parameters like depth to water, net recharge, aquifer media, soil media, impact of vadose zone, hydraulic conductivity and land use pattern, owing to its bearing on groundwater regime, were considered to prepare vulnerability map. The vulnerability index is computed as the sum of the products of weight and rating assigned to each of the input considered as above. The vulnerability index ranges from 140 to 180, and is classified into four classes i.e. 140–150, 150–160, 160–170 and 170–180 corresponding to low, medium, high and very high vulnerability zones respectively. Using this index, a groundwater vulnerability potential map was generated which shows that 7%, 40% and 53% of the study area falls in low, medium and high to very high vulnerability zones respectively. The map, thus generated, can be used as a tool for protection and management of aquifers from contamination.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aller, L., Lehr, J.H., Petty, R. and Bennett, T. (1987) DRASTIC: A standardized system to evaluate Groundwater Pollution using Hydrogeologic setting. sJour. Geol. Soc. India, v.29(1), pp.23–37.
Bhatnagar, N.C., Agashe, R.M. and Mishra, A.K. (1982) “Subsurface Mapping of Aquifer System” Water balance study of Upper Yamuna Basin, Section-Hydrogeology, Technical report No.2, Upper Yamuna Project, CGWB, NW region, Chandigarh.
Bhosle, B., Prakash, B., Awasthi, A.K., Singh, V.N. and Singh, S. (2007) Remote sensing-GIS and GPR studies of two active faults, Western Gangetic Plains, India. Jour. Appld. Geophys., v.61, pp.155–164.
Goosens, M. and van Damme, M. (1987) Vulnerability mapping in Flanders, Belgium. In: W. van Duijvenbooden and H.G. van Waegeningh (Eds.), Vulnerability of soil and groundwater to pollutants. TNO Committee on Hydrogeological Research, The Hague, Proc. and Information No.38, pp.355–360.
Herlinger, Jr. R. and Viero, A.P. (2007) Groundwater vulnerability assessment in coastal plain of Rio Grande do Sul State, Brazil, using drastic and adsorption capacity of soils. Environ. Geol., v.52, pp.819–829.
Hussain, M.H., Singhal, D.C., Joshi, H. and Kumar, S. (2006) Assessment of Groundwater vulnerability in a tropical alluvial interfluves, India. Bhu-Jal News Jour., v.21(1–4), pp.31–43.
Kumar, G. (2005) Geology of Uttar Pradesh and Uttranchal, Geological Society of India, Bangalore, pp. 267–291.
Qinghai, G., Yanxin, W., Xubo, G. and Teng, M. (2007) A new model (DRARCH) for assessing groundwater vulnerability to arsenic contamination at basin scale: a case study in Taiyuan basin, northern China. Environ. Geol., v.52, pp.923–932.
Todd, D.K. (1980) Groundwater Hydrology. 2nd Edition, John Wiley & Sons, New York, 535p.
Umar, R. and Ahmed, I. (2007) Hydrochemical characteristics of groundwater in parts of Krishni-Yamuna Basin, Muzaffarnagar district, U.P. Jour. Geol. Soc. India, v.69, pp.989–995.
Vias, J.M., Andreo, B., Perles, M.J. and Carrasco, F. (2005) A comparative study of four schemes for groundwater vulnerability mapping in a diffuse flow carbonate aquifer under Mediterranean climatic conditions. Environ. Geol., v.47, pp.586–595
Vrba, J. and Zeporozec, A. (1994) Guidebook on mapping Groundwater vulnerability. International contributions to Hydrogeology 16:129p.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Umar, R., Ahmed, I. & Alam, F. Mapping groundwater vulnerable zones using modified DRASTIC approach of an alluvial aquifer in parts of central Ganga plain, Western Uttar Pradesh. J Geol Soc India 73, 193–201 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12594-009-0075-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12594-009-0075-z