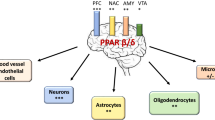
Abstract
The proliferation, differentiation, and migration of neural precursor cells occur not only during embryonic development but also within distinct regions of the adult brain through the process of adult neurogenesis. As neurogenesis can potentially regulate brain cognition and neuronal plasticity, the factors that enhance neurogenesis can be attractive therapeutic targets for improving cognitive function and regulating neurodegenerative and neuropsychiatric disorders, including affective and mood disorders. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors (PPARs) are a class of ligand-activated transcription factors belonging to the nuclear receptor superfamily. PPARγ is a target for insulin sensitizers and plays an essential role in regulating various metabolic processes, including adipogenesis and glucose homeostasis. Interestingly, evidence demonstrates the role of PPARγ activation in regulating neurogenesis. The pharmacological activation of PPARγ using specific ligands increases the proliferation and differentiation of neural stem cells in specific brain regions, including the hippocampus, and prevents neurodegeneration and improves cognition and anxiety/depression-like behaviors in animal models. We summarize here recent reports on the role of PPARγ in adult neurogenesis, as well as the mechanisms involved, and suggest that PPARγ can serve as a potential therapeutic target for neurological and/or neurodegenerative diseases.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Al-Alem L, Southard RC, Kilgore MW, Curry TE (2011) Specific thiazolidinediones inhibit ovarian cancer cell line proliferation and cause cell cycle arrest in a PPARgamma independent manner. PLoS ONE 6:e16179s. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0016179
Arvidsson A, Collin T, Kirik D, Kokaia Z, Lindvall O (2002) Neuronal replacement from endogenous precursors in the adult brain after stroke. Nat Med 8:963–970. https://doi.org/10.1038/nm747
Barbiero JK, Santiago R, Tonin FS, Boschen S, Da Silva LM, Werner MF, Da Cunha C, Lima MM, Vital MA (2014) PPAR-alpha agonist fenofibrate protects against the damaging effects of MPTP in a rat model of Parkinson’s disease. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 53:35–44. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pnpbp.2014.02.009
Beheshti F, Hosseini M, Hashemzehi M, Soukhtanloo M, Khazaei M, Shafei MN (2019) The effects of PPAR-gamma agonist pioglitazone on hippocampal cytokines, brain-derived neurotrophic factor, memory impairment, and oxidative stress status in lipopolysaccharide-treated rats. Iran J Basic Med Sci 22:940–948. https://doi.org/10.22038/ijbms.2019.36165.8616
Ben Abdallah NM, Slomianka L, Vyssotski AL, Lipp HP (2010) Early age-related changes in adult hippocampal neurogenesis in C57 mice. Neurobiol Aging 31:151–161. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2008.03.002
Boldrini M, Santiago AN, Hen R, Dwork AJ, Rosoklija GB, Tamir H, Arango V, John Mann J (2013) Hippocampal granule neuron number and dentate gyrus volume in antidepressant-treated and untreated major depression. Neuropsychopharmacology 38:1068–1077. https://doi.org/10.1038/npp.2013.5
Bonato JM, Bassani TB, Milani H, Vital M, De Oliveira RMW (2018) Pioglitazone reduces mortality, prevents depressive-like behavior, and impacts hippocampal neurogenesis in the 6-OHDA model of Parkinson’s disease in rats. Exp Neurol 300:188–200. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.expneurol.2017.11.009
Bruck A, Kurki T, Kaasinen V, Vahlberg T, Rinne JO (2004) Hippocampal and prefrontal atrophy in patients with early non-demented Parkinson’s disease is related to cognitive impairment. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 75:1467–1469. https://doi.org/10.1136/jnnp.2003.031237
