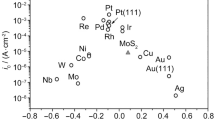
Abstract
Electrocatalytic water splitting into hydrogen is one of the most favorable approaches to produce renewable energy. MoS2 has received great research attention for both hydrogen evolution reaction (HER) and oxygen evolution reaction (OER) due to its unique structure and ability to be chemically modified, enabling its electrocatalytic activity to be further enhanced or made comparable to that of Pt-based materials. In this review, we discuss the important fabrication approaches of MoS2 ultrathin nanosheet (MoS2 NS) to improve the intrinsic catalytic activity of bulk MoS2. Moreover, several modification strategies involve either morphology modulation or electron structural modulation to improve the charge transfer kinetics, including doping, vacancy, and heterojunction construction or single-atom anchor. Our perspectives on the key challenges and future directions of developing high-performance MoS2-based electrocatalysts for overall water splitting are also discussed.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zhang, N. Q.; Ye, C. L.; Yan, H.; Li, L. C.; He, H.; Wang, D. S.; Li, Y. D. Single-atom site catalysts for environmental catalysis. Nano Res. 2020, 13, 3165–3182.
Wang, Q. L.; Xu, C. Q.; Liu, W.; Hung, S. F.; Yang, H. B.; Gao, J. J.; Cai, W. Z.; Chen, H. M.; Li, J.; Liu, B. Coordination engineering of iridium nanocluster bifunctional electrocatalyst for highly efficient and pH-universal overall water splitting. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 4246.
Ye, S.; Shi, W. W.; Liu, Y.; Li, D. F.; Yin, H.; Chi, H. B.; Luo, Y. L.; Ta, N.; Fan, F. T.; Wang, X. L. et al. Unassisted photoelectrochemical cell with multimediator modulation for solar water splitting exceeding 4% solar-to-hydrogen efficiency. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2021, 143, 12499–12508.
Yang, J. R.; Li, W. H.; Tan, S. D.; Xu, K. N.; Wang, Y.; Wang, D. S.; Li, Y. D. The electronic metal-support interaction directing the design of single atomic site catalysts: Achieving high efficiency towards hydrogen evolution. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 19085–19091.
Li, X. P.; Zheng, L. R.; Liu, S. J.; Ouyang, T.; Ye, S. Y.; Liu, Z. Q. Heterostructures of NiFe LDH hierarchically assembled on MoS2 nanosheets as high-efficiency electrocatalysts for overall water splitting. Chin. Chem. Lett., in press, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cclet.2021.12.095.
Seitz, L. C.; Dickens, C. F.; Nishio, K.; Hikita, Y.; Montoya, J.; Doyle, A.; Kirk, C.; Vojvodic, A.; Hwang, H. Y.; Norskov, J. K. et al. A highly active and stable IrOx/SrIrO3 catalyst for the oxygen evolution reaction. Science 2016, 353, 1011–1014.
Wang, Y.; Zheng, M.; Li, Y. R.; Ye, C. L.; Chen, J.; Ye, J. Y.; Zhang, Q. H.; Li, J.; Zhou, Z. Y.; Fu, X. Z. et al. p-d Orbital hybridization induced by a monodispersed ga site on a Pt3Mn nanocatalyst boosts ethanol electrooxidation. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2022, 61, e202115735.
Han, A. L.; Wang, X. J.; Tang, K.; Zhang, Z. D.; Ye, C. L.; Kong, K. J.; Hu, H. B.; Zheng, L. R.; Jiang, P.; Zhao, C. X. et al. An adjacent atomic platinum site enables single-atom iron with high oxygen reduction reaction performance. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 19262–19271.
Zhang, N. Q.; Zhang, X. X.; Kang, Y. K.; Ye, C. L.; Jin, R.; Yan, H.; Lin, R.; Yang, J. R.; Xu, Q.; Wang, Y. et al. A supported Pd2 dual-atom site catalyst for efficient electrochemical CO2 reduction. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 13388–13393.
Jing, H. Y.; Zhu, P.; Zheng, X. B.; Zhang, Z. D.; Wang, D. S.; Li, Y. D. Theory-oriented screening and discovery of advanced energy transformation materials in electrocatalysis. Adv. Powder Mater., in press, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apmate.2021.10.004.
Cui, C. H.; Gan, L.; Heggen, M.; Rudi, S.; Strasser, P. Compositional segregation in shaped Pt alloy nanoparticles and their structural behaviour during electrocatalysis. Nat. Mater. 2013, 12, 765–771.
You, B.; Sun, Y. J. Innovative strategies for electrocatalytic water splitting. Acc. Chem. Res. 2018, 51, 1571–1580.
Guo, D. Z.; Li, X.; Jiao, Y. Q.; Yan, H. J.; Wu, A. P.; Yang, G. C.; Wang, Y.; Tian, C. G.; Fu, H. G. A dual-active Co−CoO heterojunction coupled with Ti3C2-MXene for highly-performance overall water splitting. Nano Res. 2022, 15, 238–247.
Gong, M.; Zhou, W.; Kenney, M. J.; Kapusta, R.; Cowley, S.; Wu, Y. P.; Lu, B. G.; Lin, M. C.; Wang, D. Y.; Yang, J. et al. Blending Cr2O3 into a NiO−Ni electrocatalyst for sustained water splitting. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2015, 54, 11989–11993.
Dionigi, F.; Zhu, J.; Zeng, Z. H.; Merzdorf, T.; Sarodnik, H.; Gliech, M.; Pan, L. J.; Li, W. X.; Greeley, J.; Strasser, P. Intrinsic electrocatalytic activity for oxygen evolution of crystalline 3d-transition metal layered double hydroxides. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 14446–14457.
Yu, L.; Zhou, H. Q.; Sun, J. Y.; Qin, F.; Yu, F.; Bao, J. M.; Yu, Y.; Chen, S.; Ren, Z. F. Cu nanowires shelled with NiFe layered double hydroxide nanosheets as bifunctional electrocatalysts for overall water splitting. Energy Environ. Sci. 2017, 10, 1820–1827.
