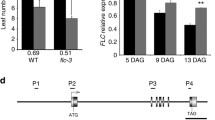
Abstract
Arabidopsis thaliana plants flower in Spring in order to produce offspring before they are out-competed by other species. By contrast, rice (Oryza sativa) flowers in Summer after a lengthy period of vegetative growth that will support the maximum amount of seed production. As model systems, these two species are valuable for studies that explore how plants perceive their environmental conditions and optimize the timing of floral development. In both Arabidopsis and rice, FLOWERING LOCUS T (FT) family proteins, or florigens, are produced in the leaf phloem and moved to the shoot apical meristem (SAM). Whereas the florigens in rice immediately induce downstream genes in the SAM to initiate the transition from vegetative to reproductive growth, their functioning in Arabidopsis is inhibited by FLOWERING LOCUS C (FLC). Transcript levels of FT and FLC are regulated epigenetically. Lysine residues of the histone N-tails covering the FT and FLC chromatins are methylated by SET-domain group (SDG) proteins that contain the evolutionarily conserved SET domain while the methyl groups are removed by Jumonji C domain-containing demethylases. Transcript levels of both genes are also modulated by altering the acetylation of the histone tail. In rice, expression by Heading date 3a and Rice FT 1 (RFT1) that produces major florigens are epigenetically controlled by OsSDG724 and OsSDG725. These SDG proteins also methylate OsMADS50 chromatin, a long daypreferential flowering activator. Two other methyltransferases, OsSDG711 and OsSDG718, down-regulate OsLF, a repressor of Heading date 1. Finally, the demethylase OsJMJ701 protein delays flowering by suppressing RFT1 expression.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abe M, Kobayash Y, Yamamoto S, Daimon Y, Yamaguchi A, Ikeda Y, Ichinoki H, Notaguchi M, Goto K, Araki T (2005) FD, a bZIP protein mediating signals from the floral pathway integrator FT at the shoot apex. Science 309:1052–1056
Achard P, Herr A, Baulcombe DC, Harberd NP (2004) Modulation of floral development by a gibberellin-regulated microRNA. Development 131:3357–3365
Andrés F, Coupland G (2012) The genetic basis of flowering responses to seasonal cues. Nat Rev 13:627–639
Ausin I, Alonso-Blanco C, Jarillo JA, Ruiz-Garcia L, Martínez-Zapater JM (2004) Regulation of flowering time by FVE, a retinoblastomaassociated protein. Nat Genet 36:162–166
Ben-Naim O, Eshed R, Parnis A, Teper-Bamnolker P, Shalit A, Coupland G, Samach A, Lifschitz E (2006) The CCAAT binding factor can mediate interactions between CONSTANS-like proteins and DNA. Plant J 46:462–476
Baulcombe DC, Dean C (2014) Epigenetic regulation in plant responses to the environment. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol 6: a019471
Berger S (2007) The complex language of chromatin regulation during transcription. Nature 447:407–412
Berr A, Xu L, Gao J, Cognat V, Steinmetz A, Dong A, Shen WH (2009) SET DOMAIN GROUP25 encodes a histone methyltransferase and is involved in FLOWERING LOCUS C activation and repression of flowering. Plant Physiol 151:1476–1485
Berr A, Shafiq S, Shen WH (2011) Histone modifications in transcriptional activation during plant development. Biochim Biophys Acta 1809:567–576
Cartagena JA, Matsunaga S, Seki M, Kurihara D, Yokoyama M, Shinozaki K, Fujimoto S, Azumi Y, Uchiyama S, Fukui K (2008) The Arabidopsis SDG4 contributes to the regulation of pollen tube growth by methylation of histone H3 lysines 4 and 36 in mature pollen. Dev Biol 315:355–368
Cazzonelli CI, Roberts AC, Carmody ME, Pogson BJ (2010) Transcriptional control of SET DOMAIN GROUP 8 and CAROTENOID ISOMERASE during Arabidopsis development. Mol Plant 3:174–191