Cai W, Yang T, Liu H, Han L, Zhang K, Hu X, Zhang X, Yin KJ, Gao Y, Bennett MVL, Leak RK, Chen J (2018) Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ (PPARγ): a master gatekeeper in CNS injury and repair. Prog Neurobiol 163–164:27–58. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pneurobio.2017.10.002
Chandra S, Roy A, Jana M, Pahan K (2019) Cinnamic acid activates PPARalpha to stimulate Lysosomal biogenesis and lower Amyloid plaque pathology in an Alzheimer’s disease mouse model. Neurobiol Dis 124:379–395. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nbd.2018.12.007
Cheng Y, Rodriguiz RM, Murthy SR, Senatorov V, Thouennon E, Cawley NX, Aryal DK, Ahn S, Lecka-Czernik B, Wetsel WC, Loh YP (2015) Neurotrophic factor-alpha1 prevents stress-induced depression through enhancement of neurogenesis and is activated by rosiglitazone. Mol Psychiatry 20:744–754. https://doi.org/10.1038/mp.2014.136
Cheng HS, Tan WR, Low ZS, Marvalim C, Lee JYH, Tan NS (2019) Exploration and development of PPAR modulators in health and disease: an update of clinical evidence. Int J Mol Sci. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20205055
Cippitelli A, Domi E, Ubaldi M, Douglas JC, Li HW, Demopulos G, Gaitanaris G, Roberto M, Drew PD, Kane CJM, Ciccocioppo R (2017) Protection against alcohol-induced neuronal and cognitive damage by the PPARgamma receptor agonist pioglitazone. Brain Behav Immun 64:320–329. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbi.2017.02.001
Colle R, De Larminat D, Rotenberg S, Hozer F, Hardy P, Verstuyft C, Feve B, Corruble E (2017) PPAR-gamma agonists for the treatment of major depression: a review. Pharmacopsychiatry 50:49–55. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0042-120120
Combs CK, Bates P, Karlo JC, Landreth GE (2001) Regulation of beta-amyloid stimulated proinflammatory responses by peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha. Neurochem Int 39:449–457. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0197-0186(01)00052-3
Cortez I, Denner L, Dineley KT (2019) Divergent mechanisms for PPARgamma agonism in ameliorating aging-related versus cranial irradiation-induced context discrimination deficits. Front Aging Neurosci 11:38. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnagi.2019.00038
Crews L, Mizuno H, Desplats P, Rockenstein E, Adame A, Patrick C, Winner B, Winkler J, Masliah E (2008) Alpha-synuclein alters Notch-1 expression and neurogenesis in mouse embryonic stem cells and in the hippocampus of transgenic mice. J Neurosci 28:4250–4260. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0066-08.2008
Crews L, Adame A, Patrick C, Delaney A, Pham E, Rockenstein E, Hansen L, Masliah E (2010) Increased BMP6 levels in the brains of Alzheimer’s disease patients and APP transgenic mice are accompanied by impaired neurogenesis. J Neurosci 30:12252–12262. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1305-10.2010
D’angelo B, Benedetti E, Di Loreto S, Cristiano L, Laurenti G, Ceru MP, Cimini A (2011) Signal transduction pathways involved in PPARbeta/delta-induced neuronal differentiation. J Cell Physiol 226:2170–2180. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcp.22552
Das M, Mayilsamy K, Tang X, Han JY, Foran E, Willing AE, Mohapatra SS, Mohapatra S (2019) Pioglitazone treatment prior to transplantation improves the efficacy of human mesenchymal stem cells after traumatic brain injury in rats. Sci Rep 9:13646. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-49428-y
Del Zoppo G, Ginis I, Hallenbeck JM, Iadecola C, Wang X, Feuerstein GZ (2000) Inflammation and stroke: putative role for cytokines, adhesion molecules and iNOS in brain response to ischemia. Brain Pathol 10:95–112. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1750-3639.2000.tb00247.x
Denner LA, Rodriguez-Rivera J, Haidacher SJ, Jahrling JB, Carmical JR, Hernandez CM, Zhao Y, Sadygov RG, Starkey JM, Spratt H, Luxon BA, Wood TG, Dineley KT (2012) Cognitive enhancement with rosiglitazone links the hippocampal PPARgamma and ERK MAPK signaling pathways. J Neurosci 32:16725–16735a. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2153-12.2012
