Abstract
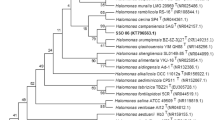
moderately halophilic spore forming, motile, Gram-positive, rod-shaped bacterial strain designated as KGW1T was isolated from water sample of Chilika Lake and characterized taxonomically using polyphasic approach. The strain grew in the presence of 0–25% (w/v) NaCl in marine salt agar media, hydrolyzes casein, and gelatin and shows presence of alkaline proteases. The major cell wall menaquinone was MK7 and major cellular fatty acids were anteiso-C15:0 (44.89%), anteiso-C17:0 (6.18%), isoC15:0 (19.38%), and iso-C16:0 (7.39%). Several chemotaxonomic features conform the isolate be a member of genus Halobacillus. The isolate KGW1T contained A1γ meso-Dpm-direct type of peptidoglycan which is different from its phylogenetically closest neighbours. The 16S rRNA gene sequence based phylogenetic analysis also revealed the strain KGW1T was affiliated to the genus Halobacillus and sequence similarity between the isolated strain and the type strains of Halobacillus species were found closest to, H. dabanensis D-8 DSM 18199T (99.08%) and H. faecis IGA7-4 DSM 21559T (99.01%), H. trueperi SL-5 DSM 10404T (98.94%). The in silico DDH showed that the values in a range of 14.2–17.5% with the most closest strain H. dabanensis D-8 DSM 18199T and other type strains of the genus Halobacillus for which whole genome sequence is reported. DNA-DNA relatedness between strain KGW1T and the closest type strain Halobacillus trueperi DSM 10404T was 11.75% (± 1.15). The draft genome sequence includes 3,683,819 bases and comprises of 3898 predicted coding sequences with a G + C content of 46.98%. Thus, the significant distinctiveness supported by phenotypic and genotypic data with its closest neighbors and other closely related species confirm the strain KGW1T to be classified as a novel species within the genus Halobacillus, for which the name Halobacillus marinus sp. nov. is proposed. The type strain is KGW1T (= DSM 29522 = JCM 30443).
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Altschul, S.F., Madden, T.L., Schaffer, A.A., Zhang, J., Zhang, Z., Miller, W., and Lipman, D.J. 1997. Gapped BLAST and PSIBLAST: a new generation of protein database search programs. Nucleic Acids Res. 25, 3389–3402.
An, S.Y., Kanoh, K., Kasai, H., Goto, K., and Yokota, A. 2007. Halobacillus faecis sp. nov., in a spore-forming bacterium isolated from a mangrove area on Ishigaki Island, Japan. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 57, 2476–2479.
Auch, A.F., Klenk, H.P., and Göker, M. 2010. Standard operating procedure for calculating genome-to-genome distances based on high-scoring segment pairs. Stand. Genomic Sci. 2, 142–148.
Aygan, A. and Arikan, B. 2007. Mini Review An overview on bacterial motility detection. Int. J. Agri. Biol. 9, 193–196.
Bligh, E.G. and Dyer, W.J. 1959. A rapid method of total lipid extraction and purification. Can. J. Biochem. Physiol. 37, 911–917.
Cashion, P., Holder-Franklin, M.A., McCully, J., and Franklin, M. 1977. A rapid method for the base ratio determination of bacterial DNA. Anal. Biochem. 81, 461–466.
Chen, Y.G., Liu, Z.X., Zhang, Y.Q., Zhang, Y.X., Tang, S.K., Borrathybay, E., Li, W.J., and Cui, X.L. 2009a. Halobacillus naozhouensis sp. nov., a moderately halophilic bacterium isolated from a sea anemone. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek 96, 99–107.
Chen, Y.G., Zhang, Y.Q., Liu, Z.X., Zhuang, D.C., Klenk, H.P., Tang, S.K., Cui, X.L., and Li, W.J. 2009b. Halobacillus salsuginis sp. nov., a moderately halophilic bacterium from a subterranean brine. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 59, 2505–2509.
