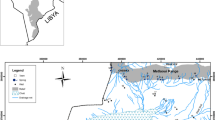
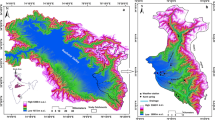
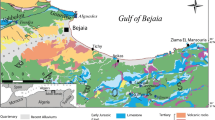
Abstract
In the present study, an integration of a hydrogeochemical investigation involving multivariate statistical analysis was conducted to identify the main processes governing spring water geochemistry in southeastern Tunisia. Springs geochemical composition is mainly controlled by water–rock interaction, dissolution of evaporite minerals, evaporation, and ion exchange reactions. The principal component analysis (PCA) confirms the dominance of the classical hydrochemical variables, originating from the natural weathering processes of sedimentary and evaporitic rocks in springs mineralization. Total dissolved solids (TDS), electrical conductivity (EC), and water quality parameters (sodium percentage, sodium adsorption ratio, magnesium hazard, permeability index, and Kelly’s ratio) confirm the irrigational suitability of the springs located in the Dahar plateau. Springs located in the wettest areas of the Dahar mountains were grouped separately in Gibb’s diagrams and in the PCA classification due to their low TDS values (< 866 mg/L). These springs show enrichment with stable isotopes (18O and 2H) composition confirming the current recharge by direct infiltration of rainwater. However, springs depleted in stable isotopes represent a probably longer residence time in the aquifer and exhibit mixing evaporation-dissolution processes. The d-excess values of springs located in the Gabes region show evidence of recharge water evaporation before infiltration. However higher values in the Dahar springs imply that rainwater is relatively less subjected to secondary evaporation during the recharge process. Results from this study demonstrate the benefits of using geochemical and isotopic data to confirm the possibility of spring water management in arid and semi-arid regions.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abid K, Hadj Ammara F, Weise S, Zouari K, Chkir N, Rozanski K, Osenbrück K (2014) Geochemistry and residence time estimation of groundwater from MioceneePliocene and Upper Cretaceous aquifers of Southern Tunisia. Quatern Int 338:59–70. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.quaint.2014.04.036
Ahmed MA, Abdel Samie SG, Badawy HA (2013) Factors controlling mechanisms of groundwater salinization and hydrogeochemical processes in the Quaternary aquifer of the Eastern Nile Delta. Egypt Environ Earth Sci 68:369–394. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-012-1744-6
Ako AA, Shimada J, Hosono T, Ichiyanagi K, Nkeng GE, Eyong GET, Roger NN (2012) Hydrogeochemical and isotopic characteristics of groundwater in Mbanga, Njombe and Penja (Banana plain)-Cameroon. J Afr Earth Sci 75:25–36. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jafrearsci.2012.06.003
Aksever F (2019) Hydrogeochemical characterization and water quality assessment of springs in the Emirdağ (Afyonkarahisar) basin. Turkey Arab J Geosci 12:780. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-019-4942-7
Alaya MB, Saidi S, Zemni T, Zargouni F (2014) Suitability assessment of deep groundwater for drinking and irrigation use in the Djeffara aquifers (northern Gabes, South-Eastern Tunisia). Environ Earth Sci 71(8):3387–3421. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-013-2729-9
Al-Taani A (2011) Seasonal variations in water quality of Al-Wehda Dam north of Jordan and water suitability for irrigation in summer. Arab J Geosci 6:1131–1140. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-011-0428-y
Ansari MDA, Deodhar A, Kumar US, Khatti VS (2015) Water quality of few springs in outer Himalayas: a study on the groundwater–bedrock interactions and hydrochemical evolution. Groundw Sustain Dev 1:59–67. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gsd.2016.01.002
Ayers RS, Westcot DW (1985) Water quality for agriculture. FAO Irrig Drain Paper 29:8–96
