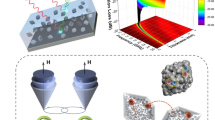
Abstract
The weak dielectric properties and the lack of magnetic loss of manganese-based absorbers are obstructed as the new generation of electromagnetic wave absorption (EMA) materials applying in microelectronic devices. Herein, the sulfuration and subsequent compounding strategies have been employed to enhance the EMA performance of multi-shell nanosphere-shaped Mn2O3 materials. With the narrow bandgap, the as-obtained MnS possesses reinforced electrical conductivity, which is conducive to conductivity loss. More importantly, the presence of potential difference between different phases will form space charge region at the heterogeneous interface, thus favoring interfacial polarization. Additionally, the improvement of magnetic loss is attributed to the presence of Co3O4 nanoparticles. Consequently, the composites present enhanced EMA performance than original Mn2O3. Specifically, the minimum reflection loss of as-prepared composites is −51.4 dB at the thickness of 1.8 mm and the broad effective absorption bandwidth reaches 6.2 GHz at 1.9 mm. The low matching thickness and high absorption efficiency in this work can provide a convincing reference when designing distinguished manganese-based absorbers.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lv, H. L.; Yang, Z. H.; Xu, H. B.; Wang, L. Y.; Wu, R. B. An electrical switch-driven flexible electromagnetic absorber. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 30, 1907251.
Zhou, X. F.; Jia, Z. R.; Zhang, X. X.; Wang, B. B.; Liu, X. H.; Xu, B. H.; Bi, L.; Wu, G. L. Electromagnetic wave absorption performance of NiCo2X4 (X = O, S, Se, Te) spinel structures. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 420, 129907.
Yang, L. J.; Lv, H. L.; Li, M.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, J. C.; Yang, Z. H. Multiple polarization effect of shell evolution on hierarchical hollow C@MnO2 composites and their wideband electromagnetic wave absorption properties. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 392, 123666.
Gao, Z. G.; Ma, Z. H.; Lan, D.; Zhao, Z. H.; Zhang, L. M.; Wu, H. J.; Hou, Y. L. Synergistic polarization loss of MoS2-based multiphase solid solution for electromagnetic wave absorption. Adv. Funct. Mater., in press, https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.202112294.
Sun, Y.; Zhang, J. W.; Zong, Y.; Deng, X.; Zhao, H. Y.; Feng, J.; He, M.; Li, X. H.; Peng, Y.; Zheng, X. L. Crystalline-amorphous permalloy@iron oxide core—shell nanoparticles decorated on graphene as high-efficiency, lightweight, and hydrophobic microwave absorbents. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 6374–6383.
Dong, Y. Y.; Zhu, X. J.; Pan, F.; Deng, B. W.; Liu, Z. C.; Zhang, X.; Huang, C.; Xiang, Z.; Lu, W. Mace-like carbon fiber/ZnO nanorod composite derived from Typha orientalis for lightweight and high-efficient electromagnetic wave absorber. Adv. Compos. Hybrid. Mater. 2021, 4, 1002–1014.
Xu, X. F.; Shi, S. H.; Tang, Y. L.; Wang, G. Z.; Zhou, M. F.; Zhao, G. Q.; Zhou, X. C.; Lin, S. W.; Meng, F. B. Growth of NiAl-layered double hydroxide on graphene toward excellent anticorrosive microwave absorption application. Adv. Sci. 2021, 8, 2002658.
Quan, B.; Gu, W. H.; Sheng, J. Q.; Lv, X. F.; Mao, Y. Y.; Liu, L.; Huang, X. G.; Tian, Z. J.; Ji, G. B. From intrinsic dielectric loss to geometry patterns: Dual-principles strategy for ultrabroad band microwave absorption. Nano Res. 2021, 14, 1495–1501.