Cheng XF, Wang ZY (2005) Overexpression of COL9, a CONSTANSLIKE gene, delays flowering by reducing expression of CO and FT in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J 43:758–768
Choi SC, Lee S, Kim SR, Lee YS, Liu C, Cao X, An G (2014) Trithorax group protein Oryza sativa Trithorax1 controls flowering time in rice via interaction with early heading date3. Plant Physiol 164:1326–1337
Datta S, Hettiarachchi GHCM, Deng XW, Holm M (2006) Arabidopsis CONSTANS-LIKE3 is a positive regulator of red light signaling and root growth. Plant Cell 18:70–84
De Lucia F, Crevillen P, Jones AM, Greb T, Dean C (2008) A PHDPolycomb Repressive Complex 2 triggers the epigenetic silencing of FLC during vernalization. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105:16831–16836
Farrona S, Thorpe FL, Engelhorn J, Adrian J, Dong X, Sarid-Krebs L, Goodrich J, Turck F (2011) Tissue-specific expression of FLOWERING LOCUS T in Arabidopsis is maintained independently of polycomb group protein repression. Plant Cell 23:3204–3214
Fischer A, Hofmann I, Naumann K, Reuter G (2006) Heterochromatin proteins and the control of heterochromatic gene silencing in Arabidopsis. J Plant Physiol 163:358–368
Fornara F, Panigrahi KCS, Gissot L, Sauerbrunn N, Ruhl M, Jarillo JA, Coupland G (2009) Arabidopsis DOF transcription factors act redundantly to reduce CONSTANS expression and are essential for a photoperiodic flowering response. Dev Cell 17:75–86
Gan ES, Xu Y, Wong JY, Goh JG, Sun B, Wee WY, Huang J, Ito T (2014) Jumonji demethylases moderate precocious flowering at elevated temperature via regulation of FLC in Arabidopsis. Nat Commun 5:5098
Grini PE, Thorstensen T, Alm V, Vizcay-Barrena G, Windju SS, Jorstad TS, Wilson ZA, Aalen RB (2009) The ASH1 HOMOLOG 2 (ASHH2) histone H3 methyltransferase is required for ovule and anther development in Arabidopsis. PLoS One 4: e7817
Grzenda A, Lomberk G, Zhang JS, Urrutia R (2009) Sin3: master scaffold and transcriptional corepressor. Biochim Biophys Acta 1789:443–450
Gu X, Wang Y, He Y (2013) Photoperiodic regulation of flowering time through periodic histone deacetylation of the florigen gene FT. PLoS Biol 11: e1001649
Guo L, Yu Y, Law JA, Zhang X (2010) SET DOMAIN GROUP2 is the major histone H3 lysine 4 trimethyltransferase in Arabidopsis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 107:18557–18562
Hassidim M, Harir Y, Yakir E, Kron I, Green RM (2009) Overexpression of CONSTANS-LIKE 5 can induce fowering in shortday grown Arabidopsis. Planta 230:481–491
He Y (2009) Control of the transition to flowering by chromatin modifications. Mol Plant 4:554–564
He Y (2012) Chromatin regulation of flowering. Trends Plant Sci 17:556–562
He Y, Michaels SD, Amasino RM (2003) Regulation of flowering time by histone acetylation in Arabidopsis. Science 302:1751–1754
Hepworth SR, Valverge F, Ravenscoft D, Mouradov A, Coupland G (2002) Antagonistic regulation of flowering-time gene SOC1 by CONSTANS and FLC via separate promoter motifs. EMBO J 21:4207–4391
Imaizumi T, Schultz TF, Harmon FG, Ho LA, Kay SA (2005) FKF1 F-box protein mediates cyclic degradation of a repressor of CONSTANS in Arabidopsis. Science 309:293–297
Ishikawa R, Aoki M, Kurotani K, Yokoi S, Shinomura T, Takano M, Shimamoto K (2011) Phytochrome B regulates Heading date 1 (Hd1)-mediated expression of rice florigen Hd3a and critical day lenHd3agth in rice. Mol Genet Genom 285:461–470
Itoh H, Nonoue Y, Yano M, Izawa T (2010) A pair of floral regulators sets critical day length for Hd3a florigen expression in rice. Nat Genet 42:635–638
