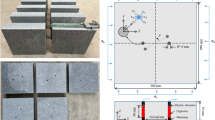
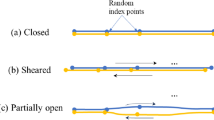
Abstract
To investigate the mechanism of water–sediment inrush during coal mining, the characteristics of water–sediment flow in rock fractures were quantitatively analyzed by computational fluid dynamics (CFD). Based on the two-phase flow theory, a resistance model of water–sediment flow in fractures was established and verified by a laboratory-scale test. The results showed that: (1) With increases sediment particle diameter, volume fraction, and initial water phase velocity, the resistance of sediment particles grows gradually. (2) The drag force of sediment particles is mainly generated from the collision of the water phase and fracture wall. The velocity distribution of sediment particles can be divided into three stages, i.e., continuous increase, rapid decrease, and slow fluctuation. (3) The numerical model was shown to have high predictive accuracy by comparison with the test results. The model’s predictive accuracy decreases with increased water phase velocity and decreases of the sediment particle diameter and volume fraction. (4) The smaller the fracture width, the larger the inclination and bending angles, and the greater the resistance of the two-phase flow in the fracture. Collisions between the particles and fracture wall cause velocity attenuation of the sediment particles. We propose water–sediment inrush prevention and control technology based on the numerical analysis results.
摘要
采动覆岩裂隙水-沙两相流灾变机理为研究开采条件下水沙突涌灾变机理,采用计算流体力学方法(CFD)定量分析了裂隙岩体水―沙两相流运移特征。基于液-固两相流理论建立采动裂隙岩体水-沙两相流阻力模型,并得到了室内试验验证。研究表明:(1)沙粒粒径、体积分数和初始流速越大,沙粒的流动阻力越大;(2)沙粒曳力主要来自液相与裂隙壁面碰撞;沙粒速度变化可分为三个阶段,即持续增大、快速减小和缓慢波动;(3)与试验结果对比,数值模型具有较高预测精度;预测精度随液相流速增大、沙粒粒径和体积分数减小而降低;(4)裂隙开度越小、倾角及弯曲程度越大,裂隙内两相流阻力越大。沙粒与裂隙壁面的碰撞是沙粒速度衰减的原因。基于数值分析结果,初步提出了水-沙突涌防治技术。
Zusammenfassung
Zur Erforschung der Vorgänge bei einem Wasser-Sediment-Einbruch in ei-nen Kohlebergbau wurden die Charakteristika der Wasser-Sediment-Strö-mung in Felsklüften quantitativ analysiert. Dazu wurde die numerische Strö¬mungs¬mechanik (CFD) genutzt. Basierend auf der Theorie der Zwei-phasen¬strömung wurde ein Wider¬stands¬modell für die Wasser-Sediment-Strömung in Klüf¬ten auf¬gebaut und verifiziert. Die Ergebnisse zeigten, dass
-
1.
mit steigendem Sedimentpartikeldurchmesser, steigendem Men-gen¬anteil und steigender Anfangsgeschwindigkeit der Wasser-pha¬se der Widerstand der Sedimentpartikel allmählich ansteigt.
-
2.
die Schleppkraft der Sedimentpartikel hauptsächlich bei der Kol-li¬sion der Wasserphase mit den Kluftwänden generiert wird. Der zeit¬liche Ver¬lauf der Ge¬schwindig¬keitsverteilung der Sediment-par¬ti¬kel kann in drei Sta¬dien unterteilt werden: kontinuierlicher An¬stieg, schnel¬les Ab¬sin¬ken und langsame Fluktuation.
-
3.
das numerische Modell eine hohe Vorhersagegenauigkeit hat. Da-bei dienten reale Testergebnisse als Referenz. Die Vor¬her¬sage-genau¬ig¬keit des Modells verringert sich mit steigender Ge¬schwin-digkeit der Wasserphase sowie mit geringer werdendem Sedi-ment¬par¬tikel¬durchmesser und -massenanteil.