Zhang, M.; Li, Z. J.; Wang, T.; Ding, S. Q.; Song, G. Y.; Zhao, J.; Meng, A. L.; Yu, H. Y.; Li, Q. D. Preparation and electromagnetic wave absorption performance of Fe3Si/SiC@SiO2 nanocomposites. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 362, 619–627.
Huang, X. G.; Qiao, M.; Lu, X. C.; Li, Y. F.; Ma, Y. B.; Kang, B.; Quan, B.; Ji, G. B. Evolution of dielectric loss-dominated electromagnetic patterns in magnetic absorbers for enhanced microwave absorption performances. Nano Res. 2021, 14, 4006–4013.
Guo, J.; Chen, Z. R.; Xu, X. J.; Li, X.; Liu, H.; Xi, S. H.; Abdul, W.; Wu, Q.; Zhang, P.; Xu, B. B. et al. Enhanced electromagnetic wave absorption of engineered epoxy nanocomposites with the assistance of polyaniline fillers. Adv. Compos. Hybrid. Mater., in press, https://doi.org/10.1007/s42114-022-00417-2.
Wu, N. N.; Zhao, B. B.; Liu, J. Y.; Li, Y. L.; Chen, Y. B.; Chen, L.; Wang, M.; Guo, Z. H. MOF-derived porous hollow Ni/C composites with optimized impedance matching as lightweight microwave absorption materials. Adv. Compos. Hybrid Mater. 2021, 4, 707–715.
Guo, Y.; Jian, X.; Zhang, L.; Mu, C. H.; Yin, L. J.; Xie, J. L.; Mahmood, N.; Dou, S. X.; Che, R. C.; Deng, L. J. Plasma-induced FeSiAl@Al2O3@SiO2 core—shell structure for exceptional microwave absorption and anti-oxidation at high temperature. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 384, 123371.
Gao, S.; Zhang, G. Z.; Wang, Y.; Han, X. P.; Huang, Y.; Liu, P. B. MOFs derived magnetic porous carbon microspheres constructed by core—shell Ni@C with high-performance microwave absorption. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2020, 88, 56–65.
Lou, Z. C.; Wang, Q. Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, X. D.; Li, R.; Liu, J.; Li, Y. J.; Lv, H. L. In-situ formation of low-dimensional, magnetic core—shell nanocrystal for electromagnetic dissipation. Compos. Part B:Eng. 2020, 274, 108744.
Cao, X. L.; Jia, Z. R.; Hu, D. Q.; Wu, G. L. Synergistic construction of three-dimensional conductive network and double heterointerface polarization via magnetic FeNi for broadband microwave absorption. Adv. Compos. Hybrid. Mater., in press, https://doi.org/10.1007/s42114-021-00415-w.
Gao, S. T.; Zhang, Y. C.; Xing, H. L.; Li, H. X. Controlled reduction synthesis of yolk-shell magnetic@void@C for electromagnetic wave absorption. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 387, 124149.
Wang, F.; Gu, W. H.; Chen, J. B; Wu, Y.; Zhou, M.; Tang, S. L.; Cao, X. Z.; Zhang, P.; Ji, G. B. The point defect and electronic structure of K doped LaCo0.9Fe0.1O3 perovskite with enhanced microwave absorbing ability. Nano Res. 2022, 15, 3720–3728.
Zhang, M.; Ling, H. L.; Ding, S. Q.; Xie, Y. X.; Cheng, T. T.; Zhao, L. B.; Wang, T.; Bian, H. G.; Lin, H.; Li, Z. J. et al. Synthesis of CF@PANI hybrid nanocomposites decorated with Fe3O4 nanoparticles towards excellent lightweight microwave absorber. Carbon 2021, 174, 248–259
Wang, C. X.; Jia, Z. R.; He, S. Q.; Zhou, J. X.; Zhang, S.; Tian, M. L.; Wang, B. B.; Wu, G. L. Metal-organic framework-derived CoSn/NC nanocubes as absorbers for electromagnetic wave attenuation. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2022, 108, 236–243.
