Abstract
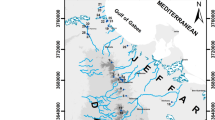
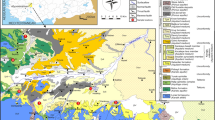
In the beginning, irrigation water in Metlaoui oasis is largely derived from springs discharging mainly from sandy Miocene aquifer in the southern flank of Metlaoui range in southwestern Tunisia. It was only from the considerable drops in the flow rates of the springs that recourse was had to the digging of boreholes. Hydro-geochemical studies were carried out in this area with the objective of identifying the geochemical processes influencing spring water chemical composition. Water samples were selected from 12 springs and 11 wells to analyze δ18O and δ2H, major and trace element concentrations. Physical (pH, electrical conductivity, total dissolved solids) and hydro-chemical characteristics (Na, K, Ca, Mg, Sr, Li, HCO3, Cl, SO4, NO3, Br, B, F) of groundwater samples were determined. Water quality parameters show that the majority of studied springs are suitable for irrigational activities. However, the Water Quality Index (WQI) reveals that all springs have poor to very poor water quality. Springs have significantly different geochemistry and reflect interaction with different lithologies. Dissolution of evaporates and cation exchange represent the major mechanisms responsible for groundwater salinization. The multivariate technique of principal component analysis shows that loading distributions of the first factor pair Na and Cl, commonly attributed to the evolution of groundwater due to evaporation and dissolution of halite and evaporated minerals, and SO4, Mg, and Ca ions associated with gypsum and/or anhydrite dissolution and cation exchange processes. Stable isotopes represent the first group of spring plotting along the evaporation line. While the second spring group connected to the shallow unsaturated zone exhibits a mixing trend of evaporation-dissolution processes. Hamda Spring (sample N°4) was subjected to higher evaporation and is considered as a closed system not connected to the deep Miocene aquifer.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abidi I (2007) Caractérisation hydrogéologique, géochimique et isotopique des systèmes aquifères du synclinal de Tamerza et de la plaine de Chott El Gharsa (Sud-Ouest de la Tunisie). Dissertation, University of Sfax
Ahmadi R, Ouali J, Mercier E, Mans JL, Van-Vliet Lanoe B, Launeau P, Rhekhiss F, Rafini S (2006) The geomorphologic responses to hinge migration in the fault-related folds in the Southern Tunisian Atlas. J Struct Geol 28:721–728. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsg.2006.01.004
Alaya MB, Saidi S, Zemni T, Zargouni F (2013) Suitability assessment of deep groundwater for drinking and irrigation use in the Djeffara aquifers (Northern Gabes, south-eastern Tunisia). Environmental Earth Sciences 71:3387–3421
Alaya MB, Saidi S, Zemni T, Zargouni F (2014) Suitability assessment of deep groundwater for drinking and irrigation use in the Djeffara aquifers (northern Gabes, South-Eastern Tunisia). Environ Earth Sci 71(8):3387–3421. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-013-2729-9
Alberto WD, Del Pilar DM, Valeria AM, Fabiana PS, Cecilia HA, De Los Angeles BM (2001) Pattern recognition techniques for the evaluation of spatial and temporal variations in water quality, a case study: Suquia river basin (Cordoba–Argentina). Water Res 35(12):2881–2894
Alcalá FJ, Gustodio E (2008) Using the Cl/Br ratio as a tracer to identify the origin of salinity in aquifers in Spain and Portugal. Hydrogeological Journal 359:189–207. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2008.06.028
Al-Taani A (2017) Seasonal variations in water quality of Al-Wehda Dam north of Jordan and water suitability for irrigation in summer. Arab J Geosci 6:1131–1140. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-011-0428-y
Andrews JN, Fontes JC, Aranyossy JF, Dodo A, Edmunds WM, Joseph A, Travi Y (1994) The evolution of alkaline groundwaters in the continental intercalaire aquifer of the Irhazer Plain. Niger Water Resources Research 30:45–61. https://doi.org/10.1029/93WR02226
Appelo CAJ (1988) Hydrochemistry for hydrogeotogists. Free University, Amsterdam
Ayadi Y, Redhaounia B, Mokadem N, Zighmi K, Dhaoui M, Hamed Y (2018) Hydro-geophysical and geochemical studies of the aquifer systems in El Kef region (Northwestern Tunisia). Carbonates Evaporites 34:1391–1413. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13146-018-0460-z
Barquin NJ, Scarsbrook M (2008) Management and conservation strategies for coldwater Springs. Aquatic Conserv: Mar Freshw Ecosyst 18:580–591
