Abstract
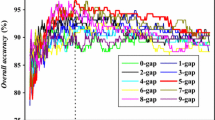
Malaria parasite secretes various proteins in infected red blood cell for its growth and survival. Thus identification of these secretory proteins is important for developing vaccine or drug against malaria. In this study, the modified method of quadratic discriminant analysis is presented for predicting the secretory proteins. Firstly, 20 amino acids are divided into five types according to the physical and chemical characteristics of amino acids. Then, we used five types of amino acids compositions as inputs of the modified quadratic discriminant algorithm. Finally, the best prediction performance is obtained by using 20 amino acid compositions, the sensitivity of 96 %, the specificity of 92 % with 0.88 of Mathew’s correlation coefficient in fivefold cross-validation test. The results are also compared with those of existing prediction methods. The compared results shown our method are prominent in the prediction of secretory proteins.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Snow RW, Guerra CA, Noor AM, Myint HY, Hay SI (2005) The global distribution of clinical episodes of Plasmodium falciparum malaria. Nature 434:214–217
Birkholtz LM, Blatch G, Coetzer TL, Hoppe HC, Human E, Morris EJ, Ngcete Z, Oldfield L, Roth R, Shonhai A, Stephens L, Louw AI (2008) Heterologous expression of plasmodial proteins for structural studies and functional annotation. Malar J 7:197. doi:10.1186/1475-2875-7-197
Liu H, Yang J, Liu DQ, Shen HB, Chou KC (2007) Using a new alignment kernel function to identify secretory proteins. Protein Pept Lett 14(2):203–208
Verma R, Tiwari A, Kaur S, Varshney GC, Raghava GP (2008) Identification of proteins secreted by malaria parasite into erythrocyte using SVM and PSSM profiles. BMC Bioinf 9:201–212
Zuo YC, Li QZ (2010) Using K-minimum increment of diversity to predict secretory proteins of malaria parasite based on groupings of amino acids. Amino Acids 38:859–867
Lin WZ, Fang JA, Xiao X, Chou KC (2012) Predicting secretory proteins of malaria parasite by incorporating sequence evolution information into pseudo amino acid composition via grey system model. PLoS One 7(11):e49040. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0049040
Garg A, Raghava GP (2008) A machine learning based method for the prediction of secretory proteins using amino acid composition, their order and similarity-search. Silico Biol 8(2):129–140
Hayakawa T, Arisue N, Udono T, Hirai H, Sattabongkot J, Toyama T, Tsuboi T, Horii T, Tanabe K (2009) Identification of Plasmodium malariae, a human malaria parasite, in imported chimpanzees. PLoS One 4:e7412
Huang WL (2012) Ranking gene ontology terms for predicting non-classical secretory proteins in eukaryotes and prokaryotes. J Theor Biol 312:105–113. doi:10.1016/j.jtbi.2012.07.027
Oyelade J, Ewejobi I, Brors B, Eils R, Adebiyi E (2011) Computational identification of signalling pathways in Plasmodium falciparum. Infect Genet Evol 11:755–764
Tedder PM, Bradford JR, Needham CJ, McConkey GA, Bulpitt AJ, Westhead DR (2010) Gene function prediction using semantic similarity clustering and enrichment analysis in the malaria parasite Plasmodium falciparum. Bioinformatics 26:2431–2437
Tonkin CJ, Kalanon M, McFadden GI (2008) Protein targeting to the malaria parasite plastid. Traffic 9:166–175
Yu L, Guo Y, Zhang Z, Li Y, Li M, Li G, Xiong W, Zeng Y (2010) SecretP: a new method for predicting mammalian secreted proteins. Peptides 31(4):574–578. doi:10.1016/j.peptides.2009.12.026
Zhang VM, Chavchich M, Waters NC (2012) Targeting protein kinases in the malaria parasite: update of an antimalarial drug target. Curr Top Med Chem 12:456–472
Ding H, Deng EZ, Yuan LF, Liu L, Lin H, Chen W, Chou KC (2014) iCTX-type: a sequence-based predictor for identifying the types of conotoxins in targeting ion channels. Biomed Res Int 2014:286419. doi:10.1155/2014/286419
Ding H, Feng PM, Chen W, Lin H (2014) Identification of bacteriophage virion proteins by the ANOVA feature selection and analysis. Mol Biosyst 10(8):2229–35. doi:10.1039/c4mb00316k
Ding H, Lin H, Chen W, Li ZQ, Guo FB, Huang J, Rao N (2014) Prediction of protein structural classes based on feature selection technique. Interdiscip Sci 6(3):235–240. doi:10.1007/s12539-013-0205-6
Liu WX, Deng EZ, Chen W, Lin H (2014) Identifying the subfamilies of voltage-gated potassium channels using feature selection technique. Int J Mol Sci 15(7):12940–12951. doi:10.3390/ijms150712940