Ma, Z. L.; Xiang, X. L.; Shao, L.; Zhang, Y. L.; Gu, J. W. Multifunctional wearable silver nanowire decorated leather nanocomposites for joule heating, electromagnetic interference shielding and piezoresistive sensing. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., in press, https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.202200705.
Wang, Y.; Gao, X.; Wu, X. M.; Luo, C. Y. Facile synthesis of Mn3O4 hollow polyhedron wrapped by multiwalled carbon nanotubes as a high-efficiency microwave absorber. Ceram. Int. 2020, 46, 1560–1568.
Wang, R. L.; He, M.; Zhou, Y. M.; Nie, S. X.; Wang, Y. J.; Liu, W. Q.; He, Q.; Wu, W. T.; Bu, X. H.; Yang, X. M. Metal-organic frameworks self-templated cubic hollow Co/N/C@MnO2 composites for electromagnetic wave absorption. Carbon 2020, 156, 378–388.
Qiao, M. T.; Li, J. X.; Wei, D.; He, X. W.; Lei, X. F.; Wei, J.; Zhang, Q. Y. Chain-like Fe3O4@void@mSiO2@MnO2 composites with multiple porous shells toward highly effective microwave absorption application. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2021, 314, 110867.
Sun, C. H.; Jia, Z. R.; Xu, S.; Hu, D. Q.; Zhang, C. H.; Wu, G. L. Synergistic regulation of dielectric-magnetic dual-loss and triple heterointerface polarization via magnetic MXene for high-performance electromagnetic wave absorption. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2022, 113, 128–137.
Lin, X. Y.; Wang, J.; Chu, Z. Y.; Liu, D. Q.; Guo, T. T.; Yang, L. N.; Huang, Z. Y.; Mu, S. T.; Li, S. The optimization of hydrothermal process of MoS2 nanosheets and their good microwave absorption performances. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2020, 37, 1124–1128.
Liu, C.; Wang, B. C.; Mu, C. P.; Zhai, K.; Wen, F. S.; Xiang, J. Y.; Nie, A. M.; Liu, Z. Y. Enhanced microwave absorption properties of MnS2 microspheres interspersed with carbon nanotubes. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2020, 502, 166432.
Liu, J. K.; Jia, Z. R.; Zhou, W. H.; Liu, X. H.; Zhang, C. H.; Xu, B. H.; Wu, G. L. Self-assembled MoS2/magnetic ferrite CuFe2O4 nanocomposite for high-efficiency microwave absorption. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 429, 132253.
Hou, T. Q.; Jia, Z. R.; Wang, B. B.; Li, H. B.; Liu, X. H.; Bi, L.; Wu, G. L. MXene-based accordion 2D hybrid structure with Co9S8/C/Ti3C2Tx as efficient electromagnetic wave absorber. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 414, 128875.
Zhang, D. Q.; Jia, Y. X.; Cheng, J. Y.; Chen, S. M.; Chai, J. X.; Yang, X. Y.; Wu, Z. Y.; Wang, H.; Zhang, W. J.; Zhao, Z. L. et al. High-performance microwave absorption materials based on MoS2-graphene isomorphic hetero-structures. J. Alloys Compd. 2018, 758, 62–71.
Dong, S.; Hu, P. T.; Li, X. T.; Hong, C. Q.; Zhang, X. H.; Han, J. C. NiCo2S4 nanosheets on 3D wood-derived carbon for microwave absorption. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 398, 125588.
He, M.; Zhou, Y. M.; Huang, T. Y.; Nie, S. X.; Wang, Y. J.; Xu, Z. J.; Huo, Y.; Xu, R.; Chen, X.; Peng, H. Flower-like CoS hierarchitectures@polyaniline organic-inorganic heterostructured composites: Preparation and enhanced microwave absorption performance. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2020, 200, 108403.
