Abstract
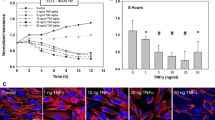
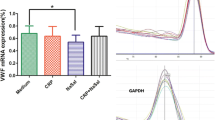
Carvedilol, a nonselective β-adrenoceptor antagonist, has been shown to possess antioxidant effects and reduce the risk of hospitalization and death in patients with severe congestive heart failure, which is featured by the activation of pro-inflammatory cytokines, including tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), and leads to thrombotic complications. Thrombomodulin (TM) plays protective roles against thrombosis. Treatment of ECs with TNF-α resulted in a down-regulation in the TM expression in a time-dependent manner. Pre-treatment of ECs with carvedilol (1 and 10 μM) for 1 h significantly up-regulated the TM expression in ECs in response to TNF-α. When ECs were pre-treated with a nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) inhibitor, i.e., parthenolide, their TNF-α-mediated down-regulation of TM expression was inhibited. Pre-treatment of ECs with carvedilol inhibited the NF-κB-DNA binding activity in ECs induced by TNF-α. Our findings provide insights into the mechanisms by which carvedilol exerts anti-thrombotic effects by inducing TM expression in ECs in response to pro-inflammatory stimulation.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rauchhaus M, Doehner W, Francis DP, Davos C, Kemp M, Liebenthal C, Niebauer J, Hooper J, Volk HD, Coats AJ, Anker SD (2000) Plasma cytokine parameters and mortality in patients with chronic heart failure. Circulation 102:3060–3067
Tsutamoto T, Hisanaga T, Wada A, Maeda K, Ohnishi M, Fukai D, Mabuchi N, Sawaki M, Kinoshita M (1998) Interleukin-6 spillover in the peripheral circulation increases with the severity of heart failure, and the high plasma level of interleukin-6 is an important prognostic predictor in patients with congestive heart failure. J Am Coll Cardiol 31:391–398. doi:10.1016/S0735-1097(97)00494-4
Testa M, Yeh M, Lee P, Fanelli R, Loperfido F, Berman JW, LeJemtel TH (1996) Circulating levels of cytokines and their endogenous modulators in patients with mild to severe congestive heart failure due to coronary artery disease or hypertension. J Am Coll Cardiol 28:964–971. doi:10.1016/S0735-1097(96)00268-9
Torre-Amione G, Kapadia S, Benedict C, Oral H, Young JB, Mann DL (1996) Proinflammatory cytokine levels in patients with depressed left ventricular ejection fraction: a report from the studies of left ventricular dysfunction (SOLVD). J Am Coll Cardiol 27:1201–1206. doi:10.1016/0735-1097(95)00589-7
Deswal A, Petersen NJ, Feldman AM, Young JB, White BG, Mann DL (2001) Cytokines and cytokine receptors in advanced heart failure: an analysis of the cytokine database from the vesnarinone trial (VEST). Circulation 103:2055–2059
Yokoyama T, Vaca L, Rossen RD, Durante W, Hazarika P, Mann DL (1993) Cellular basis for the negative inotropic effects of tumor necrosis factor-alpha in the adult mammalian heart. J Clin Invest 92:2303–2312. doi:10.1172/JCI116834
Mann DL (2002) Inflammatory mediators and the failing heart: past, present, and the foreseeable future. Circ Res 91:988–998. doi:10.1161/01.RES.0000043825.01705.1B
Madge LA, Pober JS (2001) TNF signaling in vascular endothelial cells. Exp Mol Pathol 70:317–325. doi:10.1006/exmp.2001.2368
Harrison DG (1997) Cellular and molecular mechanisms of endothelial cell dysfunction. J Clin Invest 100:2153–2157. doi:10.1172/JCI119751
Nichols AJ, Sulpizio AC, Ashton DJ, Hieble JP, Ruffolo RR Jr (1989) In vitro pharmacologic profile of the novel beta-adrenoceptor antagonist and vasodilator, carvedilol. Pharmacology 39:327–336. doi:10.1159/000138616
Packer M, Coats AJ, Fowler MB, Katus HA, Krum H, Mohacsi P, Rouleau JL, Tendera M, Castaigne A, Roecker EB et al (2001) Effect of carvedilol on survival in severe chronic heart failure. N Engl J Med 344:1651–1658. doi:10.1056/NEJM200105313442201
Cinquegrana G, D’Aniello L, Landi M, Spinelli L, Grande G, De Prisco F, Petretta M (2005) Effects of different degrees of sympathetic antagonism on cytokine network in patients with ischemic dilated cardiomyopathy. J Card Fail 11:213–219. doi:10.1016/j.cardfail.2004.07.006
