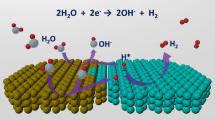
Abstract
Chemical functional groups on solid surfaces greatly influence contact electrification (CE) at water-solid interfaces. Previous studies of their effects mainly swapped materials or bonded related molecules to a substrate, introducing other factors of influence. This work aims at unambiguously demonstrating the role of functional groups in water-polymer CE. We study the contribution of functional groups, by using ion coupled plasma etching to modify a high-density polyethylene (HDPE) film, a polymer with a naturally quasi-null charge transfer ability. Fluoride (HDPE−F) and hydroxyl (HDPE−OH) functional groups are generated and endowed HDPE with charge withdrawing ability. HDPE−F withdraws 2.5–2.7 times more charges than HDPE−OH. Concurrently, the surface charges accumulated generate electrostatic forces, altering the droplets motion. This phenomenon provides another approach to study CE, helping to evaluate the contribution of electrons to solid-liquid CE. Finally, employing HDPE−F to perform contact-electro-catalysis shows its activity is 2.4 times higher than that of commercial fluorinated films.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bard, A. J.; Fan, F. R. F.; Pierce, D. T.; Unwin, P. R.; Wipf, D. O.; Zhou, F. M. Chemical imaging of surfaces with the scanning electrochemical microscope. Science 1991, 254, 68–74.
Ciampi, S.; Darwish, N.; Aitken, H. M.; Díez-Pérez, I.; Coote, M. L. Harnessing electrostatic catalysis in single molecule, electrochemical and chemical systems: A rapidly growing experimental tool box. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2018, 47, 5146–5164.
Vogel, Y. B.; Evans, C. W.; Belotti, M.; Xu, L. K.; Russell, I. C.; Yu, L. J.; Fung, A. K. K.; Hill, N. S.; Darwish, N.; Gonçales, V. R. et al. The corona of a surface bubble promotes electrochemical reactions. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 6323.
Vogel, Y. B.; Molina, A.; Gonzalez, J.; Ciampi, S. Quantitative analysis of cyclic voltammetry of redox monolayers adsorbed on semiconductors: Isolating electrode kinetics, lateral interactions, and diode currents. Anal. Chem. 2019, 91, 5929–5937.
Favaro, M.; Jeong, B.; Ross, P. N.; Yano, J.; Hussain, Z.; Liu, Z.; Crumlin, E. J. Unravelling the electrochemical double layer by direct probing of the solid/liquid interface. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 12695.
Chandler, D. Interfaces and the driving force of hydrophobic assembly. Nature 2005, 437, 640–647.
Ball, P. Water as an active constituent in cell biology. Chem. Rev. 2008, 108, 74–108.
Xu, W. H.; Zheng, H. X.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, X. F.; Zhang, C.; Song, Y. X.; Deng, X.; Leung, M.; Yang, Z. B.; Xu, R. X. et al. A droplet-based electricity generator with high instantaneous power density. Nature 2020, 578, 392–396.
Wang, Z. L. Catch wave power in floating nets. Nature 2017, 542, 159–160.
Chatterjee, S.; Burman, S. R.; Khan, I.; Saha, S.; Choi, D.; Lee, S.; Lin, Z. H. Recent advancements in solid–liquid triboelectric nanogenerators for energy harvesting and self-powered applications. Nanoscale 2020, 12, 17663–17697.
Khan, U.; Kim, S. W. Triboelectric nanogenerators for blue energy harvesting. ACS Nano 2016, 10, 6429–6432.
Wang, Z. L. Triboelectric nanogenerator (TENG)-sparking an energy and sensor revolution. Adv. Energy Mater. 2020, 10, 2000137.
Wang, Z. M.; Berbille, A.; Feng, Y. W.; Li, S. T.; Zhu, L. P.; Tang, W.; Wang, Z. L. Contact-electro-catalysis for the degradation of organic pollutants using pristine dielectric powders. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 130.
Zhao, X.; Su, Y. S.; Berbille, A.; Wang, Z. L.; Tang, W. Degradation of methyl orange by dielectric films based on contact-electrocatalysis. Nanoscale 2023, 15, 6243–6251.
Thomas III, S. W.; Vella, S. J.; Dickey, M. D.; Kaufman, G. K.; Whitesides, G. M. Controlling the kinetics of contact electrification with patterned surfaces. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 8746–8747.
Lin, S. Q.; Xu, L.; Wang, A. C.; Wang, Z. L. Quantifying electron-transfer in liquid–solid contact electrification and the formation of electric double-layer. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 399.
Zhang, J. Y.; Lin, S. Q.; Zheng, M. L.; Wang, Z. L. Triboelectric nanogenerator as a probe for measuring the charge transfer between liquid and solid surfaces. ACS Nano 2021, 15, 14830–14837.
Zhang, J. Y.; Lin, S. Q.; Wang, Z. L. Triboelectric nanogenerator array as a probe for in situ dynamic mapping of interface charge transfer at a liquid–solid contacting. ACS Nano 2023, 17, 1646–1652.
Zhan, F.; Wang, A. C.; Xu, L.; Lin, S. Q.; Shao, J. J.; Chen, X. Y.; Wang, Z. L. Electron transfer as a liquid droplet contacting a polymer surface. ACS Nano 2020, 14, 17565–17573.