Han, A. L.; Zhou, X. F.; Wang, X. J.; Liu, S.; Xiong, Q. H.; Zhang, Q. H.; Gu, L.; Zhuang, Z. C.; Zhang, W. J.; Li, F. X. et al. One-step synthesis of single-site vanadium substitution in 1T−WS2 monolayers for enhanced hydrogen evolution catalysis. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 709.
Guo, Y. N.; Park, T.; Yi, J. W.; Henzie, J.; Kim, J.; Wang, Z. L.; Jiang, B.; Bando, Y.; Sugahara, Y.; Tang, J. et al. Nanoarchitectonics for transition-metal-sulfide-based electrocatalysts for water splitting. Adv. Mater. 2019, 31, 1807134.
Miao, R.; Dutta, B.; Sahoo, S.; He, J. K.; Zhong, W.; Cetegen, S. A.; Jiang, T.; Alpay, S. P.; Suib, S. L. Mesoporous iron sulfide for highly efficient electrocatalytic hydrogen evolution. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 13604–13607.
Tan, Y. W.; Wang, H.; Liu, P.; Shen, Y. H.; Cheng, C.; Hirata, A.; Fujita, T.; Tang, Z.; Chen, M. W. Versatile nanoporous bimetallic phosphides towards electrochemical water splitting. Energy Environ. Sci. 2016, 9, 2257–2261.
Li, Y.; Dong, Z. H.; Jiao, L. F. Multifunctional transition metal-based phosphides in energy-related electrocatalysis. Adv. Energy Mater. 2020, 10, 1902104.
Gao, R.; Dai, Q. B.; Du, F.; Yan, D. P.; Dai, L. M. C60-adsorbed single-walled carbon nanotubes as metal-free, pH-universal, and multifunctional catalysts for oxygen reduction, oxygen evolution, and hydrogen evolution. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 11658–11666.
Fu, N. H.; Liang, X.; Li, Z.; Chen, W. X.; Wang, Y.; Zheng, L. R.; Zhang, Q. H.; Chen, C.; Wang, D. S.; Peng, Q. et al. Fabricating Pd isolated single atom sites on C3N4/rGO for heterogenization of homogeneous catalysis. Nano Res. 2020, 13, 947–951.
Sun, X. H.; Tuo, Y. X.; Ye, C. L.; Chen, C.; Lu, Q.; Li, G. N.; Jiang, P.; Chen, S. H.; Zhu, P.; Ma, M. et al. Phosphorus induced electron localization of single iron sites for boosted CO2 electroreduction reaction. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 23614–23618.
Cui, T. T.; Wang, Y. P.; Ye, T.; Wu, J.; Chen, Z. Q.; Li, J.; Lei, Y. P.; Wang, D. S.; Li, Y. D. Engineering dual single-atom sites on 2D ultrathin N-doped carbon nanosheets attaining ultra-low-temperature zinc-air battery. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2022, 61, e202115219.
Yang, J. R.; Li, W. H.; Xu, K. N.; Tan, S. D.; Wang, D. S.; Li, Y. D. Regulating the tip effect on single-atom and cluster catalysts: Forming reversible oxygen species with high efficiency in chlorine evolution reaction. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. in press, https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.202200366.
Zhang, P.; Xiang, H. Y.; Tao, L.; Dong, H. J.; Zhou, Y. G.; Hu, T. S.; Chen, X. L.; Liu, S.; Wang, S. Y.; Garaj, S. Chemically activated MoS2 for efficient hydrogen production. Nano Energy 2019, 57, 535–541.
Anjum, M. A. R.; Jeong, H. Y.; Lee, M. H.; Shin, H. S.; Lee, J. S. Efficient hydrogen evolution reaction catalysis in alkaline media by all-in-one MoS2 with multifunctional active sites. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1707105.
Kumar, R.; Sahoo, S.; Joanni, E.; Singh, R. K.; Yadav, R. M.; Verma, R. K.; Singh, D. P.; Tan, W. K.; del Pino, A. P.; Moshkalev, S. A. et al. A review on synthesis of graphene, h-BN and MoS2 for energy storage applications: Recent progress and perspectives. Nano Res. 2019, 12, 2655–2694.
Shah, S. A.; Shen, X. P.; Xie, M. H.; Zhu, G. X.; Ji, Z. Y.; Zhou, H. B.; Xu, K. Q.; Yue, X. Y.; Yuan, A. H.; Zhu, J. et al. Nickel@nitrogen-doped carbon@MoS2 nanosheets: An efficient electrocatalyst for hydrogen evolution reaction. Small 2019, 15, 1804545.
Nguyen, D. C.; Tran, D. T.; Doan, T. L. L.; Kim, D. H.; Kim, N. H.; Lee, J. H. Rational design of core@shell structured CoSx@Cu2MoS4 hybridized MoS2/N, S-codoped graphene as advanced electrocatalyst for water splitting and Zn-air battery. Adv. Energy Mater. 2020, 10, 1903289.
Zhang, J. F.; Wang, Y.; Cui, J. W.; Wu, J. J.; Li, Y.; Zhu, T. Y.; Kang, H. R.; Yang, J. P.; Sun, J.; Qin, Y. Q. et al. Water-soluble defect-rich MoS2 ultrathin nanosheets for enhanced hydrogen evolution. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2019, 10, 3282–3289.
Lukowski, M. A.; Daniel, A. S.; Meng, F.; Forticaux, A.; Li, L. S.; Jin, S. Enhanced hydrogen evolution catalysis from chemically exfoliated metallic MoS2 nanosheets. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 10274–10277.
Zhu, D. D.; Liu, J. L.; Zhao, Y. Q.; Zheng, Y.; Qiao, S. Z. Engineering 2D metal-organic framework/MoS2 interface for enhanced alkaline hydrogen evolution. Small 2019, 15, 1805511.
Dimple; Jena, N.; Rawat, A.; Ahammed, R.; Mohanta, M. K.; De Sarkar, A. Emergence of high piezoelectricity along with robust electron mobility in Janus structures in semiconducting group IVB dichalcogenide monolayers. J. Mater. Chem. A 2018, 6, 24885–24898.