Yang, X. T.; Fan, S. G.; Li, Y.; Guo, Y. Q.; Li, Y. G.; Ruan, K. P.; Zhang, S. M.; Zhang, J. L.; Kong, J.; Gu, J. W. Synchronously improved electromagnetic interference shielding and thermal conductivity for epoxy nanocomposites by constructing 3D copper nanowires/thermally annealed graphene aerogel framework. Compos. Part A:Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2020, 128, 105670.
Wang, Z. D.; Zhang, T.; Wang, J. K.; Yang, G. Q.; Li, M. L.; Wu, G. L. The investigation of the effect of filler sizes in 3D-BN skeletons on thermal conductivity of epoxy-based composites. Nanomaterials (Basel) 2022, 12, 446.
Meng, F. B.; Wang, H. G.; Wei, W.; Chen, Z. J.; Li, T.; Li, C. Y.; Xuan, Y.; Zhou, Z. W. Generation of graphene-based aerogel microspheres for broadband and tunable high-performance microwave absorption by electrospinning-freeze drying process. Nano Res. 2018, 11, 2847–2861.
Wang, X. L.; Huang, X.; Chen, Z. R.; Liao, X. P.; Liu, C.; Shi, B. Ferromagnetic hierarchical carbon nanofiber bundles derived from natural collagen fibers: Truly lightweight and high-performance microwave absorption materials. J. Mater. Chem. C 2015, 3, 10146–10153.
Xing, L. S.; Li, X.; Wu, Z. C.; Yu, X. F.; Liu, J. W.; Wang, L.; Cai, C. Y.; You, W. B.; Chen, G. Y.; Ding, J. J. et al. 3D hierarchical local heterojunction of MoS2/FeS2 for enhanced microwave absorption. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 379, 122241.
Xiang, Z.; Huang, C.; Song, Y. M.; Deng, B. W.; Zhang, X.; Zhu, X. J.; Batalu, D.; Tutunaru, O.; Lu, W. Rational construction of hierarchical accordion-like Ni@porous carbon nanocomposites derived from metal-organic frameworks with enhanced microwave absorption. Carbon 2020, 167, 364–377.
Luo, J. H.; Zhang, K.; Cheng, M. L.; Gu, M. M.; Sun, X. K. MoS2 spheres decorated on hollow porous ZnO microspheres with strong wideband microwave absorption. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 380, 122625.
Huang, X. M.; Liu, X. H.; Jia, Z. R.; Wang, B. B.; Wu, X. M.; Wu, G. L. Synthesis of 3D cerium oxide/porous carbon for enhanced electromagnetic wave absorption performance. Adv. Compos. Hybrid Mater. 2021, 4, 1398–1412.
Xu, Z. J.; He, M.; Zhou, Y. M.; Nie, S. X.; Wang, Y. J.; Huo, Y.; Kang, Y. F.; Wang, R. L.; Xu, R.; Peng, H. et al. Spider web-like carbonized bacterial cellulose/MoSe2 nanocomposite with enhanced microwave attenuation performance and tunable absorption bands. Nano Res. 2021, 14, 738–746.
Zhang, Y. L.; Ruan, K. P.; Gu, J. W. Flexible sandwich-structured electromagnetic interference shielding nanocomposite films with excellent thermal conductivities. Small 2021, 17, 2101951.
Li, Z. J.; Lin, H.; Ding, S. Q.; Ling, H. L.; Wang, T.; Miao, Z. Q.; Zhang, M.; Meng, A. L.; Li, Q. D. Synthesis and enhanced electromagnetic wave absorption performances of Fe3O4@C decorated walnut shell-derived porous carbon. Carbon 2021, 167, 148–159.
Hou, T. Q.; Jia, Z. R.; Dong, Y. H.; Liu, X. H.; Wu, G. L. Layered 3D structure derived from MXene/magnetic carbon nanotubes for ultra-broadband electromagnetic wave absorption. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 431, 13319.
Sun, L. F.; Jia, Z. R.; Xu, S.; Ling, M. B.; Hu, D. Q.; Liu, X. H.; Zhang, C. H.; Wu, G. L. Synthesis of NiCo2-0.5xCr2O3@C nanoparticles based on hydroxide with the heterogeneous interface for excellent electromagnetic wave absorption properties. Compos. Commun. 2022, 29, 100993.
