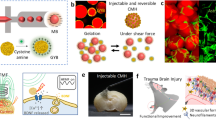
Abstract
Superparamagnetic iron oxide (SPIO) nanoparticles play an important role in mediating precise and effective magnetic neurostimulation and can help overcome limitations related to penetration depth and spatial resolution. However, nanoparticles readily diffuse in vivo, decreasing the spatial resolution and activation efficiency. In this study, we employed a microfluidic means to fabricate injectable microhydrogels encapsulated with SPIO nanoparticles, which significantly improved the stability of nanoparticles, increased the magnetic properties, and reinforced the stimulation effectivity. The fabricated magnetic microhydrogels were highly uniform in size and sphericity, enabling minimally invasive injection into brain tissue. The long-term residency in the cortex up to 22 weeks and the safety of brain tissue were shown using a mouse model. In addition, we quantitatively determined the magneto-mechanical force yielded by only one magnetic microhydrogel using a video-based method. The force was found to be within 7–8 pN under 10 Hz magnetic stimulation by both theoretical simulation and experimental measurement. Lastly, electrophysiological measurement of brain slices showed that the magnetic microhydrogels offer significant advantages in terms of neural activation relative to dissociative SPIO nanoparticles. A universal strategy is thus offered for performing magnetic neuro-stimulation with an improved prospect for biomedical translation.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Li, N. F.; Baldermann, J. C.; Kibleur, A.; Treu, S.; Akram, H.; Elias, G. J. B.; Boutet, A.; Lozano, A. M.; Al-Fatly, B.; Strange, B. et al. A unified connectomic target for deep brain stimulation in obsessive-compulsive disorder. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 3364.
Cotero, V.; Graf, J.; Miwa, H.; Hirschstein, Z.; Qanud, K.; Huerta, T. S.; Tai, N. W.; Ding, Y. Y.; Jimenez-Cowell, K.; Tomaio, J. N. et al. Stimulation of the hepatoportal nerve plexus with focused ultrasound restores glucose homoeostasis in diabetic mice, rats and swine. Nat. Biomed. Eng. 2022, 6, 683–705.
Burke, M. J.; Fried, P. J.; Pascual-Leone, A. Transcranial magnetic stimulation: Neurophysiological and clinical applications. Handb. Clin. Neurol. 2019, 163, 73–92.
Hallett, M. Transcranial magnetic stimulation and the human brain. Nature 2000, 406, 147–150.
Liu, X. D.; Qiu, F.; Hou, L. J.; Wang, X. H. Review of noninvasive or minimally invasive deep brain stimulation. Front. Behav. Neurosci. 2022, 15, 820017.
Zhong, G. L.; Yang, Z. Y.; Jiang, T. Z. Precise modulation strategies for transcranial magnetic stimulation: Advances and future directions. Neurosci. Bull. 2021, 37, 1718–1734.
Sánchez, C. C.; García, J. J. J.; Cabello, M. R.; Pantoja, M. F. Design of coils for lateralized TMS on mice. J. Neural Eng. 2020, 17, 036007.
Oliveria, S. F.; Rodriguez, R. L.; Bowers, D.; Kantor, D.; Hilliard, J. D.; Monari, E. H.; Scott, B. M.; Okun, M. S.; Foote, K. D. Safety and efficacy of dual-lead thalamic deep brain stimulation for patients with treatment-refractory multiple sclerosis tremor: A single-centre, randomised, single-blind, pilot trial. Lancet Neurol. 2017, 16, 691–700.
Scangos, K. W.; Khambhati, A. N.; Daly, P. M.; Makhoul, G. S.; Sugrue, L. P.; Zamanian, H.; Liu, T. X.; Rao, V. R.; Sellers, K. K.; Dawes, H. E. et al. Closed-loop neuromodulation in an individual with treatment-resistant depression. Nat. Med. 2021, 27, 1696–1700.
Hescham, S. A.; Chiang, P. H.; Gregurec, D.; Moon, J.; Christiansen, M. G.; Jahanshahi, A.; Liu, H. J.; Rosenfeld, D.; Pralle, A.; Anikeeva, P. et al. Magnetothermal nanoparticle technology alleviates parkinsonian-like symptoms in mice. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 5569.
Bobo, D.; Robinson, K. J.; Islam, J., Thurecht, K. J.; Corrie, S. R. Nanoparticle-based medicines: A review of FDA-approved materials and clinical trials to date. Pharm. Res. 2016, 33, 2373–2387.
Chen, R.; Romero, G.; Christiansen, M. G.; Mohr, A.; Anikeeva, P. Wireless magnetothermal deep brain stimulation. Science 2015, 347, 1477–1480.
Stanley, S. A.; Kelly, L.; Latcha, K. N.; Schmidt, S. F.; Yu, X. F.; Nectow, A. R.; Sauer, J.; Dyke, J. P.; Dordick, J. S.; Friedman, J. M. Bidirectional electromagnetic control of the hypothalamus regulates feeding and metabolism. Nature 2016, 531, 647–650.