Jacob Y, Feng S, LeBlanc CA, Bernatavichute YV, Stroud H, Cokus S, Johnson LM, Pellegrini M, Jacobsen SE, Michaels SD (2009) ATXR5 and ATXR6 are H3K27 monomethyltransferases required for chromatin structure and gene silencing. Nat Struct Mol Biol 16:763–768
Jeong JH, Song HR, Ko JH, Jeong YM, Kwon YE, Seol JH, Amasino RM, Noh B, Noh YS (2009) Repression of FLOWERING LOCUS T chromatin by functionally redundant histone H3 lysine 4 demethylases in Arabidopsis. PLoS One 4: e8033
Jiang D, Wang Y, Wang Y, He Y (2008) Repression of FLOWERING LOCUS C and FLOWERING LOCUS T by the Arabidopsis Polycomb repressive complex 2 components. PLoS One 3: e3404
Jiang D, Yang W, He Y, Amasino RM (2007) Arabidopsis relatives of the human lysine-specific demethylase1 repress the expression of FWA and FLOWERING LOCUS C and thus promote the floral transition. Plant Cell 19:2975–2987
Jung JH, Seo YH, Seo PJ, Reyes JL, Yun J, Chua NH, Park CM (2007) The GIGANTEA-regulated microRNA172 mediates photoperiodic flowering independent of CONSTANS in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 19:2736–2748
Kim SL, Lee S, Kim HJ, Nam HG, An G (2007) OsMADS51 is a short-day flowering promoter that functions upstream of Ehd1, OsMADS14, and Hd3a. Plant Physiol 145:1484–1494
Kim SY, He Y, Jacob Y, Noh YS, Michaels S, Amasino R (2005) Establishment of the vernalization-responsive, winter-annual habit in Arabidopsis requires a putative histone H3 methyl transferase. Plant Cell 17:3301–3310
Klose RJ, Kallin EM, Zhang Y (2006) JmjC-domain-containing proteins and histone demethylation. Nat Rev Genet 7:715–727
Kohler C, Villar CB (2008) Programming of gene expression by polycomb group proteins. Trends Cell Biol 18:236–243
Komiya R, Ikegami A, Tamaki S, Yokoi S, Shimamoto K (2008) Hd3a and RTT1 are essential for flowering in rice. Development 135:767–774
Kouzarides T (2007) Chromatin modifications and their function. Cell 128:693–705
Lan F, Nottke AC, Shi Y (2008) Mechanisms involved in the regulation of histone lysine demethylases. Curr Opin Cell Biol 20:316–325
Lee S, An G (2007) Diversified mechanisms for regulating flowering time in a short-day plant rice. J Plant Biol 50:241–248
Lee S, Kim J, Han JJ, Han MJ, An G (2004) Functional analyses of the flowering time gene OsMADS50, the putative SUPPRESSOR OF OVEREXPRESSION OF CO 1/AGAMOUS-LIKE 20 (SOC1/AGL20) ortholog in rice. Plant J 38:754–764
Lee YS, An G (2015) OsGI controls flowering time by modulating rhythmic flowering time regulators preferentially under short day in rice. J Plant Biol 58:137–145
Lee YS, Jeong DH, Lee DY, Yi J, Ryu CH, Kim SL, Jeong HJ, Choi SC, Jin P, Yang J, Cho LH, Choi H, An G (2010) OsCOL4 is a constitutive flowering repressor upstream of Ehd1 and downstream of OsphyB. Plant J 63:18–30
Lee YS, Lee DY, Cho LH, An G (2014) Rice miR172 induces flowering by suppressing OsIDS1 and SNB, two AP2 genes that negatively regulate expression of Ehd1 and florigens. Rice 7:31
Li C, Huang L, Xu C, Zhao Y, Zhou DX (2011) Altered levels of histone deacetylase OsHDT1 affect differential gene expression patterns in hybrid rice. PLoS One 6: e21789
Liu C, Lu F, Cui X, Cao X (2010) Histone methylation in higher plants. Annu Rev Plant Biol 61:395–420
Liu X, Zhou C, Zhao Y, Zhou S, Wang W, Zhou DX (2014) The rice enhancer of zeste [E(z)] genes SDG711 and SDG718 are respectively involved in long day and short day signaling to mediate the accurate photoperiod control of flowering time. Front Plant Sci 5:591
Lu F, Cui X, Zhang S, Jenuwein T, Cao X (2011) Arabidopsis REF6 is a histone H3 lysine 27 demethylase. Nat Genet 43:715–719