-
4.
mit geringerer Breite der Klüfte sowie größerem Neigungs- und Beuge¬winkel der Widerstand der Zweiphasenströmung in der Kluft zu¬nimmt. Kollisionen zwischen den Partikeln und der Kluft-wand füh¬ren zu einer Geschwindigkeitsverringerung der Sedi-ment¬par¬ti¬kel. Zur Prävention von Wasser-Sedi¬ment-Ein¬brüchen werden Maßnahmen sowie Regelungs¬technik auf der Grundlage der Er¬geb¬nisse der nu¬me¬rischen Analyse vorgeschlagen.
Resumen
Para investigar el mecanismo de la irrupción de sedimentos y agua durante la extracción de carbón, las características del flujo de sedimentos de agua en las fracturas de rocas se analizaron cuantitativamente mediante dinámica de fluidos computacional (CFD). Basado en la teoría del flujo de dos fases, se estableció y verificó un modelo de resistencia del flujo de sedimentos y agua en fracturas. Los resultados mostraron que: (1) Con el aumento del diámetro de las partículas de sedimento, la fracción de volumen y la velocidad inicial de la fase de agua, la resistencia de las partículas de sedimento crece gradualmente. (2) La fuerza de arrastre de las partículas de sedimento se genera principalmente a partir de la colisión de la fase acuosa y la pared de fractura. La distribución de velocidad de las partículas de sedimento se puede dividir en tres etapas, es decir, aumento continuo, disminución rápida y fluctuación lenta. (3) Se demostró que el modelo numérico tiene una alta precisión predictiva en comparación con los resultados de la prueba. La precisión predictiva del modelo disminuye al aumentar la velocidad de la fase de agua y las disminuciones del diámetro de las partículas de sedimento y de la fracción de volumen. (4) Cuanto más pequeño es el ancho de la fractura, mayor es la inclinación y los ángulos de flexión y mayor es la resistencia del flujo de dos fases en la fractura. Las colisiones entre las partículas y la pared de fractura causan la atenuación de la velocidad de las partículas de sedimento. Proponemos una tecnología de prevención y control de irrupción de sedimentos de agua basada en los resultados del análisis numérico.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Berkowitz B (2002) Characterizing flow and transport in fractured geological media: a review. Adv Water Resour 25:861–884. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0309-1708(02)00042-8
Brouwers LB, Dippenaar MA (2019) Partially saturated flow from sand into a discrete smooth open vertical fracture at the soil–rock interface: experimental studies. Bull Eng Geol Environ 78:2575–2590. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-018-1258-x
Elbaz K, Shen JS, Arulrajah A, Horpibulsuk S (2016) Geohazards induced by anthropic activities of geoconstruction: a review of recent failure cases. Arab J Geosci 9:708. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-016-2740-z
Fan H, Zheng H (2013) MRT-LBM-based numerical simulation of seepage flow through fractal fracture networks. Sci China Technol Sci 56:3115–3122. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11431-013-5402-3
Fan G, Zhang D, Zhang S, Zhang C (2018) Assessment and prevention of water and sand inrush associated with coal mining under a water-filled buried gully: a case study. Mine Water Environ 37:565–576. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10230-017-0487-8
Gu H, Tao M, Li X, Momeni A, Cao W (2019) The effects of water content and external incident energy on coal dynamic behaviour. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 123:104088. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmms.2019.104088
Guihéneuf N, Boisson A, Bour O, Dewandel B, Perrin J, Dausse A, Viossanges M, Chandra S, Ahmed S, Maréchal JC (2014) Groundwater flows in weathered crystalline rocks: impact of piezometric variations and depth-dependent fracture connectivity. J Hydrol 511:320–334. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2014.01.061
Hamm S-Y, Kim M, Cheong J-Y, Kim J-Y, Son M, Kim T-W (2007) Relationship between hydraulic conductivity and fracture properties estimated from packer tests and borehole data in a fractured granite. Eng Geol 92:73–87. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2007.03.010
Huang Y-H, Yang S-Q (2019) Mechanical and cracking behavior of granite containing two coplanar flaws under conventional triaxial compression. Int J Damage Mech 28:590–610. https://doi.org/10.1177/1056789518780214
Huang Z, Jiang Z, Zhu S, Wu X, Yang L, Guan Y (2016) Influence of structure and water pressure on the hydraulic conductivity of the rock mass around underground excavations. Eng Geol 202:74–84. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2016.01.003
