Abstract
Genetic variation in wheat is needed to address global food security challenges, particularly as climates change. Crop wild relatives are unique reservoirs of useful alleles for crop improvement and are important components of genebank collections. We analyzed how the derivatives of ‘goat grass’ (Aegilops tauschii) have been used to widen the genetic base for wheat breeding and surveyed wheat breeders to elicit adoption estimates. Synthetic hexaploid wheat (SHW) is derived by crossing goat grass with durum wheat, serving as a bridge to transfer desirable traits into modern varieties of bread wheat. Our data show that wheat scientists used 629 unique accessions from 15 countries for pre-breeding, producing 1577 primary SHWs. These derivatives represented 21% of the germplasm distributed by the genebank of the International Maize and Wheat Improvement Center between 2000 and 2018. Over the period, more than 10,000 samples of SHW were sent to 110 institutions in 40 countries, with rising numbers of synthetic hexaploid-derived lines (SHDL) included in international nurseries. Lines were screened for major diseases of wheat. At least 86 varieties have been selected from SHDL and released in 20 countries. Survey estimates indicate the highest scale of adoption in southwest China and India, with 34% and 7% of reported wheat area, respectively. These varieties demonstrate resistance to pests and pathogens, high yield potential, good quality attributes, and suitability for biofortified wheat.
Similar content being viewed by others
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
1 Introduction
Changes in climate and human society pose immense challenges for global food security. The world population is expected to reach 9.3 billion by the year 2050 with a doubling of global food demand (Barrett 2010; Dempewolf et al. 2014; Zhang et al. 2017). As a consequence, agricultural systems will be subject to ever-increasing pressure to supply more food under less optimal conditions. Wheat is among the four crops that provide 75% of calories to the world’s population. More than 4.5 billion people obtain 21% of their calories and 20% of their protein from wheat (Lobell et al. 2011; Ogbonnaya et al. 2013).
Lobell et al. (2011) reported that climate change slowed yield growth trends in wheat from 1980 to 2008. By 2080, the predicted increase of drought and extreme temperatures are expected to cause yield losses of 10–30% (Kumar et al. 2013). Diseases and insect pathogens also cause considerable yield loss and new, more virulent races and biotypesFootnote 1 are threatening global wheat production (Bahrani and Hagh Joo 2011).
Wheat yields are now reaching a plateau in many regions of the world, most likely due to a lack of genetic variation (King et al. 2018). Access to diverse genetic resources allows plant breeders to select and improve crops for desirable characteristics, including productivity; for example, it is estimated that half of the yield gains in cereals grown in the United States since the 1930s have been attributed to genetic improvement (Day-Rubenstein et al. 2005). In stressed environments, yield annual genetic gain in wheat yields reaches only 0.3–0.5%, though an increase of 2% per annum is needed to meet future global demand (Velu and Singh 2013). Future enhancement of wheat production can be achieved by increasing productivity per unit of area, but this will require the development of high-yielding, environmentally adapted wheat varieties with resistance to pests and a pathogens and tolerance to abiotic stresses such as heat and drought (Velu and Singh 2013; Zhang et al. 2017; King et al. 2018).
In order to combat the deleterious impact of climate change, breeders will require access to a large genepool, including landracesFootnote 2 and crop wild relativesFootnote 3 (CWR). Wheat wild relatives provide an important reservoir of genetic diversity distributed over a wide range of geographic conditions (Mickelbart et al. 2015). A survey of over 13 crops showed that CWR have been used extensively as a source of resistance to pests and diseases, while 11 wheat wild relatives were used for disease and pest resistance (Hajjar and Hodgkin 2007). Aegilops tauschii is the donor of stem rust resistance genes Sr33, Sr45, and Sr46 (Rouse et al. 2011). A high level of tolerance to drought, heat, and salinity has been found in Triticum dicoccum, Triticum diccoicoides, Aegilops tauschii, Aegilops geniculate, Aegilops speltoides, Aegilops searsi. and Aegilops biuncialis. Triticum turgidum subsp. dicoccoides was found to hold high genetic diversity for grain nutrients and protein content. Zinc and iron concentrations were twice as high in wild accessionsFootnote 4 as in the accessions of cultivated genotypes (Chatzav et al. 2010; Dempewolf et al. 2017).
The survival of CWR in their natural habitats is subject to several threats, including climate change and land reclamation and degradation. There is a need to reduce the loss of biodiversity by promoting in situ conservation and sustainable use according to the targets of the Convention on Biological Diversity (Ford-Lloyd et al. 2011). At the same time, ex situ conservation in genebanks is needed to house and maintain this fundamental raw material in a form that can be directly accessed by plant breeders and researchers in the process of selection and crop improvement. Genebanks represent a wealth of genetic potential, genetic variation, and an insurance against future challenges (Xepapadeas et al. 2014). GenesysFootnote 5 records 283,282 wheat accessions worldwide, of which 13,183 are wild relatives. The International Maize and Wheat Improvement Center (CIMMYT) and the International Center for Agricultural Research in the Dry Areas (ICARDA) hold 50% of the global wheat collection. The CIMMYT genebank conserves the largest wheat collection for a single crop with more than 150,000 wheat accessions. To date, Genesys records 5876 accessions of wheat wild relatives conserved at ICARDA and CIMMYT.
Although the total economic value of these collections is virtually inestimable, we know that the greatest share of that value is derived from the use of its accessions mainly in wheat genetic improvement (Smale and Jamora, this issue). Gollin et al. (2000) showed that much of the value of large collections is derived from the shape of the probability distribution for traits. The rarer the trait, and the greater the economic size of the problem, the greater the payoff. Yet, it is difficult to assess the economic value derived from CWR once their allelic variation is introduced into bred cultivars.
CWR accessions cannot be used by breeders in their original wild form but must be pre-bred into germplasm that is then deployed to transfer valuable traits. In other words, a genetic ‘bridge’ is needed to link conservation to use of CWR. Gollin et al. (1998) showed that much of the value of large collections is derived from the shape of the probability distribution for traits. The rarer the trait, and the greater the economic size of the problem, the greater the payoff. It is also difficult to assess the economic value derived from CWR once their allelic variation is introduced into bred cultivars.