Brondi M, Dall’aglio MD, Vitrano F (1973) Lithium as path finder element in the large-scale hydrochemical exploration for hydrothermal systems. Geothermics 283:142–153. https://doi.org/10.1016/0375-6505(73)90021-7
Brown RM, McClelland NI, Deininger RA, Tozer RG (1970) A water quality index – do we dare? Water Sew Works 117:339–343
Bryant RG, Sellwood BW, Millington AC, Drake NA (1994) Marine-like potash evaporite formation on a continental playa: case study Chott el Djerid, southern Tunisia. Sed Geol 90:269–291
Burrolet PF (1956) Contribution à l’étude stratigraphique de la Tunisie Centrale. Ann Mines Geol Tunis 18:345
Castany G, Domergue CH (1951) Les ressources hydrauliques du Sud tunisien, Djérid et Nefzaoua. Report Imp. LARAPIDE: Tunis, Tunisia
Celati R, Grassi S, Calore C (1990) Overflow thermal springs of Tuscany (Italy). J Hydrol 118:191–207. https://doi.org/10.1016/0022-1694(90)90258-Y
Chaabani F (1978) Les phosphorites de la coupe-type de Foum Selja (Metlaoui, Tunisie). Une série sédimentaire séquentielle à évaporites du Paléogène.Dissertation, University of L Pasteur
Colombani N, Cuoco E, Mastrocicco M (2017) Origin and pattern of salinization in the Holocene aquifer of the southern Po Delta (NE Italy). J Geochem Explor 175:130–137
Craig H (1961) Standard for reporting concentrations of deuterium and oxygen-18 in natural waters. Science 133:1833–1834https://doi.org/10.1126/science.133.3467.1833
Dansgaard W (1964) Stable Isotopes in Precipitation. Tellus 16:436–468
De Waele J, Di Gregorio F, Gasmi N, Melis MT, Talbi M (2005) Geomorphosites of Tozeur region (south-West Tunisia). Il Quaternario 18:223–232
Dhaoui M, Gabtni H (2013) Fault pattern delineation and structural interpretation of the Gafsa trough (onshore central Tunisia) using gravity data. Arab J Geosci 6:1559–1568. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-011-0436-y
Doneen LD (1964) Water quality for agriculture. Department Of Irrigation, University Of California, Davis, p 48
Edmunds WM (1996) Bromine geochemistry of British groundwaters. Mineral Mag 60:275–284
Edmunds WM, Shand P, Guendouz AH, Moula A, Mamou A, Zouari K (1997) Recharge characteristics and groundwater quality of the grand Erg oriental basin, Report Wd/97/46R. IAEA, Vienna
Edmunds WM et al (2003) Groundwater evolution in the Continental Intercalaire aquifer of southern Algeria and Tunisia: trace element and isotopic indicators. Appl Geochem 18:805–822
Fontes JC, Yousefi M, Allison GB (1986) Estimation of the long-term groundwater discharge in the Northern Sahara using stable isotope profiles in soil water. J Hydrol 86:315–327
Fontes JC (1976) Isotopes du milieu et cycles des eaux naturelles: quelques aspects. Dissertation, University of Paris VI, France
Garcia MG, Del Hidalgo M, Blesa MA (2001) Geochemistry of groundwater in the alluvial plain of ucuman province Argentina. Hydrogeology 9:597–610
Gueddari M (1984) Géochimie et thermodynamique des évaporites continentales. Mémoire des Sciences Géologiques, 76: 1–143. Etude du lac natron en Tanzanie et du Chott El-Jerid en Tunisie
Gupta S, Nayek S, Chakraborty D (2016) Hydrochemical evaluation of Rangit river, Sikkim, India: using Water Quality Index and multivariate statistics. Environ Earth Sci 75:567
Handa BK (1975) Geochemistry and genesis of fluoride-containing groundwaters in India. Groundwater 13:275–281
Hanshaw BB, Back W (1979) Major geochemical processes in the evolution of carbonate-aquifer systems. J Hydrol 43:287–312
Hem JD (1985) Study and interpretation of the chemical characteristics of natural waters. Geological Survey Water-supply paper 1473
Hlaiem A (1999) Halokinesis and structural evolution of the major features in eastern and southern Tunisian Atlas. Tectonophysics 306:79–95
Jeribi L (1997) Contribution à la mise en évidence de l’alimentation de la nappe du Complexe Terminal à partir de la chaîne de Metlaoui-Gafsa. University of Tunis, DEA
Joshi DM, Kumar A, Agrawal N (2009) Assessment of the irrigation water quality of river Ganga in Haridwar district. Rasayan J Chem 2:285–292
Kamel S (2011) Recharge of the plio-quaternary water table aquifer in Tunisian chotts region estimated from stable isotopes. Environ Earth Sci 63:189–199. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-010-0683-3
Kamel S, Chelbi MB, Jedoui Y (2013) Investigation of sulphate origins in the Jeffara aquifer, southeastern Tunisia: a geochemical approach. J Earth Syst Sci 122:15–28. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12040-012-0252-0