Di Loreto S, D’angelo B, D’amico MA, Benedetti E, Cristiano L, Cinque B, Cifone MG, Ceru MP, Festuccia C, Cimini A (2007) PPARbeta agonists trigger neuronal differentiation in the human neuroblastoma cell line SH-SY5Y. J Cell Physiol 211:837–847. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcp.20996
Donovan MH, Yazdani U, Norris RD, Games D, German DC, Eisch AJ (2006) Decreased adult hippocampal neurogenesis in the PDAPP mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. J Comp Neurol 495:70–83. https://doi.org/10.1002/cne.20840
Eissa Ahmed AA, Al-Rasheed NM, Al-Rasheed NM (2009) Antidepressant-like effects of rosiglitazone, a PPARgamma agonist, in the rat forced swim and mouse tail suspension tests. Behav Pharmacol 20:635–642. https://doi.org/10.1097/FBP.0b013e328331b9bf
Frodl T, Meisenzahl EM, Zetzsche T, Born C, Groll C, Jager M, Leinsinger G, Bottlender R, Hahn K, Moller HJ (2002) Hippocampal changes in patients with a first episode of major depression. Am J Psychiatry 159:1112–1118. https://doi.org/10.1176/appi.ajp.159.7.1112
Fuster-Matanzo A, Llorens-Martin M, Hernandez F, Avila J (2013) Role of neuroinflammation in adult neurogenesis and Alzheimer disease: therapeutic approaches. Mediators Inflamm 2013:260925. https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/260925
Gemma C, Stellwagen H, Fister M, Coultrap SJ, Mesches MH, Browning MD, Bickford PC (2004) Rosiglitazone improves contextual fear conditioning in aged rats. NeuroReport 15:2255–2259. https://doi.org/10.1097/00001756-200410050-00023
Ghoochani A, Shabani K, Peymani M, Ghaedi K, Karamali F, Karbalaei K, Tanhaie S, Salamian A, Esmaeili A, Valian-Borujeni S, Hashemi M, Nasr-Esfahani MH, Baharvand H (2012) The influence of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma(1) during differentiation of mouse embryonic stem cells to neural cells. Differentiation 83:60–67. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.diff.2011.08.009
Ghosal K, Stathopoulos A, Pimplikar SW (2010) APP intracellular domain impairs adult neurogenesis in transgenic mice by inducing neuroinflammation. PLoS ONE 5:e11866. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0011866
Gil JM, Mohapel P, Araujo IM, Popovic N, Li JY, Brundin P, Petersen A (2005) Reduced hippocampal neurogenesis in R6/2 transgenic Huntington’s disease mice. Neurobiol Dis 20:744–751. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nbd.2005.05.006
Giordano TJ, Haugen BR, Sherman SI, Shah MH, Caoili EM, Koenig RJ (2018) Pioglitazone therapy of PAX8-PPARgamma fusion protein thyroid carcinoma. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 103:1277–1281. https://doi.org/10.1210/jc.2017-02533
Govindarajulu M, Pinky PD, Bloemer J, Ghanei N, Suppiramaniam V, Amin R (2018) Signaling mechanisms of selective PPARgamma modulators in Alzheimer’s disease. PPAR Res 2018:2010675. https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/2010675
Grochowski C, Radzikowska E, Maciejewski R (2018) Neural stem cell therapy-brief review. Clin Neurol Neurosurg 173:8–14. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clineuro.2018.07.013
Gronemeyer H, Gustafsson JA, Laudet V (2004) Principles for modulation of the nuclear receptor superfamily. Nat Rev Drug Discov 3:950–964. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrd1551
Gronska-Peski M, Goncalves JT, Hebert JM (2021) Enriched environment promotes adult hippocampal neurogenesis through FGFRs. J Neurosci 41:2899–2910. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2286-20.2021
Grygiel-Gorniak B (2014) Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors and their ligands: nutritional and clinical implications—a review. Nutr J 13:17. https://doi.org/10.1186/1475-2891-13-17
Han YG, Spassky N, Romaguera-Ros M, Garcia-Verdugo JM, Aguilar A, Schneider-Maunoury S, Alvarez-Buylla A (2008) Hedgehog signaling and primary cilia are required for the formation of adult neural stem cells. Nat Neurosci 11:277–284. https://doi.org/10.1038/nn2059