Bahrouni N, Bouaziz S, Soumaya A, Ben Ayed N, Attafi K, Houla Y, El Ghali A, Rebai N (2014) Neotectonic and seismotectonic investigation of seismically active regions in Tunisia: a multidisciplinary approach. J Seismol 18:235–256. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10950-013-9395-y
Ball JW, Nordstrom DK (1992) User’s manual for WATEQ4F with revised thermodynamic database and test cases for calculating speciation of minor, trace and redox elements in natural waters. US Geol Surv Open File Rep 91–183:189
Banner JL, Wasserburg GJ, Dobson PF, Carpenter AB, Mooren CH (1989) Isotopic and trace-element constraints on the origin and evolution of saline groundwaters from central Missouri. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 53:383–398
Bouaziz S, Barrier E, Soussi M, Turki MM, Zouari H (2002) Tectonic evolution of the northern African margin in Tunisia from paleostress data and sedimentary record. Tectonophysics 357:227–253. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0040-1951(02)00370-0
Bouaziz S (1995) Study of brittle tectonics in the Saharan platform and Atlas (southern Tunisia): evolution of paleochamps of constraints and geodynamic implications. Dissertation, University of Tunis
Bouri S, Makni J, Ben Dhia H (2008) A synthetic approach integrating surface and subsurface data for prospecting deep aquifers: the southeast Tunisia. Environ Geol 54:1473–1484. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00254-007-0928-y
Calianno M, Fallot J-M, Ben Fraj T, Ben Ouezdou H, Reynard E, Milano M, Abbassi M, Ghram Messedi A, Adatte T (2020) Benefits of water-harvesting systems (jessour) on soil water retention in Southeast Tunisia. Water 12:295. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12010295
Colombani N, Cuoco EB, Mastrocicco M (2017) Origin and pattern of salinization in the Holocene aquifer of the southern Po Delta (NE Italy). J Geochem Explor 175:130–137. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gexplo.2017.01.011
Courel L, Ait SH, Benaouiss N, Et-Touhami M, Fekirine B, Oujidi M, Soussi M, Tourani A (2003) Mid-Triassic to early Liassic clastic/evaporitic deposits over the Maghreb platform. Palaeogeogr Palaeoclimatol Palaeoecol 196:157–176. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0031-0182(03)00317-1
Chebbah M, Allia Z (2015) Geochemistry and hydrogeochemical process of groundwater in the Souf valley of low septentrional Sahara, Algeria. Afr J Environ Sci Technol 9:261–273. https://doi.org/10.5897/ajest2014.1710
CPCB (2000) Water quality status of Yamuna River, Central Pollution Control Board, New Delhi, series ADSORBS/32/1999–2000
Craig H (1961) Standard for reporting concentrations of deuterium and oxygen-18 in natural waters. Science 133:1833–1834. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.133.3467.1833
Dansgaard W (1964) Stable isotopes in precipitation. Tellus 16:436–468
Dhaouia Z, Chkir N, Zouari K, HadjAmmar F, Agoun A (2016) Investigation of uranium geochemistry along groundwater flow path in the Continental Intercalaire aquifer (Southern Tunisia). J Environ Radioact 157:67–76. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvrad.2016.03.005
Doneen LD (1964) Notes on water quality in agriculture. Published as a water science and engineering paper 4001, Dept. of Water Science and Engineering, University of California.
Edmunds WM (1996) Bromine geochemistry of British groundwaters. Miner Mag 60:275–284
Edmunds WM, Guendouz AH, Mamou A, Moulla A, Shand P, Zouari K (2003) Groundwater evolution in the Continental Intercalaire aquifer of southern Algeria and Tunisia: trace element and isotopic indicators. Appl Geochem 18:805–822. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00254-007-0682-1
Edmunds WM, Shand P, Guendouz AH, Moulla AS, Mamou A, Zouari K (1997) Recharge characteristics and groundwater quality of the Grand Erg Oriental basin. Avicennes, Technical Report WD/97/46R, Hydrogeology series, British Geol. Survey.
