Abstract
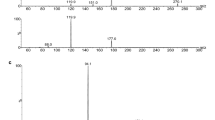
This study reports the pharmacokinetics and tissue distribution of a novel histone deacetylase and DNA methyltransferase inhibitor, psammaplin A (PsA), in mice. PsA concentrations were determined by a validated LC-MS/MS assay method (LLOQ 2 ng/mL). Following intravenous injection at a dose of 10 mg/kg in mice, PsA was rapidly eliminated, with the average half-life (t1/2, λn) of 9.9 ± 1.4 min and the systemic clearance (CLs) of 925.1 ± 570.1 mL/min. The in vitro stability of PsA was determined in different tissue homogenates. The average degradation t1/2 of PsA in blood, liver, kidney and lung was found relatively short (≤ 12.8 min). Concerning the in vivo tissue distribution characteristics, PsA was found to be highly distributed to lung tissues, with the lung-to-serum partition coefficients (Kp) ranging from 49.9 to 60.2. In contrast, PsA concentrations in other tissues were either comparable with or less than serum concentrations. The high and specific lung targeting characteristics indicates that PsA has the potential to be developed as a lung cancer treatment agent.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahn, M. Y., Jung, J. H., Na, Y. J., and Kim, H. S., A natural histone deacetylase inhibitor, Psammaplin A, induces cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in human endometrial cancer cells. Gynecol. Oncol., 108, 27–33 (2008).
Arabshahi, L. and Schmitz, F. J., Brominated tyrosine metabolites from an unidentified sponge. J. Org. Chem., 52, 3584–3586 (1987).
Brown, R. P., Delp, M. D., Lindstedt, S. L., Rhomberg, L. R., and Beliles, R. P., Physiological parameter values for physiologically based pharmacokinetic models. Toxicol. Ind. Health, 13, 407–484 (1997).
Davie, J. R., Covalent modifications of histones: expression from chromatin templates. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev., 8, 173–178 (1998).
Egger, G., Liang, G., Aparicio, A., and Jones, P. A., Epigenetics in human disease and prospects for epigenetic therapy. Nature, 429, 457–463 (2004).
Esteller, M., Relevance of DNA methylation in the management of cancer. Lancet Oncol., 4, 351–358 (2003).
Fouladi, M., Histone deacetylase inhibitors in cancer therapy. Cancer Invest., 24, 521–527 (2006).
Glozak, M. A. and Seto, E., Histone deacetylases and cancer. Oncogene, 26, 5420–5432 (2007).
Grignani, F., De, Matteis, S., Nervi, C., Tomassoni, L., Gelmetti, V., Cioce, M., Fanelli, M., Ruthardt, M., Ferrara, F. F., Zamir, I., Seiser, C., Grignani, F., Lazar, M. A., Minucci, S., and Pelicci, P. G., Fusion proteins of the retinoic acid receptor-alpha recruit histone deacetylase in promyelocytic leukaemia. Nature, 391, 815–818 (1998).
Jones, P. A. and Baylin, S. B., The fundamental role of epigenetic events in cancer. Nat. Rev. Genet., 3, 415–428 (2002).
Kim, D., Lee, I. S., Jung, J. H., Lee, C. O., and Choi, S. U., Psammaplin A, a natural phenolic compound, has inhibitory effect on human topoisomerase II and is cytotoxic to cancer cells. Anticancer Res., 19, 4085–4090 (1999a).
Kim, D., Lee, I. S., Jung, J. H., and Yang, S. I., Psammaplin A, a natural bromotyrosine derivative from a sponge, possesses the antibacterial activity against methicillinresistant Staphylococcus aureus and the DNA gyraseinhibitory activity. Arch. Pharm. Res., 22, 25–29 (1999b).
Kim, D. H., Shin, J., and Kwon, H. J., Psammaplin A is a natural prodrug that inhibits class I histone deacetylase. Exp. Mol. Med., 28, 47–55 (2007).
Kim, H. J., Kim, J. H., Chie, E. K., Young, P. D., Kim, I. A., and Kim, I. H., DNMT (DNA methyltransferase) inhibitors radiosensitize human cancer cells by suppressing DNA repair activity. Radiat. Oncol., 7, 39–48 (2012).
Litterst, C. L., Mimnaugh, E. G., Reagan, R. L., and Gram, T. E., Comparison of in vitro drug metabolism by lung, liver, and kidney of several common laboratory species. Drug Metab. Dispos., 3, 259–265 (1975).
Nan, X., Ng, H. H, Johnson, C. A., Laherty, C. D., Turner, B. M., Eisenman, R. N., and Bird, A., Transcriptional repression by methyl-CpG-binding protein MeCP2 involves a histone deacetylase complex. Nature, 393, 386–389 (1998).
Nicholas, G. M., Eckman, L. L., Ray, S., Hughes, R. O., Pfefferkorn, J. A., Barluenga, S., Nicolaou, K. C., and Bewley, C. A., Bromotyrosine-derived natural and synthetic products as inhibitors of mycothiol-S-conjugate amidase. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett., 12, 2487–2490 (2002).
Park, Y., Liu, Y., Hong, J., Lee, C.-O., Cho, H., Kim, D.-K., Im, K. S., and Jung, J. H., New bromotyrosine derivatives from an association of two sponges, Jaspis wondoensis and Poecillastra wondoensis. J. Nat. Prod., 66, 1495–1498 (2003).
Piña, I. C., Gautschi, J. T., Wang, G. Y., Sanders, M. L., Schmitz, F. J., France, D., Cornell-Kennon, S., Sambucetti, L. C., Remiszewski, S. W., Perez, L. B., Bair, K. W., and Crews, P., Psammaplins from the sponge Pseudoceratina purpurea: inhibition of both histone deacetylase and DNA methyltransferase. J. Org. Chem., 68, 3866–3873 (2003).
Shin, J., Lee, H. S., Seo, Y., Rho, J. R., Cho, K. W., and Paul, V. J., New bromotyrosine metabolites from the sponge Aplysinella rhax. Tetrahedron, 56, 9071–9077 (2000).
Tabudravu, J. N., Eijsink, V. G., Gooday, G. W., Jaspars, M., Komander, D., Legg, M., Synstad, B., and van, Aalten, D. M., Psammaplin A, a chitinase inhibitor isolated from the Fijian marine sponge Aplysinella rhax. Bioorg. Med. Chem., 10, 1123–1128 (2002).
Watt, F. and Molloy, P. L., Cytosine methylation prevents binding to DNA of a HeLa cell transcription factor required for optimal expression of the adenovirus major late promoter. Genes Dev., 2, 1136–1143 (1988).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, H.J., Kim, T.H., Seo, W.S. et al. Pharmacokinetics and tissue distribution of psammaplin A, a novel anticancer agent, in mice. Arch. Pharm. Res. 35, 1849–1854 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-012-1019-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-012-1019-5