Abstract
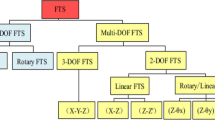
Micro-machining has been widely used for manufacturing of micro molds for flat panel displays. Because the mold has a large area and heavy weight, the workpiece setup system with a high stiffness and ultraprecise positioning control is required to obtain a longterm manufacturing stability and precision. In this study, a novel ultra-precision tilting stage with 3-DOF motions (z-translation, pitch, and roll) has been developed to setup a heavy duty and large area workpiece. The structure is designed to realize a long motion range via an amplified guide mechanism of high stiffness flexure guide and the piezo-electric actuators are integrated to achieve the motion resolution of less than 100 nm. The guide mechanism has a large stiffness with long-term stability through the unique combination of a closed-lying bridge and a half-standing bridge, which can amplify the motion rage double and minimize the overall volume of tilting system. The static, dynamic, and thermal characteristic of the system was optimized by structural analysis using finite element modeling. Finally, the tilting stage provides 50 nm positioning repeatability for a workpiece of 150 kg within a vertical stroke of 160 μm and a machining area of 400×400 mm2.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- F L :
-
Workpiece load to upper guide
- F w :
-
Workpiece load to lower quide
- F k :
-
Actuating force of the piezo actuator
- M o :
-
Moment of mount
- L a , L b , L c :
-
Length of each guide
References
Elfizy, A. T., Bone, G. M., and Elbestawi, M. A., “Design and Control of a Dual-Stage Feed Drive,” International Journal of Machine Tools and Manufacture, Vol. 45, No. 2, pp. 153–165, 2005.
Gao, P., Swei, S.-M., and Yuan, Z., “A New Piezodriven Precision Micropositioning Stage Utilizing Flexure Hinges,” Nanotechnology, Vol. 10, No. 4, pp. 394–398, 1999.
Kim, K.-H., Choi, Y.-M., Gweon, D.-G., Hong, D.-P., Kim, K.-S., Lee, S.-W., and Lee, M.-G., “Design of Decoupled Dual Servo Stage with Voice Coil Motor and Linear Motor for XY Long Stroke Ultra-Precision Scanning System,” Proc. of SPIE, Paper No. 60401C, 2005.
Liu, C.-H., Jywe, W.-Y., Jeng, Y.-R., Hsu, T.-H., and Li, Y.-t., “Design and Control of a Long-Traveling Nano-Positioning Stage,” Precision Engineering, Vol. 34, No. 3, pp. 497–506, 2010.
Yoo, D.-Y., Lee, S.-K., and Lee, D.-H., “Ultraprecision Machining-Based Micro-Hybrid Lens Design for Micro Scanning Devices,” Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf., Vol. 16, No. 4, pp. 639–646, 2015.
Ju, J., Lim, S., Seok, J., and Kim, S.-m., “A Method to Fabricate Low-Cost and Large Area Vitreous Carbon Mold for Glass Molded Microstructures,” Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf., Vol. 16, No. 2, pp. 287–291, 2015.
Duong, T.-H. and Kim, H.-C., “Deformation Analysis of Rectangular Channel Structures in Micro Pattern Machining,” Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf., Vol. 16, No. 4, pp. 619–627, 2015.
Chun, S.-H. and Ko, T. J., “Study on the Response Surface Model of Machining Error in Internal Lathe Boring,” Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf., Vol. 12, No. 2, pp. 177–182, 2011.
Heo, S., Lee, M., Kim, S. H., Lee, W., and Min, B.-K., “Compensation of Tool Deflection in Micromilling Using Workpiece Holder Control Device,” Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf., Vol. 16, No. 6, pp. 1205–1208, 2015.
Jeong, J.-h., Kim, M.-h., Woo, S., Gweon, D.-g., Ahn, D., and Hong, D., “Design of a Six-Degree-of-Freedom Motion Fine Stage Driven by Voice Coil Motors with Flexural Guides,” Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf., Vol. 16, No. 1, pp. 203–207, 2015.
Lee, D.-J., Lee, S.-K., and Kim, W.-S., “Precise Contour Motion of XY Stage Driven by Ultrasonic Linear Motors in a High Vacuum Environment,” Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf., Vol. 17, No. 3, pp. 293–301, 2016.
Chang, S. H., Tseng, C. K., and Chien, H. C., “An Ultra-Precision XYTheta(Z) Piezo-Micropositioner. II. Experiment and Performance,” IEEE Trans Ultrason Ferroelectr Freq Control Vol. 46, No. 4, pp. 906–912, 1999.
Lee, S.-Q. and Gweon, D.-G., “A New 3-DOF Z-Tilts Micropositioning System Using Electromagnetic Actuators and Air Bearings,” Precision Engineering, Vol. 24, No. 1, pp. 24–31, 2000.
Huang, S.-C. and Dao, T.-P., “Design and Computational Optimization of a Flexure-Based XY Positioning Platform Using FEA-Based Response Surface Methodology,” Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf., Vol. 17, No. 8, pp. 1035–1048, 2016.
Choi, K.-B., Lee, J. J., Kim, G. H., and Lim, H. J., “A Compliant Parallel Mechanism with Flexure-Based Joint Chains for Two Translations,” Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf., Vol. 13, No. 9, pp. 1625–1632, 2012.
Scire, F. E. and Teague, E. C., “Piezodriven 50-μm Range Stage with Subnanometer Resolution,” Review of Scientific Instruments, Vol. 49, No. 12, pp. 1735–1740, 1978.