Ma, J. R.; Shu, J. C.; Cao, W. Q.; Zhang, M.; Wang, X. X.; Yuan, J.; Cao, M. S. A green fabrication and variable temperature electromagnetic properties for thermal stable microwave absorption towards flower-like Co3O4@rGO/SiO2 composites. Compos. Part B:Eng. 2019, 166, 187–195.
Deng, R. X.; Chen, B. B.; Li, H. G.; Zhang, K.; Zhang, T.; Yu, Y.; Song, L. X. MXene/Co3O4 composite material: Stable synthesis and its enhanced broadband microwave absorption. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 488, 921–930.
Zhang, H. X.; Wang, B. B.; Feng, A. L.; Zhang, N.; Jia, Z. R.; Huang, Z. Y.; Liu, X. H.; Wu, G. L. Mesoporous carbon hollow microspheres with tunable pore size and shell thickness as efficient electromagnetic wave absorbers. Compos. Part B:Eng. 2019, 167, 690–699.
Zhang, W. D.; Zhang, X.; Wu, H. J.; Yan, H. X.; Qi, S. H. Impact of morphology and dielectric property on the microwave absorbing performance of MoS2-based materials. J. Alloys Compd. 2018, 751, 34–42.
Xu, D. M.; Wu, N. N.; Le, K.; Wang, F. L.; Wang, Z.; Wu, L. L.; Liu, W.; Ouyang, A. C.; Liu, J. R. Bimetal oxides-derived flower-like heterogeneous Co/MnO@C composites with synergistic magnetic-dielectric attenuation for electromagnetic wave absorption. J. Mater. Chem. C 2020, 8, 2451–2459.
Song, L. L.; Duan, Y. P.; Liu, J.; Pang, H. F. Transformation between nanosheets and nanowires structure in MnO2 upon providing Co2+ ions and applications for microwave absorption. Nano Res. 2020, 13, 95–104.
Feng, A. L.; Hou, T. Q.; Jia, Z. R.; Wu, G. L. Synthesis of a hierarchical carbon fiber@cobalt ferrite@manganese dioxide composite and its application as a microwave absorber. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 10510–10518.
Yi, H. H.; Song, L. L.; Tang, X. L.; Zhao, S. Z.; Yang, Z. Y.; Xie, X. Z.; Ma, C. B.; Zhang, Y. Y.; Zhang, X. D. Effect of microwave absorption properties and morphology of manganese dioxide on catalytic oxidation of toluene under microwave irradiation. Ceram. Int. 2020, 46, 3166–3176.
Hu, F. F.; Nan, H.; Wang, M. Q.; Lin, Y.; Yang, H. B.; Qiu, Y.; Wen, B. Construction of core—shell BaFe12O19@MnO2 composite for effectively enhancing microwave absorption performance. Ceram. Int. 2021, 47, 16579–16587.
Ding, J. J.; Wang, L.; Zhao, Y. H.; Xing, L. S.; Yu, X. F.; Chen, G. Y.; Zhang, J.; Che, R. C. Boosted interfacial polarization from multishell TiO2@Fe3O4@PPy heterojunction for enhanced microwave absorption. Small 2019, 15, 1902885.
Zhang, X. Y.; Jia, Z. R.; Zhang, F.; Xia, Z. H.; Zou, J. X.; Gu, Z.; Wu, G. L. MOF-derived NiFe2S4/porous carbon composites as electromagnetic wave absorber. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2022, 610, 610–620.
Zhang, S. J.; Cheng, B.; Gao, Z. G.; Lan, D.; Zhao, Z. W.; Wei, F. C.; Zhu, Q. S.; Lu, X. P.; Wu, G. L. Two-dimensional nanomaterials for high-efficiency electromagnetic wave absorption: An overview of recent advances and prospects. J. Alloys Compd. 2022, 893, 162343.