Zhang, S.; Deng, Q. C.; Shangguan, H. J.; Zheng, C.; Shi, J.; Huang, F. H.; Tang, B. Design and preparation of carbon nitride-based amphiphilic Janus N-doped carbon/MoS2 nanosheets for interfacial enzyme nanoreactor. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 12227–12237.
Nguyen, D. C.; Doan, T. L. L.; Prabhakaran, S.; Tran, D. T.; Kim, D. H.; Lee, J. H.; Kim, N. H. Hierarchical Co and Nb dual-doped MoS2 nanosheets shelled micro-TiO2 hollow spheres as effective multifunctional electrocatalysts for HER, OER, and ORR. Nano Energy 2021, 82, 105750.
Yu, X. Y.; Hu, H.; Wang, Y. W.; Chen, H. Y.; Lou, X. W. Ultrathin MoS2 nanosheets supported on N-doped carbon nanoboxes with enhanced lithium storage and electrocatalytic properties. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2015, 54, 7395–7398.
Gong, F. L.; Liu, M. M.; Ye, S.; Gong, L. H.; Zeng, G.; Xu, L.; Zhang, X. L.; Zhang, Y. H.; Zhou, L. M.; Fang, S. M. et al. All-pH stable sandwich-structured MoO2/MoS2/C hollow nanoreactors for enhanced electrochemical hydrogen evolution. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021, 31, 2101715.
Chen, J. Z.; Liu, G. G.; Zhu, Y. Z.; Su, M.; Yin, P. F.; Wu, X. J.; Lu, Q. P.; Tan, C. L.; Zhao, M. T.; Liu, Z. Q. et al. Ag@MoS2 core-shell heterostructure as SERS platform to reveal the hydrogen evolution active sites of single-layer MoS2. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2020, 142, 7161–7167.
Qin, Q.; Chen, L. L.; Wei, T.; Liu, X. E. MoS2/NiS yolk-shell microsphere-based electrodes for overall water splitting and asymmetric supercapacitor. Small 2019, 15, 1803639.
Zhang, Q. Q.; Bai, H.; Zhang, Q.; Ma, Q.; Li, Y. H.; Wan, C. Q.; Xi, G. C. MoS2 yolk-shell microspheres with a hierarchical porous structure for efficient hydrogen evolution. Nano Res. 2016, 9, 3038–3047.
Gong, F. L.; Ye, S.; Liu, M. M.; Zhang, J. W.; Gong, L. H.; Zeng, G.; Meng, E. C.; Su, P. P.; Xie, K. F.; Zhang, Y. H. et al. Boosting electrochemical oxygen evolution over yolk-shell structured O−MoS2 nanoreactors with sulfur vacancy and decorated Pt nanoparticles. Nano Energy 2020, 78, 105284.
Hu, H.; Han, L.; Yu, M. Z.; Wang, Z. Y.; Lou, X. W. Metal-organic-framework-engaged formation of Co nanoparticle-embedded carbon@Co9S8 double-shelled nanocages for efficient oxygen reduction. Energy Environ. Sci. 2016, 9, 107–111.
Wan, Y.; Zhang, Z. Y.; Xu, X. L.; Zhang, Z. H.; Li, P.; Fang, X.; Zhang, K.; Yuan, K.; Liu, K. H.; Ran, G. Z. et al. Engineering active edge sites of fractal-shaped single-layer MoS2 catalysts for high-efficiency hydrogen evolution. Nano Energy 2018, 51, 786–792.
Li, Y.; Zuo, S. W.; Li, Q. H.; Wu, X.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, H. B.; Zhang, J. Vertically aligned MoS2 with in-plane selectively cleaved Mo−S bond for hydrogen production. Nano Lett. 2011, 21, 1848–1855.
Zhang, J.; Wang, T.; Pohl, D.; Rellinghaus, B.; Dong, R. H.; Liu, S. H.; Zhuang, X. D.; Feng, X. L. Interface engineering of MoS2/Ni3S2 heterostructures for highly enhanced electrochemical overall-watersplitting activity. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 6702–6707.
Yu, X. Y.; Feng, Y.; Jeon, Y.; Guan, B. Y.; Lou, X. W.; Paik, U. Formation of Ni−Co−MoS2 nanoboxes with enhanced electrocatalytic activity for hydrogen evolution. Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 9006–9011.
Lin, J. H.; Wang, P. C.; Wang, H. H.; Li, C.; Si, X. Q.; Qi, J. L.; Cao, J.; Zhong, Z. X.; Fei, W. D.; Feng, J. C. Defect-rich heterogeneous MoS2/NiS2 nanosheets electrocatalysts for efficient overall water splitting. Adv. Sci. 2019, 6, 1900246.
Lu, A. Y.; Yang, X. L.; Tseng, C. C.; Min, S. X.; Lin, S. H.; Hsu, C. L.; Li, H. N.; Idriss, H.; Kuo, J. L.; Huang, K. W. et al. High-sulfur-vacancy amorphous molybdenum sulfide as a high current electrocatalyst in hydrogen evolution. Small 2016, 12, 5530–5537.
Tan, C. L.; Luo, Z. M.; Chaturvedi, A.; Cai, Y. Q.; Du, Y. H.; Gong, Y.; Huang, Y.; Lai, Z. C.; Zhang, X.; Zheng, L. R. et al. Preparation of high-percentage 1T-phase transition metal dichalcogenide nanodots for electrochemical hydrogen evolution. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1705509.
Zheng, Z. L.; Yu, L.; Gao, M.; Chen, X. Y.; Zhou, W.; Ma, C.; Wu, L. H.; Zhu, J. F.; Meng, X. Y.; Hu, J. T. et al. Boosting hydrogen evolution on MoS2 via co-confining selenium in surface and cobalt in inner layer. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 3315.
Solomon, G.; Kohan, M. G.; Vagin, M.; Rigoni, F.; Mazzaro, R.; Natile, M. M.; You, S. J.; Morandi, V.; Concina, I.; Vomiero, A. Decorating vertically aligned MoS2 nanoflakes with silver nanoparticles for inducing a bifunctional electrocatalyst towards oxygen evolution and oxygen reduction reaction. Nano Energy 2021, 81, 105664.
