Abstract
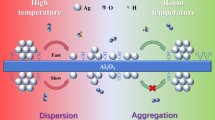
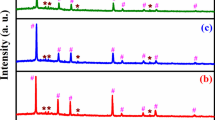
Small Ag clusters confined in the channels of ordered mesoporous anatase TiO2 have been fabricated via a vacuum-assisted wet-impregnation method, utilizing well-ordered mesoporous anatase TiO2 with high thermal stability as the host. The composites have been characterized in detail by X-ray diffraction, X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy, X-ray absorption fine structure (XAFS) spectroscopy, N2 adsorption, UV-visible diffuse reflectance spectroscopy and transmission electron microscopy. The results indicate that small Ag clusters are formed and uniformly confined in the channels of mesoporous TiO2 with an obvious confinement effect. The presence of strong Ag-O interactions involving the Ag clusters in intimate contact with the pore walls of mesoporous TiO2 is confirmed by XAFS analysis, and favors the separation of photogenerated electron-hole pairs, as shown by steady-state surface photovoltage spectroscopy and transient-state surface photovoltage measurements. The ordered mesoporous Ag/TiO2 composites exhibit excellent solar-light-driven photocatalytic performance for the degradation of phenol. This is attributed to the synergistic effects between the small Ag clusters acting as traps to effectively capture the photogenerated electrons, and the surface plasmon resonance of the Ag clusters promoting the absorption of visible light. This study clearly demonstrates the high-efficiency utilization of noble metals in the fabrication of high-performance solar-light-driven photocatalysts.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Crossland, E. J. W.; Noel, N.; Sivaram, V.; Leijtens, T.; Alexander-Webber, J. A.; Snaith, H. J. Mesoporous TiO2 single crystals delivering enhanced mobility and optoelectronic device performance. Nature 2013, 495, 215–219.
Etgar, L.; Gao, P.; Xue, Z. S.; Peng, Q.; Chandiran, A. K.; Liu, B.; Nazeeruddin, M. K.; Grätzel, M. Mesoscopic CH3NH3PbI3/TiO2 heterojunction solar cells. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 17396–17399.
Zhou, W.; Sun, F. F.; Pan, K.; Tian, G. H.; Jiang, B. J.; Ren, Z. Y.; Tian, C. G.; Fu, H. G. Well-ordered large-pore mesoporous anatase TiO2 with remarkably high thermal stability and improved crystallinity: Preparation, characterization, and photocatalytic performance. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2011, 21, 1922–1930.
Bai, H.; Li, X. S.; Hu, C.; Zhang, X.; Li, J. F.; Yan, Y.; Xi, G. C. Large-scale, three-dimensional, free-standing, and mesoporous metal oxide networks for high-performance photocatalysis. Sci. Rep. 2013, 3, 2204.
Lü, R. J.; Zhou, W.; Shi, K. Y.; Yang, Y.; Wang, L.; Pan, K.; Tian, C. Q.; Ren, Z. Y.; Fu, H. G. Alumina decorated TiO2 nanotubes with ordered mesoporous walls as high sensitivity NOx gas sensors at room temperature. Nanoscale 2013, 5, 8569–8576.
Deng, Y. H.; Wei, J.; Sun, Z. K.; Zhao, D. Y. Large-pore ordered mesoporous materials template from non-Pluronic amphiphilic block copolymers. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 4054–4070.
Qiao, Z.; Brown, S. S.; Adcock, J.; Veith, G. M.; Bauer, J. C.; Payzant, E. A.; Unocic, R. R.; Dai, S. A topotactic synthetic methodology for highly fluorine-doped mesoporous metal oxides. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 2888–2893.
Joo, J. B.; Dahl, M.; Li, N.; Zaera, F.; Yin, Y. D. Tailored synthesis of mesoporous TiO2 hollow nanostructures for catalytic applications. Energy Environ. Sci. 2013, 6, 2082–2092.
