Abstract
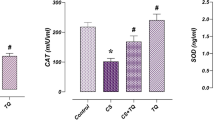
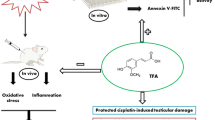
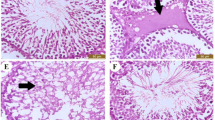
The clinical application of the anticancer drug cisplatin is limited by its deleterious side effects, including male reproductive toxicity. In this context, the potential protective effect of carvedilol on testicular and spermatological damage induced by cisplatin in male Sprague–Dawley rats was investigated. Carvedilol was orally administered at a dose of 10 mg/kg for 2 weeks, and cisplatin was given as a single intraperitoneal injection of 10 mg/kg on the 12th day to induce toxicity. Cisplatin significantly reduced reproductive organ weight, sperm count and sperm motility, and increased sperm abnormalities and histopathological damage of testicular tissue. In addition, it resulted in a significant decline in serum testosterone as well as levels of testicular enzymatic and non-enzymatic antioxidants (superoxide dismutase, catalase, glutathione peroxides, and reduced glutathione). Moreover, cisplatin remarkably augmented malondialdehyde, nitric oxide, tumor necrosis factor-α, and nuclear factor-kappa B contents in testicular tissue. Conversely, carvedilol administration markedly mitigated cisplatin-induced testicular and spermatological injury as demonstrated by suppression of oxidative/nitrosative and inflammatory burden, amendment of antioxidant defenses, enhancement of steroidogenesis and spermatogenesis, and mitigation of testicular histopathological damage. The current study reveals a promising protective action of carvedilol against cisplatin-induced reproductive toxicity by virtue of its anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adejuwon SA, Femi-Akinlosotu OM, Omirinde JO (2015) Cisplatin-induced testicular dysfunction and its amelioration by Launaea taraxacifolia leaf extract. Andrologia 47:553–559
Ahmed LA, Shehata NI, Abdelkader NF, Khattab MM (2014) Tempol, a superoxide dismutase mimetic agent, ameliorates cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity through alleviation of mitochondrial dysfunction in mice. PLoS One 9:e108889
Aitken RJ, Curry BJ (2011) Redox regulation of human sperm function: from the physiological control of sperm capacitation to the etiology of infertility and DNA damage in the germ line. Antioxid Redox Signal 14:367–381
Alfieri AB, Briceno L, Fragasso G, Spoladore R, Palloshi A, Bassanelli G, Montano C, Arioli F, Cuko A, Ruotolo G, Margonato A (2008) Differential long-term effects of carvedilol on proinflammatory and antiinflammatory cytokines, asymmetric dimethylarginine, and left ventricular function in patients with heart failure. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 52:49–54
Almaghrabi OA (2015) Molecular and biochemical investigations on the effect of quercetin on oxidative stress induced by cisplatin in rat kidney. Saudi J Biol Sci 22:227–231
Amin A, Hamza AA, Kambal A, Daoud S (2008) Herbal extracts counteract cisplatin-mediated cell death in rat testis. Asian J Androl 10:291–297
Amin A, Abraham C, Hamza AA, Abdalla ZA, Al-Shamsi SB, Harethi SS, Daoud S (2012) A standardized extract of Ginkgo biloba neutralizes cisplatin-mediated reproductive toxicity in rats. J Biomed Biotechnol. doi:10.1155/2012/362049
Arab HH, El-Sawalhi MM (2013) Carvedilol alleviates adjuvant-induced arthritis and subcutaneous air pouch edema: modulation of oxidative stress and inflammatory mediators. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 268:241–248
Arozal W, Watanabe K, Veeraveedu PT, Ma M, Thandavarayan RA, Sukumaran V, Suzuki K, Kodama M, Aizawa Y (2010) Protective effect of carvedilol on daunorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity and nephrotoxicity in rats. Toxicol 274:18–26
Atessahin A, Sahna E, Turk G, Ceribasi AO, Yilmaz S, Yuce A, Bulmus O (2006) Chemoprotective effect of melatonin against cisplatin-induced testicular toxicity in rats. J Pineal Res 41:21–27
Bearden HJ, Fluquary J (1980) Applied animal reproduction. Restore Publishing Co. Inc., Reston
Beutler E, Duron O, Kelly BM (1963) Improved method for the determination of blood glutathione. J Lab Clin Med 61:882–888
Beytur A, Ciftci O, Oguz F, Oguzturk H, Yilmaz F (2012) Montelukast attenuates side effects of cisplatin including testicular, spermatological, and hormonal damage in male rats. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 69:207–213