Gao, Z. G.; Lan, D.; Zhang, L. M.; Wu, H. J. Simultaneous manipulation of interfacial and defects polarization toward Zn/Co phase and ion hybrids for electromagnetic wave absorption. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021, 31, 2106677.
Han, Y. X.; Ruan, K. P.; Gu, J. W. Janus (BNNS/ANF)-(AgNWs/ANF) thermal conductivity composite films with superior electromagnetic interference shielding and Joule heating performances. Nano Res. 2022, 15, 4747–4755.
Yan, H.; Dai, X. J.; Ruan, K. P.; Zhang, S. J.; Shi, X. T.; Guo, Y. Q.; Cai, H. Q.; Gu, J. W. Flexible thermally conductive and electrically insulating silicone rubber composite films with BNNS@Al2O3 fillers. Adv. Compos. Hybrid. Mater. 2021, 4, 36–50.
Liu, Y.; Liu, X. H.; E, X. Y.; Wang, B. B.; Jia, Z. R.; Chi, Q. G.; Wu, G. L. Synthesis of Mn.xOy@C hybrid composites for optimal electromagnetic wave absorption capacity and wideband absorption. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2022, 103, 157–164.
Zhang, F.; Jia, Z. R.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, C. H.; Wang, B. B.; Xu, B. H.; Liu, X. H.; Wu, G. L. Tailoring nanoparticles composites derived from metal-organic framework as electromagnetic wave absorber. Mater. Today Phys. 2021, 20, 100475.
Wu, N. N.; Qiao, J.; Liu, J. R.; Du, W. J.; Xu, D. M.; Liu, W. Strengthened electromagnetic absorption performance derived from synergistic effect of carbon nanotube hybrid with Co@C beads. Adv. Compos. Hybrid. Mater. 2018, 1, 149–159.
Wang, X.; Pan, F.; Xiang, Z.; Zeng, Q. W.; Pei, K.; Che, R. C.; Lu, W. Magnetic vortex core—shell Fe3O4@C nanorings with enhanced microwave absorption performance. Carbon 2020, 157, 130–139.
Zhang J. J.; Li, Z. H.; Qi, X. S.; Gong, X.; Xie, R.; Deng, C. Y.; Zhong, W.; Du, Y. W. Constructing flower-like core@shell MoSe2-based nanocomposites as a novel and high-efficient microwave absorber. Compos. Part B:Eng. 2021, 222, 109067.
Wang, J. W.; Jia, Z. R.; Liu, X. H.; Dou, J. L.; Xu, B. H.; Wang, B. B.; Wu, G. L. Construction of 1D heterostructure NiCo@C/ZnO nanorod with enhanced microwave absorption. Nano-Micro Lett. 2021, 13, 175.
Li, C.; Li, Z. H.; Qi, X. S.; Gong, X.; Chen, Y. L.; Peng, Q.; Deng, C. Y.; Jing, T.; Zhong, W. A generalizable strategy for constructing ultralight three-dimensional hierarchical network heterostructure as high-efficient microwave absorber. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2022, 605, 13–22.
Wang, L.; Yu, X. F.; Li, X.; Zhang, J.; Wang, M.; Che, R. C. MOF-derived yolk-shell Ni@C@ZnO Schottky contact structure for enhanced microwave absorption. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 383, 123099.
Acknowledgements
This work is financially supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Shandong Province (No. ZR2019YQ24), Taishan Scholars and Young Experts Program of Shandong Province (No. tsqn202103057) and the Qingchuang Talents Induction Program of Shandong Higher Education Institution (Research and Innovation Team of Structural-Functional Polymer Composites).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Electronic Supplementary Material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, Y., Jia, Z., Zhan, Q. et al. Magnetic manganese-based composites with multiple loss mechanisms towards broadband absorption. Nano Res. 15, 5590–5600 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-022-4287-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-022-4287-5