Haskew-Layton RE, Payappilly JB, Xu H, Bennett SA, Ratan RR (2013) 15-Deoxy-Delta 12,14-prostaglandin J2 (15d-PGJ2) protects neurons from oxidative death via an Nrf2 astrocyte-specific mechanism independent of PPARgamma. J Neurochem 124:536–547. https://doi.org/10.1111/jnc.12107
Heming M, Gran S, Jauch SL, Fischer-Riepe L, Russo A, Klotz L, Hermann S, Schafers M, Roth J, Barczyk-Kahlert K (2018) Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma modulates the response of macrophages to lipopolysaccharide and glucocorticoids. Front Immunol 9:893. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2018.00893
Heneka MT, Klockgether T, Feinstein DL (2000) Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma ligands reduce neuronal inducible nitric oxide synthase expression and cell death in vivo. J Neurosci 20:6862–6867. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.20-18-06862.2000
Hoglinger GU, Rizk P, Muriel MP, Duyckaerts C, Oertel WH, Caille I, Hirsch EC (2004) Dopamine depletion impairs precursor cell proliferation in Parkinson disease. Nat Neurosci 7:726–735. https://doi.org/10.1038/nn1265
Hou Y, Moreau F, Chadee K (2012) PPARγ is an E3 ligase that induces the degradation of NFκB/p65. Nat Commun 3:1300. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms2270
Jurgenson M, Aonurm-Helm A, Zharkovsky A (2012) Partial reduction in neural cell adhesion molecule (NCAM) in heterozygous mice induces depression-related behaviour without cognitive impairment. Brain Res 1447:106–118. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainres.2012.01.056
Kapadia R, Yi JH, Vemuganti R (2008) Mechanisms of anti-inflammatory and neuroprotective actions of PPAR-gamma agonists. Front Biosci 13:1813–1826. https://doi.org/10.2741/2802
Kariharan T, Nanayakkara G, Parameshwaran K, Bagasrawala I, Ahuja M, Abdel-Rahman E, Amin AT, Dhanasekaran M, Suppiramaniam V, Amin RH (2015) Central activation of PPAR-gamma ameliorates diabetes induced cognitive dysfunction and improves BDNF expression. Neurobiol Aging 36:1451–1461. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2014.09.028
Keledjian K, Tsymbalyuk O, Semick S, Moyer M, Negoita S, Kim K, Ivanova S, Gerzanich V, Simard JM (2020) The peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma (PPARgamma) agonist, rosiglitazone, ameliorates neurofunctional and neuroinflammatory abnormalities in a rat model of Gulf War Illness. PLoS ONE 15:e0242427. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0242427
Kemp DE, Ismail-Beigi F, Calabrese JR (2009) Antidepressant response associated with pioglitazone: support for an overlapping pathophysiology between major depression and metabolic syndrome. Am J Psychiatry 166:619. https://doi.org/10.1176/appi.ajp.2008.08081195
Kinouchi T, Kitazato KT, Shimada K, Yagi K, Tada Y, Matsushita N, Kurashiki Y, Satomi J, Sata M, Nagahiro S (2018) Treatment with the PPARgamma agonist pioglitazone in the early post-ischemia phase inhibits pro-inflammatory responses and promotes neurogenesis via the activation of innate- and bone marrow-derived stem cells in rats. Transl Stroke Res 9:306–316. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12975-017-0577-8
Korbecki J, Bobiński R, Dutka M (2019) Self-regulation of the inflammatory response by peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors. Inflamm Res 68:443–458. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00011-019-01231-1
Kowianski P, Lietzau G, Czuba E, Waskow M, Steliga A, Morys J (2018) BDNF: a key factor with multipotent impact on brain signaling and synaptic plasticity. Cell Mol Neurobiol 38:579–593. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-017-0510-4
Kuhn HG, Dickinson-Anson H, Gage FH (1996) Neurogenesis in the dentate gyrus of the adult rat: age-related decrease of neuronal progenitor proliferation. J Neurosci 16:2027–2033