Boekelheide K (2005) Mechanisms of toxic damage to spermatogenesis. J Natl Cancer Inst Monogr 34:6–8
Bubici C, Papa S, Dean K, Franzoso G (2006) Mutual cross-talk between reactive oxygen species and nuclear factor-kappa B: molecular basis and biological significance. Oncog 25:6731–6748
Carvalho Rodrigues MA, Silva Faria MC, Santos NA, Gobe GC, Dos Santos AC (2013) Carvedilol efficiently protects kidneys without affecting the antitumor efficacy of cisplatin in mice. Chem Biol Interact 206:90–99
Chirino YI, Pedraza-Chaverri J (2009) Role of oxidative and nitrosative stress in cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity. Exp Toxicol Pathol 61:223–242
Ciftci O, Cetin A, Aydin M, Kaya K, Oguz F (2014) Fish oil, contained in eicosapentaenoic acid and docosahexaenoic acid, attenuates testicular and spermatological damage induced by cisplatin in rats. Andrologia 46:1161–1168
Dandona P, Ghanim H, Brooks DP (2007) Antioxidant activity of carvedilol in cardiovascular disease. J Hypertens 25:731–741
Erdinçler DS, Seven A, Inci F, Beǧer T, Candan G (1997) Lipid peroxidation and oxidant status in experimental animals: effect of aging and hypercholestrolemic diet. Clin Chim Acta 265:77–84
Fung C, Vaughn DJ (2011) Complications associated with chemotherapy in testicular cancer management. Nat Rev Urol 8:213–222
Hamdy N, El-Demerdash E (2012) New therapeutic aspect for carvedilol: antifibrotic effects of carvedilol in chronic carbon tetrachloride-induced liver damage. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 261:292–299
Hamza AA, Elwy HM, Badawi AM (2016) Fenugreek seed extract attenuates cisplatin-induced testicular damage in Wistar rats. Andrologia 48:211–221
Hayashi T, De Velasco MA, Saitou Y, Nose K, Nishioka T, Ishii T, Uemura H (2010) Carvedilol protects tubular epithelial cells from ischemia–reperfusion injury by inhibiting oxidative stress. Int J Urol 17:989–995
Ilbey YO, Ozbek E, Simsek A, Otunctemur A, Cekmen M, Somay A (2009) Potential chemoprotective effect of melatonin in cyclophosphamide- and cisplatin-induced testicular damage in rats. Fertil Steril 92:1124–1132
Kawai Y, Nakao T, Kunimura N, Kohda Y, Gemba M (2006) Relationship of intracellular calcium and oxygen radicals to Cisplatin-related renal cell injury. J Pharmacol Sci 100:65–72
Kaya K, Ciftci O, Cetin A, Dogan H, Basak N (2015) Hesperidin protects testicular and spermatological damages induced by cisplatin in rats. Andrologia 47:793–800
Kelland L (2007) The resurgence of platinum-based cancer chemotherapy. Nat Rev Cancer 7:573–584
Khan MA, Liu J, Kumar G, Skapek SX, Falck JR, Imig JD (2013) Novel orally active epoxyeicosatrienoic acid (EET) analogs attenuate cisplatin nephrotoxicity. FASEB J 27:2946–2956
Kleinert H, Pautz A, Linker K, Schwarz PM (2004) Regulation of the expression of inducible nitric oxide synthase. Eur J Pharmacol 500:255–266
Kumar A, Dogra S (2009) Neuroprotective effect of carvedilol, an adrenergic antagonist against colchicine induced cognitive impairment and oxidative damage in rat. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 92:25–31
Lin P-Y, Shen H-C, Chen C-J, Wu S-E, Kao H-L, Huang J-H, Wang D, Chen S-C (2010) The inhibition in tumor necrosis factor-α-induced attenuation in endothelial thrombomodulin expression by carvedilol is mediated by nuclear factor-κB and reactive oxygen species. J Thromb Thrombolysis 29:52–59
Longo V, Gervasi PG, Lubrano V (2011) Cisplatin induced toxicity in rat tissues: the protective effect of Lisosan G. Food Chem Toxicol 49:233–237
Migliavacca E, Ancerewicz J, Carrupt P-A, Testa B (1998) Theoretical parameters to characterize antioxidants. Part 2. The cases of melatonin and carvedilol. Helv Chim Acta 81:1337–1348
Naidu PS, Singh A, Kulkarni SK (2002) Carvedilol attenuates neuroleptic-induced orofacial dyskinesia: possible antioxidant mechanisms. Br J Pharmacol 136:193–200
Nakayama K, Milbourne A, Schover LR, Champlin RE, Ueno NT (2008) Gonadal failure after treatment of hematologic malignancies: from recognition to management for health-care providers. Nat Clin Pract Oncol 5:78–89