Wheat synthetic hexaploids (SHW) are the result of the artificial crossing of the wild progenitor goat grass (Aegilops tauschii DD) to tetraploid wheat (T. turgidum ssp. durum, AABB). The procedure for developing SHW is described by Mujeeb-Kazi (1995). The durum line is selected based on agronomic performance and is used as a female. After pollination using Aegilops tauschii selected for a certain trait (e.g. resistance to pests and diseases), the chromosomes of the F1 hybrid are doubled. The result is a primary SHW. The development of SHW is based on the origin of the wild parents and the agronomic performance of the tetraploid parent. This approach was criticized for being random rather than strategic. However, SHW exhibited traits that are not expressed in either parent and vice versa, which justifies the approach.
SHW represents the ideal bridge for transferring desirable traits from either parent to adapted bread wheat (Triticum aestivum subsp. aestivum AABBDD) and broadening the genetic base for wheat breeding (Singh et al. 2018). CIMMYT used approximately 900 Aegilops tauschii accessions maintained in the genebank collections to produce approximately 1300 primary SHW between 1988 and 2010. In turn, the lines derived from SHW represent an important source of untapped genetic variation for improved traits like high yield potential, tolerance to heat and drought, and resistance to pests and diseases (Ogbonnaya et al. 2013).
Since the 1990s, the number of citations for breeding use of CWR has grown substantially. In 2003, Carmona and Chuanmai 42 were released in Spain and China, respectively. Both varieties have SHW backgrounds obtained from CIMMYT. Li et al. (2018) reported 62 varieties registered in many countries. Despite this, there is delayed recognition and a lack of information about the incorporation of these traits in released varieties of wheat (Hajjar and Hodgkin 2007; Zhang et al. 2017).
Wheat follows only sunflower in the number of documented uses of CWR. Most of those uses are associated with resistance to pests and diseases in addition to tolerance to stresses from abiotic factors such as heat and drought (Dempewolf et al. 2017; Zhang et al. 2017). Our assessment of the use of SHW highlights the contribution of CWR conservation and pre-breeding to variety releases and potential impact on farms. Analysis by component (i.e. conservation, pre-breeding, distribution and breeding, and use in farmers’ fields) widens our perspective about the role of genebanks in genetic improvement. We first examine how the development of SHW mobilized Aegilops tauschii from the genebanks. We then assess the use of synthetic hexaploid-derived lines (SHDL) by plant breeders. Finally, we provide survey estimates of the adoption of derived varieties in farmers’ fields.
2 Data and methods
2.1 ICARDA/CIMMYT collections
CIMMYT and ICARDA are the two CGIAR centres working on wheat improvement. Their genebanks conserve and supply germplasm to several national and international partners under the Multilateral System of the International Treaty on Plant Genetic Resources for Food and Agriculture (ITPGRFA). Therefore, the analysis of their Aegilops tauschii collections is essential to address the availability of this raw germplasm.
Data on the number of accessions and passport information were compiled for collections of Aegilops tauschii at CIMMYT and ICARDA. Passport information includes the origin of an accession, such as details recorded at the collecting site and other relevant information that assists in its identification. The information for ICARDA was collected from the genebank database. The documentation system used by CIMMYT is the Germplasm Resource Information Network (GRIN-Global). Genesys, a global portal for plant genetic resources, was also consulted to compare and complete some of the information. The data collected included the accession number, country of origin, and latitude and longitude based on the availability of georeferenced information. The georeferenced data were then used to plot the origins of materials in the two collections in order to ascertain the complementarity and level of duplication between the two collections. During a visit to the Wheat Genetic Resources Center (WGRC) at Kansas State University (KSU), we accessed hard copy records of collecting missions, which allowed us to identify the country of origin for 54 Aegilops tauschii accessions used in the development of SHW.
2.2 Aegilops tauschii pre-breeding and development of SHW
We compiled data about the SHW developed by CIMMYT since 1986. The data included the year of development, the female and male parents, and the full pedigree (record of the ancestry) of the line. The CIMMYT genebank provided the accession number and passport data for the Aegilops tauschii accessions used in SHW crosses.
Our analysis focused on three aspects: the variation in the parents used for the development of SHW, the origin of these parents, and the evolution of SHW development over the years. Spatial analysis was performed to assess the patterns in use of Aegilops tauschii parents and see which region is more represented in the SHW collection. We then sought the reasons behind the geographical distribution. We used GRIN-Global, Genesys, and reports provided by KSU to complete the passport data and related information for the accessions used in SHW development. The origins of 498 accessions were identified, while 131 remained with an unknown country of origin. We used the online app MapmakerFootnote 6 to visualize the geographic distribution of Aegilops tauschii used in the crosses to develop SHW.
2.3 Distribution of SHW by CIMMYT genebank
Distribution of germplasm is a core genebank activity. The first step toward making an impact is to make the germplasm available for potential users. We evaluated the direct distribution of SHW by the CIMMYT genebank from 2000, with a focus on external requests. The data collected consisted of the list of accessions distributed by year, country, institution, and requestor. Once the 10,167 externally distributed samples were identified, we calculated the percentage of SHW in the total number of samples distributed and the number of samples received by each country and institution.
2.4 Incorporation of SHDL in international nurseries
In order to assess the evolution of lines derived from SHW wheat in the international nurseries (IN), we selected seven wheat IN based on their importance to the wheat breeding programmes. Data were available for all years until 2018 for six of the nurseries. The International Septoria Observation Nursery (ISEPTON) was analyzed from the 10th nursery onwards due to a lack of data for the first 9 years. The main IN included yield trials nurseries, elite spring wheat yield trials (ESWYT), semi-arid wheat yield trials (SAWYT), and high rainfall wheat yield trials (HRWYT). The other nurseries for disease screening, scab resistance screening nursery (SRSN) and Fusarium head blight screening nursery (FHBSN), are complementary nurseries.
