Abstract
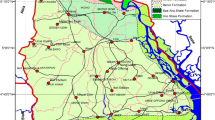
The present study is aiming to assess tiltation and subsidence of the houses in the heart of the Agartala City based on near-surface electrical resistivity (ER). The near-surface electrical resistivity (ER) testing is done on the 13 sites within the city using Wenner-Alfa array. The field instrumentation is done by four-pin (electrode) method. The DC electrical current passes through the electrode at the same time. Each soil layer is represented by the single data set. The resistivity of the soil is calculated by 2лaR formula. The ER data is indicating best possible visualisation of the near subsurface (up to the depth of 15 m) imaging of the soil structure of the Agartala City and its surrounding areas. On the basis of spatial distribution of electrical resistivity reveals that the flood plain land with average elevation 12 m where less ER value (<150 Ωm) and the areas of dissected highlands (Tilla land) with average elevation are 30 m which are marked with high ER value (>300 Ωm). The ER data shows that Agartala and its surrounding areas are characterised by different types of soil which are related to different geomorphic and geological units. The dry sandy soil and sandy clay soil on the highland areas and wet sandy alluvium and clayey alluvium of the flood plain area make differences of ER data.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akram SM, Mudiar B, Sahu A (2004) Geodata integration leads to reserve accretion in baramura gas field of Tripura, AssamArakan Fold Belt- a case study. In: 5th Conference & Exposition on Petroleum Geophysics, Hyderabad, pp 767–771
Alam M, Alam MM, Curray JR, Chowdhury MLR, Gani MR (2003) An overview of the sedimentary geology of the Bengal Basin in relation to the regional tectonic framework and basin-fill history. Sediment. Geol 155:179–208
Allah SA, Mogi T, Ito H, Jomori A, Yuuki Y, Fomenko E, Kiho K, Kaieda H, Suzuki K, Tsukuda K (2013) Three-dimensional resistivity characterization of a coastal area: application of grounded electrical-source airborne transient electromagnetic (GREATEM) survey data from Kujukuri Beach. Japan. J. Appl. Geophys 99:1–11
Anchuela ÓP, Luzón A, Garbi HG, Pérez A, Juan AP, Soriano MA (2014) Combination of electromagnetic, geophysical methods and sedimentological studies for the development of 3D models in alluvial sediments affected by karst (Ebro Basin, NE Spain). J. Appl. Geophys 102:81–95
Apostolopoulos GV (2014) Combined geophysical investigation for the detection of ancient metallurgical installations near Keratea City. Greece. J. Appl. Geophys 104:17–25
Balamir M (2004) Urban Seismic Risk Management: the earthquake master plan of Istanbul (EMPI). In: 13th World Conference on Earthquake Engineering, vol no. 9005, Vancouver, B.C., Canada, Paper
Bandyopadhyay S, Saha S, Ghosh K, De SK (2013) Channel planform change and detachment of tributary: a study on the Haora and Katakhal Rivers, Tripura, India. Geomorphology 193:25–35
Bashir K, Debnath R, Saha R (2022) Estimation of local site effects and seismic vulnerability using geotechnical dataset at flyover site Agartala India. Acta Geophysica:1–34
Bhattacharjee S (1998) Earthquakes in northeast India mitigation-a possible approach. In: Sharma GD (ed) Status of landslides in northeast India and natural disaster management. Assam University Press, pp 77–84
Caylak C, Kocaslan A, Gorgulu K, Buyuksarac A, Arpaz E (2014) Importance of ground properties in the relationship of ground vibration–structural hazard and land application. J. Appl. Geophys 104:6–16
Das S, Ghosh S, Kayal JR (2019) Liquefaction potential of Agartala City in Northeast India using a GIS platform. Bull. Eng. Geol. Environ 78:2919–2931
Dey S (2005) Conceptual models for the assessment of Tertiary-Quaternary geomorphic evolution of Paleocoastal Tripura. Ann Assoc Am Geogr XXV(1):73–80
Dey S, Mukherjee G, Paul S (2012) Imaging and visualizing the spectral signatures from Landsat TM and ‘τ’ value-based surface soil microzonation mapping at and around Agartala (India). Geocarto Int:1–15
Fargier Y, Lopes SP, Fauchard C, François D, Côte P (2014) DC-Electrical resistivity imaging for embankment dike investigation: a 3D extended normalisation approach. J. Appl. Geophys 103:245–256
Gable GG (1994) Integrating case study and survey research methods: an example in information systems. European J. Info.Sys 3(2):112–126
Islam T, Chik Z, Mustafa MM, Sanusi H (2012) Modeling of electrical resistivity and maximum dry density in soil compaction measurement. Earth.Sci, Environ. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-012-1573-7
Jade S, Mukul M, Bhattacharyya AK, Vijayan MSM, Jaganathan S, Kumar A, Tiwari RP, Kumar A, Kalita S, Sahu SC, Krishna AP, Gupta SS, Murthy MVRL, Gaur VK (2007) Estimates of inter seismic deformation in Northeast India from GPS measurements. EPSL 263:221–234
Joshi M (2022) Co-seismic landslides in the Sikkim Himalaya during the 2011 Sikkim earthquake: lesson learned from the past and inference for the future. Geol. J 57(12):5039–5060
Joshi M, Prasobh PR, Rajappan S, Rao BP, Gond A, Misra A et al (2021) Detection of soil pipes through remote sensing and electrical resistivity method: insight from southern Western Ghats, India. Quat. Int 575:51–61
Kayal JR (1987) Microseismicity and source mechanism study: Shillong Plateau. Northeast India. Bull. Seism. Soc. Am 77(1):184–194
Kayal JR (1998) Seismicity of Northeast India and surroundings: development over the past 100 years. J. Geophys 19(1):9–34
Kemna A, Vanderborght J, Kulessa B, Vereecken H (2002) Imaging and characterisation of subsurface solute transport using electrical resistivity tomography (ERT) and equivalent transport models. J. Hydro 267:125–146
Loke, M.H., 2004. Tutorial: 2-D and 3-D electrical imaging surveys, 1-3.