Lazic SE, Grote H, Armstrong RJ, Blakemore C, Hannan AJ, Van Dellen A, Barker RA (2004) Decreased hippocampal cell proliferation in R6/1 Huntington’s mice. NeuroReport 15:811–813. https://doi.org/10.1097/00001756-200404090-00014
Lee CH, Choi JH, Yoo KY, Park OK, Moon JB, Sohn Y, Cho JH, Hwang IK, Won MH (2010) Rosiglitazone, an agonist of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma, decreases immunoreactivity of markers for cell proliferation and neuronal differentiation in the mouse hippocampus. Brain Res 1329:30–35. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainres.2010.03.027
Li G, Zhou L, Zhu Y, Wang C, Sha S, Xian X, Ji Y, Liu G, Chen L (2015) Seipin knockout in mice impairs stem cell proliferation and progenitor cell differentiation in the adult hippocampal dentate gyrus via reduced levels of PPARgamma. Dis Model Mech 8:1615–1624. https://doi.org/10.1242/dmm.021550
Lie DC, Colamarino SA, Song HJ, Desire L, Mira H, Consiglio A, Lein ES, Jessberger S, Lansford H, Dearie AR, Gage FH (2005) Wnt signalling regulates adult hippocampal neurogenesis. Nature 437:1370–1375. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature04108
Lieberwirth C, Liu Y, Jia X, Wang Z (2012) Social isolation impairs adult neurogenesis in the limbic system and alters behaviors in female prairie voles. Horm Behav 62:357–366. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yhbeh.2012.03.005
Lim J, Bang Y, Choi HJ (2018) Abnormal hippocampal neurogenesis in Parkinson’s disease: relevance to a new therapeutic target for depression with Parkinson’s disease. Arch Pharmacal Res 41:943–954. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-018-1063-x
Lindgren L, Bergdahl J, Nyberg L (2016) Longitudinal evidence for smaller hippocampus volume as a vulnerability factor for perceived stress. Cereb Cortex 26:3527–3533. https://doi.org/10.1093/cercor/bhw154
Liu H, Song N (2016) Molecular mechanism of adult neurogenesis and its association with human brain diseases. J Cent Nerv Syst Dis 8:5–11. https://doi.org/10.4137/JCNSD.S32204
Locci A, Geoffroy P, Miesch M, Mensah-Nyagan AG, Pinna G (2017) Social isolation in early versus late adolescent mice is associated with persistent behavioral deficits that can be improved by neurosteroid-based treatment. Front Cell Neurosci 11:208. https://doi.org/10.3389/fncel.2017.00208
Lv S, Wang W, Wang H, Zhu Y, Lei C (2019) PPARgamma activation serves as therapeutic strategy against bladder cancer via inhibiting PI3K-Akt signaling pathway. BMC Cancer 19:204. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12885-019-5426-6
Malberg JE, Eisch AJ, Nestler EJ, Duman RS (2000) Chronic antidepressant treatment increases neurogenesis in adult rat hippocampus. J Neurosci 20:9104–9110. https://doi.org/10.1523/jneurosci.20-24-09104.2000
Marder W, Khalatbari S, Myles JD, Hench R, Lustig S, Yalavarthi S, Parameswaran A, Brook RD, Kaplan MJ (2013) The peroxisome proliferator activated receptor-gamma pioglitazone improves vascular function and decreases disease activity in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. J Am Heart Assoc 2:e000441. https://doi.org/10.1161/JAHA.113.000441
Margeli A, Kouraklis G, Theocharis S (2003) Peroxisome proliferator activated receptor-gamma (PPAR-gamma) ligands and angiogenesis. Angiogenesis 6:165–169. https://doi.org/10.1023/B:AGEN.0000021377.13669.c0
Martinez L, Berenguer M, Bruce MC, Le Marchand-Brustel Y, Govers R (2010) Rosiglitazone increases cell surface GLUT4 levels in 3T3-L1 adipocytes through an enhancement of endosomal recycling. Biochem Pharmacol 79:1300–1309. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcp.2009.12.013
Masciopinto F, Di Pietro N, Corona C, Bomba M, Pipino C, Curcio M, Di Castelnuovo A, Ciavardelli D, Silvestri E, Canzoniero LM, Sekler I, Pandolfi A, Sensi SL (2012) Effects of long-term treatment with pioglitazone on cognition and glucose metabolism of PS1-KI, 3xTg-AD, and wild-type mice. Cell Death Dis 3:e448. https://doi.org/10.1038/cddis.2012.189