Chen, X. B.; Liu, L.; Liu, Z.; Marcus, M. A.; Wang, W.-C.; Oyler, N. A.; Grass, M. E.; Mao, B. H.; Glans, P. A.; Yu, P. Y., et al. Properties of disorder-engineered black titanium dioxide nanoparticles through hydrogenation. Sci. Rep. 2013, 3, 1510.
Jing, L. Q.; Zhou, W.; Tian, G. H.; Fu, H. G. Surface tuning for oxide-based nanomaterials as efficient photocatalysts. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 9509–9549.
Du, J.; Lai, X.; Yang, N.; Zhai, J.; Kisailus, D.; Su, F.; Wang, D.; Jiang, L. Hierarchically ordered macro-mesoporous TiO2-graphene composite films: Improved mass transfer, reduced charge recombination, and their enhanced photocatalytic activities. ACS Nano, 2011, 5, 590–596.
Panayotov, D. A.; DeSario, P. A.; Pietron, J. J.; Brintlinger, T. H.; Szymczak, L. C.; Rolison, D. R.; Morris, J. R. Ultraviolet and visible photochemistry of methanol at 3D mesoporous networks: TiO2 and Au-TiO2. J. Phys. Chem. C 2013, 117, 15035–15049.
Li, W.; Wu, Z. X.; Wang, J. X.; Elzatahry, A. A.; Zhao, D. Y. A perspective on mesoporous TiO2 materials. Chem. Mater. 2014, 26, 287–298.
Joo, J. B.; Zhang, Q.; Lee, I.; Dahl, M.; Zaera, F.; Yin, Y. D. Mesoporous anatase titania hollow nanostructures though silica-protected calcination. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2012, 22, 166–174.
Wei, W.; Yu, C.; Zhao, Q. F.; Li, G. S.; Wan, Y. Improvement of the visible-light photocatalytic performance of TiO2 by carbon mesostructures. Chem. Eur. J. 2013, 19, 566–577.
Ismail, A. A.; Bahnemann, D. W. One-step synthesis of mesoporous platinum/titania nanocomposites as photocatalyst with enhanced photocatalytic activity for methanol oxidation. Green Chem. 2011, 13, 428–435.
Kochuveedu, S. T.; Jang, Y. H.; Kim, D. H. A study on the mechanism for the interaction of light with noble metal-metal oxide semiconductor nanostructures for various photophysical applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 8467–8493.
Wang, X. D.; Choi, J.; Mitchell, D. R. G.; Truong, Y. B.; Kyratzis, I. L.; Caruso, R. A. Enhanced photocatalytic activity: Macroporous electrospun mats of mesoporous Au/TiO2 nanofibers. ChemCatChem 2013, 5, 2646–2654.
Wang, G. N.; Wang, X. F.; Liu, J. F.; Sun, X. M. Mesoporous Au/TiO2 nanocomposite microspheres for visible-light photocatalysis. Chem. Eur. J. 2012, 18, 5361–5366.
Lu, J. W.; Zhang, P.; Li, A.; Su, F. L.; Wang, T.; Liu, Y.; Gong, J. L. Mesoporous anatase TiO2 nanocups with plasmonic metal decoration for highly active visible-light photocatalysis. Chem. Commun. 2013, 49, 5817–5819.
Pineider, F.; Fernández, C. J.; Videtta, V.; Carlino, E.; Hourani, A.; Wilhelm, F.; Rogalev, A.; Cozzoli, P. D.; Ghigna, P.; Sangregorio, C. Spin-polarization transfer in colloidal magnetic-plasmonic Au/iron oxide hetero-nanocrystals. ACS Nano 2013, 7, 857–866.
Bian, Z. F.; Zhu, J.; Cao, F. L.; Lu, Y. F.; Li, H. X. In situ encapsulation of Au nanoparticles in mesoporous core-shell TiO2 microspheres with enhanced activity and durability. Chem. Commun. 2009, 3789–3791.
Jiang, C. X.; Hara, K.; Fukuoka, A. Low-temperature oxidation of ethylene over platinum nanoparticles supported on mesoporous silica. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 6265–6268.