Kuang, P. Y.; Tong, T.; Fan, K.; Yu, J. G. In situ fabrication of Ni−Mo bimetal sulfide hybrid as an efficient electrocatalyst for hydrogen evolution over a wide pH range. ACS Catal. 2017, 7, 6179–6187.
Jian, W. J.; Cheng, X. L.; Huang, Y. Y.; You, Y.; Zhou, R.; Sun, T. T.; Xu, J. Arrays of ZnO/MoS2 nanocables and MoS2 nanotubes with phase engineering for bifunctional photoelectrochemical and electrochemical water splitting. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 328, 474–483.
Luo, M.; Liu, S. Q.; Zhu, W. W.; Ye, G. Y.; Wang, J.; He, Z. An electrodeposited MoS2−MoO3−x/Ni3S2 heterostructure electrocatalyst for efficient alkaline hydrogen evolution. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 428, 131055.
Zhou, Y.; Hao, W.; Zhao, X. X.; Zhou, J. D.; Yu, H. M.; Lin, B.; Liu, Z.; Pennycook, S. J.; Li, S. Z.; Fan, H. J. Electronegativity-induced charge balancing to boost stability and activity of amorphous electrocatalysts. Adv. Mater., in press, https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.202100537.
Wu, T.; Song, E. H.; Zhang, S. N.; Luo, M. J.; Zhao, C. D.; Zhao, W.; Liu, J. J.; Huang, F. Q. Engineering metallic heterostructure based on Ni3N and 2M−MoS2 for alkaline water electrolysis with industry-compatible current density and stability. Adv. Mater. 2022, 34, 2108505.
Li, R. Z.; Wang, D. S. Superiority of dual-atom catalysts in electrocatalysis: One step further than single-atom catalysts. Adv. Energy Mater. 2022, 12, 2103564.
Qi, K.; Cui, X. Q.; Gu, L.; Yu, S. S.; Fan, X. F.; Luo, M. C.; Xu, S.; Li, N. B.; Zheng, L. R.; Zhang, Q. H. et al. Single-atom cobalt array bound to distorted 1T MoS2 with ensemble effect for hydrogen evolution catalysis. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 5231.
Zhang, J. M.; Xu, X. P.; Yang, L.; Cheng, D. J.; Cao, D. P. Single-atom Ru doping induced phase transition of MoS2 and S vacancy for hydrogen evolution reaction. Small Methods 2019, 3, 1900653.
Wang, Y.; Zheng, X. B.; Wang, D. S. Design concept for electrocatalysts. Nano Res. 2022, 15, 1730–1752.
Wei, H.; Si, J. C.; Zeng, L. B.; Lyu, S. L.; Zhang, Z. G.; Suo, Y. G.; Hou, Y. Electrochemically exfoliated Ni-doped MoS2 nanosheets for highly efficient hydrogen evolution and Zn-H2O battery. Chin. Chem. Lett., in press, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cclet.2022.01.037.
Zheng, M. Y.; Guo, K. L.; Jiang, W. J.; Tang, T.; Wang, X. Y.; Zhou, P. P.; Du, J.; Zhao, Y. Q.; Xu, C. L.; Hu, J. S. When MoS2 meets FeOOH: A “one-stone-two-birds” heterostructure as a bifunctional electrocatalyst for efficient alkaline water splitting. Appl. Catal. B:Environ. 2019, 244, 1004–1012.
Yin, J.; Jin, J.; Lin, H. H.; Yin, Z. Y.; Li, J. Y.; Lu, M.; Guo, L. C.; Xi, P. X.; Tang, Y.; Yan, C. H. Optimized metal chalcogenides for boosting water splitting. Adv. Sci. 2020, 7, 1903070.
Sun, K. A.; Zeng, L. Y.; Liu, S. H.; Zhao, L.; Zhu, H. Y.; Zhao, J. C.; Liu, Z.; Cao, D. W.; Hou, Y. C.; Liu, Y. Q. et al. Design of basal plane active MoS2 through one-step nitrogen and phosphorus co-doping as an efficient pH-universal electrocatalyst for hydrogen evolution. Nano Energy 2019, 58, 862–869.
Xie, J. F.; Zhang, H.; Li, S.; Wang, R. X.; Sun, X.; Zhou, M.; Zhou, J. F.; Lou, X. W.; Xie, Y. Defect-rich MoS2 ultrathin nanosheets with additional active edge sites for enhanced electrocatalytic hydrogen evolution. Adv. Mater. 2013, 25, 5807–5813.
Li, G. Q.; Zhang, D.; Qiao, Q.; Yu, Y. F.; Peterson, D.; Zafar, A.; Kumar, R.; Curtarolo, S.; Hunte, F.; Shannon, S. et al. All the catalytic active sites of MoS2 for hydrogen evolution. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 16632–16638.
Ma, Q.; Qiao, H.; Huang, Z. Y.; Liu, F.; Duan, C. G.; Zhou, Y.; Liao, G. C.; Qi, X. Photo-assisted electrocatalysis of black phosphorus quantum dots/molybdenum disulfide heterostructure for oxygen evolution reaction. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2021, 562, 150213.
Zhang, G.; Liu, H. J.; Qu, J. H.; Li, J. H. Two-dimensional layered MoS2: Rational design, properties and electrochemical applications. Energy Environ. Sci. 2016, 9, 1190–1209.
Wang, Y. F.; Yu, Y.; Wang, J. L.; Peng, L. H.; Zuo, Y. X.; Zuo, C. C. Novel multifunctional Janus-type membrane on Al anode for corrosion protection. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 8, 2100786.
Lu, A. Y.; Zhu, H. Y.; Xiao, J.; Chuu, C. P.; Han, Y. M.; Chiu, M. H.; Cheng, C. C.; Yang, C. W.; Wei, K. H.; Yang, Y. M. et al. Janus monolayers of transition metal dichalcogenides. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2017, 12, 744–749.
Zhou, L.; Zhang, H. W.; Bao, H. M.; Wei, Y.; Fu, H.; Cai, W. P. Monodispersed snowman-like Ag-MoS2 Janus nanoparticles as chemically self-propelled nanomotors. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2020, 3, 624–632.