Meng Y, Chen C, Tian C, Du J, Li HH (2015) Angiotensin II-induced Egr-1 expression is suppressed by peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma ligand 15d-PGJ(2) in macrophages. Cell Physiol Biochem 35:689–698. https://doi.org/10.1159/000369729
Ming GL, Song H (2011) Adult neurogenesis in the mammalian brain: significant answers and significant questions. Neuron 70:687–702. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2011.05.001
Miranda M, Morici JF, Zanoni MB, Bekinschtein P (2019) Brain-derived neurotrophic factor: a key molecule for memory in the healthy and the pathological brain. Front Cell Neurosci 13:363. https://doi.org/10.3389/fncel.2019.00363
Morales-Garcia JA, Luna-Medina R, Alfaro-Cervello C, Cortes-Canteli M, Santos A, Garcia-Verdugo JM, Perez-Castillo A (2011) Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma ligands regulate neural stem cell proliferation and differentiation in vitro and in vivo. Glia 59:293–307. https://doi.org/10.1002/glia.21101
Moreno S, Farioli-Vecchioli S, Ceru MP (2004) Immunolocalization of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors and retinoid X receptors in the adult rat CNS. Neuroscience 123:131–145. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2003.08.064
Mu Y, Lee SW, Gage FH (2010) Signaling in adult neurogenesis. Curr Opin Neurobiol 20:416–423. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conb.2010.04.010
Murai K, Qu Q, Sun G, Ye P, Li W, Asuelime G, Sun E, Tsai GE, Shi Y (2014) Nuclear receptor TLX stimulates hippocampal neurogenesis and enhances learning and memory in a transgenic mouse model. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 111:9115–9120. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1406779111
Niklison-Chirou MV, Agostini M, Amelio I, Melino G (2020) Regulation of adult neurogenesis in mammalian brain. Int J Mol Sci. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21144869
Ohta K, Endo T, Haraguchi K, Hershman JM, Onaya T (2001) Ligands for peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma inhibit growth and induce apoptosis of human papillary thyroid carcinoma cells. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 86:2170–2177. https://doi.org/10.1210/jcem.86.5.7493
Parent JM, Yu TW, Leibowitz RT, Geschwind DH, Sloviter RS, Lowenstein DH (1997) Dentate granule cell neurogenesis is increased by seizures and contributes to aberrant network reorganization in the adult rat hippocampus. J Neurosci 17:3727–3738
Parihar VK, Hattiangady B, Shuai B, Shetty AK (2013) Mood and memory deficits in a model of Gulf War illness are linked with reduced neurogenesis, partial neuron loss, and mild inflammation in the hippocampus. Neuropsychopharmacology 38:2348–2362. https://doi.org/10.1038/npp.2013.158
Pedersen WA, Mcmillan PJ, Kulstad JJ, Leverenz JB, Craft S, Haynatzki GR (2006) Rosiglitazone attenuates learning and memory deficits in Tg2576 Alzheimer mice. Exp Neurol 199:265–273. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.expneurol.2006.01.018
Prakash A, Kumar A (2014) Role of nuclear receptor on regulation of BDNF and neuroinflammation in hippocampus of beta-amyloid animal model of Alzheimer’s disease. Neurotox Res 25:335–347. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12640-013-9437-9
Pushpakom S, Iorio F, Eyers PA, Escott KJ, Hopper S, Wells A, Doig A, Guilliams T, Latimer J, Mcnamee C, Norris A, Sanseau P, Cavalla D, Pirmohamed M (2019) Drug repurposing: progress, challenges and recommendations. Nat Rev Drug Discov 18:41–58. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrd.2018.168
Reddy RC, Srirangam A, Reddy K, Chen J, Gangireddy S, Kalemkerian GP, Standiford TJ, Keshamouni VG (2008) Chemotherapeutic drugs induce PPAR-gamma expression and show sequence-specific synergy with PPAR-gamma ligands in inhibition of non-small cell lung cancer. Neoplasia 10:597–603. https://doi.org/10.1593/neo.08134
Robinson-Rechavi M, Escriva Garcia H, Laudet V (2003) The nuclear receptor superfamily. J Cell Sci 116:585–586. https://doi.org/10.1242/jcs.00247