El Amami S (1982) The traditional hydraulic structures in the Maghreb. Arab Center for Studies on Arid Lands (ACSAD), Damascus, Syria, 35pp + Annexes
Ellouze M, Azri C, Abida H (2009) Spatial variability of monthly and annual rainfall data over Southern Tunisia. Atmos Res 93:832–839. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosres.2009.04.005
Ennabli N (1993) Les aménagements hydrauliques et hydro-agricoles en Tunisie. Institut national agronomique de Tunis. Département de génie rural des eaux et des forêts, Tunis
ERESS (1972) Etude des Ressources en eau du Sahara Septentrional. UNESCO, Paris
Essefi E (2013) Wet Aeolian Sedimentology and sequence stratigraphy within the terrestrial analogues in eastern Tunisia: implications for wet aeolian sedimentology and sequence stratigraphy on Mars. Dissertation, National Engineering School of Sfax
Essefi E, Fairén AG, Komatsu G, Rekhiss F, Yaich C (2012a) Study of cores from a spring mound at the mars analog of Boujmal, eastern Tunisia: coring martian spring mounds as potential efficient tool for a geologic exploration of early Mars. Hydrol Clim Evol Impl Life 1680:7029
Essefi E, Komatsu G, Fairén AG, Ben Jmaa H, Rekhiss F, Yaich C (2012b) Spring mounds at Sidi El Hani saline environment, eastern Tunisia: terrestrial analog for Mars. In: Lunar and Planetary Science Conference Mars, pp 1289
Essefi E, Komatsu G, Fairén AG, Chan MA, Yaich C (2013a) Alignment of fault spring mounds at El-Guetiate, Southeast Tunisia: terrestrial analogue implications for martian tectonics. In: Lunar and Planetary Science Conference Mar, pp1545
Essefi E, Touir J, Tagorti MA, Yaich C (2013b) Effect of the groundwater contribution, the climatic change, and the human-induced activities on the hydrological behavior of discharge playas: a case study Sidi El Hani discharge playa, Tunisian Sahel. Arab J Geosci 10:3997–4009
Essefi E, Komatsu G, Fairén AG, Chan MA, Yaich C (2014) Models of formation and activity of spring mounds in the Mechertate-Chrita-Sidi El Hani system, eastern Tunisia: implications for the habitability of Mars. Life 4:386–432
Farid I, Zouari K, Rigane A, Beji R (2015) Origin of the groundwater salinity and geochemical processes in detrital and carbonate aquifers: Case of Chougafiya basin (Central Tunisia). J Hydrol 530:508–532. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2015.10.009
Finley T (2020) Fault-hosted geothermal systems in southeastern British Columbia. Master's thesis, University of Alberta
Ford DC, Williams PF (2007) Karst geomorphology and hydrology. Wiley, Hoboken
Fromm R, Hachichaa T, Smykatz-Klossa W (2005) Aridic crusts and vein mineralisations in the playa Areg el Makrzene, South Tunisia. Chem Erde 65:357–373. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemer.2005.01.005
Gabtni H, Jallouli C, Kevin M, Zouari H, Turki MM (2005) Geophysical Constraints on the Location and Nature of the North Saharan Flexure in Southern Tunisia. Pure Appl Geophys 162:2051–2069. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00024-005-2704-9
Garcia MG, Del Hidalgo M, Blesa MA (2001) Geochemistry of groundwater in the alluvial plain of Tucumán province Argentina. Hydrogeol J 9:597–610. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10040-001-0166-4
Gat JR, Klein B, Kushnir Y, Roether W, Wernli H, Yam R, Shemesh A (2003) Isotope composition of air moisture over the Mediterranean Sea: an index of the air-sea interaction pattern. Tellus B 55:953–965
Gerritse RG, George RJ (1988) The role of soil organic matter in the geochemical cycling of chloride and bromide. J Hydrology 101:83–95
Gibbs RJ (1970) Mechanism controlling world water chemistry. Science 170:1088–1090. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.170.3962.1088
IAEA/WMO (2006) Global Network of Isotopes in Precipitation. The GNIP Database. Accessible at http://isohis.iaea.org
Jankowski J, Acworth RI (1997) Impact of debris-flow deposits on hydrogeochemical processes and the development of dryland salinity in the Yass River catchment, New South Wales, Australia. Hydrogeol J 5:71–88
Johnson G, Zhang H (1990) Classification of irrigation water quality. Oklahoma Cooperative Extension Fact Sheets (available at https://www.osuextra.com).