Collee, J.G. and Miles, R.S. 1989. Tests for identification of bacteria, pp. 141–160. In Collee, J.G., Duguid, J.P., Fraser, A.G., and Marmion, B.P. (eds.), Mackie and McCartney’s practical medical microbiology, 13th ed. Churchill Livingstone, Edinburgh, UK.
De Ley, J., Cattoir, H., and Reynaerts, A. 1970. The quantitative measurement of DNA hybridization from renaturation rates. Eur. J. Biochem. 12, 133–142.
Fahmy, F., Mayer, F., and Claus, D. 1985. Endospores of Sporosarcina halophila: characteristics and ultrastructure. Arch. Microbiol. 140, 338–342.
Felsenstein, J. 1985. Confidence limits on phylogenetic: an approach using the bootstrap. Evolution 39, 783–791.
Fitch, W.M. 1971. Towards defining the course of evolution: minimum change for a specific tree topology. Syst. Zool. 20, 406–416.
Galardini, M., Biondi, E.G., Bazzicalupo, M., and Mengoni, A. 2011. CONTIGuator: a bacterial genomes finishing tool for structural insights on draft genomes. Source Code Biol. Med. 6, 11.
Garland, J.L. and Millis, A.L. 1991. Classification and characterization of heterotrophic microbial communities on the basis of patterns of community-level sole carbon source utilization. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 57, 2351–2359.
Hopwood, D.A., Bibb, M.J., Chater, K.F., Kieser, T., Bruton, C.J., Kieser, H.M., Lydiate, D.J., Smith, C.P., and Ward, J.M. 1985. Preparation of chromosomal, plasmid and phage DNA, pp. 79–80. In genetic manipulation of streptomyces: a laboratory manual, John Innes Foundation, Norwich, UK.
Hua, N.P., Kanekiyo, A., Fujikura, K., Yasuda, H., and Nagamura, T. 2007. Halobacillus profundi sp. nov. and Halobacillus kuroshimensis sp. nov., moderately halophilic bacteria isolated from a deep-sea methanecold seep. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 57, 1243–1249.
Huss, V.A.R., Festl, H., and Schleifer, K.H. 1983. Studies on the spectrophotometric determination of DNA hybridization from renaturation rates. Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 4, 184–192.
Kim, O.S., Cho, Y.J., Lee, K., Yoon, S.H., Kim, M., Na, H., Park, S.C., Jeon, Y.S., Lee, J.H., Yi, H., et al. 2012. Introducing EzTaxon-e: a prokaryotic 16S rRNA gene sequence database with phylotypes that represent uncultured species. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 62, 716–721.
Kimura, M. 1980. A simple method for estimating evolutionary rates of base substitutions through comparative studies of nucleotide sequences. J. Mol. Evol. 16, 111–120.
Kumar, S., Glen Stecher, G., and Tamura, K. 2016. MEGA 7: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 7.0. Mol. Biol. Evol. 33, 1870–1874.
Larkin, M.A., Blackshields, G., Brown, N.P., Chenna, R., McGettigan, P.A., McWilliam, H., Valentin, F., Wallace, I.M., Wilm, A., Lopez, R., et al. 2007. Clustal W and Clustal X version 2. Bioinformatics 23, 2947–2948.
Liu, W.Y., Zeng, J., Wang, L., Dou, Y.T., and Yang, S.S. 2005. Halobacillus dabanensis sp. nov. and Halobacillus aidingensis sp. nov., isolated from salt lakes in Xinjiang, China. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 55, 1991–1996.
Logan, N.A., Berge, O., Bishop, H., Busse, H.J., De Vos, P., Fritze, D., Heyndrickx, M., Kämpfer, P., Rabinovitch, L., Salkinoja-Salonen, M.S., et al. 2009. Proposed minimal standards for describing new taxa of aerobic, endospore-forming bacteria. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 59, 2114–2121.
Meier-Kolthoff, J.P., Göker, M., Spröer, C., and Klenk, H.P. 2013. When should a DDH experiment be mandatory in microbial taxonomy? Arch. Microbiol. 195, 413–418.