Kelly WP (1957) Adsorbed sodium cation exchange capacity and percentage sodium sorption in alkali soils. Science 84:473–477
Kelly WP (1963) Use of saline irrigation water. Soil Sci 95:355–391
Leeman WP, Sisson VB (2018) Geochemistry of boron and its implications for crustal and mantle processes. Boron, pp. 645–708
Lindsey BD, Belitz K, Cravotta CA, Toccalino PL, Dubrovsky NM (2021) Lithium in groundwater used for drinking-water supply in the United States. Sci Total Environ 767:144–691
Mahamuni K, Kulkarni H (2012) Groundwater resources and spring hydrogeology in South Sikkim, with special reference to climate change. In: Arrawatia ML, Tambe S (eds) Climate change in Sikkim - Patterns, impacts and initiatives. Gangtok, India: Information and Public Relations Department, Government of Sikkim, pp 261–274
Mamou A (1990) Caractéristiques, évaluation et gestion des ressources en eau du Sud-Tunisien. Dissertation, University of Tunis
Margat J, Foster S, Droubi A (2006) Concept and importance of non‐renewable resources, in non‐renewable groundwater resources: a guidebook on socially‐sustainable management for water‐policy makers, vol. 10, U. N. Educ., Sci. and Cult. Organ, Paris, pp 13–24
McIntosh JC, Walter LM (2006) Paleowaters in Silurian-Devonian carbonate aquifers: geochemical evolution of groundwater in the Great Lakes region since the Late Pleistocene. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 70:2454–2479
Meglen RR (1992) Examining large databases: a chemometric approach using principal component analysis. Mar Chem 39:217–237. https://doi.org/10.1016/0304-4203(92)90103-H
Mehri A, Sogut AR (2020) Hydrochemical and statistical study of the groundwater salinization in the region of Gabes in Tunisia. Arab J Geosci 13:1–8
Meisler H, Becher AE (1967) Hydrogeologic significance of calcium-magnesium ratios in ground water from carbonate rocks in the Lancaster quadrangle, southeastern Pennsylvania. In: Geological Survey Professional Paper. Washington, pp 232–235
Meredith K, Moriguti T, Tomascak P, Hollins S, Nakamura E (2013) The lithium, boron and strontium isotopic systematics of groundwaters from an arid aquifer system: implications for recharge and weathering processes. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 112:20–31
Mester A, Balla D, Szabó G (2020) Assessment of groundwater quality changes in the rural environment of the Hungarian Great Plain based on selected water quality indicators. Water Air Soil Pollut 231:536. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-020-04910-6
Meybeck M (1987) Global chemical weathering of surficial rocks estimated from river dissolved loads. Am J Sci 287:401–428
Morgan-Jones M, Eggboro MD (1981) The hydrogeochemistry of the Jurassic limestones in Gloucestershire, England. Q J Eng GeolHydrogeol 14:25–39
Nasri N, Bouhlila R, Saaltink MW, Gamazo P (2015) Modeling the hydrogeochemical evolution of brine in saline systems: case study of the Sabkha of Oum El Khialate in South East Tunisia. Appl Geochem 55:160–169. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apgeochem.2014.11.003
Nishanthiny C, Thushyanthy M, Barathithasan T, Saravanan S (2010) Irrigation water quality based on hydro chemical analysis, Jaffna, Sri Lanka. American-Eurasian J Agric Environ Sci 7:100–102
Outtani F, Addoum B, Mercier E, Frizon de Lamotte D, Andrieux J (1995) Geometry and kinematics of the South Atlas Front, Algeria and Tunisia. Tectonophysics 249:233–248
Pan C, Ng KTW, Richter A (2019) An integrated multivariate statistical approach for the evaluation of spatial variations in groundwater quality near an unlined landfill. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26:5724–5737. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-3967-x
Plummer LN, Jones BF, Truesdell AH (1976) WATEQF, a Fortan IV version of WATEQ, a computer program for calculating chemical equilibrium of natural waters. US Geol Surv Water Resour Invest 76:61
Rajmohan N, Elango LJEG (2004) Identification and evolution of hydrogeochemical processes in the groundwater environment in an area of the Palar and Cheyyar River Basins, Southern India.". Environ Geol 46:47–61
Riley P, Gordon C, Simo JA, Tikoff B, Soussi M (2011) Structure of the Alima and associated anticlines in the foreland basin of the southern Atlas Mountains, Tunisia. Lithosphere 3:76–91. https://doi.org/10.1130/L119.1
Roberts C, Mitchell CW (1987) Spring mounds in southern Tunisia. In Desert Sediments: Ancient and Modern, L. Frostick and J. Reid, Eds. Blackwell, UK: Geol. Soc. London, 1987, Special Pub. no. 35, pp 321–336