Table 1 presents a summary of the years and the number of nurseries for each IN. We focus on the number of SHDL in each nursery, applying this as an indicator of SHW use in the spring wheat breeding. International winter wheatFootnote 7 nurseries were analyzed for the last five years. Detailed results are not presented for winter wheat since no clear conclusion could be drawn from such a brief time period.
2.5 Variety releases from SHW
After mapping the lines derived from SHW wheat in the IN, we then traced SHW through the release of the wheat varieties that contain them in their pedigrees to their adoption in farmers’ fields. The list of bread wheat varieties grown worldwide was compiled from online databases,Footnote 8 literature reviews, wheat breeders in national agricultural research systems (NARS), and national official sources. We started by collecting the lists of varieties for 92 countries available in the Wheat Atlas. The list of varieties in each country was compiled with additional information on year, pedigree, growth habit, and any other information about the variety. Using the pedigree information, we identified the varieties that included SHW in their pedigree.
After we identified the varieties with SHDL in their pedigrees, we conducted an expert consultation to assess the extent of adoption by farmers and trace the way the candidate parents reached the NARS. Out of the 86 varieties identified in 21 countries, a total of 62 varieties were included in the survey based on the availability of survey respondents (i.e. NARS breeders or CIMMYT representatives) in the target countries. We sent 13 surveys to NARS breeders and CIMMYT representatives in 13 countries: Afghanistan, Argentina, Australia, Bolivia, China, Ethiopia, India, Iran, Kazakhstan, Mexico, Pakistan, Turkey, and Uruguay. The questionnaires were customized based on the country, number of varieties, and available information about each variety. We collected information about the growing conditions, the area cultivated under the variety, yield potential, the traits associated with these varieties, and expectations concerning their adoption over the next five years. We also inquired about the use of SHW in crosses by NARS. Seven responses were received representing 45 varieties from seven countries (Argentina, Bolivia, China, India, Kazakhstan, Pakistan, and Turkey).
3 Results
3.1 Aegilops tauschii in genebank collections
ICARDA and CIMMYT hold 1570 accessions of Aegilops tauschii with country origins from Turkey to west of China. Iran and Azerbaijan are the most represented countries with 23 and 17% of the genebank holdings, respectively, coinciding with parts of the major areas of distribution of this species. Recently, Singh et al. (2018) used genotypic data to demonstrate a large number of duplicates among Aegilops tauschii collections in the Punjab Agricultural University, WGRC at KSU, and CIMMYT genebanks. CIMMYT was found to have only 57% unique accessions. The level of duplicates among the three centres was estimated at 50%.
The geographic distribution of georeferenced accessions at ICARDA and CIMMYT shows some redundancies in the two collections based on the collecting sites (Fig. 1). Part of the duplication is linked to the germplasm exchange among the different genebanks. Instead, the level of duplication should be assessed in the global collection of Aegilops tauschii in order to locate gaps of less represented hotspots and identify unique accessions. The gap analysis conducted by the Global Crop Diversity Trust classified Aegilops tauschii as a species with low priority for collecting. However, any new assessments should take into consideration the current threats to the natural habitat of goat grass. Compiling information on accessions held by other genebanks, and especially in India, Iran, Georgia, and Russia, would be informative. In addition, trait gap analysis is needed to better target adaptive traits in future collecting missions.
3.2 Aegilops tauschii in pre-breeding and development of SHW
Our results show that 629 unique accessions of Aegilops tauschii were used to develop 1577 primary SHW since 1986. These accessions originated from collections in at least 15 countries represented in different proportions. In addition to Aegilops tauschii, CIMMYT is now using Aegilops speltoides, Triticum urartu, and Triticum monococcum to enhance diversity and introduce new traits through the donors of A and B genomes. Moreover, 185 tetraploid wheat parents (Triticum turgidum subsp. durum and Triticum dicoccon) were used with an average of 16 parents each year. The use of Triticum dicoccon in the development of SHW at CIMMYT started in 1998 and resulted in the development of 99 primary SHW using 36 emmer parents. On average, 42 Aegilops accessions were used every year to produce around 62 SHW. Since 2008, the number of tetraploid parents used in the crosses has increased. Since 2013, more diversity has been introduced as we observed the use of 105 tetraploid parents and 95 Aegilops tauschii accessions (Fig. 2).
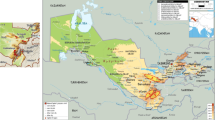
Iran was the most significant contributor to the development of SHW and was the origin of 231 accessions of Aegilops tauschii, followed by Afghanistan (111 accessions) (Fig. 3). The two countries provided more than 54% of the total accessions used to create SHW. The richness of genebank collections of accessions from Azerbaijan is not reflected in the development of SHW (only 44 accessions are involved in the crosses). The origin of the 131 Aegilops tauschii accessions is unknown (Fig. 3). Mapping the geo-localized accessions allowed us to clearly visualize the regions that extensively used pre-bred materials (Fig. 4).
Country of origin for the Aegilops tauschii accessions used to develop SHW since 1986. IRN=Iran; AFG = Afghanistan; UNK=Unknown; RUS = Russia; CHN=China; AZE = Azerbaijan; UZB=Uzbekistan; PAK=Pakistan; TKM = Turkmenistan; ARM = Armenia; TUR = Turkey; GEO = Georgia; KGZ = Kyrgzstan; SYR = Syria; TJK = Tajikistan; CIS = Commonwealth of Independent States (ten former Soviet Republics). Sources: list of primary synthetics provided by Masahiro Kishi from CIMMYT and CIMMYT GRIN-Global database
Geographic distribution of geo-localized Aegilops tauschii accessions used for the development of SHW by CIMMYT (Authors). Note: Red areas represent the regions where a high number of accessions are sourced and used in the development of SHW. Numbers in circles represent the number of accessions used in the development of SHW. Source: Aegilops tauschii passport information from GRIN-Global and Genesys
3.3 Distribution of SHW by CIMMYT genebank
The analysis of SHW distribution by the CIMMYT genebank provides a clear view of the demand for this germplasm and the role of the genebank in supporting other institutions. Since 2000, CIMMYT has distributed 10,167 samples to 110 institutions in 40 countries. ICARDA received 988 samples representing nearly 10% of the total samples distributed (Figs. 5 and 6). China is ranked first in requests of SHW from CIMMYT (1322 samples) followed by the United States of America (957 samples) and the United Kingdom (877 samples). This ranking is reflected in the number of institutions that received the material in each country. Fifteen institutions are based in the USA, followed by China, which has 13 institutions (Fig. 5). Between 2000 and 2013, SHW represented, on average, 21% of the germplasm distributed externally by the CIMMYT genebank.