Rodriguez JJ, Jones VC, Tabuchi M, Allan SM, Knight EM, Laferla FM, Oddo S, Verkhratsky A (2008) Impaired adult neurogenesis in the dentate gyrus of a triple transgenic mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. PLoS ONE 3:e2935. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0002935
Rosa AO, Kaster MP, Binfare RW, Morales S, Martin-Aparicio E, Navarro-Rico ML, Martinez A, Medina M, Garcia AG, Lopez MG, Rodrigues AL (2008) Antidepressant-like effect of the novel thiadiazolidinone NP031115 in mice. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 32:1549–1556. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pnpbp.2008.05.020
Sadaghiani MS, Javadi-Paydar M, Gharedaghi MH, Fard YY, Dehpour AR (2011) Antidepressant-like effect of pioglitazone in the forced swimming test in mice: the role of PPAR-gamma receptor and nitric oxide pathway. Behav Brain Res 224:336–343. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbr.2011.06.011
Sharma AN, Elased KM, Lucot JB (2012) Rosiglitazone treatment reversed depression-but not psychosis-like behavior of db/db diabetic mice. J Psychopharmacol 26:724–732. https://doi.org/10.1177/0269881111434620
Shi Y, Chichung Lie D, Taupin P, Nakashima K, Ray J, Yu RT, Gage FH, Evans RM (2004) Expression and function of orphan nuclear receptor TLX in adult neural stem cells. Nature 427:78–83. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature02211
Shimazu T, Inoue I, Araki N, Asano Y, Sawada M, Furuya D, Nagoya H, Greenberg JH (2005) A peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma agonist reduces infarct size in transient but not in permanent ischemia. Stroke 36:353–359. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.STR.0000152271.21943.a2
Sung PS, Lin PY, Liu CH, Su HC, Tsai KJ (2020) Neuroinflammation and neurogenesis in Alzheimer’s disease and potential therapeutic approaches. Int J Mol Sci. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21030701
Toaldo C, Pizzimenti S, Cerbone A, Pettazzoni P, Menegatti E, Daniela B, Minelli R, Giglioni B, Dianzani MU, Ferretti C, Barrera G (2010) PPARgamma ligands inhibit telomerase activity and hTERT expression through modulation of the Myc/Mad/Max network in colon cancer cells. J Cell Mol Med 14:1347–1357. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1582-4934.2009.00966.x
Tobin MK, Musaraca K, Disouky A, Shetti A, Bheri A, Honer WG, Kim N, Dawe RJ, Bennett DA, Arfanakis K, Lazarov O (2019) Human hippocampal neurogenesis persists in aged adults and Alzheimer’s disease patients. Cell Stem Cell 24:974-982 e973. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.stem.2019.05.003
Trombetta A, Maggiora M, Martinasso G, Cotogni P, Canuto RA, Muzio G (2007) Arachidonic and docosahexaenoic acids reduce the growth of A549 human lung-tumor cells increasing lipid peroxidation and PPARs. Chem Biol Interact 165:239–250. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbi.2006.12.014
Troubat R, Barone P, Leman S, Desmidt T, Cressant A, Atanasova B, Brizard B, El Hage W, Surget A, Belzung C, Camus V (2021) Neuroinflammation and depression: a review. Eur J Neurosci 53:151–171. https://doi.org/10.1111/ejn.14720
Tsubouchi Y, Sano H, Kawahito Y, Mukai S, Yamada R, Kohno M, Inoue K, Hla T, Kondo M (2000) Inhibition of human lung cancer cell growth by the peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma agonists through induction of apoptosis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 270:400–405. https://doi.org/10.1006/bbrc.2000.2436
Tufano M, Pinna G (2020) Is there a future for PPARs in the treatment of neuropsychiatric disorders? Molecules. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25051062
Wada K, Nakajima A, Katayama K, Kudo C, Shibuya A, Kubota N, Terauchi Y, Tachibana M, Miyoshi H, Kamisaki Y, Mayumi T, Kadowaki T, Blumberg RS (2006) Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma-mediated regulation of neural stem cell proliferation and differentiation. J Biol Chem 281:12673–12681. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M513786200
