Abstract
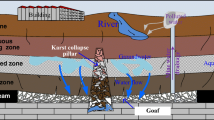
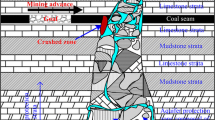
The Karst collapse pillar (KCP) is a special geological structure, which is easy to form the fissure channels between the coal seam working face and the aquifer to cause the water inrush disasters. The KCP was sampled on site in this paper. The confined uniaxial compression test was carried out on the KCP to simulate its field consolidation, and seepage test on the KCP under different axial loads was conducted by using self-developed seepage test system. The KCP connecting to the underground Ordovician limestone aquifer in the sampling area was considered; the difference in the seepage properties between the KCP and the broken limestone was analyzed. The results show that the water-resisting capacity of the KCPs in 3# coal seam floor is 6.24–13.74 MPa, which is far greater than the water pressure of aquifer on 3# coal seam. The water-resisting capacity of the KCPs in 15# coal seam floor is in the range of 1.89–4.71 MPa, which is less than the water pressure of aquifer on 15# coal seam. The specific measures were conducted to prevent the water inrush during the mining process. Before exposing the X3 KCP, the roof drainage borehole drained the roof water to avoid the excessive water inflow in a short time. The grouting holes were arranged to reinforce the floor of sandstone aquifer. According to these treatment methods, the mining work safely passed through the X3 KCP, ensuring engineering safety and economic production. It is not recommended to directly expose the X3 KCP in the roadway or working face of 15# coal seam, and the floor of 15# coal seam should be grouted and reinforced in the future.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bai HB (2011) Seepage characteristics of top stratum of Ordovician system and its application study as key aquifuge. Chin J Rock Mech Eng 30(6):1297–1297
Boldini D, Graziani A (2012) Remarks on axisymmetric modelling of deep tunnels in argillaceous formations-II: fissured argillites. Tunn Undergr Sp Tech 28(3):80–89. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tust.2011.10.007
Chilingar GV (1964) Relationship between porosity, permeability, and grain-size distribution of sands and sandstones. Dev Sedimentol 1:71–75. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0070-4571(08)70469-2
Kong HL, Chen ZQ, Wang LZ, Shen HD (2013) Experimental study on permeability of crushed gangues during compaction. Int J Miner Process 124(6):95–101. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.minpro.2013.04.012
Koronakis N, Kontothanassis P, Kazilis N, Gikas N (2004) Stabilization measures for shallow tunnels with ongoing translational movements due to slope instability. Tunn Undergr Sp Tech 19(4-5):495. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tust.2004.02.093
Li LC, Yang TH, Liang ZZ, Zhu WC, Tang CA (2011) Numerical investigation of groundwater outbursts near faults in underground coal mines. Int J Coal Geol 85(3-4):276–288. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.coal.2010.12.006
Li LN, Xie DL, Wei JC, Yin HY, Li GH, Man XQ, Zhang WJ (2020a) Analysis and control of water inrush under high-pressure and complex karstic water-filling conditions. Environ Earth Sci 79:493. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-020-09242-6
Li YC, Wu CZ, Jang BA (2020b) Effect of bedding plane on the permeability evolution of typical sedimentary rocks under triaxial compression. Rock Mech Rock Eng 53:5283–5291. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-020-02204-1
Liu WQ, Fei XD, Fang JN (2012) Rules for confidence intervals of permeability coefficients for water flow in over-broken rock mass. Int J Min Sci Technol 22(1):29–33. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmst.2011.06.003
Liu RC, Li B, Jiang YJ, Yu LY (2018) A numerical approach for assessing effects of shear on equivalent permeability and nonlinear flow characteristics of 2-D fracture networks. Adv Water Resour 111(1):289–300. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.advwatres.2017.11.022
Liu RC, Huang N, Jiang YJ, Jing HW, Yu LY (2020) A numerical study of shear-induced evolutions of geometric and hydraulic properties of self-affine rough-walled rock fractures. Int J Rock Mech Min 127(3):104211. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmms.2020.104211
Ma D, Zhang JX, Duan HY, Huang YL, Li M, Sun Q, Zhou N (2021) Reutilization of gangue wastes in underground backfilling mining: Overburden aquifer protection. Chemosphere 264(1):128400. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.128400
Ma D, Duan HY, Zhang Q, Zhang JX, Li WX, Zhou ZL, Liu WT (2020a) A numerical gas fracturing model of coupled thermal, flowing and mechanical effects. Comput Mater Con 65(3):2123-2141. https://doi.org/10.32604/cmc.2020.011430
Ma D, Duan HY, Li XB, Li ZH, Zhou ZL, Li TB (2019a) Effects of seepage-induced erosion on nonlinear hydraulic properties of broken red sandstones. Tunn Undergr Sp Tech 91:102993. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tust.2019.102993
Ma D, Duan HY, Liu JF, Li XB, Zhou ZL (2019b) The role of gangue on the mitigation of mining-induced hazards and environmental pollution: an experimental investigation. Sci Total Environ 664:636–448. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.02.059
