Abstract
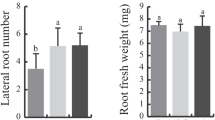
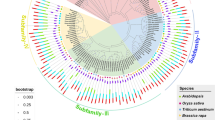
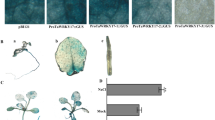
The bread wheat gene TaCRK41 encodes a cysteine-rich receptor kinase. It is down-regulated by various abiotic stresses and by exposure to abscisic acid. A transient expression experiment in Arabidopsis thaliana protoplasts involving a fusion between the sequence encoding green fluorescence protein and the TaCRK41 allele from either the salinity tolerant bread wheat cultivar Shanrong No. 3 (SR3) or its salinity sensitive progenitor cultivar Jinan 177 (JN177) showed that the TaCRK41 product is deposited in the cytoplasm. Recombinant TaCRK41 originating from both SR3 and JN177 displayed no kinase activity in vitro. The constitutive expression of TaCRK41 in A. thaliana resulted in a marked reduction in the plants’ sensitivity to both exogenous abscisic acid and to salinity during germination. The level of ABA-induced transcription of ABI3, ABI5 and the ABI5-controlled genes EM1 and EM6 was significantly reduced in plants subjected to stress. The data support the idea that TaCRK41 is involved in the regulation of ABA-dependent germination under conditions of osmotic stress.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Acharya BR, Raina S, Maqbool SB, Jagadeeswaran G, Mosher SL, Appel HM, Schultz JC, Klessig DF, Raina R (2007) Overexpression of CRK13, an Arabidopsis cysteine-rich receptor-like kinase, results in enhanced resistance to Pseudomonas syringae. Plant J 50:488–499
Bassel GW, Glaab E, Marquez J, Holdsworth MJ, Bacardit J (2011) Functional network construction in Arabidopsis using rule-based machine learning on large-scale data sets. Plant Cell 23:3101–3116
Bensmihen S, Rippa S, Lambert G, Jublot D, Pautot V, Granier F, Giraudat J, Parcy F (2002) The homologous ABI5 and EEL transcription factors function antagonistically to fine-tune gene expression during late embryogenesis. Plant Cell 14:1391–1403
Bourdais G, Burdiak P, Gauthier A, Nitsch L, Salojarvi J, Rayapuram C, Idanheimo N, Hunter K, Kimura S, Merilo E, Vaattovaara A, Oracz K, Kaufholdt D, Pallon A, Anggoro DT, Glow D, Lowe J, Zhou J, Mohammadi O, Puukko T, Albert A, Lang H, Ernst D, Kollist H, Brosche M, Durner J, Borst JW, Collinge DB, Karpinski S, Lyngkjaer MF, Robatzek S, Wrzaczek M, Kangasjarvi J (2015) Large-scale phenomics identifies primary and fine-tuning roles for CRKs in responses related to oxidative stress. PLoS Genet 11:e1005373
Castells E, Casacuberta JM (2007) Signalling through kinase-defective domains: the prevalence of atypical receptor-like kinases in plants. J Exp Bot 58:3503–3511
Chae L, Sudat S, Dudoit S, Zhu T, Luan S (2009) Diverse transcriptional programs associated with environmental stress and hormones in the Arabidopsis receptor-like kinase gene family. Mol Plant 2:84–107
Clough SJ, Bent AF (1998) Floral dip: a simplified method for Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J 16:735–743
Finkelstein RR, Gampala SS, Rock CD (2002) Abscisic acid signaling in seeds and seedlings. Plant Cell S15−45
Finkelstein RR, Lynch TJ (2000) The Arabidopsis abscisic acid response gene ABI5 encodes a basic leucine zipper transcription factor. Plant Cell 12:599–609
Finkelstein RR, Wang ML, Lynch TJ, Rao S, Goodman HM (1998) The Arabidopsis abscisic acid response locus ABI4 encodes an APETALA 2 domain protein. Plant Cell 10:1043–1054
Gifford ML, Dean S, Ingram GC (2003) The Arabidopsis ACR4 gene plays a role in cell layer organisation during ovule integument and sepal margin development. Development 130:4249–4258
