Abstract
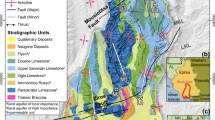
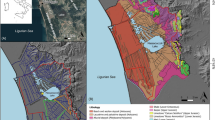
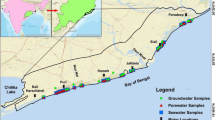
The analysis of the hydrochemical characteristics of different water bodies in coal mining areas and the influencing factors is of great important for sustainable water resources management and the regulation of water hazards. This study analyzed 22 sets of samples of mine water (MW), accumulated water (AW) from the surface subsidence area, and Quaternary pore groundwater (QPW) from the Liangjia coal mine area. The results showed that the dominant anion and cation in MW were HCO3− and Na+, respectively, whereas those in AW and PW were Cl− and Na+, respectively. The water of the study area could be characterized as having relatively high salinity and being of weak alkalinity. While most QPW samples were not suitable for drinking, they were suitable for agricultural irrigation water. The hydrochemical types of MW and AW were mainly HCO3-Na and SO4·Cl-Na, respectively, whereas QPW had a relatively complex hydrochemistry, with the SO4·Cl-Ca·Mg type dominating. The dominant factors influencing the water chemistry characteristics of different water bodies in the Liangjia coal mine area were determined to be rock weathering and cation exchange. Silicate rock weathering was the main driver of the hydrochemical characteristics of MW, whereas the weathering of silicate and carbonate rocks and the dissolution of gypsum regulated that of AW and QPW. The hydrochemistry of QPW was clearly affected by coal mining-induced mixing and input. Atmospheric precipitation was determined to be the main source of recharge of the different water bodies, which was impacted by evaporation. In addition, individual water samples may have been affected by seawater intrusion.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Atanacković N, Dragišić V, Stojković J, Papić P, Živanović V (2013) Hydrochemical characteristics of mine waters from abandoned mining sites in Serbia and their impact on surface water quality. Environ Sci Pollut Res 20(11):7615–7626
Craig H (1961) Isotopic Variations in Meteoric Waters. Science 133(3465):1702–1703
Gao Y, Qian H, Ren W, Wang H, Liu F, Yang F (2020) Hydrogeochemical characterization and quality assessment of groundwater based on integrated-weight water quality index in a concentrated urban area. J Clean Prod 260:121006
Gavrishin AI (2018) Formation patterns of the chemical composition of mine waters in eastern Donbas. Dokl Earth Sci 481(1):916–917
Gibbs RJ (1970) Mechanisms controlling world water chemistry. Science 170(3962):1088
Huang X, Wang G, Liang X, Cui L, Ma L, Xu Q (2018) Hydrochemical and stable isotope (δD and δ18O) characteristics of groundwater and hydrogeochemical processes in the Ningtiaota Coalfield, Northwest China. Mine Water Environ 37(1):119–136
Karroum M, Elgettafi M, Elmandour A, Wilske C, Himi M, Casas A (2017) Geochemical processes controlling groundwater quality under semi arid environment: a case study in central Morocco. Sci Total Environ 609:1140–1151
Li C, Gao Z, Chen H, Wang J, Liu J, Li C, Teng Y, Liu C, Xu C (2021) Hydrochemical analysis and quality assessment of groundwater in southeast North China Plain using hydrochemical, entropy-weight water quality index, and GIS techniques. Environmental Earth Sciences 80(16):523
Li P (2018) Mine water problems and solutions in China. Mine Water Environ 37(2):217–221
Li P, Wu J, Qian H (2015) Hydrochemical appraisal of groundwater quality for drinking and irrigation purposes and the major influencing factors: a case study in and around Hua County. China Arabian Journal of Geosciences 9(1):15
Li P, Wu J, Tian R, He S, He X, Xue C, Zhang K (2018) Geochemistry, hydraulic connectivity and quality appraisal of multilayered groundwater in the Hongdunzi Coal Mine, Northwest China. Mine Water Environ 37(2):222–237
Li P, Zhang Y, Yang N, Jing L, Yu P (2016) Major ion chemistry and quality assessment of groundwater in and around a mountainous tourist town of China. Expo Health 8(2):239–252
Liu J, Gao Z, Wang M, Li Y, Yu C, Shi M, Zhang H, Ma Y (2019) Stable isotope characteristics of different water bodies in the Lhasa River Basin. Environmental Earth Sciences 78(3):71
Liu J, Hao Y, Gao Z, Wang M, Liu M, Wang Z, Wang S (2019) Determining the factors controlling the chemical composition of groundwater using multivariate statistics and geochemical methods in the Xiqu coal mine. North China Environmental Earth Sciences 78(12):364