Kamel S (2013) Salinization origin and hydrogeochemical behavior of the Djerid oasis water table aquifer (southern Tunisia). Arab J Geosci 6:2103–2117. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-011-0502-5
Kamel S, Hamed Y, Chkir N, Zouari K (2007) The hydro geochemical characterization of ground waters in Tunisian Chott’s region. Environ Geol 54:843–854. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00254-007-0867-7
Kelly WP (1963) Use of saline irrigation water. Soil Sci 95:355–391
Khalil MM, Hamer K, Pichler T, Abotalib AZ (2021) Fault zone hydrogeology in arid environments: the origin of cold springs in the Wadi Araba Basin, Eqypt. Hydrol Process 35(5):e14176
Konikow LF (2002) Groundwater depletion and over-exploitation: a global problem. Denver Annual Meeting, Geological Society of America
Krouse HR (1980) Sulphur isotopes in our environment. In: Fritz P, Fontes JC (eds) Handbook of environmental isotope geochemistry, the terrestrial environment. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 435–471
Lopez-Chicano M, Bouamama M, Vallejos A, Pulido BA (2001) Factors which determine the hydrogeochemical behaviour of karstic springs: a case study from the Betic Cordilleras. Spain Appl Geochem 16:1179–1192. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0883-2927(01)00012-9
Machavaram MV, Krishnamurthy RV (1995) Earth surface evaporative process: a case study from the Great Lakes region of the United States based on deuterium excess in precipitation. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 59:4279–4283
Maliki MA, Krimissa M, Michelot JL, Zouari K (2000) Relation entre nappes superficielles et aquifère profond dans le bassin de Sfax (Tunisie) Relationship between shallow and deep aquifers in the Sfax basin (Tunisia). Comptes Rendus de l’Académie des Sciences - Series IIA. Earth Planet Sci 331:1–6. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1251-8050(00)01386-0
Mamou A (1990) Caractéristiques et évaluation des ressources en eau du Sud tunisien. Dissertation, University of Paris Sud
Mamou A, Kassah A (2002) Eau et développement dans le sud tunisien. Cahier du CERES, Série Géographique no. 23. Tunis
Mayo AL, Loucks MD (1995) Solute and isotopic geochemistry and groundwater flow in the Central Wasatch Range, Utah. J Hydrol 172:31–59. https://doi.org/10.1016/0022-1694(95)02748-E
McLean W, Jankowski J, Lavitt N (2000) Groundwater quality and sustainability in an alluvial aquifer, Australia. In: Sililo O (ed) Groundwater, past achievement and future challenges. Balkema, Rotterdam, pp 567–573
Mehri A, Sogut AR (2020) Hydrochemical and statistical study of the groundwater salinization in the region of Gabes in Tunisia. Arab J Geosci 13:1128. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-020-06141-9
Mensching H (1964) Zur Geomorphologie Sudtunesiens. Z Geomorph 8:424–429
Merkel B, Planer-Friedrich B (2008) Groundwater geochemistry: a practical guide to modeling of natural and contaminated aquatic systems. Springer Verlag, Berlin
Merlivat M, Jouzel J (1979) Global climatic interpretation of the deuterium -oxygen-18 relationship for precipitation, d. Geophys Res 84:5029–5033
Meybeck M (1987) Global chemical weathering of surficial rocks estimated from river dissolved loads. Am J Sci 287:401–428. https://doi.org/10.2475/ajs.287.5.401
Mokadem N, Redhaounia B, Besser H, Ayadi Y, Khelifi F, Hamad A, Hamed Y, Bouri S (2018) Impact of climate change on groundwater and the extinction of ancient “Foggara” and springs systems in arid lands in North Africa: a case study in Gafsa basin (Central of Tunisia). Euro-Mediterr J Environ Integr. https://doi.org/10.1007/s41207-018-0070-0
Murray LC, Halford KJ (1996) Hydrogeologic conditions and simulation of ground-water flow in the greater Orlando metropolitan area, east-central Florida. U.S. Geological Survey Water-Resources Investigations Report 96-4181, p 100
Newell D (2020) EAGER-Mantle fluid contribution to springs along the denali fault system: constraints on the crustal scale nature of the main strand and splays. Utah State University. https://doi.org/10.26078/PMCH-TN55
Nishanthiny C, Thushyanthy M, Barathithasan T, Saravanan S (2010) Irrigation Water Quality Based on Hydro Chemical Analysis, Jaffna, Sri Lanka. Am-Eurasian J Agric Environ Sci 7:100–102
OSS (2003) Syste`me Aquife` re du Sahara Septentrional. Hydrogeologie, 2nd edn. Int. Rep. Projet SASS, OSS, Tunis
Ouaja M, Ferry S, Barale G, Srarfi D (2002) Faciès de dépôt du Jurassique et du Crétacé du bassin de Tataouine (Sud de la Tunisie). Field Excursion Guidebook, Association des Sédimentologistes Français, 20–26 October 2002, p 100
Ouessar M (2007) Hydrological impacts of rainwater harvesting in wadi Oum Zessar watershed (southern Tunisia). Ghent University, Ghent
Plummer LN, Jones BF, Truesdell AH (1976) WATEQF, a Fortan IV version of WATEQ, a computer program for calculating chemical equilibrium of natural waters. US Geol Surv Water Resour Invest 76:61