Lu F, Li G, Cui X, Liu C, Wang XJ, Cao X (2008) Comparative analysis of JmjC domain-containing proteins reveals the potential histone demethylases in Arabidopsis and rice. J Integr Plant Biol 50:886–896
Lu Z, Huang X, Ouyang Y, Yao J (2013) Genome-wide identification, phylogenetic and co-expression analysis of OsSET gene family in rice. PLoS One 8: e65426
Matsubara K, Yamanouchi U, Nonoue Y, Sugimoto K, Wang ZX, Minobe Y, Yano M (2011) Ehd3, encoding a plant homeodomain finger-containing protein, is a critical promoter of rice flowering. Plant J 66:603–612
Ng DW, Wang T, Chandrasekharan MB, Aramayo R, Kertbundit S, Hall TC (2007) Plant SET domain-containing proteins: structure, function and regulation. Biochim Biophys Acta 1769:316–329
Onouchi H, Igeno MI, Perileux C, Graves K, Coupland G (2000) Mutagenesis of plants overexpressing CONSTANS demonstrates novel interactions among Arabidopsis flowering-time genes. Plant Cell 12:885–900
Palma K, Thorgrimsen S, Malinovsky FG, Fiil BK, Nielsen HB, Brodersen P, Hofius D, Petersen M, Mundy J (2010) Autoimmunity in Arabidopsis acd11 is mediated by epigenetic regulation of an immune receptor. PLoS Pathog 6: e1001137
Park SJ, Kim SL, Lee S, Je BI, Piao HL, Park SH, Kim CM, Ryu CH, Park SH, Xuan YH, Colasanti J, An G, Han CD (2008) Rice Indeterminate 1 (OsId1) is necessary for the expression of Ehd1 (Early heading date 1) regardless of photoperiod. Plant J 56:1018–1029
Pien S, Fleury D, Mylne JS, Crevillen P, Inze D, Avramova Z, Dean C, Grossniklaus U (2008) ARABIDOPSIS TRITHORAX1 dynamically regulates FLOWERING LOCUS C activation via histone 3 lysine 4 trimethylation. Plant Cell 20:580–588
Pien S, Grossniklaus U (2007) Polycomb group and trithorax group proteins in Arabidopsis. Biochim Biophys Acta 1769:375–382
Pineiro M, Gomez-Mena C, Schaffer R, Martinez-Zapater JM, Coupland G (2003) EARLY BOLTING IN SHORT DAYS is related to chromatin remodeling factors and regulates flowering in Arabidopsis by repressing FT. Plant Cell 7:1552–1562
Saleh A, Alvarez-Venegas R, Yilmaz M, Le O, Hou G, Sadder M, Al-Abdallat A, Xia Y, Lu G, Ladunga I, Avramova Z (2008) The highly similar Arabidopsis homologs of trithorax ATX1 and ATX2 encode proteins with divergent biochemical functions. Plant Cell 20:568–579
Samach A, Coupland G (2000) Time measurement and the control of flowering in plants. Bioessays 22:38–47
Schuettengruber B, Cavalli G (2009) Recruitment of polycomb group complexes and their role in the dynamic regulation of cell fate choice. Development 136:3531–3542
Sheldon CC, Finnegan EJ, Dennis ES, Peacock WJ (2006) Quantitative effects of vernalization on FLC and SOC1 expression. Plant J 45:871–883
Shrestha R, Gomez-Ariza J, Brambilla V, Fornara F (2014) Molecular control of seasonal flowering in rice, Arabidopsis and temperate cereals. Ann Bot 114:1445–1458
Song YH, Ito S, Imaizumi T (2013) Flowering time regulation: photoperiod- and temperature-sensing in leaves. Trend Plant Sci 18:575–583
Song YH, Lee I, Lee SY, Imaizumi T, Hong JH (2012) CONSTANS and ASYMMETRIC LEAVES 1 complex is involved in the induction of FLOWERING LOCUS T in photoperiodic flowering in Arabidopsis. Plant J 69:332–342
Sui P, Shi J, Gao X, Shen WH, Dong A (2013) H3K36 methylation is involved in promoting rice flowering. Mol Plant 6:975–977
Sun C, Fang J, Zhao T, Xu B, Zhang F, Liu L, Tang J, Zhang G, Deng X, Chen F, Qian Q, Cao X, Chu C (2012) The histone methyltransferase SDG724 mediates H3K36me2/3 deposition at MADS50 and RFT1 and promotes flowering in rice. Plant Cell 24:3235–3247
Sung S, Amasino RM (2004) Vernalization in Arabidopsis thaliana is mediated by the PHD finger protein VIN3. Nature 427:159–164