Liu J, Peng Y, Li C, Gao Z, Chen S (2021) Characterization of the hydrochemistry of water resources of the Weibei Plain, Northern China, as well as an assessment of the risk of high groundwater nitrate levels to human health. Environ Pollut 268:115947
Liu J, Peng Y, Li C, Gao Z, Chen S (2021) An investigation into the hydrochemistry, quality and risk to human health of groundwater in the central region of Shandong Province, North China. J Clean Prod 282:125416
Liu J, Wang H, Jin D, Xu F, Zhao C (2020) Hydrochemical characteristics and evolution processes of karst groundwater in Carboniferous Taiyuan formation in the Pingdingshan coalfield. Environ Earth Sci 79(6):151
Nematollahi MJ, Ebrahimi P, Razmara M, Ghasemi A (2015) Hydrogeochemical investigations and groundwater quality assessment of Torbat-Zaveh plain, Khorasan Razavi. Iran Environ Monit Assess 188(1):2
Piper AM (1944) A graphic procedure in the geochemical interpretation of water-analyses. EOS Trans Am Geophys Union 25(6):914–928
Qian J, Tong Y, Ma L, Zhao W, Zhang R, He X (2018) Hydrochemical Characteristics and Groundwater Source Identification of a Multiple Aquifer System in a Coal Mine. Mine Water Environ 37(3):528–540
Singh AK, Varma NP, Mondal GC (2016) Hydrogeochemical investigation and quality assessment of mine water resources in the Korba coalfield. India Arab J Geosci 9(4):278
Singh R, Venkatesh AS, Syed TH, Surinaidu L, Pasupuleti S, Rai SP, Kumar M (2018) Stable isotope systematics and geochemical signatures constraining groundwater hydraulics in the mining environment of the Korba Coalfield. Central India Environ Earth Sci 77(15):548
Stallard RF, Edmond JM (1983) Geochemistry of the Amazon: 2. The influence of geology and weathering environment on the dissolved load. J Geophys Res: Oceans 88(C14):9671–9688
Wang Q, Dong S, Wang H, Yang J, Huang H, Dong X, Yu B (2020) Hydrogeochemical processes and groundwater quality assessment for different aquifers in the Caojiatan coal mine of Ordos Basin, northwestern China. Environmental Earth Sciences 79(9):199
Wu C, Wu X, Qian C, Zhu G (2018) Hydrogeochemistry and groundwater quality assessment of high fluoride levels in the Yanchi endorheic region, northwest China. Appl Geochem 98:404–417
Xie H, Wang J, Wang G, Ren H, Liu J, Ge S, Zhou H, Wu G, Ren S (2018) New ideas of coal revolution and layout of coal science and technology development. J China Coal Soc 43(05):1187–1197
Xie H, Wu L, Zheng D (2019) Prediction on the energy consumption and coal demand of China in 2025. J China Coal Soc 44(07):1949–1960
Xiong G, Fu T, Han J, Chen G, Xu X, Xu X, Liu G, Liu W (2019) Hydrogeochemical and isotopic characteristics of groundwater in Dagu River Basin. Adv Mar Sci 37(04):626–637
Xu K, Dai G, Duan Z, Xue X (2018) Hydrogeochemical evolution of an ordovician limestone aquifer influenced by coal mining: a case study in the Hancheng mining area. China Mine Water Environ 37(2):238–248
Zhang H, Xu G, Chen X, Mabaire A, Zhou J, Zhang Y, Zhang G, Zhu L (2020) Groundwater hydrogeochemical processes and the connectivity of multilayer aquifers in a coal mine with karst collapse columns. Mine Water Environ 39(2):356–368
Zhang J, Chen L, Chen Y, Ge R, Ma L, Zhou K, Shi X (2020) Discrimination of water-inrush source and evolution analysis of hydrochemical environment under mining in Renlou coal mine, Anhui Province. China Environ Earth Sci 79(2):61
Acknowledgements
The authors thank the anonymous reviewers and editors for their useful comments, which have helped improve the manuscript.
Funding
This study was financially supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Shandong Province (ZR2021QD048), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (52174159), and Liangjia Coal Mine of Shandong Energy Longkou Mining Group Co., Ltd.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Broder J. Merkel
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Y., Zhou, J., Zou, Y. et al. An analysis of the hydrochemical characteristics and influencing factors of different water bodies in the Liangjia coal mine area, North China. Arab J Geosci 15, 1216 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-022-10513-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-022-10513-8