Abstract
Background
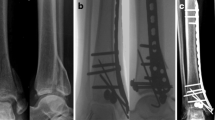
Minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis (MIPO) became an important option for treating distal tibia fractures. All the surgeons insert the plate from distal to proximal (retrograde), but we used antegrade plate insertion, if the distal fragment is displaced laterally in relation to the proximal fragment and vice versa. We noticed less soft tissue complications at the distal incision with antegrade plate insertion.
Methods
In this retrospective cohort study, we reviewed our patients for whom we used MIPO to treat distal tibia fractures, either through antegrade or retrograde plate insertion. We could match 22 patients treated with antegrade plate insertion (group A) to another 22 patients treated with retrograde plate insertion (group B). As per AO classification, 26 fractures were type A, 14 type B, and 4 type C. Statistical analyses were performed in SPSS version 20, and P value less than 0.05 was considered significant.
Results
The antegrade group showed a statistically significant better results with reference to length of the distal incision (P = 0.000), AOFAS score (P = 0.025), the time to return to job (P = 0.000), sports practice (P = 0.046), the time to return to sports (P = 0.002), and the number of received physiotherapy treatments (P = 0.000).
Conclusions
Both modes of plate insertion were safe and effective in treating distal tibia fractures. Antegrade plate insertion minimizes additional trauma to the already traumatized zone, showed less complications, and better functional results. Faster return to job and sports support antegrade plate insertion to be preferred for athletic persons. A prospective comparative study is recommended.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aksekili MA, Celik I, Arslan AK, Kalkan T, Uğurlu M (2012) The results of minimally invasive percutaneous plate osteosynthesis (MIPPO) in distal and diaphyseal tibial fractures. Acta Orthop Traumatol Turc 46(3):161–167
Bahari S, Lenehan B, Khan H, McElwain JP (2007) Minimally invasive percutaneous plate fixation of distal tibia fractures. Acta Orthop Belg 73:635–640
Casstevens C, Le T, Archdeacon MT, Wyrick JD (2012) Management of extra-articular fractures of the distal tibia: Intramedullary nailing versus plate fixation. J Am Acad Orthop Surg 20–11:675–683
Collinge C, Kuper M, Larson K, Protzman R (2007) Minimally invasive plating of high-energy metaphyseal distal tibia fractures. J Orthop Trauma 21:355–361
Farouk O, Krettek C, Miclau T, Schandelmaier P, Guy P, Tscherne H (1999) Minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis and vascularity: preliminary results of a cadaveric injection study. Injury 28:A7–A12
Gupta RK, Rohilla RK, Sangwan K, Singh V, Walia S (2010) Locking plate fixation in distal metaphyseal tibial fractures: series of 79 patients. Int Orthop 34(8):1285–1290
Kitaoka HB, Alexander IJ, Adelaar RS, Nunley JA, Myerson MS, Sanders M (1994) Clinical rating systems for the ankle-hindfoot, midfoot, hallux, and lesser toes. Foot Ankle Int 15:349–353
Leonard M, Magill P, Khayyat G (2009) Minimally-invasive treatment of high velocity intraarticular fractures of the distal tibia. Int Orthop 33(4):1149–1153
Guo JJ, Tang N, Yang HL, Tang TS (2010) A prospective, randomised trial comparing closed intramedullary nailing with percutaneous plating in the treatment of distal metaphyseal fractures of the tibia. J Bone Joint Surg (Br) 92(7):984–988
Hazarika S, Chakravarthy J, Cooper J (2006) Minimally invasive locking plate osteosynthesis for fractures of the distal tibia: results in 20 patients. Injury 37:877–887
Janssen KW, Biert J, VanKampen A (2007) Treatment of distal tibial fractures: plate versus nail: a retrospective outcome analysis of matched pairs of patients. Int Orthop 31(5):709–714
Maffulli N, Toms AD, McMurtie A, Oliva F (2004) Percutaneous plating of distal tibial fractures. Int Orthop 28:159–162
Vallier HA, Cureton BA, Paterson BM (2011) Randomized prospective comparison of plate versus intramedullary nail fixation for distal tibia shaft fractures. J Orthop Trauma 25(12):736–741
Yang SW, Tzeng HM, Chou YJ, Teng HP, Liu HH, Wong CY (2006) Treatment of distal tibial metaphyseal fractures: plating versus shortened intramedullary nailing. Injury 37:531–535
Zelle BA, Bhandari M, Espiritu M, Koval KJ, Zlowodzki M (2006) Treatment of distal tibia fractures without articular involvement: a systematic review of 1125 fractures. J Orthop Trauma 20:76–79
Ronga M, Longo UG, Maffulli N (2010) Minimally invasive locked plating of distal tibia fractures is safe and effective. Clin Orthop Relat Res 468(4):975–982
Conflict of interest
The author declares that he had no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
What is known about the subject: No former study stated this mode of insertion or discussed its effect on improving the results.
What this study adds to existing knowledge: It adds a new idea that may help to improve the results
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ali, M. Faster return to job and sports after antegrade plate insertion in minimally invasive plating of distal tibia fractures. Eur Orthop Traumatol 6, 255–259 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12570-014-0280-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12570-014-0280-0