Rose EF, Chausidon M, France-Lanord C (2000) Fractionation of boron isotopes during erosion processes: the exemple of the Himalayan Rivers. Geochim Cosmachin Acta 64:397–408. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0016-7037(99)00117-9
Rozanski K (1985) Deuterium and oxygen-18 in European groundwaters; links to atmospheric circulation in the past. Chem Geol 52:349–363
Sahal S, Kamel S (2018) Investigation of water quality origins (hydrochemical, mineralogical and isotopic) in the Jeffara of Medenine aquifer system (South-Eastern Tunisia). J Water Supply Res Technol AQUA 67:586–606. https://doi.org/10.2166/aqua.2018.019
Sassi S (1974) La sédimentation phosphatée au paléocène dans le sud et le Centre-Ouest de la Tunisie. Dissertation, University of Paris sud
Sonntag C, Klitzsch E, Löhnert EP, Shazly EM, nMünnich KO, Junghans C, Thorweihe U, Weistroffer K, Swailem FM (1978) Paleoclimatic information from deuterium and oxygen-18 in 14C dated North Saharian groundwaters: groundwater formation in the past. Isotope Hydrology. Int. At. Energy Agency, Vienna, pp 569–581
Suppe J (1985) Principles of structural geology. Prentice-Hall, Englewood Cliffs, New Jersey
Swan ARH, Sandilands M (1995) Introduction to geological data analysis. Blackwell, Oxford
Szabolcs I, Darab C (1964) The influence of irrigation water of high sodium carbonate content of soils. Proceedings of 8th ISSS Trans 2:802–812
Tagorti MA, Guellala R, Gallala W, Essefi E, Tlig S (2013) Geochemical and hydrogeological studies of a sodium sulphate deposits: the case of Sabkhet El Ghine Oum El Khialate, southeast Tunisia. Carbonates Evaporites 29:299–307. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13146-013-0180-3
Tellam JH (1995) Hydrochemistry of the saline groundwaters of the lower Mersey Basin Permo-Triassic sandstone aquifer, UK. J Hydrol 165:45–84
Tijani MN (1994) Hydrochemical assessment of groundwater in Moro Area, Kwara State, Nigeria. Environ Geol 24:194–202. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00766889
Turekiann KK, Wedepohl KH (1961) Distribution of the elements in some major units of the earth’s crust. Geol Soc Am Bull 72:175–192
Varol S, Davraz A (2015) Evaluation of the groundwater quality with WQI (Water Quality Index) and multivariate analysis: a case study of the Tefenni plain (Burdur/Turkey). Environ Earth Sci 73:1725–1744. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-014-3531-z
World Health Organization (2011) Guidelines for drinking-water quality. 4th ed: 219–443
Wilcox LV (1955) Classification and use of irrigation water. US Department of Agriculture, Washington, p 969
Yangui H, Abidi I, Zouari K, Rozanski K (2012) Deciphering groundwater flow between the Complex Terminal and Plio-Quaternary aquifers in Chott Gharsa plain (southwestern Tunisia) using isotopic and chemical tools. Hydrol Sci J 57:967–984. https://doi.org/10.1080/02626667.2012.689110
Zargouni F (1984) Style et chronologie des deformations des structures de 1’Atlas tunisien meridional, Evolution recente de l’accident Sud-atlasique, Comptes Rendus Academic Sciences (Paris)
Zargouni F (1985) Tectonique de l’Atlas méridional de Tunisie : évolutions géométrique et cinématique des structures en zone de cisaillement. Dissertation, University of Strasbourg
Zouari H (1995) Evolution géodynamique de l’Atlas centro-méridional de la Tunisie. Dissertation, University of Tunis
Acknowledgements
The authors are highly indebted to the anonymous reviewers who improved the quality of the manuscript. All thanks and gratitude to Professors El Houcine Essefi et Bedoui Nafti for their good review and enrichment of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors confirm that there is no funding received for the establishment of this research work, and no conflict of interests/competing interests exists. All data used in this paper are therefore taken from the L.57 RAF/8/35 IAEA Project database that is part of a project of the Tunisian state and which has been the subject of numerous publications by directors of this project. We recall this as being part of a project financed by the Tunisian state, and no one can claim that the data can only be used by the aforementioned directors.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Broder J. Merkel
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Essamin, R., Kamel, S. Geochemical characterization and water quality evaluation of springs emerging along with the Metlaoui range (Southwestern Tunisia). Arab J Geosci 16, 179 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-023-11272-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-023-11272-w