Lu, Q. B.; Sun, J. F.; Yang, Q. Y.; Cai, W. W.; Xia, M. Q.; Wu, F. F.; Gu, N.; Zhang, Z. J. Magnetic brain stimulation using iron oxide nanoparticle-mediated selective treatment of the left prelimbic cortex as a novel strategy to rapidly improve depressive-like symptoms in mice. Zool. Res. 2020, 41, 381–394.
Lu, Q. B.; Wu, F. F.; Jiao, J.; Xue, L.; Song, R. Z.; Shi, Y. C.; Kong, Y.; Sun, J. F.; Gu, N.; Han, M. H. et al. Selective activation of ABCA1/ApoA1 signaling in the V1 by magnetoelectric stimulation ameliorates depression via regulation of synaptic plasticity. iScience 2022, 25, 104201.
Tay, A.; Kunze, A.; Murray, C.; Di Carlo, D. Induction of calcium influx in cortical neural networks by nanomagnetic forces. ACS Nano 2016, 10, 2331–2341.
Tay, A.; Sohrabi, A.; Poole, K.; Seidlits, S.; Di Carlo, D. A 3D magnetic hyaluronic acid hydrogel for magnetomechanical neuromodulation of primary dorsal root ganglion neurons. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1800927.
Lee, J. U.; Shin, W.; Lim, Y.; Kim, J.; Kim, W. R.; Kim, H.; Lee, J. H.; Cheon, J. Non-contact long-range magnetic stimulation of mechanosensitive ion channels in freely moving animals. Nat. Mater. 2021, 20, 1029–1036.
Yu, Y. C.; Payne, C.; Marina, N.; Korsak, A.; Southern, P.; García-Prieto, A.; Christie, I. N.; Baker, R. R.; Fisher, E. M. C.; Wells, J. A. et al. Remote and selective control of astrocytes by magnetomechanical stimulation. Adv. Sci. 2022, 9, 2104194.
van Landeghem, F. K. H.; Maier-Hauff, K.; Jordan, A.; Hoffmann, K. T.; Gneveckow, U.; Scholz, R.; Thiesen, B.; Brück, W.; von Deimling, A. Post-mortem studies in glioblastoma patients treated with thermotherapy using magnetic nanoparticles. Biomaterials 2009, 30, 52–57.
Li, R. R.; Wang, J.; Yu, X. Y.; Xu, P. F.; Zhang, S.; Xu, J. H.; Bai, Y. J.; Dai, Z. Z.; Sun, Y. X.; Ye, R. D. et al. Enhancing the effects of transcranial magnetic stimulation with intravenously injected magnetic nanoparticles. Biomater. Sci. 2019, 7, 2297–2307.
Sandhir, R.; Onyszchuk, G.; Berman, N. E. J. Exacerbated glial response in the aged mouse hippocampus following controlled cortical impact injury. Exp. Neurol. 2008, 213, 372–380.
Gansau, J.; Kelly, L.; Buckley, C. T. Influence of key processing parameters and seeding density effects of microencapsulated chondrocytes fabricated using electrohydrodynamic spraying. Biofabrication 2018, 10, 035011.
Li, J. W.; He, J. M.; Huang, Y. D.; Li, D. L.; Chen, X. T. Improving surface and mechanical properties of alginate films by using ethanol as a co-solvent during external gelation. Carbohydr. Polym. 2015, 123, 208–216.
Yuan, M.; Ju, X. J.; Xie, R.; Wang, W.; Chu, L. Y. Micromechanical properties of poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) hydrogel microspheres determined using a simple method. Particuology 2015, 19, 164–172.
Liu, Y. X.; Liu, J.; Chen, S. C.; Lei, T.; Kim, Y.; Niu, S. M.; Wang, H. L.; Wang, X.; Foudeh, A. M.; Tok, J. B. H. et al. Soft and elastic hydrogel-based microelectronics for localized low-voltage neuromodulation. Nat. Biomed. Eng. 2019, 3, 58–68.
Liu, H. Y.; Sun, J. F.; Wang, H. Y.; Wang, P.; Song, L. N.; Li, Y.; Chen, B.; Zhang, Y.; Gu, N. Quantitative evaluation of the total magnetic moments of colloidal magnetic nanoparticles: A kinetics-based method. ChemPhysChem 2015, 16, 1598–1602.
Issa, B.; Obaidat, I. M.; Albiss, B. A.; Haik, Y. Magnetic nanoparticles: Surface effects and properties related to biomedicine applications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 21266–21305.
Feng, Q. S.; Xu, X. Y.; Wei, C.; Li, Y. Z.; Wang, M.; Lv, C.; Wu, J. J.; Dai, Y. L.; Han, Y.; Lesniak, M. S. et al. The dynamic interactions between nanoparticles and macrophages impact their fate in brain tumors. Small 2021, 17, 2103600.
Jacob, S.; Nair, A. B.; Shah, J.; Sreeharsha, N.; Gupta, S.; Shinu, P. Emerging role of hydrogels in drug delivery systems, tissue engineering and wound management. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 357.