At the regional level, Asia received 30% of the samples, followed by Europe and Latin America, with 24 and 20%, respectively. The United Kingdom has worked closely with CIMMYT to include SHW in the improvement of winter bread wheat, as reflected on the number of SHW received from CIMMYT genebank. The exchange of germplasm under the CIMMYT Australia ICARDA Germplasm Evaluation project allowed the evaluation and screening of a high number of SHDL for several traits. This evaluation data is publicly available and could provide information on the contribution of SHDL to different traits.
3.4 Distribution of IN
The analysis of the distribution of IN indicates the use of SHW within the international research network, which includes centres such as CIMMYT, ICARDA, and NARS. IN are the gateway of germplasm before it is tested by NARS and proposed for release. We assessed 142 spring bread wheat IN in order to determine the number of SHW evaluated every year (Table 1). The results show that the first two lines derived from SHW were sent to the ESWYT nursery in 1996. Since then, 853 lines derived from crosses with Aegilops tauschii have been sent within the seven IN studied (Fig. 7), and of these lines, more than 50% (446 lines) are unique. It is noticeable that the presence of SHW in the IN has been increasing, with more SHDL screened for disease resistance. In 2016, 66 out of 119 SHDL were screened for stem rust resistance, representing 40% of the total lines in the stem rust resistance screening nursery (STEMRRSN) for that year. In the last 9 years, the Septoria screening nursery received around 30% of the total SHDL screened for disease resistance.
Evolution number of SHDL in seven spring wheat INs. Sources: list of INs from CIMMYT International Wheat Improvement Network, data provided by CIMMYT (http://orderseed.cimmyt.org/iwin-results.php)
The analysis of 22 years of data from ESWYT and SAWYT revealed that SHW are used twice as often in SAWYT (17% compared to 9% for ESWYT). SAWYT received 190 SHDL, with an average of eight lines per year, whereas 110 SHDL lines were sent to ESWYT with the average of five lines per year. In the 15th SAWYT, SHDL represented 46% of the total lines, a finding that was previously highlighted by Lage and Trethowan (2008). Their analysis of the coefficient of parentage (CoP) showed that between the 5th and 15th SAWYT, the average CoP declined from 75 to 19%. This suggests that the increase in numbers of SHDL was associated with an increase in the latent diversity conferred through parentage of the elite germplasm. The conclusion we draw from these findings is that SHDL attracted the interest of breeders to acquire them and use them in their programmes.
As most SHW is developed using spring durum wheat as parents, the winter wheat IN were analyzed separately to avoid any misleading conclusions. Between 2013 and 2018, facultativeFootnote 9 and winter wheat IN showed less incorporation of SHDL in these nurseries than in the spring wheat IN. Since 2013, strictly winter wheat nurseries received only 19 lines out of the 76 sent for both facultative and winter wheat nurseries. However, we observed a growing use of Aegilops speltoides (the donor of the B genome to wheat) over the five-year period.
3.5 Variety release
Voskehask was the first variety derived from Aegilops tauschii as a parent and was released in Armenia in 1994. It is the result of a direct cross of bread wheat with goat grass. Since 2003, 86 varieties resulting from SHW have been released in 21 countries. The pedigree analysis showed that five Aegilops tauschii accessions from China, Iran, and Russia contributed to the release of 22 cultivars in 13 countries.
Among the 13 countries included in the survey, China, India, and Pakistan have the highest number of varieties released with 18, 10, and nine varieties, respectively (see Table 2 in Appendix). These countries are also the top producers of wheat in the developing world.
The survey revealed that IN are the first source of germplasm for NARS in more than 57% of candidate lines that reached national programmes. Except for Pakistan, the NARS in the surveyed countries are using SHW and their derived varieties in the breeding programme. In China, the success of the cultivar Chuanmai 42 released in 2004 triggered the use of more SHW in the breeding programme. Chuanmai 42 broke the yield record by surpassing the commercial check with 35% grain yield (Li et al. 2014), leading to more varieties released with SHW germplasm. High yield stability, good quality attributes, disease resistance and drought tolerance made Chuanmai 42 successful. Currently, our survey respondent reports that Chuanmai 42 is planted in over 100,000 ha in southwest China. The wheat area in southwest China totals two million ha, and at the time of our survey, varieties derived from SHW occupied an estimated 34% of this area (689,000 ha). The leading varieties are Chuanmai 104, grown on 200,000 ha, followed by Chuanmai 42, Shumai 969, and Mianmai 367, cultivated on 100,000 ha each (Fig. 8). All of these cultivars are grown under irrigated conditions and their yield potential ranges from 8 to 9 t/ha. With the exception of Chuanmai 42, it is expected that each cultivar will be grown on larger areas in the future. Wheat area planted to Chuanmai 42 is decreasing, although it is still used in the crosses by national breeders. The varieties released from 2011 to 2014 with Chuanmai 42 as a parent yield 8.5% higher than varieties released from 2006 to 2010. This variety is now playing a crucial role in enhancing the production of modern wheat in southwest China (Li et al. 2014).
In India, the 10 cultivars derived from SHW are now grown on two million ha, representing 6.7% of the total area cultivated by wheat. WH-1142 and MP 1203 are the two major varieties adopted on 1 and 0.4 million ha, respectively (Fig. 9). Interestingly, WH-1142 wheat variety reached this area only 4 years after its release. WH-1142 is resistant to yellow rust, possesses high levels of protein (12.1%), iron (36.4 ppm), and zinc (33.7 ppm), and has a good bread quality score. This variety is cultivated in the northwest plains zone of India under restricted irrigation. MP1203 is grown in the central zone for late sowing under irrigation. The cultivar KRL 213 has been adopted in the salt affected areas of the northern plains and covers around 100,000 ha. Zinc Sakhti, a biofortified variety, is desired for its bold attractive grains. These two varieties are expected to be grown on larger acreage in the next five years.