Lin, S. Q.; Chen, X. Y.; Wang, Z. L. Contact electrification at the liquid–solid interface. Chem. Rev. 2022, 122, 5209–5232.
Zhao, Z. H.; Zhou, L. L.; Li, S. X.; Liu, D.; Li, Y. H.; Gao, Y. K.; Liu, Y. B.; Dai, Y. J.; Wang, J.; Wang, Z. L. Selection rules of triboelectric materials for direct-current triboelectric nanogenerator. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 4686.
Liu, D.; Zhou, L. L.; Cui, S. N.; Gao, Y. K.; Li, S. X.; Zhao, Z. H.; Yi, Z. Y.; Zou, H. Y.; Fan, Y. J.; Wang, J. et al. Standardized measurement of dielectric materials’ intrinsic triboelectric charge density through the suppression of air breakdown. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 6019.
Liu, Z. Q.; Huang, Y. Z.; Shi, Y. X.; Tao, X. L.; He, H. Z.; Chen, F. D.; Huang, Z. X.; Wang, Z. L.; Chen, X. Y.; Qu, J. P. Fabrication of triboelectric polymer films via repeated rheological forging for ultrahigh surface charge density. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 4083.
Nan, Y.; Shao, J. J.; Willatzen, M.; Wang, Z. L. Understanding contact electrification at water/polymer interface. Research 2022, 2022, 9861463.
Li, S. Y.; Nie, J. H.; Shi, Y. X.; Tao, X. L.; Wang, F.; Tian, J. W.; Lin, S. Q.; Chen, X. Y.; Wang, Z. L. Contributions of different functional groups to contact electrification of polymers. Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, 2001307.
Lin, S. Q.; Zheng, M. L.; Luo, J. J.; Wang, Z. L. Effects of surface functional groups on electron transfer at liquid–solid interfacial contact electrification. ACS Nano 2020, 14, 10733–10741.
Shin, S. H.; Kwon, Y. H.; Kim, Y. H.; Jung, J. Y.; Lee, M. H.; Nah, J. Triboelectric charging sequence induced by surface functionalization as a method to fabricate high performance triboelectric generators. ACS Nano 2015, 9, 4621–4627.
Chen, B. L.; Xia, Y.; He, R. X.; Sang, H. Q.; Zhang, W. C.; Li, J.; Chen, L. F.; Wang, P.; Guo, S. S.; Yin, Y. G. et al. Water–solid contact electrification causes hydrogen peroxide production from hydroxyl radical recombination in sprayed microdroplets. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2022, 119, e2209056119.
Ma, X.; Li, S. Y.; Dong, S. J.; Nie, J. H.; Iwamoto, M.; Lin, S. Q.; Zheng, L.; Chen, X. Y. Regulating the output performance of triboelectric nanogenerator by using P(VDF-TrFE) Langmuir monolayers. Nano Energy 2019, 66, 104090.
Zou, H. Y.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, L. T.; Wang, P. H.; He, X.; Dai, G. Z.; Zheng, H. W.; Chen, C. Y.; Wang, A. C.; Xu, C. et al. Quantifying the triboelectric series. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1427.
Li, X. M.; Bista, P.; Stetten, A. Z.; Bonart, H.; Schür, M. T.; Hardt, S.; Bodziony, F.; Marschall, H.; Saal, A.; Deng, X. et al. Spontaneous charging affects the motion of sliding drops. Nat. Phys. 2022, 18, 713–719.
Wang, X. J.; Zhang, J. Y.; Liu, X.; Lin, S. Q.; Wang, Z. L. Studying the droplet sliding velocity and charge transfer at a liquid–solid interface. J. Mater. Chem. A 2023, 11, 5696–5702.
Zhang, J. Y.; Rogers, F. J. M.; Darwish, N.; Gonçales, V. R.; Vogel, Y. B.; Wang, F.; Gooding, J. J.; Peiris, M. C. R.; Jia, G. H.; Veder, J. P. et al. Electrochemistry on tribocharged polymers is governed by the stability of surface charges rather than charging magnitude. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 5863–5870.
Xu, C.; Zhang, B. B.; Wang, A. C.; Zou, H. Y.; Liu, G. L.; Ding, W. B.; Wu, C. S.; Ma, M.; Feng, P. Z.; Lin, Z. Q. et al. Contact-electrification between two identical materials: Curvature effect. ACS Nano 2019, 13, 2034–2041.
Berbille, A.; Li, X. F.; Su, Y. S.; Li, S. N.; Zhao, X.; Zhu, L. P.; Wang, Z. L. Mechanism for generating H2O2 at water–solid interface by contact-electrification. Adv. Mater., in press, https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.202304387.
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by the National Key R & D Project from Minister of Science and Technology (No. 2021YFA1201601) and National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 52192610), Youth Innovation Promotion Association (W.T.), and CAS-TWAS President’s Fellowship (A.B.).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic Supplementary Material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Su, Y., Berbille, A., Wang, Z.L. et al. Water-solid contact electrification and catalysis adjusted by surface functional groups. Nano Res. 17, 3344–3351 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-023-6125-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-023-6125-9