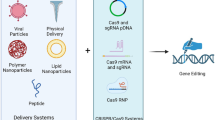
Abstract
The rapid development of the new genome editing technique CRISPR/ Cas9 enables easy and efficient modifications to the human genome. In combination with autologous cell transplants derived from induced pluripotent stem cells, a versatile platform for individualised cell therapies is entering pre-clinical evaluation.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literatur
Kim YG, Cha J, Chandrasegaran S (1996) Hybrid restriction enzymes: zinc finger fusions to Fok I cleavage domain. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93:1156–1160
Jinek M, Chylinski K, Fonfara I et al. (2012) A programmable dual-RNA-guided DNA endonuclease in adaptive bacterial imunity. Science 337:816–821
Cong L, Ran FA, Cox D et al. (2013) Multiplex genome engineering using CRISPR/Cas systems. Science 339:819–823
Sander JD, Joung JK (2014) CRISPR-Cas systems for editing, regulating and targeting genomes. Nat Biotechnol 32:347–355
Chapman JR, Taylor MR, Boulton SJ (2012) Playing the end game: DNA double-strand break repair pathway choice. Mol Cell 47:497–510
Ceccaldi R, Rondinelli B, D´Andrea AD (2016) Repair pathway choices and consequences at the double-strand break. Trends Cell Biol 26:52–64
Shibata A (2017) Regulation of repair pathway choice at two-ended DNA double-strand breaks. Mutat Res 803–805:51–55
Komor AC, Kim YB, Packer MS et al. (2016) Programmable editing of a target base in genomic DNA without double-stranded DNA cleavage. Nature 533:420–424
Thakore PI, Black JB, Hilton IB et al. (2016) Editing the epigenome: technologies for programmable transcription and epigenetic modulation. Nat Methods 13:127–137
Mandai M, Watanabe A, Kurimoto Y et al. (2017) Autologous induced stem-cell-derived retinal cells for macular degeneration. New Engl J Med 376:1038–1046
Delhove JMKM, Qasim W (2017) Genome-edited T cell therapies. Curr Stem Cell Rep 3:124–136
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Susan Sgodda Jahrgang 1977. Biologiestudium an der Universität Halle-Wittenberg mit dem Schwerpunkt Entwicklungsbiologie; dort 2004–2005 wissenschaftliche Mitarbeiterin am Institut für Physiologische Chemie und 2005–2009 wissenschaftliche Mitarbeiterin am Institut für Biochemie. Seit 2011 wissenschaftliche Mitarbeiterin in verschiedenen interdisziplinären BMBF-Projekten an der Medizinischen Hochschule Hannover.
Tobias Cantz Jahrgang 1972. Medizinstudium an der Universität Heidelberg. 2000 Promotion in der Abteilung Tumorbiochemie bei Prof. Dr. D. Keppler am DKFZ Heidelberg. 2000–2004 Assistenzarzt an der Klinik für Gastroenterologie, Hepatologie und Endokrinologie bei Prof. Dr. M. Manns, Medizinische Hochschule Hannover. 2004–2008 Postdoc am Max- Planck-Institut für molekulare Biomedizin Münster bei Prof. Dr. H. Schöler. Seit 2008 Gruppenleiter im Exzellenzcluster REBIRTH und seit 2014 Professor für Translationale Hepatologie und Stammzellbiologie an der Medizinischen Hochschule Hannover.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sgodda, S., Cantz, T. Editierung induzierter pluripotenter Stammzellen mittels CRISPR/Cas9. Biospektrum 24, 707–708 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12268-018-0984-8
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12268-018-0984-8