Li, T.; Zhou, W.; Wang, J. Q.; Qu, Y.; Tian, C. G.; Pan, K.; Tian, G. H.; Fu, H. G. Confinement effect on Ag clusters in the channels of well-ordered mesoporous TiO2 and their enhanced photocatalytic performance. ChemCatChem 2013, 5, 1354–1358.
Wang, S.; Zhao, Q. F.; Wei, H. M.; Wang, J.-Q.; Cho, M.; Cho, H. S.; Terasaki, O.; Wan, Y. Aggregation-free gold nanoparticles in ordered mesoporous carbons: Toward highly active and stable heterogeneous catalysts. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 11849–11860.
Dutta, S.; Bhaumik, A. Continuous mesoporous titania nanocrystals: Their growth in confined space and scope for application. ChemSusChem 2013, 6, 2039–2041.
Guin, D.; Manorama, S. V.; Latha, J. N. L.; Singh, S. Photoreduction of silver on bare and colloidal TiO2 nanoparticles/nanotubes: Synthesis, characterization, and tested for antibacterial outcome. J. Phys. Chem. C 2007, 111, 13393–13397.
Yu, D.-H.; Yu, X. D.; Wang, C. H.; Liu, X.-C.; Xing, Y. Synthesis of natural cellulose-templated TiO2/Ag nanosponge composites and photocatalytic properties. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2012, 4, 2781–2787.
Lee, J.-S.; Kim, S.-I.; Yoon, J.-C.; Jang, J.-H. Chemical vapor deposition of mesoporous graphene nanoballs for supercapacitor. ACS Nano 2013, 7, 6047–6055.
Liu, Y. R.; Jennings, J. R.; Zakeeruddin, S. M.; Grätzel, M.; Wang, Q. Heterogeneous electron transfer from dye-sensitized nanocrystalline TiO2 to [Co(bpy)3]3+: Insights gained from impedance spectroscopy. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 3939–3952.
Xia, X. H.; Zeng, J.; Zhang, Q.; Moran, C. H.; Xia, Y. N. Recent developments in shape-controlled synthesis of silver nanocrystals. J. Phys. Chem. C 2012, 116, 21647–21656.
Choi, H.; Ko, S.-J.; Choi, Y.; Joo, P.; Kim, T.; Lee, B. R.; Jung, J.-W.; Choi, H. J.; Cha, M.; Jeong, J. R., et al. Versatile surface plasmon resonance of carbon-dot-supported silver nanoparticles in polymer optoelectronic devices. Nature Photon. 2013, 7, 732–738.
Luan, Y.; Jing, L.; Xie, Y.; Sun, X.; Feng, Y.; Fu, H. Exceptional photocatalytic activity of 001-facet-exposed TiO2 mainly depending on enhanced adsorbed oxygen by residual hydrogen fluoride. ACS Catal. 2013, 3, 1378–1385.
He, L. M.; Jing, L. Q.; Li, Z. J.; Sun, W. T.; Liu, C. Enhanced visible photocatalytic activity of nanocrystalline α-Fe2O3 by coupling phosphate-functionalized graphene. RSC Adv. 2013, 3, 7438–7444.
Wei, X.; Xie, T. F.; Peng, L. L.; Fu, W.; Chen, J. S.; Gao, Q.; Hong G. Y.; Wang, D. J. Effect of heterojunction on the behavior of photogenerated charges in Fe3O4@Fe2O3 nanoparticle photocatalysts. J. Phys. Chem. C 2011, 115, 8637–8642.
Huang, Q. W.; Tian, S. Q.; Zeng, D. W.; Wang, X. X.; Song, W. L.; Li, Y. Y.; Xiao, W.; Xie C. S. Enhanced photocatalytic activity of chemically bonded TiO2/graphene composites based on the effective interfacial charge transfer through the C-Ti bond. ACS Catal. 2013, 3, 1477–1485.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, W., Li, T., Wang, J. et al. Composites of small Ag clusters confined in the channels of well-ordered mesoporous anatase TiO2 and their excellent solar-light-driven photocatalytic performance. Nano Res. 7, 731–742 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-014-0434-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-014-0434-y