Fahlbusch SA, Tsikas D, Mehls C, Gutzki FM, Boger RH, Frolich JC, Stichtenoth DO (2004) Effects of carvedilol on oxidative stress in human endothelial cells and healthy volunteers. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 60:83–88. doi:10.1007/s00228-004-0729-0
Kukin ML, Kalman J, Charney RH, Levy DK, Buchholz-Varley C, Ocampo ON, Eng C (1999) Prospective, randomized comparison of effect of long-term treatment with metoprolol or carvedilol on symptoms, exercise, ejection fraction, and oxidative stress in heart failure. Circulation 99:2645–2651
Lysko PG, Webb CL, Gu JL, Ohlstein EH, Ruffolo RR Jr, Yue TL (2000) A comparison of carvedilol and metoprolol antioxidant activities in vitro. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 36:277–281. doi:10.1097/00005344-200008000-00020
Nakamura K, Kusano K, Nakamura Y, Kakishita M, Ohta K, Nagase S, Yamamoto M, Miyaji K, Saito H, Morita H et al (2002) Carvedilol decreases elevated oxidative stress in human failing myocardium. Circulation 105:2867–2871. doi:10.1161/01.CIR.0000018605.14470.DD
Yuan Z, Shioji K, Kihara Y, Takenaka H, Onozawa Y, Kishimoto C (2004) Cardioprotective effects of carvedilol on acute autoimmune myocarditis: anti-inflammatory effects associated with antioxidant property. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 286:H83–H90. doi:10.1152/ajpheart.00536.2003
Yue TL, McKenna PJ, Gu JL, Cheng HY, Ruffolo RE Jr, Feuerstein GZ (1994) Carvedilol, a new vasodilating beta adrenoceptor blocker antihypertensive drug, protects endothelial cells from damage initiated by xanthine-xanthine oxidase and neutrophils. Cardiovasc Res 28:400–406. doi:10.1093/cvr/28.3.400
Frishman WH (1998) Carvedilol. N Engl J Med 339:1759–1765. doi:10.1056/NEJM199812103392407
Yue TL, McKenna PJ, Lysko PG, Gu JL, Lysko KA, Ruffolo RR Jr, Feuerstein GZ (1994) SB 211475, a metabolite of carvedilol, a novel antihypertensive agent, is a potent antioxidant. Eur J Pharmacol 251:237–243. doi:10.1016/0014-2999(94)90405-7
Aruoma OI (1997) Scavenging of hypochlorous acid by carvedilol and ebselen in vitro. Gen Pharmacol 28:269–272. doi:10.1016/S0306-3623(96)00232-7
Poole-Wilson PA, Swedberg K, Cleland JG, Di Lenarda A, Hanrath P, Komajda M, Lubsen J, Lutiger B, Metra M, Remme WJ et al (2003) Comparison of carvedilol and metoprolol on clinical outcomes in patients with chronic heart failure in the carvedilol or metoprolol european trial (COMET): randomised controlled trial. Lancet 362:7–13. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(03)13800-7
Uretsky BF, Thygesen K, Armstrong PW, Cleland JG, Horowitz JD, Massie BM, Packer M, Poole-Wilson PA, Ryden L (2000) Acute coronary findings at autopsy in heart failure patients with sudden death: results from the assessment of treatment with lisinopril and survival (ATLAS) trial. Circulation 102:611–616
Narang R, Cleland JG, Erhardt L, Ball SG, Coats AJ, Cowley AJ, Dargie HJ, Hall AS, Hampton JR, Poole-Wilson PA (1996) Mode of death in chronic heart failure. A request and proposition for more accurate classification. Eur Heart J 17:1390–1403
Sohn RH, Deming CB, Johns DC, Champion HC, Bian C, Gardner K, Rade JJ (2005) Regulation of endothelial thrombomodulin expression by inflammatory cytokines is mediated by activation of nuclear factor-kappa B. Blood 105:3910–3917. doi:10.1182/blood-2004-03-0928
Chiu JJ, Wung BS, Hsieh HJ, Lo LW, Wang DL (1999) Nitric oxide regulates shear stress-induced early growth response-1. Expression via the extracellular signal-regulated kinase pathway in endothelial cells. Circ Res 85:238–246
Hsieh HJ, Cheng CC, Wu ST, Chiu JJ, Wung BS, Wang DL (1998) Increase of reactive oxygen species (ROS) in endothelial cells by shear flow and involvement of ROS in shear-induced c-fos expression. J Cell Physiol 175:156–162. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1097-4652(199805)175:2<156::AID-JCP5>3.0.CO;2-N
Sundaresan M, Yu ZX, Ferrans VJ, Irani K, Finkel T (1995) Requirement for generation of H2O2 for platelet-derived growth factor signal transduction. Science 270:296–299. doi:10.1126/science.270.5234.296