We were able to gather relatively less information on variety releases for Pakistan, Turkey, and Argentina. In Pakistan, the yield potential reported by survey respondents ranged from 2.7 to 3.5 t/ha based on growing conditions. SHW-derived varieties are in initial phases of diffusion and it is estimated that they currently occupy 12,180 ha. Yakamoz and Altinbasak are two wheat varieties released for irrigated conditions in Turkey. Their yield potential ranges from 6.5 to 9.5 t/ha, and Yakamoz is cultivated on 5000 ha. According to the survey, SRM NOGAL was released in Argentina (2006), targeting 25% of the national area, and has now been replaced by new varieties that are also derived from SHW. Currently, BIOINTA-1006, released in 2009, is planted to 5–10% of the national area. Our survey revealed that SHDL represents 30–40% of the germplasm used in the national breeding programme in Argentina. In China, by comparison, the share of SHDL rises to 80%. In Morocco, Aguilal was the first SHW-derived variety, released in 1998, with resistance to Hessian fly and UG99, but it was susceptible to yellow rust new virulences. Kharoba, also derived from SHW, is resistant to yellow rust, stem rust, and Hessian fly, with the latter being the major pest for wheat production in Morocco (Elhaddoury et al. 2012).
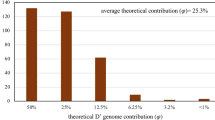
Out of all 45 varieties for which we received a survey response in seven countries, 93% were characterized by resistance to pests and pathogens. Yield potential and stability are the secondary traits for which these varieties are desired, as 38 of 45 have good stability associated with high yield potential. An interesting finding is that end-use quality (i.e. high protein and micronutrient content) is a key trait in the varieties derived from SHW. Tolerance of drought and heat are each reported in around 15% of the cases (Fig. 10), whereas tolerance of abiotic stresses characterize 28% of the cultivars.
4 Discussion
The development of synthetic hexaploid wheat (SHW) illustrates the use of crop wild relatives (CWR) in pre-breeding, their impact on breeding and variety release, and their potential impact on farms. Genebanks are crucial to the development of SHW because they protect against the loss of wild crop relatives in natural habitats, conserving and making them available in raw form or as pre-bred germplasm to plant breeders and other users. The initial Aegilops tauschii accession used to develop SHW was obtained from several genebanks, including CIMMYT’s (Mujeeb-Kazi 1995). The trends of SHW distribution by the CIMMYT genebank indicate the extensive use of SHW in research and breeding.
SHW also illustrates the importance of pre-breeding in linking the conservation of CWR to their use. The Aegilops tauschii collection has been well used in pre-breeding, although use varies by geographical region. Some countries, like Azerbaijan, are underrepresented in the development of SHW. Azerbaijan conserves a high level of diversity of Aegilops tauschii in its ex situ collection. Efforts should be implemented to identify the gaps in the global collection and fill them, while reducing the duplication within and between Aegilops tauschii collections. As suggested by Dempewolf et al. (2014), a gap analysis should assess the vulnerability of goat grass natural habitat and prioritize the most endangered areas. Pre-breeding activities can be strengthened by using passport data and information about CWR to target specific traits. Other wheat wild relatives are needed to widen the genetic bases of the A and B genome for wheat. The CIMMYT pre-breeding programme has recognized this need and has incorporated new species (Aegilops speltoides, Triticum urartu, and Triticum monococcum).
Contrary to the classic use of genebank germplasm, where the accession used is based on the identification of a specific trait, the development of SHW aims to bring the maximum allelic variation and introduce it to an adapted background. That is why the crosses are random and the selection of the parents is based on practical considerations such as crossability and pollen quality from the parents. Moreover, the performance of the SHW cannot be predicted based on the performance of the Aegilops tauschii or the tetraploid parent, especially when it comes to tolerance of environmental factors, because some allelesFootnote 10 from both parents are not detected in SHW. Performance may be due to epistatic gene interaction,Footnote 11 modified gene expression, and high genetic diversity in Aegilops tauschii, which results in phenotypic variation in the SHW (Dreisigacker et al. 2008). In another example, screening for Hessian fly resistance found that SHDL derived from the same Aegilops tauschii accession showed differences in their reaction to Hessian fly ranging from susceptible to resistant (Yu et al. 2012). Moreover, because of the winter and weedy growth habit of Aegilops tauschii, it is hard to grow and test it for several traits under field conditions.
With the combination of traits from both parents (Aegilops tauschii and tetraploid wheat), SHW represents the ideal material to simultaneously increase yield potential and diversity of several traits (Dreisigacker et al. 2008). The use of simple sequence repeat markers showed that breeding lines derived from SHW had higher diversity compared to the wheat of the Green Revolution. In fact, the level of allelic diversity is close to that of landraces cultivated prior to the Green Revolution (Warburton et al. 2006). Ogbonnaya et al. (2013) reported more than 42 mapping populationsFootnote 12 for yellows rust, head scab, Hessian fly, drought tolerance, milling and baking quality, and other traits. They also reported more than 100 sources of useful genes for resistance to major pests and disease. Transferring these traits into released varieties is challenging because breeders are reluctant to use exotic germplasm because it is a long-term process. Additionally, necrosis of the F1 is a major limitation to the use of SHW by the breeders. Most of the SHW inherit the Ne1 dominant gene from a durum wheat parent located on chromosome arm 5BL. When SHDL carrying this gene are crossed with bread wheat lines that have another dominant gene (Ne2) located on their chromosome arm 2BS, there is a problem of necrosis at the F1 progeny; this occurs in 1–50% of cross-breeding cases (van Ginkel and Ogbonnaya 2006; Chu et al. 2006).
Despite these constraints, we showed that SHW have found their way into breeders’ collections, and the IN results indicate that SHW were extensively explored for disease and pest resistance and agronomic performance. Almost all of the adopted varieties that were listed by survey respondents had been characterized by resistance to stresses from pests and pathogens, with resistance to yellow rust, leaf rust, and Septoria as the most registered. More than 50% of the traits associated with the use of wheat wild relatives are resistances to pests and diseases, as reported by Dempewolf et al. (2017).