Oliveira PJ, Bjork JA, Santos MS, Leino RL, Froberg MK, Moreno AJ, Wallace KB (2004) Carvedilol-mediated antioxidant protection against doxorubicin-induced cardiac mitochondrial toxicity. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 200:159–168
Parlaktas BS, Atilgan D, Gencten Y, Akbas A, Markoc F, Erdemir F, Ozyurt H, Uluocak N (2014) The effects of carvedilol on ischemia-reperfusion injury in the rat testis. Int Braz J Urol 40:109–117
Ramzy MM, El-Sheikh AA, Kamel MY, Abdelwahab SA, Morsy MA (2014) Mechanism of testicular protection of carvedilol in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Indian J Pharmacol 46:161–165
Rezvanfar MA, Rezvanfar MA, Shahverdi AR, Ahmadi A, Baeeri M, Mohammadirad A, Abdollahi M (2013) Protection of cisplatin-induced spermatotoxicity, DNA damage and chromatin abnormality by selenium nano-particles. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 266:356–365
Rodrigues MA, Rodrigues JL, Martins NM, Barbosa F, Curti C, Santos NA, Santos AC (2011) Carvedilol protects against cisplatin-induced oxidative stress, redox state unbalance and apoptosis in rat kidney mitochondria. Chem Biol Interact 189:45–51
Sahu BD, Koneru M, Bijargi SR, Kota A, Sistla R (2014) Chromium-induced nephrotoxicity and ameliorative effect of carvedilol in rats: involvement of oxidative stress, apoptosis and inflammation. Chem Biol Interact 223C:69–79
Salem EA, Salem NA, Maarouf AM, Serefoglu EC, Hellstrom WJ (2012) Selenium and lycopene attenuate cisplatin-induced testicular toxicity associated with oxidative stress in Wistar rats. Urology 79:1184.e1–1184.e6
Sari FR, Arozal W, Watanabe K, Harima M, Veeravedu PT, Thandavarayan RA, Suzuki K, Arumugam S, Soetikno V, Kodama M (2011) Carvedilol attenuates inflammatory-mediated cardiotoxicity in daunorubicin-induced rats. Pharmaceuticals 4:551–566
Savoia C, Schiffrin EL (2007) Vascular inflammation in hypertension and diabetes: molecular mechanisms and therapeutic interventions. Clin Sci 112:375–384
Sherif IO, Abdel-Aziz A, Sarhan OM (2014) Cisplatin-induced testicular toxicity in rats: the protective effect of arjunolic acid. J Biochem Mol Toxicol 28:515–521
Stahl O, Eberhard J, Jepson K, Spano M, Cwikiel M, Cavallin-Stahl E, Giwercman A (2006) Sperm DNA integrity in testicular cancer patients. Hum Reprod 21:3199–3205
Tak PP, Firestein GS (2001) NF-kappa B: a key role in inflammatory diseases. J Clin Invest 107:7–11
Todd RC, Lippard SJ (2009) Inhibition of transcription by platinum antitumor compounds. Metallomics 1:280–291
Tomao F, Miele E, Spinelli G, Tomao S (2006) Anticancer treatment and fertility effects. Literature review. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 25:475–481
Wilop S, Von Hobe S, Crysandt M, Esser A, Osieka R, Jost E (2009) Impact of angiotensin I converting enzyme inhibitors and angiotensin II type 1 receptor blockers on survival in patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer undergoing first-line platinum-based chemotherapy. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 135:1429–1435
Yang SP, Ho LJ, Lin YL, Cheng SM, Tsao TP, Chang DM, Hsu YL, Shih CY, Juan TY, Lai JH (2003) Carvedilol, a new antioxidative beta-blocker, blocks in vitro human peripheral blood T cell activation by downregulating NF-kappaB activity. Cardiovasc Res 59:776–787
Yao X, Panichpisal K, Kurtzman N, Nugent K (2007) Cisplatin nephrotoxicity: a review. Am J Med Sci 334:115–124
Yue TL, Cheng HY, Lysko PG, Mckenna PJ, Feuerstein R, Gu JL, Lysko KA, Davis LL, Feuerstein G (1992) Carvedilol, a new vasodilator and beta adrenoceptor antagonist, is an antioxidant and free radical scavenger. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 263:92–98
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to Prof. Dr. Bakeir A and Prof. Dr. Ahmed KA (Department of Histology, Faculty of Veterinary Medicine, Cairo University, Cairo, Egypt) for performing the histopathological and immunohistochemical examinations.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Eid, A.H., Abdelkader, N.F., Abd El-Raouf, O.M. et al. Carvedilol alleviates testicular and spermatological damage induced by cisplatin in rats via modulation of oxidative stress and inflammation. Arch. Pharm. Res. 39, 1693–1702 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-016-0833-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-016-0833-6