Yuan LF, Ding C, Guo SH, Ding H, Chen W, Lin H (2013) Prediction of the types of ion channel-targeted conotoxins based on radial basis function network. Toxicol In Vitro 27(2):852–856. doi:10.1016/j.tiv.2012.12.024
Feng PM, Chen W, Lin H, Chou KC (2013) iHSP-PseRAAAC: identifying the heat shock protein families using pseudo reduced amino acid alphabet composition. Anal Biochem 442(1):118–125. doi:10.1016/j.ab.2013.05.024
Feng PM, Ding H, Chen W, Lin H (2013) Naïve Bayes classifier with feature selection to identify phage virion proteins. Comput Math Methods Med 2013:530696. doi:10.1155/2013/530696
Feng PM, Lin H, Chen W (2013) Identification of antioxidants from sequence information using Naïve Bayes. Comput Math Methods Med 2013:567529. doi:10.1155/2013/567529
Ding H, Guo SH, Deng EZ, Yuan LF, Guo FB, Huang J, Rao NN, Chen W, Lin H (2013) Prediction of Golgi-resident protein types by using feature selection technique. Chemom Intell Lab Syst 124:9–13. doi:10.1016/j.chemolab.2013.03.005
Lin H, Chen W, Yuan LF, Li ZQ, Ding H (2013) Using over-represented tetrapeptides to predict protein submitochondria locations. Acta Biotheor 61(2):259–268. doi:10.1007/s10441-013-9181-9
Lin H, Ding C, Yuan LF, Chen W, Ding H, Li ZQ, Guo FB, Huang J, Rao NN (2013) Predicting subchloroplast locations of proteins based on the general form of Chou’s pseudo amino acid composition: approached from optimal tripeptide composition. Int J Biomath 62(2):1350003
Lin WZ, Fang JA, Xiao X, Chou KC (2013) iLoc-Animal: a multi-label learning classifier for predicting subcellular localization of animal proteins. Mol BioSyst 9:634–644
Feng YE (2014). Prediction of four kinds of simple super-secondary structures in protein by using chemical shifts. Sci World J (Article ID 978503), http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/978503
Feng YE, Luo LF (2008) Use of tetrapeptide signals for protein secondary structure prediction. Amino acids 35:607–614
Chou KC, Shen HB (2010a) Plant-mPLoc: a top-down strategy to augment the power for predicting plant protein subcellular localization. PLoS One 5:e11335
Chen W, Feng PM, Lin H, Chou KC (2013) iRSpot-PseDNC: identify recombination spots with pseudo dinucleotide composition. Nucleic Acids Res 41(6):e68
Chen W, Lin H, Feng PM, Ding C, Zuo YC, Chou KC (2012) iNuc-PhysChem: a sequence-based predictor for identifying nucleosomes via physicochemical properties. PLoS One 7:e47843
Chen C, Shen ZB, Zou XY (2012) Dual-layer wavelet SVM for predicting protein structural class via the general form of Chou’s pseudo amino acid composition. Protein Pept Lett 19:422–429
Chou KC, Shen HB (2010b). Cell-PLoc 2. 0: an improved package of web-servers for predicting subcellular localization of proteins in various organisms. Nat Sci 2:1090–1103. doi:10.4236/ns.2010.210136 (openly accessible at http://www.scirp.org/journal/NS/)
Esmaeili M, Mohabatkar H, Mohsenzadeh S (2010) Using the concept of Chou’s pseudo amino acid composition for risk type prediction of human papillomaviruses. J Theor Biol 263:203–209
Guo J, Rao N, Liu G, Yang Y, Wang G (2011) Predicting protein folding rates using the concept of Chou’s pseudo amino acid composition. J Comput Chem 32:1612–1617
Hayat M, Khan A (2012) Discriminating outer membrane proteins with fuzzy K-nearest neighbor algorithms based on the general form of Chou’s PseAAC. Protein Pept Lett 19:411–421
Xiao X, Wang P, Lin WZ, Jia JH, Chou KC (2013) iAMP-2L: a two-level multi-label classifier for identifying antimicrobial peptides and their functional types. Anal Biochem 436:168–177
Acknowledgments
The author is grateful to the anonymous reviewers for their valuable suggestions and comments, which have led to the improvement of this paper. The work was supported by National Science foundation of China (No. 31360206) and the project of “prairie excellence” engineering in Inner Mongolia and the Inner Mongolia autonomous region higher school science and technology research projects (No. NJZY067) and Basic Science of Inner Mongolia Agriculture University Research Fund (No. JC2013004).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Appendices
Appendix 1
See Table 3.
Appendix 2
See Table 4.
Appendix 3
See Table 5.
Appendix 4
See Table 6.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Feng, YE. Identify Secretory Protein of Malaria Parasite with Modified Quadratic Discriminant Algorithm and Amino Acid Composition. Interdiscip Sci Comput Life Sci 8, 156–161 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12539-015-0112-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12539-015-0112-0