Chuanmai 42 inherited its resistance to stripe rust from the tetraploid durum parent (Decoy 1) of the SHW. Other SHW screened in China inherited their resistance to powdery mildew from the Aegilops tauschii parent (Chu et al. 2006). Aegilops tauschii is the donor of stem rust resistance genes Sr33, Sr45, and Sr46. Twelve Aegilops tauschii accessions distributed across Azerbaijan, Iran, Turkmenistan, and Uzbekistan showed combined resistance to six different races of stem rust. The findings suggest that these countries could be the hotspot for resistance to Pgt races (Rouse et al. 2011). In another study, despite the durum parent being susceptible to tan spot, Hessian fly, and Stagonospora nodorum blotch, the synthetics derived from this parent showed resistance to these pests and diseases. Likewise, research by Friesen et al. (2008) suggests that Aegilops tauschii parents are a potential source of resistance.
Yield potential and stability are ranked as the second most important trait in the released varieties and are the first requirement for release and adoption by the farmers. Previous studies reported an increase of SHDL yield in comparison to the recurrent parents. This increase was mainly associated with an increase in seed weight, number of spikes per meter square, and the number of seeds per spike (del Blanco et al. 2001; Cooper et al. 2013). Chuanmai 104 and Chuanmais 64 inherited a higher production of seed numbers per spike and higher thousand seed weight from Chuanmai 42 (Li et al. 2014). Results suggest that a suitable breeding procedure can take advantage of the beneficial traits from SHW and overcome the undesirable traits originating mainly from the wild parent. Attaining good yield stability is associated with the tolerance to drought, heat, and other abiotic stresses where wheat is grown under rainfed condition. These traits were reported in 60% of the response in the survey.
Twenty-four marker trait associations (MTA) were identified on the D genome of SHW for several grain minerals, suggesting that Aegilops tauschii can be a source for biofortified wheat. Other MTAs were located on A and B genome, which means the cumulative effect of multiple alleles could be positive on nutritional quality of wheat grains (Bhatta et al. 2018). In Bolivia, for example, INIAF-Yesera is a biofortified bread wheat cultivar released in a participatory approach for its yield potential (3.6 t/ha), richness in protein, high micronutrients content, and good baking quality. The protein content of the INIAF-Yesera variety in dry base was 16.51%, which greatly exceeds the control of 11.28%, and the zinc and iron concentrations are 4.9 and 3.5 mg 100 g−1, respectively. This result guarantees that the INIAF-Yesera variety meets the wheat requirements for good bread making. Zinc Sakhti, WB02, and HPBW-01 are also zinc biofortified wheat varieties released and adopted in over 250,000 ha in India. The zinc concentration of Zinc Sakhti and WB02 is more than 14 and 7 ppm, respectively, the former of which was released in a participatory approach with farmers and has early maturity (Singh and Govindan 2017). According to the survey we conducted, the area of Zinc Sakhti grown is expected to increase over the next five years. Currently, it is grown in the northeastern plain zones of India.
In summary, varieties derived from SHW combine resistance to pests and pathogens, yield potential and stability, and quality attributes of wheat (e.g. protein content, micronutrients content and bread making quality). The attributes of SHW-derived varieties make them especially suitable for adoption today, since in addition to grain yield, quality traits are a necessary requirement to commercialize grain and grain products.
5 Conclusion
In this study, we traced the path of wild germplasm from the genebank through its incorporation by pre-breeding into varieties released and adopted by farmers. We highlighted the importance of using wheat wild relatives in pre-breeding to ensure the incorporation of beneficial traits into adapted genetic backgrounds. The analysis of the distribution data and IN showed the impact of SHW development on breeding through the number of samples distributed by the CIMMYT genebank, which number more than 10,167 samples since 2000. This distribution highlights breeders’ efforts to screen SHW and explore potential traits. The IN analysis provided evidence on the evolution of SHW’s role in the CIMMYT breeding programme over time and its importance as the first source of germplasm for NARS, especially in countries that rely on the CGIAR centres as a main source of germplasm. Thus, any change in the type of germplasm included in the IN is likely to be translated into changes in the variety release patterns of those countries. We identified 86 SHW-derived varieties in 13 countries. The breeder survey demonstrated that, along with resistance to pests and pathogens and agronomic performance, SHW-derived varieties have good end-use quality and improved nutritional traits. High reported adoption rates of SHW-derived varieties in several countries attest to their potential contribution to farmer incomes and well-being.
CWR are an important component of genebank collections and contain a wide range of beneficial, economically important traits for crop improvement, including adaptive traits needed to cope with climate change. The utilization of CWR in crop improvement is limited by time and funding constraints and the need to eliminate undesirable traits from the progeny. Due to the inherent long-term process of pre-breeding, projects should be strategic and designed to cope with future challenges. For example, our study identified varieties that were released from crosses made in 1987, and unless these pre-breeding programs are linked to genebank collections, CWR will remain underutilized. The case of Aegilops tauschii collections clearly shows how the pre-breeding program was extensively used in the development of SHW.
New genes for resistance to pests and pathogens, tolerance of abiotic stresses, agronomic performance, and quality attributes were identified in SHW. Some of these traits are expressed only after combining both parents in SHW, meaning that these genetic resources can expand allelic variation. The use of SHW in breeding and research has expanded over the last 20 years, as demonstrated by the rising numbers of requests from the CIMMYT genebank. The role of CGIAR centres is clear since many of the varieties identified are either derived from an advanced line or have at least one parent from CIMMYT. This underscores the need for well-informed uses of resources to collect and conserve unique accessions.
Notes
Biotypes: a group of organisms having an identical genetic constitution.
A crop cultivar that has evolved through many years of farmer-directed selection and that is specifically adapted to local conditions; landraces are usually genetically heterogeneous.
The possible progenitors of the cultivated crops that have a relatively close genetic relationship to a crop.