Huang Z, Li X, Li S, Zhao K, Zhang R (2018) Investigation of the hydraulic properties of deep fractured rocks around underground excavations using high-pressure injection tests. Eng Geol 245:180–191. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2018.07.020
Huang Y-H, Yang S-Q, Tian W-L (2019a) Crack coalescence behavior of sandstone specimen containing two pre-existing flaws under different confining pressures. Theor Appl Fracture Mech 99:118–130. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tafmec.2018.11.013
Huang Y, Li J, Ma D, Gao H, Guo Y, Ouyang S (2019b) Triaxial compression behaviour of gangue solid wastes under effects of particle size and confining pressure. Sci Total Environ 693:133607. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.133607
Javadi M, Sharifzadeh M, Shahriar K (2010) A new geometrical model for non-linear fluid flow through rough fractures. J Hydrol 389:18–30. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2010.05.010
Ju F, Xiao M, He Z, Ning P, Huang P (2018) Study on fracture and stress evolution characteristics of ultra-thick hard sandstone roof in the fully mechanized mining face with large mining height: a case study of Xiaojihan coal mine in western China. Adv Civil Eng 2018:12. https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/5474165
Kristinof R, Ranjith PG, Choi SK (2010) Finite element simulation of fluid flow in fractured rock media. Environ Earth Sci 60:765–773. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-009-0214-2
Li LC, Tang CA, Li G, Wang SY, Liang ZZ, Zhang YB (2012) Numerical simulation of 3D hydraulic fracturing based on an improved flow-stress-damage model and a parallel FEM technique. Rock Mech Rock Eng 45:801–818. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-012-0252-z
Li S, Wang J, Li L, Shi S, Zhou Z (2019) The theoretical and numerical analysis of water inrush through filling structures. Math Comput Simulat 162:115–134. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matcom.2018.12.014
Liang YK, Sui WH, Qi JF (2019) Experimental investigation on chemical grouting of inclined fracture to control sand and water flow. Tunn Undergr Space Technol 83:82–90. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tust.2018.09.038
Liu Y, Li S (2016) Influence of particle size on non-Darcy seepage of water and sediment in fractured rock. SpringerPlus 5:2099. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40064-016-3778-9
Liu J, Chen W, Yuan J, Li C, Zhang Q, Li X (2017) Groundwater control and curtain grouting for tunnel construction in completely weathered granite. Bull Eng Geol Environ 77:515–531. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-017-1003-x
Liu J, Chen W, Liu T, Yu J, Dong J, Nie W (2018) Effects of initial porosity and water pressure on seepage-erosion properties of water inrush in completely weathered granite. Geofluids 2018:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/4103645
Liu W, Yao J, Chen Z, Zhu W (2019) An exact analytical solution of moving boundary problem of radial fluid flow in an infinite low-permeability reservoir with threshold pressure gradient. J Petrol Sci Eng 175:9–21. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.petrol.2018.12.025
Liu H, Zhu W, Yu Y, Xu T, Li R, Liu X (2020) Effect of water imbibition on uniaxial compression strength of sandstone. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 127:104200. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmms.2019.104200
Ma D, Rezania M, Yu H-S, Bai H-B (2017) Variations of hydraulic properties of granular sandstones during water inrush: effect of small particle migration. Eng Geol 217:61–70. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2016.12.006
Ma D, Duan H, Li X, Li Z, Zhou Z, Li T (2019a) Effects of seepage-induced erosion on nonlinear hydraulic properties of broken red sandstones. Tunn Undergr Space Technol 91:102993. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tust.2019.102993
Ma D, Duan HY, Liu JF, Li XB, Zhou ZL (2019b) The role of gangue on the mitigation of mining-induced hazards and environmental pollution: an experimental investigation. Sci Total Environ 664:436–448. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.02.059
Ma D, Wang J, Cai X, Ma X, Zhang J, Zhou Z, Tao M (2019c) Effects of height/diameter ratio on failure and damage properties of granite under coupled bending and splitting deformation. Eng Fract Mech 220:106640. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engfracmech.2019.106640
Ma D, Wang J, Li Z (2019d) Effect of particle erosion on mining-induced water inrush hazard of karst collapse pillar. Environ Sci Poll Res 26:19719–19728. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-05311-x
Peker SM, Helvaci SS (2008) Solid-liquid two phase flow. Elsevier, Amsterdam