Mellado, E., Sánchez-Porro, C., Martín, S., and Ventosa, A. 2004. Extracellular hydrolytic enzymes produced by moderately halophilic bacteria, pp. 285–295. In Ventosa, A. (ed.), Halophilic microorganisms. Springer-Verlag, Heidelberg, Berlin, Germany.
Nunes, I., Tiago, I., Pires, A.L., da Costa, M.S., and Veríssimo, A. 2006. Paucisalibacillus globulus gen. nov., sp. nov., a Gram-positive bacterium isolated from potting soil. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 56, 1841–1845.
Panda, A.N., Mishra, S.R., Ray, L., Sahu, N., Acharya, A., Jadhao, S., Suar, M., Adhya, T.K., Rastogi, G., Pattnaik, A.K., et al. 2016. Draft genome sequence of Halobacillus sp. strain KGW1, a moderately halophilic and alkaline protease-producing bacterium isolated from the rhizospheric region of Phragmites karka from Chilika Lake, Odisha, India. Genome Announc. 4, e00361–16.
Quesada, E., Ventosa, A., Ruiz-Berraquero, F., and Ramos-Cormenzana, A. 1984. Deleyahalophila, a new species of moderately halophilic bacteria. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 34, 287–292.
Rodriguez-Valera, F., Ruiz-Berraquero, F., and Ramos-Cormenzana, A. 1980. Isolation of extreamly halophilic bacteria able to grow in defined inorganic media withsingle carbon sources. J. Gen. Microbiol. 119, 535–538.
Romano, I., Finore, I., Nicolaus, G., Huertas, F.J., Lama, L., Nicolaus, B., and Poli, A. 2008. Halobacillus alkaliphilus sp. nov., a halophilic bacterium isolated from a salt lake in Fuente de Piedra, southern Spain. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 58, 886–890.
Rzhetsky, A. and Mei, M. 1992. A simple method for estimating and testing minimum evolution trees. Mol. Biol. Evol. 9, 945–967.
Saitou, N. and Nei, M. 1987. The neighbor-joining method: a new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol. Biol. Evol. 4, 406–425.
Sasser, M. 1990. Identification of bacteria by gas chromatography of cellular fatty acids. USFCC News 20, 16.
Schumann, P. 2011. Peptidoglycan structure, pp. 101–129. In Rainey, F. and Oren, A. (eds.), Taxonomy of prokaryotes, methods in microbiology, Vol. 38. Academic Press, London, UK.
Shida, O., Takagi, H., Kadowaki, K., Nakamura, L.K., and Komagata, K. 1997. Transfer of Bacillus alginolyticus, Bacillus chondroitinus, Bacillus curdlanolyticus, Bacillus glucanolyticus, Bacillus kobensis, and Bacillus thiaminolyticusto the genus paenibacillus and emended description of genus Paenibacillus. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 47, 289–298.
Soto-Ramírez, N., Sánchez-Porro, C., Rosas-Padilla, S., Almodóvar, K., Jiménez, G., Machado-Rodríguez, M., Zapata, M., Venrosa, A., and Montalvo-Rordíguez, R. 2008. Halobacillus mangrovei sp. nov., a moderately halophilic bacterium isolated from the black mangrove Avicennia germinans. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 58, 125–130.
Spring, S., Ludwig, W., Marquez, M.C., Ventosa, A., and Schleifer, K.H. 1996. Halobacillus gen. nov., with descriptions of Halobacillus litoralis sp. nov., and Halobacillus trueperi sp. nov., and transfer of Sporosarcina halophila to Halobacillus halophilus comb. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 46, 492–496.
Stackebrandt, E. and Ebers, J. 2006. Taxonomic parameters revisited: tarnished gold standards. Microbiol. Today 33, 152–155.
Tindall, B.J. 1990a. A comparative study of the lipid composition of Halobacterium saccharovorum from various sources. Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 13, 128–130.
Tindall, B.J. 1990b. Lipid composition of Halobacterium lacusprofundi. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 66, 199–202.
Tindall, B.J., Rosselló-Móra, R., Busse, H.J., Ludwig, W., and Kämpfer, P. 2010. Notes on the characterization of prokaryote strains for taxonomic purposes. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 60, 249–266.