Mitra, R.N, G.S. Mishra, and A.A. Rahaman (1968), Geology of Baramura Anticline: unpublished geological field party report, ONGC, Dehradun.
Mitra S, Santra A (2020) Monitoring urban expansion and land use/land cover changes of Agartala City, Tripura, India. Indian Journal of Regional Science 52(1):123–136
Mondal NC, Rao AV, Singh VP (2010) Efficacy of electrical resistivity and induced polarizationmethods for revealing fluoride contaminated groundwater in granite terrain. Environ. Monit. Assess 168:103–114
Mukherjee G, Debbarma C, Paul S, Dey S (2011) Electrical resistivity based shallow crustal deformation analysis in an active seismic zone. Indones. J. Geogr 43(2):170–180
Ng AH-M, Ge L, Li X, Abidin HZ, Andreas H, Zhang K (2012) Mapping land subsidence in Jakarta, Indonesia using persistent scatterer interferometry (PSI) technique with ALOS PALSAR.Int. J. Appl. Earth Obser.and Geoinfo 18:232–242
Razafindratsima S, Lataste J-F (2014) Estimation of the error made in pole–dipole electrical resistivity tomography depending on the location of the remote electrode: Modeling and field study. J. Appl. Geophys 100:44–57
Rosyidi SA, Lesmana SB, Wintolo J, Chik Z, Taha MR, 2008. Geo-resistivity surveys for faults identification in geotechnical damages area from Yogyakarta earthquake of May 27 (2006) The 14th World Conference on Earthquake Engineering. Beijing, China
Rumpf M, Tronicke J (2014) Predicting 2D geotechnical parameter fields in near-surface sedimentary environments. J. Appl. Geophys 101:95–107
Sahu,P, Sikdar PK (2011) Threat of land subsidence in and around Kolkata City and East Kolkata Wetlands, West Bengal. India.J. Earth Syst. Sci 120(3):435–446
Samouëlian A, Cousin I, Tabbagh A, Bruand A, Richard G (2005) Electrical resistivity survey in soil science: a review. Soil & Tillage Research 83:173–193
Sass O, Bell R, Glade T (2008) Comparison of GPR, 2D-resistivity and traditional techniques for the subsurface exploration of the Öschingen landslide, Swabian Alb (Germany). Geomorphology 93:89–103
Sen S, Mitra S, Debbarma C, De SK (2015) Impact of faults on landslide in the Atharamura Hill (along the NH 44). Tripura. Environ. Earth Sci 73:5289–5298
Shaaban F, Ismail A, Massoud U, Mesbah H, Lethy A, Abbas AM (2013) Geotechnical assessment of ground conditions arounda tilted building in Cairo–Egypt using geophysical approaches. Arab J. Basic Appl. Sci 13:63–72
Sinha RN, Sastri VV (1973) Correlation of the Tertiary geosynclinal sediments of the Surma Valley, Assam and Tripura state (India). Sedim Geol 10(2):107–137
Thingbaijam, K.K.S, S.K. Nath, A. Yadav, A. Raj, M.Y. Walling W.K. Mohanty (2008), Recent seismicity in Northeast India and its adjoining region, J Seismol, 12, 107–123.
Tiwari RK, Sri Lakshmi S, Rao KNN (2004) Characterization of earthquake dynamics in Northeastern India regions: a modern nonlinear forecasting approach. Pure Appl. Geophys 161:865–880
Vedatri A, Bashir K, Saha R (2018) Assessment of seismic local hazard of Agartala town based on nonlinear site response analysis. Disaster Adv 11(1)
Xia J (2014) Estimation of near-surface shear-wave velocities and quality factors using multichannel analysis of surface-wave methods. J. Appl. Geophys 103:140–151
Acknowledgements
Authors acknowledge their debt to Dr. R. Diwara, Chief Scientist, CSIR North-East Institute of Science and Technology, Jorhat, for providing seismo-tectonic map of North-East India. Authors also acknowledge the support of students, research scholars and faculties, Department of Geography and Disaster Management, Tripura University, to execute the research work. Authors are thankful to the people of Agartala City, India, who cooperated during the survey. The authors are also grateful to the learned reviewers and the Editor of the journal Arabian Journal of Geosciences (Prof. Abdullah M. Al-Amri) for their valuable and meticulous suggestions. We also thank Dr. Laxmi Kumari, Assistant Professor, Department of English, KL University for going through the manuscript carefully. Authors are thankful to Tripura University for caring out this research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
All the data presented in the manuscript are original, which is not yet published elsewhere.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Longjun Dong
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Sen, S., Santra, A. Assessment of leaning of houses in Agartala City: an applied geophysical approach, Tripura, India. Arab J Geosci 16, 535 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-023-11643-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-023-11643-3