Fang, J. H.; Hsu, H. H.; Hsu, R. S.; Peng, C. K.; Lu, Y. J.; Chen, Y. Y.; Chen, S. Y.; Hu, S. H. 4D printing of stretchable nanocookie@conduit material hosting biocues and magnetoelectric stimulation for neurite sprouting. NPG Asia Mater. 2020, 12, 61.
Zhou, H. J.; Mayorga-Martinez, C. C.; Pané, S.; Zhang, L.; Pumera, M. Magnetically driven micro and nanorobots. Chem. Rev. 2021, 121, 4999–5041.
Wang, H. Y.; Ge, Y. Q.; Sun, J. F.; Wang, H.; Gu, N. Magnetic sensor based on image processing for dynamically tracking magnetic moment of single magnetic mesenchymal stem cell. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2020, 169, 112593.
Tay, A.; Di Carlo, D. Magnetic nanoparticle-based mechanical stimulation for restoration of mechano-sensitive ion channel equilibrium in neural networks. Nano Lett. 2017, 17, 886–892.
Kunze, A.; Tseng, P.; Godzich, C.; Murray, C.; Caputo, A.; Schweizer, F. E.; Di Carlo, D. Engineering cortical neuron polarity with nanomagnets on a chip. ACS Nano 2015, 9, 3664–3676.
Lewis, A. H.; Cui, A. F.; McDonald, M. F.; Grandl, J. Transduction of repetitive mechanical stimuli by piezo1 and piezo2 ion channels. Cell Rep. 2017, 19, 2572–2585.
He, Q.; Yang, X. Y.; Gong, B. Q.; Bi, K. Y.; Fang, F. Boosting visual perceptual learning by transcranial alternating current stimulation over the visual cortex at alpha frequency. Brain Stimul. 2022, 15, 546–553.
Efremov, A. K.; Yao, M. X.; Sun, Y. Z.; Tee, Y. H.; Sheetz, M. P.; Bershadsky, A. D.; Martinac, B.; Yan, J. Application of piconewton forces to individual filopodia reveals mechanosensory role of L-type Ca2+ channels. Biomaterials 2022, 284, 121477.
Wang, C. L.; Xu, R. Z.; Tian, W. J.; Jiang, X. L.; Cui, Z. Y.; Wang, M.; Sun, H. M.; Fang, K.; Gu, N. Determining intracellular temperature at single-cell level by a novel thermocouple method. Cell Res. 2011, 21, 1517–1519.
Bayat, M.; Zabihi, S.; Karbalaei, N.; Haghani, M. Time-dependent effects of platelet-rich plasma on the memory and hippocampal synaptic plasticity impairment in vascular dementia induced by chronic cerebral hypoperfusion. Brain Res. Bull. 2020, 164, 299–306.
Bestmann, S.; Baudewig, J.; Siebner, H. R.; Rothwell, J. C.; Frahm, J. Functional MRI of the immediate impact of transcranial magnetic stimulation on cortical and subcortical motor circuits. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2004, 19, 1950–1962.
Manita, S.; Suzuki, T.; Inoue, M.; Kudo, Y.; Miyakawa, H. Paired-pulse ratio of synaptically induced transporter currents at hippocampal CA1 synapses is not related to release probability. Brain Res. 2007, 1154, 71–79.
Pardo, A.; Gómez-Florit, M.; Barbosa, S.; Taboada, P.; Domingues, R. M. A.; Gomes, M. E. Magnetic nanocomposite hydrogels for tissue engineering: Design concepts and remote actuation strategies to control cell fate. ACS Nano 2021, 15, 175–209.
Xue, L.; Sun, J. F. Magnetic hydrogels with ordered structure for biomedical applications. Front. Chem. 2022, 10, 1040492.
Gu, N.; Zhang, Z. H.; Li, Y. Adaptive iron-based magnetic nanomaterials of high performance for biomedical applications. Nano Res. 2022, 15, 1–17.
Acknowledgements
This study was partly supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (No. 2021YFA1201403 to JF Sun), China Science and Technology Innovation 2030-Major Project (Nos. 2022ZD0211701 to ZJ Zhang and 2022ZD0211704 to JF Sun), the National Natural Science Key Foundation of China (Nos. 81830040 and 82130042 to ZJ Zhang), the Science and Technology Program of Guangdong (No. 2018B030334001 to ZJ Zhang), and the Postgraduate Research & Practice Innovation Program of Jiangsu Province (No. SJCX21_0146 to L Xue). The authors would like to thank Dr. Huan Wang from Sun Yat-Sen University and Prof. Yuanjin Zhao from Nanjing Drum Tower Hospital for assistance with the fabrication of microhydrogels.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Electronic Supplementary Material
Supplementary material, approximately 10.2 MB.
Supplementary material, approximately 3.12 MB.
Supplementary material, approximately 29.3 MB.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xue, L., Ye, Q., Wu, L. et al. Magneto-mechanical effect of magnetic microhydrogel for improvement of magnetic neuro-stimulation. Nano Res. 16, 7393–7404 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-023-5464-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-023-5464-x