Tamada Y, Yun JY, Woo SC, Amasino RM (2009) ARABIDOPSIS TRITHORAX-RELATED7 is required for methylation of lysine 4 of histone H3 and for transcriptional activation of FLOWERING LOCUS C. Plant Cell 21:3257–3269
Teotia S, Tang G (2015) To bloom or not to bloom: role of microRNAs in plant flowering. Mol Plant 8:359–377
Tian L, Chen ZJ (2001) Blocking histone deacetylation in Arabidopsis induces pleiotropic effects on plant gene regulation and development. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98:200–205
Wenkel S, Turck F, Singer K, Gissot L, Le Gourrierec J, Samach A, Coupland G (2006) CONSTANS and the CCAAT box binding complex share a functionally important domain and interact to regulate flowering of Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 18:2971–2984
Wigge PA, Kim MC, Jaeger KE, Busch W, Schmid M, Lohmann JU, Weigel D (2005) Integration of spatial and temporal information during floral induction in Arabidopsis. Science 309:1056–1059
Wood CC, Robertson M, Tanner G, Peacock WJ, Dennis ES, Helliwell CA (2006) The Arabidopsis thaliana vernalization response requires a polycomb-like protein complex that also includes VERNALIZATION INSENSITIVE 3. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103:14631–14636
Wu G, Poethig S (2006) Temporal regulation of shoot development in Arabidopsis thaliana by miR156 and its target SPL3. Development 133:3539–3547
Xu L, Zhao Z, Dong A, Soubigou-Taconnat L, Renou JP, Steinmetz A, Shen WH (2008) Di- and tri- but not monomethylation on histone H3 lysine 36 marks active transcription of genes involved in flowering time regulation and other processes in Arabidopsis thaliana. Mol Cell Biol 28:1348–1360
Xue W, Xing Y, Weng X, Zhao Y, Tang W, Wang L, Zhou H, Yu S, Xu C, Li X, Zhang Q (2008) Natural variation in Ghd7 is an important regulator of heading date and yield potential in rice. Nat Genet 40:761–767
Yang W, Jiang D, Jiang J, He Y (2010) A plant-specific histone H3 lysine 4 demethylase represses the floral transition in Arabidopsis. Plant J 62:663–673
Yan, J, Lee S, Hang R, Kim SR, Lee YS, Cao X, Amasino R, An G (2013) OsVIL2 functions with PRC2 to induce flowering by repressing OsLFL1 in rice. Plant J 73:566–578
Yano M, Katayose Y, Ashikari M, Yamanouchi U, Monna L, Fuse T, Baba T, Yamamoto K, Umehara Y, Nagamura Y, Sasaki T (2000) Hd1, a major photoperiod sensitivity quantitative trait locus in rice, is closely related to the Arabidopsis flowering time gene CONSTANS. Plant Cell 12:2473–2484
Yao X, Feng H, Yu Y, Dong A, Shen WH (2013) SDG2-mediated H3K4 methylation is required for proper Arabidopsis root growth and development. PLoS One 8: e56537
Yokoo T, Saito H, Yoshitake Y, Xu Q, Asami T, Tsukiyama T, Teraishi M, Okumoto Y, Tanisaka T (2014) Se14, encoding a JmjC domain-containing protein, plays key roles in long-day suppression of rice flowering through the demethylation of H3K4me3 of RFT1. PLoS One 9: e96064
Yu CW, Liu X, Luo M, Chen C, Lin X, Tian G, Lu Q, Cui Y, Wu K (2011) HISTONE DEACETYLASE6 interacts with FLOWERING LOCUS D and regulates flowering in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 156:173–184
Zhou M, Ma H (2008) Evolutionary history of histone demethylase families: distinct evolutionary patterns suggest functional divergence. BMC Evo Biol 8:294
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jeong, H.J., Yang, J., Yi, J. et al. Controlling flowering time by histone methylation and acetylation in arabidopsis and rice. J. Plant Biol. 58, 203–210 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12374-015-0219-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12374-015-0219-1