Peng K, Zhou J, Zou Q, Zhang J, Wu F (2019) Effects of stress lower limit during cyclic loading and unloading on deformation characteristics of sandstones. Constr Build Mater 217:202–215. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2019.04.183
Poesen J, Nachtergaele J, Verstraeten G, Valentin C (2003) Gully erosion and environmental change: importance and research needs. CATENA 50:91–133. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0341-8162(02)00143-1
Qian X, Xia C, Gui Y, Zhuang X, Yu Q (2019) Study on flow regimes and seepage models through open rough-walled rock joints under high hydraulic gradient. Hydrogeol J 27:1329–1343. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10040-018-01914-9
Ren F, Ma G, Wang Y, Li T, Zhu H (2017) Unified pipe network method for simulation of water flow in fractured porous rock. J Hydrol 547:80–96. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2017.01.044
Sahimi M (2011) Flow and transport in porous media and fractured rock: from classical methods to modern approaches. Wiley, New York
Sun WJ, Wu Q, Dong DL, Jiao J (2012) Avoiding coal-water conflicts during the development of China's large coal-producing regions. Mine Water Environ 31:74–78. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10230-012-0173-9
Tao M, Ma A, Cao W, Li X, Gong F (2017) Dynamic response of pre-stressed rock with a circular cavity subject to transient loading. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 99:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmms.2017.09.003
Valentin C, Poesen J, Li Y (2005) Gully erosion: impacts, factors and control. CATENA 63:132–153. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2005.06.001
Wang L, Kong H (2018) Variation characteristics of mass-loss rate in dynamic seepage system of the broken rocks. Geofluids 2018:1–17. https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/7137601
Wang Y, Geng F, Yang S, Jing H, Meng B (2019) Numerical simulation of particle migration from crushed sandstones during groundwater inrush. J Hazard Mater 362:327–335. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2018.09.011
Xu P, Yu B, Qiao X, Qiu S, Jiang Z (2013) Radial permeability of fractured porous media by Monte Carlo simulations. Int J Heat Mass Transf 57:369–374. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2012.10.040
Yang W, Jin L, Zhang X (2019) Simulation test on mixed water and sand inrush disaster induced by mining under the thin bedrock. J Loss Prevent Proc 57:1–6. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jlp.2018.11.007
Zhang HQ, He YN, Tang CA, Ahmad B, Han LJ (2008) Application of an improved flow-stress-damage model to the criticality assessment of water inrush in a mine: a case study. Rock Mech Rock Eng 42:911. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-008-0004-2
Zhang R, Jiang Z, Zhou H, Yang C, Xiao S (2014) Groundwater outbursts from faults above a confined aquifer in the coal mining. Nat Hazard 71:1861–1872. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-013-0981-7
Zhang G, Zhang K, Wang L, Wu Y (2015a) Mechanism of water inrush and quicksand movement induced by a borehole and measures for prevention and remediation. Bull Eng Geol Environ 74:1395–1405. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-014-0714-5
Zhang ZZ, Bai JB, Chen Y, Yan S (2015b) An innovative approach for gob-side entry retaining in highly gassy fully-mechanized longwall top-coal caving. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 80:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmmis.2015.09.001
Zhou Q, Herrera J, Hidalgo A (2018) The numerical analysis of fault-induced mine water inrush using the extended finite element method and fracture mechanics. Mine Water Environ 37:185–195. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10230-017-0461-5
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (41977238 and 51804339), the Young Elite Scientists Sponsorship by CAST (YESS20190175), the Special Fund for the Construction of Innovative Provinces in Hunan (2019RS2007), the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (2019T120715 and 2018M640760), the Open Project Fund for State Key Laboratory of Mining Disaster Prevention and Control Co-founded by Shandong Province (MDPC201901) and the Fundamental Research Fund for the Central Universities of CSU (2019zzts675).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ma, D., Duan, H., Liu, W. et al. Water–Sediment Two-Phase Flow Inrush Hazard in Rock Fractures of Overburden Strata During Coal Mining. Mine Water Environ 39, 308–319 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10230-020-00687-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10230-020-00687-6