Abstract
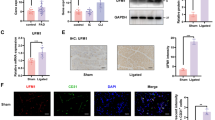
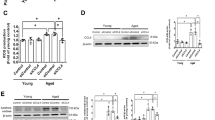
Apoptosis and inflammation of vascular endothelial cells (VECs) are the most important causes of deep vein thrombosis (DVT). cAMP response element binding protein 1 (CREB1) encodes a transcription factor that binds as a homodimer to the cAMP-responsive element and can promote inflammation. CREB1 is found to be upregulated in the plasma of patients with venous thromboembolism. However, the biological functions of CREB1 in DVT remain unknown. We evaluated the effect of CREB1 in a rat model of inferior vena cava (IVA) stenosis-induced DVT. IVC stenosis resulted in stable thrombus, inflammatory response and CREB1 upregulation, whereas CREB1 knockdown inhibited thrombus and inflammation in DVT rats. In vitro analysis showed that CREB1 knockdown inhibited VEC apoptosis. Mechanistically, CREB1 knockdown reduced Ribosomal protein L9 (RPL9) expression and blocked the NF-κB pathway. Therefore, CREB1 may become a potential therapeutic target of DVT prevention.
Graphical Abstract









Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available on request from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Wang TY, Sakamoto JT, Nayar G, Suresh V, Loriaux DB, Desai R, et al. Independent Predictors of 30-Day Perioperative Deep Vein Thrombosis in 1346 Consecutive Patients After Spine Surgery. World Neurosurg. 2015;84(6):1605–12.
Sforza M, Husein R, Saghir R, Saghir N, Okhiria R, Okhiria T, et al. Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) and Abdominoplasty: A Holistic 8-Point Protocol-Based Approach to Prevent DVT. Aesthet Surg J. 2021;41(10):Np1310-np20.
Sevuk U, Altindag R, Bahadir MV, Ay N, Demirtas E, Ayaz F. Value of platelet indices in identifying complete resolution of thrombus in deep venous thrombosis patients. Indian J Hematol Blood Trans : an official journal of Indian Society of Hematology and Blood Transfusion. 2015;31(1):71–6.
Santin BJ, Lohr JM, Panke TW, Neville PM, Felinski MM, Kuhn BA, et al. Venous duplex and pathologic differences in thrombus characteristics between de novo deep vein thrombi and endovenous heat-induced thrombi. J Vasc Surg Venous Lymphat Disord. 2015;3(2):184–9.
Cheng Z, Jia W, Tian X, Jiang P, Zhang Y, Li J, et al. Cotinine inhibits TLR4/NF-κB signaling pathway and improves deep vein thrombosis in rats. Biosci Rep 2020;40(6)
Harter K, Levine M, Henderson SO. Anticoagulation drug therapy: a review. West J Emerg Med. 2015;16(1):11–7.
Bagot CN, Arya R. Virchow and his triad: a question of attribution. Br J Haematol. 2008;143(2):180–90.
Stark K, Philippi V, Stockhausen S, Busse J, Antonelli A, Miller M, et al. Disulfide HMGB1 derived from platelets coordinates venous thrombosis in mice. Blood. 2016;128(20):2435–49.
Luther N, Shahneh F, Brähler M, Krebs F, Jäckel S, Subramaniam S, et al. Innate Effector-Memory T-Cell Activation Regulates Post-Thrombotic Vein Wall Inflammation and Thrombus Resolution. Circ Res. 2016;119(12):1286–95.
Swystun LL, Liaw PC. The role of leukocytes in thrombosis. Blood. 2016;128(6):753–62.
Martinod K, Wagner DD. Thrombosis: tangled up in NETs. Blood. 2014;123(18):2768–76.
Budnik I, Brill A. Immune Factors in Deep Vein Thrombosis Initiation. Trends Immunol. 2018;39(8):610–23.
Malaponte G, Signorelli SS, Bevelacqua V, Polesel J, Taborelli M, Guarneri C, et al. Increased Levels of NF-kB-Dependent Markers in Cancer-Associated Deep Venous Thrombosis. PLoS One. 2015;10(7):e0132496.