Zhou, L.; Zhang, H. W.; Bao, H. M.; Liu, G. Q.; Li, Y.; Cai, W. P. Decoration of Au nanoparticles on MoS2 nanospheres: From Janus to core/shell structure. J. Phys. Chem. C 2018, 122, 8628–8636.
Zhang, K. Y.; Guo, Y. F.; Larson, D. T.; Zhu, Z. Y.; Fang, S. A.; Kaxiras, E.; Kong, J.; Huang, S. X. Spectroscopic signatures of interlayer coupling in Janus MoSSe/MoS2 heterostructures. ACS Nano 2021, 15, 14394–14403.
Wang, J. Y.; Cui, Y.; Wang, D. Design of hollow nanostructures for energy storage, conversion and production. Adv. Mater. 2019, 31, 1801993.
Zhang, L.; Wu, H. B.; Yan, Y.; Wang, X.; Lou, X. W. Hierarchical MoS2 microboxes constructed by nanosheets with enhanced electrochemical properties for lithium storage and water splitting. Energy Environ. Sci. 2014, 7, 3302–3306.
Tang, B. S.; Yu, Z. G.; Zhang, Y. X.; Tang, C. H.; Seng, H. L.; Seh, Z. W.; Zhang, Y. W.; Pennycook, S. J.; Gong, H.; Yang, W. F. Metal-organic framework-derived hierarchical MoS2/CoS2 nanotube arrays as pH-universal electrocatalysts for efficient hydrogen evolution. J. Mater. Chem. A 2019, 7, 13339–13346.
Li, H. H.; Yu, S. H. Recent advances on controlled synthesis and engineering of hollow alloyed nanotubes for electrocatalysis. Adv. Mater. 2019, 31, 1803503.
Wang, C.; Zhang, L.; Xu, G. C.; Yang, L. F.; Yang, J. H. Construction of unique ternary composite MCNTs@CoSx@MoS2 with three-dimensional lamellar heterostructure as high-performance bifunctional electrocatalysts for hydrogen evolution and oxygen evolution reactions. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 417, 129270.
Li, Y. J.; Wang, W. Y.; Huang, B. J.; Mao, Z. F.; Wang, R.; He, B. B.; Gong, Y. S.; Wang, H. W. Abundant heterointerfaces in MOF-derived hollow CoS2−MoS2 nanosheet array electrocatalysts for overall water splitting. J. Energy Chem. 2021, 57, 99–108.
Kim, M.; Seok, H.; Selvam, N. C. S.; Cho, J.; Choi, G. H.; Nam, M. G.; Kang, S.; Kim, T.; Yoo, P. J. Kirkendall effect induced bifunctional hybrid electrocatalyst (Co9S8@MoS2/N-doped hollow carbon) for high performance overall water splitting. J. Power Sources 2021, 493, 229688.
Guo, Y. N.; Tang, J.; Wang, Z. L.; Kang, Y. M.; Bando, Y.; Yamauchi, Y. Elaborately assembled core-shell structured metal sulfides as a bifunctional catalyst for highly efficient electrochemical overall water splitting. Nano Energy 2018, 47, 494–502.
Li, Y.; Majewski, M. B.; Islam, S. M.; Hao, S. Q.; Murthy, A. A.; DiStefano, J. G.; Hanson, E. D.; Xu, Y. B.; Wolverton, C.; Kanatzidis, M. G. et al. Morphological engineering of winged Au@MoS2 heterostructures for electrocatalytic hydrogen evolution. Nano Lett. 2018, 18, 7104–7110.
Zhu, H.; Gao, G. H.; Du, M. L.; Zhou, J. H.; Wang, K.; Wu, W. B.; Chen, X.; Li, Y.; Ma, P. M.; Dong, W. F. et al. Atomic-scale core/shell structure engineering induces precise tensile strain to boost hydrogen evolution catalysis. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1707301.
Zhu, H.; Zhang, J. F.; Yanzhang, R. P.; Du, M. L.; Wang, Q. F.; Gao, G. H.; Wu, J. D.; Wu, G. M.; Zhang, M.; Liu, B. et al. When cubic cobalt sulfide meets layered molybdenum disulfide: A core-shell system toward synergetic electrocatalytic water splitting. Adv. Mater. 2015, 27, 4752–4759.
Doan, T. L. L.; Nguyen, D. C.; Prabhakaran, S.; Kim, D. H.; Tran, D. T.; Kim, N. H.; Lee, J. H. Single-atom Co-decorated MoS2 nanosheets assembled on metal nitride nanorod arrays as an efficient bifunctional electrocatalyst for pH-universal water splitting. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021, 31, 2100233.
Zhang, Q.; Liu, B. Q.; Ji, Y.; Chen, L. H.; Zhang, L. Y.; Li, L.; Wang, C. G. Construction of hierarchical yolk-shell nanospheres organized by ultrafine Janus subunits for efficient overall water splitting. Nanoscale 2020, 12, 2578–2586.
Wu, A. P.; Tian, C. G.; Yan, H. J.; Jiao, Y. Q.; Yan, Q.; Yang, G. Y.; Fu, H. G. Hierarchical MoS2@MoP core-shell heterojunction electrocatalysts for efficient hydrogen evolution reaction over a broad pH range. Nanoscale 2016, 8, 11052–11059.
Bai, J. M.; Meng, T.; Guo, D. L.; Wang, S. G.; Mao, B. G.; Cao, M. H. Co9S8@MoS2 core-shell heterostructures as trifunctional electrocatalysts for overall water splitting and Zn-air batteries. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 1678–1689.
Xing, Z. C.; Yang, X. R.; Asiri, A. M.; Sun, X. P. Three-dimensional structures of MoS2@Ni core/shell nanosheets array toward synergetic electrocatalytic water splitting. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 14521–14526.
Yang, T.; Yin, L. S.; He, M. S.; Wei, W. X.; Cao, G. J.; Ding, X. R.; Wang, Y. H.; Zhao, Z. M.; Yu, T. T.; Zhao, H. et al. Yolk-shell hierarchical catalyst with tremella-like molybdenum sulfide on transition metal (Co, Ni and Fe) sulfide for electrochemical water splitting. Chem. Commun. 2019, 55, 14343–14346.