Ma D, Ma HY, Duan WT, Liu XT, Ma M (2020b) Tao Water-sediment two-phase flow inrush hazard in rock fractures of overburden strata during coal mining. Mine Water Environ 39:308–319. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10230-020-00687-6
Miao XX, Li SC, Huang XW, Chen ZQ (2006) Experimental study of seepage properties of non-Darcy flow in granular gangues. J China Univ Min Technol 16(2):105–109
Miao XX, Li SC, Chen ZQ (2009) Bifurcation and catastrophe of seepage flow system in broken rock. Min Sci Technol 19(1):1–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1674-5264(09)60001-6
Miao XX, Li SC, Chen ZQ, Liu WQ (2011) Experimental study of seepage properties of broken sandstone under different porosities. Transport Porous Med 86(3):805–814. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11242-010-9653-1
Qiao L, Ranjith PG, Long XP, Kang Y, Huang M (2015) A review of shale swelling by water adsorption. J Nat Gas Sci Eng 27:1421–1431. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jngse.2015.10.004
Sweetenham MG, Maxwell RM, Santi PM (2007) Assessing the timing and magnitude of precipitation-induced seepage into tunnels bored through fractured rock. Tunn Undergr Sp Tech 65:62–75. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tust.2017.02.003
Vukovic M, Soro A (1992) Determination of hydraulic conductivity of porous media from grain-size composition. Water Resources Publications, Littleton, CO, p 83
Wang LZ, Chen ZQ, Kong HL, Shen H (2014) Effects of pore pressure on permeability of sandstone during bending deformation. Int J Rock Mech Min 2014(70):26–32. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmms.2014.03.012
Wu Q, Xing LT, Ye CH, Liu YZ (2011) The influence of coal mining on the large karst springs in North China. Environ Earth Sci 64(6):1513–1523. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-009-0376-y
Wu JY, Feng MM, Mao XB, Xu JM, Zhang WL, Ni XY, Han GS (2018) Particle size distribution of aggregate effects on mechanical and structural properties of cemented rockfill: Experiments and modeling. Constr Build Mater 193:295–311. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2018.10.208
Wu JY, Han GS, Feng MM, Kong HL, Yu BY, Wang LZ, Gao Y (2019) Mass-loss effects on the flow behavior in broken argillaceous red sandstone with different particle-size distributions. Comptes Rendus Mecanique 347(6):62–89. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.crme.2019.03.014
Wu JY, Jing HW, Yin Q, Yu LY, Meng B, Li SC (2020) Strength prediction model considering material, ultrasonic and stress of cemented waste rock backfill for recycling gangue. J Clean Prod 276:123189. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.123189
Yang TH, Liu J, Zhu WC, Elsworth D, Tham LG, Tang CA (2007) A coupled flow-stress-damage model for groundwater outbursts from an underlying aquifer into mining excavations. Int J Rock Mech Min 44(1):87–97. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmms.2006.04.012
Yang TH, Jia P, Shi WH, Wang PT, Liu HL, Yu QX (2014) Seepage-stress coupled analysis on anisotropic characteristics of the fractured rock mass around roadway. Tunn Undergr Sp Tech 43(7):11–19. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tust.2014.03.005
Yin SX, Wu Q (2004) Simulation and mechanism analysis of water inrush from karstic collapse columns in coal floor. Chin J Rock Mech Eng 23(15):2551–2556
Yin Q, Jing HW, Ma GW, Su HJ, Liu RC (2018) Investigating the roles of included angle and loading condition on the critical hydraulic gradient of real rock fracture networks. Rock Mech Rock Eng 51(10):3167–3177. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-018-1526-x
Yin Q, Liu RC, Jing HW, Su HJ, Yu LY, He LX (2019) Experimental study of nonlinear flow behaviors through fractured rock samples after high temperature exposure. Rock Mech Rock Eng 52(9):2963–2983. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-019-1741-0
Yue ZQ, Xu Q (2014) Fundamental drawbacks and disastrous consequences of current geotechnical safety design theories for slopes. Chin J Geotech Eng 36(9):1601–1606. https://doi.org/10.11779/CJGE201409005
Zhang BY, Bai HB, Zhang K (2016) Experimental research on seepage mutation mechanism of collapse column medium. Rock and Soil Mechanics 37(3):745-752 + 812. https://doi.org/10.16285/j.rsm.2016.03.017
Zhu WC, Wei CH (2011) Numerical simulation on mining-induced water inrushes related to geologic structures using a damage-based hydromechanical model. Environ Earth Sci 62(1):43–54. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-010-0494-6
Acknowledgments
The authors want to acknowledge these financial assistances.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (51904290 and 41807209), the Young Teacher Foundation of HPU (2019XQG-19) and the Henan Provincial Youth Talent Promotion Program (2020HYTP003).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
B.Y. Zhang and Z.B. Lin conceived and designed the experiments. B.Y. Zhang and Z.B. Lin performed the experiments. B.Y. Zhang and Z.B. Lin analyzed the data. B.Y. Zhang and Z.B. Lin wrote the paper.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Zeynal Abiddin Erguler
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, B., Lin, Z. Seepage property of karst collapse pillar: experiments and engineering applications. Arab J Geosci 14, 1037 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-021-07238-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-021-07238-5