Accession: a distinct, uniquely identifiable sample of seeds representing a cultivar, breeding line or a population that is maintained in storage for conservation and use.
Genesys is an online platform where you can find information about the plant genetic resources for food and agriculture conserved in genebanks worldwide. See https://www.genesys-pgr.org/.
Winter wheat: wheat that requires vernalization to reach heading; the plants should go through cold winter temperatures (0–5 °C) for 30–60 days.
Facultative wheat: wheat with partial sensitivity to vernalization. It requires short vernalization and it is less tolerant to cold than true winter wheat.
Allele: one or more alternate forms of a gene occupying the same locus on a particular chromosome.
Epistatic gene interaction: the interaction of genes at different loci.
Mapping population: Mapping populations are generated by crossing two or more genetically diverse parents and handling the progeny in a definite fashion. They are used to determine the genetic distance between pairs of genes and to map their location in the genome
References
Bahrani, A., & Hagh Joo, M. H. (2011). Response of some wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) genotypes to salinity at germination and early seedling growth stages. World Applied Sciences Journal, 16(4), 599–609.
Barrett, C. B. (2010). Measuring food insecurity. Science, 327(5967), 825–828.
Bhatta, M., Baenziger, S. P., Waters, B. M., Poudel, R., Belamkar, V., Poland, J., et al. (2018). Genome-wide association study reveals novel genomic regions associated with 10 grain minerals in synthetic hexaploid wheat. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19103237.
Chatzav, M., Peleg, Z., Ozturk, L., Yazici, A., Fahima, T., Cakmak, I., & Saranga, Y. (2010). Genetic diversity for grain nutrients in wild emmer wheat: Potential for wheat improvement. Annals of Botany, 105, 1211–1220. https://doi.org/10.1093/aob/mcq024.
Chu, C.-G., Faris, J. D., Friesen, T. L., & Xu, S. S. (2006). Molecular mapping of hybrid necrosis genes ne1 and Ne2 in hexaploid wheat using microsatellite markers. Theoretical and Applied Genetics, 112, 1374–1381. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-006-0239-9.
Cooper, J. K., Ibrahim, A. M. H., Rudd, J., Hays, D., Malla, S., & Baker, J. (2013). Increasing hard winter wheat yield potential via synthetic hexaploid wheat: II. Heritability and combining ability of yield and its components. Crop Science, 53, 67–73. https://doi.org/10.2135/cropsci2011.07.0383.
Day-Rubenstein, K., Heisey, P., Shoemaker, R., Sullivan, J., & Frisvold, G. (2005). Crop genetic resources: An economic appraisal. Economic Information Bulletin Number 2, may 2005. Washington: Economic Research Service/USDA.
Del Blanco, I. A., Rajaram, S., & Kronstad, W. E. (2001). Agronomic potential of synthetic hexaploid wheat-derived populations. Crop Science, 41, 670–676. https://doi.org/10.2135/cropsci2001.413670x.
Dempewolf, H., Eastwood, R. J., Guarino, L., Khoury, C. K., Müller, J. V., & Toll, J. (2014). Adapting agriculture to climate change: A global initiative to collect, conserve, and use crop wild relatives. Agroecology and Sustainable Food Systems, 38, 369–377. https://doi.org/10.1080/21683565.2013.870629.
Dempewolf, H., Baute, G., Anderson, J., Kilian, B., Smith, C., & Guarino, L. (2017). Past and future use of wild relatives in crop breeding. Crop Science, 57, 1070–1082. https://doi.org/10.2135/cropsci2016.10.0885.
Dreisigacker, S., Kishii, M., Lage, J., & Warburton, M. (2008). Use of synthetic hexaploid wheat to increase diversity for CIMMYT bread wheat improvement. Australian Journal of Agricultural Research, 59, 413. https://doi.org/10.1071/AR07225.
Elhaddoury, J., Lhaloui, S., Udupa, S. M., Moatassim, B., Taiq, R., Rabeh, M., Kamlaoui, M., & Hammadi, M. (2012). Registration of ‘Kharoba’: A bread wheat cultivar developed through doubled haploid breeding. Journal of Plant Registrations, 6, 169–173. https://doi.org/10.3198/jpr2011.07.0385crc.
Ford-Lloyd, B. V., Schmidt, M., Armstrong, S. J., Barazani, O., Engels, J., Hadas, R., Hammer, K., Kell, S. P., Kang, D., Khoshbakht, K., Li, Y., Long, C., Lu, B. R., Ma, K., Nguyen, V. T., Qiu, L., Ge, S., Wei, W., Zhang, Z., & Maxted, N. (2011). Crop wild relatives—Undervalued, underutilized and under threat? BioScience, 61, 559–565. https://doi.org/10.1525/bio.2011.61.7.10.
Friesen, T. L., Xu, S. S., & Harris, M. O. (2008). Stem rust, tan spot, Stagonospora nodorum blotch, and hessian fly resistance in Langdon durum–Aegilops tauschii synthetic hexaploid wheat lines. Crop Science. https://doi.org/10.2135/cropsci2007.08.0463.
Gollin, D., Smale, M., & Skovmand, B. (2000). Searching an ex situ collection of wheat genetic resources. American Journal of Agricultural Economics, 82(4), 812–827.
Hajjar, R., & Hodgkin, T. (2007). The use of wild relatives in crop improvement: A survey of developments over the last 20 years. Euphytica, 156, 1–13. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-007-9363-0.
King, J., Grewal, S., Yang, C.-Y., Edwards, S. H., Scholefield, D., Ashling, S., et al. (2018). Introgression of Aegilops speltoides segments in Triticum aestivum and the effect of the gametocidal genes. Annals of Botany, 121, 229–240. https://doi.org/10.1093/aob/mcx149.
Kumar, S., Kumari, P., Kumar, U., Grover, M., Singh, A. M., Rakesh Singh, R., et al. (2013). Molecular approaches for designing heat tolerant wheat. Journal of Plant Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 22, 359–371. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13562-013-0229-3.
Lage, J., & Trethowan, R. M. (2008). CIMMYT’s use of synthetic hexaploid wheat in breeding for adaptation to rainfed environments globally. Australian Journal of Agricultural Research, 59, 461. https://doi.org/10.1071/AR07223.