Liu, P. T.; Zhu, J. Y.; Zhang, J. Y.; Xi, P. X.; Tao, K.; Gao, D. Q.; Xue, D. S. P dopants triggered new basal plane active sites and enlarged interlayer spacing in MoS2 nanosheets toward electrocatalytic hydrogen evolution. ACS Energy Lett. 2017, 2, 745–752.
Zang, Y. P.; Niu, S. W.; Wu, Y. S.; Zheng, X. S.; Cai, J. Y.; Ye, J.; Xie, Y. F.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, J. B.; Zhu, J. F. et al. Tuning orbital orientation endows molybdenum disulfide with exceptional alkaline hydrogen evolution capability. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1217.
Deng, S. J.; Luo, M.; Ai, C. Z.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, B.; Huang, L.; Jiang, Z.; Zhang, Q. H.; Gu, L.; Lin, S. W. et al. Synergistic doping and intercalation: Realizing deep phase modulation on MoS2 arrays for high-efficiency hydrogen evolution reaction. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 16289–16296.
Xiong, J.; Li, J.; Shi, J. W.; Zhang, X. L.; Cai, W. W.; Yang, Z. H.; Cheng, H. S. Metallic 1T-MoS2 nanosheets in-situ entrenched on N, P, S-co doped hierarchical carbon microflower as an efficient and robust electro-catalyst for hydrogen evolution. Appl. Catal. B:Environ. 2019, 243, 614–620.
Luo, Z. Y.; Ouyang, Y. X.; Zhang, H.; Xiao, M. L.; Ge, J. J.; Jiang, Z.; Wang, J. L.; Tang, D. M.; Cao, X. Z.; Liu, C. P. et al. Chemically activating MoS2 via spontaneous atomic palladium interfacial doping towards efficient hydrogen evolution. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 2120.
Shi, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Yang, D. R.; Xu, W. X.; Wang, C.; Wang, F. B.; Xu, J. J.; Xia, X. H.; Chen, H. Y. Energy level engineering of MoS2 by transition-metal doping for accelerating hydrogen evolution reaction. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 15479–15485.
Yang, S. Z.; Gong, Y. J.; Manchanda, P.; Zhang, Y. Y.; Ye, G. L.; Chen, S. M.; Song, L.; Pantelides, S. T.; Ajayan, P. M.; Chisholm, M. F. et al. Rhenium-doped and stabilized MoS2 atomic layers with basal-plane catalytic activity. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1803477.
Li, Y.; Gu, Q. F.; Johannessen, B.; Zheng, Z.; Li, C.; Luo, Y. T.; Zhang, Z. Y.; Zhang, Q.; Fan, H. N.; Luo, W. B. et al. Synergistic Pt doping and phase conversion engineering in two-dimensional MoS2 for efficient hydrogen evolution. Nano Energy 2021, 84, 105898.
Sun, T.; Wang, J.; Chi, X.; Lin, Y. X.; Chen, Z. X.; Ling, X.; Qiu, C. T.; Xu, Y. S.; Song, L.; Chen, W. et al. Engineering the electronic structure of MoS2 nanorods by N and Mn dopants for ultra-efficient hydrogen production. ACS Catal. 2018, 8, 7585–7592.
Wei, C.; Wu, W. Z.; Li, H.; Lin, X. C.; Wu, T.; Zhang, Y. D.; Xu, Q.; Zhang, L. P.; Zhu, Y. H.; Yang, X. N. et al. Atomic plane-vacancy engineering of transition-metal dichalcogenides with enhanced hydrogen evolution capability. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 25264–25270.
Yin, Y.; Han, J. C.; Zhang, Y. M.; Zhang, X. H.; Xu, P.; Yuan, Q.; Samad, L.; Wang, X. J.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Z. H. et al. Contributions of phase, sulfur vacancies, and edges to the hydrogen evolution reaction catalytic activity of porous molybdenum disulfide nanosheets. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 7965–7972.
Wu, W. Z.; Niu, C. Y.; Wei, C.; Jia, Y.; Li, C.; Xu, Q. Activation of MoS2 basal planes for hydrogen evolution by zinc. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 2029–2033.
Deng, J.; Li, H. B.; Wang, S. H.; Ding, D.; Chen, M. S.; Liu, C.; Tian, Z. Q.; Novoselov, K. S.; Ma, C.; Deng, D. H. et al. Multiscale structural and electronic control of molybdenum disulfide foam for highly efficient hydrogen production. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 14430.
Luo, Z. Y.; Zhang, H.; Yang, Y. Q.; Wang, X.; Li, Y.; Jin, Z.; Jiang, Z.; Liu, C. P.; Xing, W.; Ge, J. J. Reactant friendly hydrogen evolution interface based on di-anionic MoS2 surface. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 1116.
Cheng, Y. F.; Lu, S. K.; Liao, F.; Liu, L. B.; Li, Y. Q.; Shao, M. W. Rh-MoS2 nanocomposite catalysts with Pt-like activity for hydrogen evolution reaction. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2017, 27, 1700359.
Li, H.; Tsai, C.; Koh, A. L.; Cai, L. L.; Contryman, A. W.; Fragapane, A. H.; Zhao, J. H.; Han, H. S.; Manoharan, H. C.; Abild-Pedersen, F. et al. Activating and optimizing MoS2 basal planes for hydrogen evolution through the formation of strained sulphur vacancies. Nat. Mater. 2016, 15, 48–53.
Yang, J.; Wang, Y.; Lagos, M. J.; Manichev, V.; Fullon, R.; Song, X. J.; Voiry, D.; Chakraborty, S.; Zhang, W. J.; Batson, P. E. et al. Single atomic vacancy catalysis. ACS Nano 2019, 13, 9958–9964.
Wang, X.; Zhang, Y. W.; Si, H. N.; Zhang, Q. H.; Wu, J.; Gao, L.; Wei, X. F.; Sun, Y.; Liao, Q. L.; Zhang, Z. et al. Single-atom vacancy defect to trigger high-efficiency hydrogen evolution of MoS2. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2020, 142, 4298–4308.