Tindall, B.J., Sikorski, J., Smibert, R.M., and Kreig, N.R. 2007. Phenotypic characterization and the principles of comparative systematics, pp. 330–393. In Reddy, C.A., Beveridge, T.J., Breznak, J.A., Marzluf, G.A., Schmidt, T.M., and Snyder, L.R. (eds.), Methods for general and molecular microbiology, 3rd ed. American Society for Microbiology, Washington, DC, USA.
Ventosa, A., Quesada, E., Rodriguez-Valera, F., Ruiz-Berraquero, F., and Ramos-Cormenzana, A. 1982. Numerical taxonomy of moderately halophilic Gram-negative rods. J. Gen. Microbiol. 128, 1959–1968.
Wainø, M., Tindall, B.J., Schumann, P., and Ingvorsen, K. 1999. Gracilibacillus gen. nov., with description of Gracilibacillus halotolerans gen. nov., sp. nov.; transfer of Bacillus dipsosauri to Gracilibacillus dipsosauri comb. nov., and Bacillus salexigens to the genus Salibacillus gen. nov., as Salibacillus salexigens comb. nov. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 49, 821–831.
Wang, K., Zhang, L., Yang, Y., Pan, Y., Meng, L., Liu, H., Hong, S., Huang, H., and Jiang, J. 2015. Halobacillus andaensis sp. nov., a moderately halophilic bacterium isolated from saline and alkaline soil. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 65, 1908–1914.
Wayne, L.G., Brenner, D.J., Colwell, R.R., Grimont, P.A.D., Kandler, O., Krichevsky, M.I., Moore, L.H., Moore, W.E.C., Murray, R.G.E., Stackebrandt, E., et al. 1987. Report of the ad hoc committee on reconciliation of approaches to bacterial systematics. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 37, 463–464.
Yoon, J.H., Kang, S.J., Jung, Y.T., and Oh, T.K. 2007. Halobacillus campisalis sp. nov., Containing meso-diaminopimelic acid in the cell-wall peptidoglycan, and emended description of the genus Halobacillus. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 57, 2021–2025.
Yoon, J.H., Kang, S.J., and Oh, T.K. 2008. Halobacillus seohaensis sp. nov., isolated from a marine solar saltern in Korea. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 58, 622–627.
Yoon, J.H., Kang, K.H., Oh, T.K., and Park, Y.H. 2004. Halobacillus locisalis sp. nov., A halophilic bacterium isolated from a marine solar saltern of the Yellow Sea in Korea. Extremophiles 8, 23–28.
Yoon, J.H., Kang, K.H., Oh, T.K., and Park, Y.H. 2005. Halobacillus yeomjeoni sp. nov., isolated from a marine solar saltern in Korea. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 55, 2413–2417.
Yoon, J.H., Kang, K.H., and Park, Y.H. 2003. Halobacillus salinus sp. nov., isolated from a salt lake on the coast of the East Sea in Korea. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 53, 687–693.
Yoon, J.H., Weiss, N., Lee, K.C., Lee, I.S., Kang, K.H., and Park, Y.H. 2001. Jeotgalibacillus alimentarius gen. nov., sp. nov., a novel bacterium isolated from jeotgal with L-lysine in the cell wall, reclassification of Bacillus marinus Rüger 1983 as Marinibacillus marinus gen. nov., comb. nov. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 51, 2087–2093.
Zerbino, D. and Birney, E. 2008. Velvet: Algorithms for de novo short read assembly using de Bruijn graphs. Genome Res. 18, 821–829.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
The GenBank accession number for 16S rRNA gene sequence of Halobacillus marinus KGW1T is KJ563233. The accession number for this whole genome shotgun project is LSOC00000000. The version described in this paper is LSOC01000000.
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Panda, A.N., Mishra, S.R., Ray, L. et al. Taxonomic description and genome sequence of Halobacillus marinus sp. nov., a novel strain isolated from Chilika Lake, India. J Microbiol. 56, 223–230 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12275-018-7387-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12275-018-7387-x