Giraudat J, Hauge BM, Valon C, Smalle J, Parcy F, Goodman HM (1992) Isolation of the Arabidopsis ABI3 gene by positional cloning. Plant Cell 4:1251–1261
Halter T, Imkampe J, Mazzotta S, Wierzba M, Postel S, Bucherl C, Kiefer C, Stahl M, Chinchilla D, Wang X, Nurnberger T, Zipfel C, Clouse S, Borst JW, Boeren S, de Vries SC, Tax F, Kemmerling B (2014) The leucine-rich repeat receptor kinase BIR2 is a negative regulator of BAK1 in plant immunity. Curr Biol 24:134–143
Hanks SK, Quinn AM, Hunter T (1988) The protein kinase family: conserved features and deduced phylogeny of the catalytic domains. Science 241:42–52
Himmelbach A, Yang Y, Grill E (2003) Relay and control of abscisic acid signaling. Curr Opin Plant Biol 6:470–479
Hua D, Wang C, He J, Liao H, Duan Y, Zhu Z, Guo Y, Chen Z, Gong Z (2012) A plasma membrane receptor kinase, GHR1, mediates abscisic acid- and hydrogen peroxide-regulated stomatal movement in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 24:2546–2561
Kumar D, Kumar R, Baek D, Hyun TK, Chung WS, Yun DJ, Kim JY (2017) Arabidopsis thaliana RECEPTOR DEAD KINASE1 functions as a positive regulator in plant responses to ABA. Mol Plant 10:223–243
Li CL, Wang M, Wu XM, Chen DH, Lv HJ, Shen JL, Qiao Z, Zhang W (2016) THI1, a thiamine thiazole synthase, interacts with Ca2+-dependent protein kinase CPK33 and modulates the S-type anion channels and stomatal closure in Arabidopsis. Plant physiol 170:1090–1104
Lin W, Ma X, Shan L, He P (2013) Big roles of small kinases: the complex functions of receptor-like cytoplasmic kinases in plant immunity and development. J Integr Plant Biol 55:1188–1197
Liu C, Li S, Wang M, Xia G (2012) A transcriptomic analysis reveals the nature of salinity tolerance of a wheat introgression line. Plant Mol Biol 78:159–169
Liu S, Liu S, Wang M, Wei T, Meng C, Xia G (2014) A wheat SIMILAR TO RCD-ONE gene enhances seedling growth and abiotic stress resistance by modulating redox homeostasis and maintaining genomic integrity. Plant Cell 26:164–180
Llompart B, Castells E, Rio A, Roca R, Ferrando A, Stiefel V, Puigdomenech P, Casacuberta JM (2003) The direct activation of MIK, a germinal center kinase (GCK)-like kinase, by MARK, a maize atypical receptor kinase, suggests a new mechanism for signaling through kinase-dead receptors. J Biol Chem 278:48105–48111
Lopez-Molina L, Mongrand S, Chua NH (2001) A postgermination developmental arrest checkpoint is mediated by abscisic acid and requires the ABI5 transcription factor in Arabidopsis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 98:4782–4787
Lopez-Molina L, Mongrand S, McLachlin DT, Chait BT, Chua NH (2002) ABI5 acts downstream of ABI3 to execute an ABAdependent growth arrest during germination. Plant J 32:317–328
Lu K, Liang S, Wu Z, Bi C, Yu YT, Wang XF, Zhang DP (2016) Overexpression of an Arabidopsis cysteine-rich receptor-like protein kinase, CRK5, enhances abscisic acid sensitivity and confers drought tolerance. J Exp Bot 67:5009–5027
Mittler R, Vanderauwera S, Suzuki N, Miller G, Tognetti VB, Vandepoele K, Gollery M, Shulaev V, Van Breusegem F (2011) ROS signaling: the new wave? Trends Plant Sci 16:300–309
Valon C, Smalle J, Goodman HM, Giraudat J (1993) Characterization of an Arabidopsis thaliana gene (TMKL1) encoding a putative transmembrane protein with an unusual kinase-like domain. Plant Mol Biol 23:415–421
Munne-Bosch S, Queval G, Foyer CH (2013) The impact of global change factors on redox signaling underpinning stress tolerance. Plant physiol 161:5–19
Munns R, Tester M (2008) Mechanisms of salinity tolerance. Annu Rev Plant Biol 59:651–681
Schultz J, Milpetz F, Bork P, Ponting CP (1998) SMART, a simple modular architecture research tool: identification of signaling domains. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 95:5857–5864