Cheng, Z. H.; Xiao, Y. K.; Wu, W. P.; Zhang, X. Q.; Fu, Q.; Zhao, Y.; Qu, L. T. All-pH-tolerant in-plane heterostructures for efficient hydrogen evolution reaction. ACS Nano 2021, 15, 11417–11427.
Wu, Y.; Li, F.; Chen, W. L.; Xiang, Q.; Ma, Y. L.; Zhu, H.; Tao, P.; Song, C. Y.; Shang, W.; Deng, T. et al. Coupling interface constructions of MoS2/Fe5Ni4S8 heterostructures for efficient electrochemical water splitting. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1803151.
Muthurasu, A.; Maruthapandian, V.; Kim, H. Y. Metal-organic framework derived Co3O4/MoS2 heterostructure for efficient bifunctional electrocatalysts for oxygen evolution reaction and hydrogen evolution reaction. Appl. Catal. B:Environ. 2019, 248, 202–210.
Ji, X. X.; Lin, Y. H.; Zeng, J.; Ren, Z. H.; Lin, Z. J.; Mu, Y. B.; Qiu, Y. J.; Yu, J. Graphene/MoS2/FeCoNi(OH)x and graphene/MoS2/FeCoNiPx multilayer-stacked vertical nanosheets on carbon fibers for highly efficient overall water splitting. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 1380.
Lim, K. R. G.; Handoko, A. D.; Johnson, L. R.; Meng, X.; Lin, M.; Subramanian, G. S.; Anasori, B.; Gogotsi, Y.; Vojvodic, A.; Seh, Z. W. 2H-MoS2 on Mo2CTxMXene nanohybrid for efficient and durable electrocatalytic hydrogen evolution. ACS Nano 2020, 14, 16140–16155.
Kim, M.; Anjum, M. A. R.; Lee, M.; Lee, B. J.; Lee, J. S. Activating MoS2 basal plane with Ni2P nanoparticles for Pt-like hydrogen evolution reaction in acidic media. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2019, 29, 1809151.
Li, H. Y.; Chen, S. M.; Jia, X. F.; Xu, B.; Lin, H. F.; Yang, H. Z.; Song, L.; Wang, X. Amorphous nickel-cobalt complexes hybridized with 1T-phase molybdenum disulfide via hydrazine-induced phase transformation for water splitting. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 15377.
Zhai, Z. J.; Li, C.; Zhang, L.; Wu, H. C.; Zhang, L.; Tang, N.; Wang, W.; Gong, J. L. Dimensional construction and morphological tuning of heterogeneous MoS2/NiS electrocatalysts for efficient overall water splitting. J. Mater. Chem. A 2018, 6, 9833–9838.
Chang, P.; Zhang, S.; Xu, X. M.; Lin, Y. F.; Chen, X. Y.; Guan, L. X.; Tao, J. G. Facile synthesis of MoS2/Ni2V3O8 nanosheets for pH-universal efficient hydrogen evolution catalysis. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 423, 130196.
Mao, H.; Guo, X.; Fan, Q. Z.; Fu, Y. L.; Yang, H. R.; Liu, D. L.; Wu, S. Y.; Wu, Q.; Song, X. M. Improved hydrogen evolution activity by unique NiS2−MoS2 heterostructures with misfit lattices supported on poly(ionic liquid)s functionalized polypyrrole/graphene oxide nanosheets. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 404, 126253.
Qin, C. L.; Fan, A. X.; Zhang, X.; Wang, S. Q.; Yuan, X. L.; Dai, X. P. Interface engineering: Few-layer MoS2 coupled to a NiCo-sulfide nanosheet heterostructure as a bifunctional electrocatalyst for overall water splitting. J. Mater. Chem. A 2019, 7, 27594–27602.
Lei, L.; Huang, D. L.; Lai, C.; Zhang, C.; Deng, R.; Chen, Y. S.; Chen, S.; Wang, W. J. Interface modulation of Mo2C@foam nickel via MoS2 quantum dots for the electrochemical oxygen evolution reaction. J. Mater. Chem. A 2020, 8, 15074–15085.
Tang, Y. J.; Wang, Y.; Wang, X. L.; Li, S. L.; Huang, W.; Dong, L. Z.; Liu, C. H.; Li, Y. F.; Lan, Y. Q. Molybdenum disulfide/nitrogen-doped reduced graphene oxide nanocomposite with enlarged interlayer spacing for electrocatalytic hydrogen evolution. Adv. Energy Mater. 2016, 6, 1600116.
Ibupoto, Z. H.; Tahira, A.; Tang, P. Y.; Liu, X. J.; Morante, J. R.; Fahlman, M.; Arbiol, J.; Vagin, M.; Vomiero, A. MoSx@NiO composite nanostructures: An advanced nonprecious catalyst for hydrogen evolution reaction in alkaline media. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2019, 29, 1807562.
Zhang, X.; Liang, Y. Y. Nickel hydr(oxy)oxide nanoparticles on metallic MoS2 nanosheets: A synergistic electrocatalyst for hydrogen evolution reaction. Adv. Sci. 2018, 5, 1700644.
Ji, D. X.; Peng, S. J.; Fan, L.; Li, L. L.; Qin, X. H.; Ramakrishna, S. Thin MoS2 nanosheets grafted MOFs-derived porous Co−N−C flakes grown on electrospun carbon nanofibers as self-supported bifunctional catalysts for overall water splitting. J. Mater. Chem. A 2017, 5, 23898–23908.
Lei, Y. P.; Wang, Y. C.; Liu, Y.; Song, C. Y.; Li, Q.; Wang, D. S.; Li, Y. D. Design aktiver atomarer zentren für HER-elektrokatalysatoren. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2020, 132, 20978–20998.
Chen, S. H.; Li, W. H.; Jiang, W. J.; Yang, J. R.; Zhu, J. X.; Wang, L. Q.; Ou, H. H.; Zhuang, Z. C.; Chen, M. Z.; Sun, X. H. et al. MOF encapsulating N-heterocyclic carbene-ligated copper single-atom site catalyst towards efficient methane electrosynthesis. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2022, 61, e202114450.