Wang BW, Hok V, Della-Chiesa A, Callaghan C, Barlow S, Tsanov M, Bechara R, Irving E, Virley DJ, Upton N, O’mara SM (2012) Rosiglitazone enhances learning, place cell activity, and synaptic plasticity in middle-aged rats. Neurobiol Aging 33(835):e813-830. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2011.08.013
Warden A, Truitt J, Merriman M, Ponomareva O, Jameson K, Ferguson LB, Mayfield RD, Harris RA (2016) Localization of PPAR isotypes in the adult mouse and human brain. Sci Rep 6:27618. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep27618
Weikum ER, Liu X, Ortlund EA (2018) The nuclear receptor superfamily: a structural perspective. Protein Sci 27:1876–1892. https://doi.org/10.1002/pro.3496
Winner B, Desplats P, Hagl C, Klucken J, Aigner R, Ploetz S, Laemke J, Karl A, Aigner L, Masliah E, Buerger E, Winkler J (2009) Dopamine receptor activation promotes adult neurogenesis in an acute Parkinson model. Exp Neurol 219:543–552. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.expneurol.2009.07.013
Winner B, Regensburger M, Schreglmann S, Boyer L, Prots I, Rockenstein E, Mante M, Zhao C, Winkler J, Masliah E, Gage FH (2012) Role of alpha-synuclein in adult neurogenesis and neuronal maturation in the dentate gyrus. J Neurosci 32:16906–16916. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2723-12.2012
Xue H, Li J, Xie H, Wang Y (2018) Review of drug repositioning approaches and resources. Int J Biol Sci 14:1232–1244. https://doi.org/10.7150/ijbs.24612
Yang ZH, Miyahara H, Iwasaki Y, Takeo J, Katayama M (2013) Dietary supplementation with long-chain monounsaturated fatty acids attenuates obesity-related metabolic dysfunction and increases expression of PPAR gamma in adipose tissue in type 2 diabetic KK-Ay mice. Nutr Metab 10:16. https://doi.org/10.1186/1743-7075-10-16
Yau H, Rivera K, Lomonaco R, Cusi K (2013) The future of thiazolidinedione therapy in the management of type 2 diabetes mellitus. Curr DiabRep 13:329–341. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11892-013-0378-8
Zhao X, Sun G, Zhang J, Strong R, Song W, Gonzales N, Grotta JC, Aronowski J (2007) Hematoma resolution as a target for intracerebral hemorrhage treatment: role for peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma in microglia/macrophages. Ann Neurol 61:352–362. https://doi.org/10.1002/ana.21097
Zhao X, Strong R, Zhang J, Sun G, Tsien JZ, Cui Z, Grotta JC, Aronowski J (2009) Neuronal PPARgamma deficiency increases susceptibility to brain damage after cerebral ischemia. J Neurosci 29:6186–6195. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5857-08.2009
Zhou L, Yin J, Wang C, Liao J, Liu G, Chen L (2014) Lack of seipin in neurons results in anxiety- and depression-like behaviors via down regulation of PPARgamma. Hum Mol Genet 23:4094–4102. https://doi.org/10.1093/hmg/ddu126
Ziabreva I, Perry E, Perry R, Minger SL, Ekonomou A, Przyborski S, Ballard C (2006) Altered neurogenesis in Alzheimer’s disease. J Psychosom Res 61:311–316. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpsychores.2006.07.017
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the GRRC program of Gyeonggi Province [GRRC-CHA2017-A01, Validity and Safety Evaluation of Regional Specialized Resources]; the Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Science, ICT & Future Planning [Grant Numbers: NRF-2018R1A2B6004008 and NRF-2019M3A9A8067070]; and the Ministry of Education [Grant Number: NRF-2019R1I1A1A01063630].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lim, J., Kim, H.I., Bang, Y. et al. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma: a novel therapeutic target for cognitive impairment and mood disorders that functions via the regulation of adult neurogenesis. Arch. Pharm. Res. 44, 553–563 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-021-01333-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-021-01333-7