Priestley SC, Shand P, Love AJ, Crossey LJ, Karlstrom KE, Keppel MN, Wohling DL, Rousseau-Gueutin P (2020) Hydrochemical variations of groundwater and spring discharge of the western Great Artesian Basin, Australia: implications for regional groundwater flow. Hydrogeol J 28(1):263–278
Rajmohan N, Elango L (2004) Identification and evolution of hydrogeochemical processes in the groundwater environment in an area of the Palar and Cheyyar River Basins, Southern India. Environ Geol 46:47–61. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00254-004-1012-5
Robaszynski F, Zagrarni MF, Caron M, Amédro F (2010) The global bio-events at the Cenomanian-Turonian transition in the reduced Bahloul Formation of Bou Ghanem (central Tunisia). Cretac Res 31:1–15. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cretres.2009.07.002
Sanford WE, Wood WW (2001) Hydrology of the coastal sabkhas of Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates. Hydrogeol J 9:358–366
Sappa G, Ergul S, Ferranti F (2014) Water quality assessment of carbonate aquifers in southern Latium region, Central Italy: a Case Study for Irrigation and Drinking Purposes. Appl Water Sci 4:115–128. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13201-013-0135-9
Sato T, Takahashi HA, Kawabata K, Takahashi M, Inamura A, Handa H (2020) Changes in the nitrate concentration of spring water after the 2016 Kumamoto earthquake. J Hydrol 1(580):124310
Sharma SK, Gajbhiye S, Tignath S (2015) Application of principal component analysis in grouping geomorphic parameters of a watershed for hydrological modeling. Appl Water Sci 5:89–96. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13201-014-0170-1
Tarki M, Ben Hammadi M, El Mejri H, Dassi L (2016) Assessment of hydrochemical processes and groundwater hydrodynamics in a multilayer aquifer system under long-term irrigation conditions: a case study of Nefzaoua basin, southern Tunisia. Appl Radiat Isot 110:138–149
Tellam JH (1995) Hydrochemistry of the saline groundwaters of the lower Mersey Basin Permo-Triassic sandstone aquifer, UK. J Hydrol 165:45–84. https://doi.org/10.1016/0022-1694(94)02583-W
Tijani MN (1994) Hydrochemical assessment of groundwater in Moro Area, Kwara State, Nigeria. Environ Geol 24:194–202. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00766889
Toumi N, Agoubi B, Kharroubi A (2019) Assessment of groundwater quality of El Ouara aquifer (southeastern Tunisia), geochemical and isotopic approaches. Arab J Geosci 12:116. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-018-4203-1
Varol S, Davraz A (2015) Evaluation of the groundwater quality with WQI (Water Quality Index) and multivariate analysis: a case study of the Tefenni plain (Burdur/Turkey). Environ Earth Sci. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-014-3531-z
Vernoux JF, Jarraya Horriche F, Ghoudi R (2020) Numerical groundwater flow modeling for managing the Gabes Jeffara aquifer system (Tunisia) in relation with oasis ecosystems. Hydrogeol J 28:1077–1090. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10040-020-02123-z
Wu Y, Zhou X, Wang M, Zhuo L, Xu H, Liu Y (2021) (2021) Comparison of hydrogeological characteristics and genesis of the Xiaguan Hot Spring and the Butterfly Spring in Yunnan of China. J Hydrol 593:125922
Zammouri M, Siegfried T, El-Fahem T, Kriaa S, Kinzelbach W (2007) Salinization of groundwater in the Nefzawa oases region, Tunisia. Hydrogeol J 15:1357–1375. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10040-007-0185-x
Zhang H (2016) Classification of irrigation water quality division of agricultural sciences and natural resources. Oklahoma State University, Stillwater
Zhang L, Guo L, Liu S, Yang Y, Shi D (2021) Characteristics of hydrogen and oxygen stable isotopes of hot springs in Xianshuihe-Anninghe fault zone, Sichuan Province, China. Acta Petrol Sin 37(2):589–598
Acknowledgements
The authors thank the staff members of the Dhehiba and Beni Khedeche Water Resources Division and the military for their logistic support during the fieldwork. All thanks and gratitude to Professors El houcine Essefi and Bedoui Nafti for their good reviews of this manuscript. The authors are grateful to the anonymous reviewers who helped improve the manuscript quality.
Funding
This research work was done for my phd project under the direction of Pr Samir Kamel within the research unit and the laboratory of "l'institut supérieur des sciences et techniques des eaux de Gabes". This research and analysis work was funded by the research unit.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have not disclosed any competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Essamin, R., Kamel, S. Hydrogeochemical and isotopic characteristics of emerging springs in southeastern Tunisia. Environ Earth Sci 81, 211 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-022-10337-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-022-10337-5