Liu, Y. W.; Wang, B. X.; Fu, Q.; Liu, W.; Wang, Y.; Gu, L.; Wang, D. S.; Li, Y. D. Polyoxometalate-based metal-organic framework as molecular sieve for highly selective semi-hydrogenation of acetylene on isolated single Pd atom sites. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 22522–22528.
Jiang, K.; Luo, M.; Liu, Z. X.; Peng, M.; Chen, D. C.; Lu, Y. R.; Chan, T. S.; de Groot, F. M. F.; Tan, Y. W. Rational strain engineering of single-atom ruthenium on nanoporous MoS2 for highly efficient hydrogen evolution. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 1687.
Wang, J.; Fang, W. H.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, Y. H.; Dang, J. Q.; Wu, Y.; Chen, B. Z.; Zhao, H.; Li, Z. X. Single atom Ru doping 2H-MoS2 as highly efficient hydrogen evolution reaction electrocatalyst in a wide pH range. Appl. Catal. B:Environ. 2021, 298, 120490.
Ji, L.; Yan, P. F.; Zhu, C. H.; Ma, C. Y.; Wu, W. Z.; Wei, C.; Shen, Y. L.; Chu, S. Q.; Wang, J. O.; Du, Y. et al. One-pot synthesis of porous 1T-phase MoS2 integrated with single-atom Cu doping for enhancing electrocatalytic hydrogen evolution reaction. Appl. Catal. B: Environ. 2019, 251, 87–93.
Meng, X. Y.; Ma, C.; Jiang, L. Z.; Si, R.; Meng, X. G.; Tu, Y. C.; Yu, L.; Bao, X. H.; Deng, D. H. Distance synergy of MoS2-confined rhodium atoms for highly efficient hydrogen evolution. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2020, 132, 10588–10593.
Li, X. Y.; Rong, H. P.; Zhang, J. T.; Wang, D. S.; Li, Y. D. Modulating the local coordination environment of single-atom catalysts for enhanced catalytic performance. Nano Res. 2020, 13, 1842–1855.
Zhai, P. L.; Zhang, Y. X.; Wu, Y. Z.; Gao, J. F.; Zhang, B.; Cao, S. Y.; Zhang, Y. T.; Li, Z. W.; Sun, L. C.; Hou, J. G. Engineering active sites on hierarchical transition bimetal oxides/sulfides heterostructure array enabling robust overall water splitting. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 5462.
Xiong, Q. Z.; Wang, Y.; Liu, P. F.; Zheng, L. R.; Wang, G. Z.; Yang, H. G.; Wong, P. K.; Zhang, H. M.; Zhao, H. J. Cobalt covalent doping in MoS2 to induce bifunctionality of overall water splitting. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1801450.
Yang, Y. Q.; Zhang, K.; Ling, H. L.; Li, X.; Chan, H. C.; Yang, L. C.; Gao, Q. S. MoS2−Ni3S2 heteronanorods as efficient and stable bifunctional electrocatalysts for overall water splitting. ACS Catal. 2017, 7, 2357–2366.
Kwon, I. S.; Debela, T. T.; Kwak, I. H.; Park, Y. C.; Seo, J.; Shim, J. Y.; Yoo, S. J.; Kim, J. G.; Park, J.; Kang, H. S. Ruthenium nanoparticles on cobalt-doped 1T′ phase MoS2 nanosheets for overall water splitting. Small 2020, 16, 2000081.
Kuang, P. Y.; He, M.; Zou, H. Y.; Yu, J. G.; Fan, K. 0D/3D MoS2−NiS2/N-doped graphene foam composite for efficient overall water splitting. Appl. Catal. B:Environ. 2019, 254, 15–25.
Yoon, T.; Kim, K. S. One-step synthesis of CoS-doped β-Co(OH)2@amorphous MoS2+x hybrid catalyst grown on nickel foam for high-performance electrochemical overall water splitting. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2016, 26, 7386–7393.
Lu, Y. K.; Guo, X. X.; Yang, L. Y.; Yang, W. F.; Sun, W. T.; Tuo, Y. X.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, S. T.; Pan, Y.; Yan, W. F. et al. Highly efficient CoMoS heterostructure derived from vertically anchored Co5Mo10 polyoxometalate for electrocatalytic overall water splitting. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 394, 124849.
Liu, Y. K.; Jiang, S.; Li, S. J.; Zhou, L.; Li, Z. H.; Li, J. M.; Shao, M. F. Interface engineering of (Ni, Fe)S2@MoS2 heterostructures for synergetic electrochemical water splitting. Appl. Catal. B:Environ. 2019, 247, 107–114.
Wei, S. T.; Cui, X. Q.; Xu, Y. C.; Shang, B.; Zhang, Q. H.; Gu, L.; Fan, X. F.; Zheng, L. R.; Hou, C. M.; Huang, H. H. et al. Iridium-triggered phase transition of MoS2 nanosheets boosts overall water splitting in alkaline media. ACS Energy Lett. 2019, 4, 368–374.
Wang, C. Z.; Shao, X. D.; Pan, J.; Hu, J. G.; Xu, X. Y. Redox bifunctional activities with optical gain of Ni3S2 nanosheets edged with MoS2 for overall water splitting. Appl. Catal. B:Environ. 2020, 268, 118435.
Hou, J. G.; Zhang, B.; Li, Z. W.; Cao, S. Y.; Sun, Y. Q.; Wu, Y. Z.; Gao, Z. M.; Sun, L. C. Vertically aligned oxygenated-CoS2−MoS2 heteronanosheet architecture from polyoxometalate for efficient and stable overall water splitting. ACS Catal. 2018, 8, 4612–4621.
Acknowledgements
S. Y. designed and supervised the project. All the authors discussed and commented on the manuscript. This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 21902157), Starting fund for scientific research of high-level talents, Anhui Agricultural University (No. rc382108), the Open Fund of The State Key Laboratory of Catalysis in DICP, CAS (N-21-12), and the Open Fund of The State Key Laboratory of Molecular Reaction Dynamics in DICP, CAS (SKLMRD-K202223).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, M., Zhang, C., Han, A. et al. Modulation of morphology and electronic structure on MoS2-based electrocatalysts for water splitting. Nano Res. 15, 6862–6887 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-022-4297-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-022-4297-3