Li, J., Wan, H., & Yang, W. (2014). Synthetic hexaploid wheat enhances variation and adaptive evolution of bread wheat in breeding processes. Journal of Systematics and Evolution, 52, 735–742. https://doi.org/10.1111/jse.12110.
Li, A., Liu, D., Yang, W., Kishii, M., & Mao, L. (2018). Synthetic hexaploid wheat: Yesterday, today, and tomorrow. Engineering, 4, 552–558. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eng.2018.07.001.
Lobell, D. B., Schlenker, W., & Costa-Roberts, J. (2011). Climate trends and global crop production since 1980. Science, 333, 616–620. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1204531.
Mickelbart, M. V., Hasegawa, P. M., & Bailey-Serres, J. (2015). Genetic mechanisms of abiotic stress tolerance that translate to crop yield stability. Nature Reviews Genetics, 16, 237–251. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrg3901.
Mujeeb-Kazi, A. (1995). Utilizing wild grass biodiversity in wheat improvement 15 years of wide cross research at CIMMYT. Mexico: CIMMYT.
Ogbonnaya, F. C., Abdalla, O., Mujeeb-Kazi, A., Alvina, G. K., Xu, S. S., Gosman, N., et al. (2013). Synthetic hexaploids: Harnessing species of the primary gene pool for wheat improvement. Plant Breeding Reviews, 37, 35–122.
Rouse, M. N., Olson, E. L., Gill, B. S., Pumphrey, M. O., & Jin, Y. (2011). Stem rust resistance in germplasm. Crop Science, 51, 2074–2078. https://doi.org/10.2135/cropsci2010.12.0719.
Singh, R., & Govindan, V. (2017). Zinc-biofortified wheat: harnessing genetic diversity for improved nutritional quality. Science Brief: Biofortification No. 1, May 2017. Bonn, Germany: CIMMYT, HarvestPlus, and the Global Crop Diversity Trust.
Singh, S., Vikram, P., Sehgal, D., Burgueño, J., Sharma, A., Singh, S. K., Sansaloni, C. P., Joynson, R., Brabbs, T., Ortiz, C., Solis-Moya, E., Govindan, V., Gupta, N., Sidhu, H. S., Basandrai, A. K., Basandrai, D., Ledesma-Ramires, L., Suaste-Franco, M. P., Fuentes-Dávila, G., Moreno, J. I., Sonder, K., Singh, V. K., Singh, S., Shokat, S., Arif, M. A. R., Laghari, K. A., Srivastava, P., Bhavani, S., Kumar, S., Pal, D., Jaiswal, J. P., Kumar, U., Chaudhary, H. K., Crossa, J., Payne, T. S., Imtiaz, M., Sohu, V. S., Singh, G. P., Bains, N. S., Hall, A., & Pixley, K. V. (2018). Harnessing genetic potential of wheat germplasm banks through impact-oriented-prebreeding for future food and nutritional security. Scientific Reports, 8, 12527. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-30667-4.
van Ginkel, M., & Ogbonnaya, F. (2006). Using synthetic wheats to breed cultivars better adapted to changing production conditions. Proceedings of 13th Agronomy Conference. Perth, Western Australia. 10–14 September 2006. http://www.regional.org.au/au/pdf/asa/2006/4830_vanginkelm.pdf. Accessed 1 Dec 2019.
Velu, G., & Singh, R. P. (2013). Phenotyping in wheat breeding. Phenotyping for Plant Breeding. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4614-8320-5_2.
Warburton, M. L., Crossa, J., Franco, J., Kazi, M., Trethowan, R., Rajaram, S., Pfeiffer, W., Zhang, P., Dreisigacker, S., & Ginkel, M. . (2006). Bringing wild relatives back into the family: Recovering genetic diversity in CIMMYT improved wheat germplasm. Euphytica, 149, 289–301. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-005-9077-0.
Xepapadeas, A., Ralli, P., Kougea, E., Spyrou, S., Stavropoulos, N., Tsiaousi, V., & Tsivelikas, A. (2014). Valuing insurance services emerging from a gene bank: The case of the Greek Gene Bank. Ecological Economics, 97, 140–149. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolecon.2013.11.012.
Yu, G. T., Wang, T., Anderson, K. M., Harris, M. O., Cai, X., & Xu, S. S. (2012). Evaluation and haplotype analysis of elite synthetic hexaploid wheat lines for resistance to hessian fly. Crop Science, 52, 752–763. https://doi.org/10.2135/cropsci2011.05.0290.
Zhang, H., Mittal, N., Leamy, L. J., Barazani, O., & Song, B. (2017). Back into the wild-apply untapped genetic diversity of wild relatives for crop improvement. Evolutionary Applications, 10, 5–24. https://doi.org/10.1111/eva.12434.
Acknowledgements
Funding for this research was provided by the CGIAR Genebank Platform, CIMMYT, ICARDA, and the Crop Trust through the 2018 Genebank Impacts Fellowship. We gratefully acknowledge the support of CIMMYT genebank staff and the contributions of survey respondents. We also thank the team from the WGRC at KSU for sharing their expertise on wheat conservation and pre-breeding.
Authorship contribution
The first author contributed to the research conceptualization and design, data gathering, data analysis, writing, and editing. The second, third, and fifth authors contributed to the research conceptualization and design, data provision, and data gathering. The fourth and last authors contributed to the research conceptualization and design, writing, and editing.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The first author works at the genebank in ICARDA. The second author is currently the Head of Wheat Germplasm Collections at CIMMYT. The third author is a scientist for the Global Wheat Program at CIMMYT. The fifth author is the Head of Genetic Resources Unit at ICARDA at the time the research was conducted. The sixth author is an agricultural economist at the Crop Trust. The fourth author declares no conflict of interest.
Appendix
Appendix
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Aberkane, H., Payne, T., Kishi, M. et al. Transferring diversity of goat grass to farmers’ fields through the development of synthetic hexaploid wheat. Food Sec. 12, 1017–1033 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12571-020-01051-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12571-020-01051-w