Shang Y, Dai C, Lee MM, Kwak JM, Nam KH (2016) BRI1- associated receptor kinase 1 regulates guard cell ABA signaling mediated by Open Stomata 1 in Arabidopsis. Mol Plant 9:447–460
Sheen J (2001) Signal transduction in maize and Arabidopsis mesophyll protoplasts. Plant physiol 127:1466–1475
Shiu SH, Bleecker AB (2001) Receptor-like kinases from Arabidopsis form a monophyletic gene family related to animal receptor kinases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 98:10763–10768
Shiu SH, Bleecker AB (2003) Expansion of the receptor-like kinase/Pelle gene family and receptor-like proteins in Arabidopsis. Plant physiol 132:530–543
Tamura K, Peterson D, Peterson N, Stecher G, Nei M, Kumar S (2011) MEGA5: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis using maximum likelihood, evolutionary distance, and maximum parsimony methods. Mol Biol Evol 28:2731–2739
Tanaka H, Osakabe Y, Katsura S, Mizuno S, Maruyama K, Kusakabe K, Mizoi J, Shinozaki K, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K (2012) Abiotic stress-inducible receptor-like kinases negatively control ABA signaling in Arabidopsis. Plant J 70:599–613
Vaddepalli P, Fulton L, Batoux M, Yadav RK, Schneitz K (2011) Structure-function analysis of STRUBBELIG, an Arabidopsis atypical receptor-like kinase involved in tissue morphogenesis. PLoS One 6:e19730
Vij S, Giri J, Dansana PK, Kapoor S, Tyagi AK (2008) The receptorlike cytoplasmic kinase (OsRLCK) gene family in rice: organization, phylogenetic relationship, and expression during development and stress. Mol Plant 1:732–750
Wrzaczek M, Brosche M, Salojarvi J, Kangasjarvi S, Idanheimo N, Mersmann S, Robatzek S, Karpinski S, Karpinska B, Kangasjarvi J (2010) Transcriptional regulation of the CRK/DUF26 group of receptor-like protein kinases by ozone and plant hormones in Arabidopsis. BMC Plant Biol 10:95
Wrzaczek M, Vainonen JP, Stael S, Tsiatsiani L, Help-Rinta-Rahko H, Gauthier A, Kaufholdt D, Bollhoner B, Lamminmaki A, Staes A, Gevaert K, Tuominen H, Van Breusegem F, Helariutta Y, Kangasjarvi J (2015) GRIM REAPER peptide binds to receptor kinase PRK5 to trigger cell death in Arabidopsis. EMBO J 34:55–66
Xia G, Xiang F, Zhou A, Wang H, Chen H (2003) Asymmetric somatic hybridization between wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) and Agropyron elongatum (Host) Nevishi. Theor Appl Genet 107:299–305
Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K, Shinozaki K (2006) Transcriptional regulatory networks in cellular responses and tolerance to dehydration and cold stresses. Annu Rev Plant Biol 57:781–803
Ye Y, Ding Y, Jiang Q, Wang F, Sun J, Zhu C (2017) The role of receptor-like protein kinases (RLKs) in abiotic stress response in plants. Plant Cell Rep 36:235–242
Yeh YH, Chang YH, Huang PY, Huang JB, Zimmerli L (2015) Enhanced Arabidopsis pattern-triggered immunity by overexpression of cysteine-rich receptor-like kinases. Front Plant Sci 6:322
Zhang X, Garreton V, Chua NH (2005) The AIP2 E3 ligase acts as a novel negative regulator of ABA signaling by promoting ABI3 degradation. Genes Dev 19:1532–1543
Zhu JK (2002) Salt and drought stress signal transduction in plants. Annu Rev Plant Biol 53:247–273
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, D., Wu, J., Zhao, M. et al. A novel wheat cysteine-rich receptor-like kinase gene CRK41 is involved in the regulation of seed germination under osmotic stress in Arabidopsis thaliana. J. Plant Biol. 60, 571–581 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12374-017-0248-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12374-017-0248-z