Juhas, L., Vujanić, A., Adamović, N., Nagy, L., and Borovac, B., “A Platform for Micropositioning Based on Piezo Legs,” Mechatronics, Vol. 11, No. 7, pp. 869–897, 2001.
Nguyen, P.-B. and Choi, S.-B., “Micro-Position Control of a Piezostack Actuator Using Rate-Dependent Hysteretic Compensator,” Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf., Vol. 12, No. 5, pp. 885–891, 2011.
Jung, H. J. and Kim, J. H., “Novel Piezo Driven Motion Amplified Stage,” Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf., Vol. 15, No. 10, pp. 2141–2147, 2014.
Liu, P.-B., Yan, P., Zhang, Z., and Leng, T.-T., “Flexure-Hinges Guided Nano-Stage for Precision Manipulations: Design, Modeling and Control,” Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf., Vol. 16, No. 11, pp. 2245–2254, 2015.
Witthauer, A., Kim, G.-Y., Faidley, L., Zou, Q., and Wang, Z., “Design and Characterization of a Flextensional Stage Based on Terfenol-D Actuator,” Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf., Vol. 15, No. 1, pp. 135–141, 2014.
Lu, T.-F., Handley, D. C., Kuan Yong, Y., and Eales, C., “A Three-DOF Compliant Micromotion Stage with Flexure Hinges,” Industrial Robot: An International Journal, Vol. 31, No. 4, pp. 355–361, 2004.
Jouaneh, M. and Yang, R., “Modeling of Flexure-Hinge Type Lever Mechanisms,” Precision Engineering, Vol. 27, No. 4, pp. 407–418, 2003.
Lobontiu, N., “Compliance-Based Matrix Method for Modeling the Quasi-Static Response of Planar Serial Flexure-Hinge Mechanisms,” Precision Engineering, Vol. 38, No. 3, pp. 639–650, 2014.
Liu, Y. and Xu, Q., “Design of a Flexure-Based Auto-Focusing Device for a Microscope,” Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf., Vol. 16, No. 11, pp. 2271–2279, 2015.
Park, D.-K., Lee, G.-I., Gao, J.-C., and Kim, J.-Y., “Research on the Design of the Ultra-High-Precision Positioning Control Error Compensation,” Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf., Vol. 17, No. 10, pp. 1351–1358, 2016.
Ryu, J. W., Lee, S.-Q., Gweon, D.-G., and Moon, K. S., “Inverse Kinematic Modeling of a Coupled Flexure Hinge Mechanism,” Mechatronics, Vol. 9, No. 6, pp. 657–674, 1999.
Kim, J., Kim, S., and Kwak, Y., “Optimization of a Piezoelectric Actuator Using Bridge-Type Hinge Mechanism,” J. Korean Soc. Precis. Eng., Vol. 20, No. 2, pp. 168–175, 2003.
Kang, D., Kim, K., Kim, D., Shim, J., Gweon, D.-G., and Jeong, J., “Optimal Design of High Precision XY-Scanner with Nanometer-Level Resolution and Millimeter-Level Working Range,” Mechatronics, Vol. 19, No. 4, pp. 562–570, 2009.
Woo, S. and Gweon, D.-G., “Design and Optimization of Long Stroke Planar Motion Maglev Stage Using Copper Strip Array,” Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf., Vol. 16, No. 3, pp. 479–485, 2015.
Li, T.-M., Zhang, J.-L., and Jiang, Y., “Derivation of Empirical Compliance Equations for Circular Flexure Hinge Considering the Effect of Stress Concentration,” Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf., Vol. 16, No. 8, pp. 1735–1743, 2015.
Ito, S., Cigarini, F., Unger, S., and Schitter, G., “Flexure Design for Precision Positioning Using Low-Stiffness Actuators,” IFACPapersOnLine, Vol. 49, No. 21, pp. 200–205, 2016.
Lee, S.-H., Kim, H.-C., and Jung, K.-S., “Atomic Force Microscopy Using Optical Pickup Head to Measure Cantilever Displacement,” Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf., Vol. 12, No. 5, pp. 913–915, 2011.
Jung, J.-k., Youm, W.-s., and Park, K.-h., “Vibration Reduction Control of a Voice Coil Motor (VCM) Nano Scanner,” Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf., Vol. 10, No. 3, pp. 167–170, 2009.
Pahk, H. J., Lee, D. S., and Park, J. H., “Ultra Precision Positioning System for Servo Motor-Piezo Actuator Using the Dual Servo Loop and Digital Filter Implementation,” International Journal of Machine Tools and Manufacture, Vol. 41, No. 1, pp. 51–63, 2001.
Li, Y., Xiao, S., Xi, L., and Wu, Z., “Design, Modeling, Control and Experiment for a 2-DOF Compliant Micro-Motion Stage,” Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf., Vol. 15, No. 4, pp. 735–744, 2014.
Teo, T. J., Yang, G., and Chen, I.-M., “A Flexure-Based Electromagnetic Nanopositioning Actuator with Predictable and Re-Configurable Open-Loop Positioning Resolution,” Precision Engineering, Vol. 40, pp. 249–260, 2015.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, JS., Youn, H. & Kang, B. Ultra-precision 3 DOF tilting stage for workpiece setup of scalable micro-pattern machining. Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf. 18, 1103–1109 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12541-017-0129-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12541-017-0129-x