Chen JW, Lin FY, Chen YH, Wu TC, Chen YL, Lin SJ (2004) Carvedilol inhibits tumor necrosis factor-alpha-induced endothelial transcription factor activation, adhesion molecule expression, and adhesiveness to human mononuclear cells. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 24:2075–2081. doi:10.1161/01.ATV.0000145016.69181.fa
Mizuochi Y, Okajima K, Harada N, Molor-Erdene P, Uchiba M, Komura H, Tsuda T, Katsuya H (2007) Carvedilol, a nonselective beta-blocker, suppresses the production of tumor necrosis factor and tissue factor by inhibiting early growth response factor-1 expression in human monocytes in vitro. Transl Res 149:223–230. doi:10.1016/j.trsl.2006.11.008
Bridges AB, Scott NA, Belch JJ (1991) Probucol, a superoxide free radical scavenger in vitro. Atherosclerosis 89:263–265. doi:10.1016/0021-9150(91)90068-E
Zapolska-Downar D, Zapolski-Downar A, Markiewski M, Ciechanowicz A, Kaczmarczyk M, Naruszewicz M (2001) Selective inhibition by probucol of vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 (VCAM-1) expression in human vascular endothelial cells. Atherosclerosis 155:123–130. doi:10.1016/S0021-9150(00)00553-0
Offermann MK, Medford RM (1994) Antioxidants and atherosclerosis: a molecular perspective. Heart Dis Stroke 3:52–57
Weber C, Erl W, Pietsch A, Strobel M, Ziegler-Heitbrock HW, Weber PC (1994) Antioxidants inhibit monocyte adhesion by suppressing nuclear factor-kappa B mobilization and induction of vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 in endothelial cells stimulated to generate radicals. Arterioscler Thromb 14:1665–1673
Fruebis J, Gonzalez V, Silvestre M, Palinski W (1997) Effect of probucol treatment on gene expression of VCAM-1, MCP-1, and M-CSF in the aortic wall of LDL receptor-deficient rabbits during early atherogenesis. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 17:1289–1302
Yue TL, McKenna PJ, Gu JL, Cheng HY, Ruffolo RR Jr, Feuerstein GZ (1993) Carvedilol, a new antihypertensive agent, prevents lipid peroxidation and oxidative injury to endothelial cells. Hypertension 22:922–928
Oliveira PJ, Esteves T, Rolo AP, Palmeira CM, Moreno AJ (2004) Carvedilol inhibits the mitochondrial permeability transition by an antioxidant mechanism. Cardiovasc Toxicol 4:11–20. doi:10.1385/CT:4:1:11
Ohlstein EH, Arleth AJ, Storer B, Romanic AM (1998) Carvedilol inhibits endothelin-1 biosynthesis in cultured human coronary artery endothelial cells. J Mol Cell Cardiol 30:167–173. doi:10.1006/jmcc.1997.0582
Kalinowski L, Dobrucki LW, Szczepanska-Konkel M, Jankowski M, Martyniec L, Angielski S, Malinski T (2003) Third-generation beta-blockers stimulate nitric oxide release from endothelial cells through ATP efflux: a novel mechanism for antihypertensive action. Circulation 107:2747–2752. doi:10.1161/01.CIR.0000066912.58385.DE
Romeo F, Li D, Shi M, Mehta JL (2000) Carvedilol prevents epinephrine-induced apoptosis in human coronary artery endothelial cells: modulation of Fas/Fas ligand and caspase-3 pathway. Cardiovasc Res 45:788–794. doi:10.1016/S0008-6363(99)00369-7
Rossig L, Haendeler J, Mallat Z, Hugel B, Freyssinet JM, Tedgui A, Dimmeler S, Zeiher AM (2000) Congestive heart failure induces endothelial cell apoptosis: protective role of carvedilol. J Am Coll Cardiol 36:2081–2089. doi:10.1016/S0735-1097(00)01002-0
Yue TL, Cheng HY, Lysko PG, McKenna PJ, Feuerstein R, Gu JL, Lysko KA, Davis LL, Feuerstein G (1992) Carvedilol, a new vasodilator and beta adrenoceptor antagonist, is an antioxidant and free radical scavenger. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 263:92–98
Acknowledgments
This work was supported in part by Grant Taipei Medical University-Wan Fang Hospital (94TMU-WFH-08) to S.-C·S., Grant TPCH-98-A07 and Grant NSC 96-2752-B001-001-PAE to Danny Ling Wang.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lin, PY., Shen, HC., Chen, CJ. et al. The inhibition in tumor necrosis factor-α-induced attenuation in endothelial thrombomodulin expression by carvedilol is mediated by nuclear factor-κB and reactive oxygen species. J Thromb Thrombolysis 29, 52–59 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11239-009-0318-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11239-009-0318-2