Du T, Tan Z. Relationship between deep venous thrombosis and inflammatory cytokines in postoperative patients with malignant abdominal tumors. Brazilian J Med Biol Res Revista brasileira de pesquisas medicas e biologicas. 2014;47(11):1003–7.
Liu H, Li P, Lin J, Chen W, Guo H, Lin J, et al. Danhong Huayu Koufuye prevents venous thrombosis through antiinflammation via Sirtuin 1/NF-κB signaling pathway. J Ethnopharmacol. 2019;241:111975.
Zhou H, Li N, Yuan Y, Jin YG, Guo H, Deng W, et al. Activating transcription factor 3 in cardiovascular diseases: a potential therapeutic target. Basic Res Cardiol. 2018;113(5):37.
Zhang Z, Yin D, Wang Z. Contribution of hypoxia-inducible factor-1α to transcriptional regulation of vascular endothelial growth factor in bovine developing luteal cells. Animal Sci J Nihon chikusan Gakkaiho. 2011;82(2):244–50.
Evans CE, Humphries J, Waltham M, Saha P, Mattock K, Patel A, et al. Upregulation of hypoxia-inducible factor 1 alpha in local vein wall is associated with enhanced venous thrombus resolution. Thromb Res. 2011;128(4):346–51.
Wang Y, Xu J, Chen J, Fan X, Zhang Y, Yu W, et al. Promoter variants of VTN are associated with vascular disease. Int J Cardiol. 2013;168(1):163–8.
Wang B, Wang M, Jia S, Li T, Yang M, Ge F. Systematic Survey of the Regulatory Networks of the Long Noncoding RNA BANCR in Cervical Cancer Cells. J Proteome Res. 2022;21(4):1137–52.
Kuijpers MJ, de Witt S, Nergiz-Unal R, van Kruchten R, Korporaal SJ, Verhamme P, et al. Supporting roles of platelet thrombospondin-1 and CD36 in thrombus formation on collagen. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2014;34(6):1187–92.
Prakash P, Kulkarni PP, Chauhan AK. Thrombospondin 1 requires von Willebrand factor to modulate arterial thrombosis in mice. Blood. 2015;125(2):399–406.
Su Y, Li Q, Zheng Z, Wei X, Hou P. Identification of genes, pathways and transcription factor-miRNA-target gene networks and experimental verification in venous thromboembolism. Sci Rep. 2021;11(1):16352.
Gao LN, Li Q, Xie JQ, Yang WX, You CG. Immunological analysis and differential genes screening of venous thromboembolism. Hereditas. 2021;158(1):2.
Pan L, Niu Z, Gao Y, Wang L, Liu Z, Liu J, et al. Silencing of CREB Inhibits HDAC2/TLR4/NF-κB Cascade to Relieve Severe Acute Pancreatitis-Induced Myocardial Injury. Inflammation. 2021;44(4):1565–80.
Hu Z, Zhou G. CREB1 Transcriptionally Activates LTBR to Promote the NF-κB Pathway and Apoptosis in Lung Epithelial Cells. Comput Math Methods Med. 2022;2022:9588740.
Baik IH, Jo GH, Seo D, Ko MJ, Cho CH, Lee MG, et al. Knockdown of RPL9 expression inhibits colorectal carcinoma growth via the inactivation of Id-1/NF-κB signaling axis. Int J Oncol. 2016;49(5):1953–62.
Zhou Z, Zhou H, Zou X, Wang X, Yan M. Formononetin regulates endothelial nitric oxide synthase to protect vascular endothelium in deep vein thrombosis rats. Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol. 2022;36:3946320221111117.
Ou M, Zhang Y, Cui S, Zhao S, Tu J. Upregulated MiR-9-5p Protects Against Inflammatory Response in Rats with Deep Vein Thrombosis via Inhibition of NF-κB p50. Inflammation. 2019;42(6):1925–38.
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods (San Diego, Calif). 2001;25(4):402–8.
Zhang Z, Hu L, Chen W, Zhou C, Gui G, Lin B. Danhong huayu koufuye prevents deep vein thrombosis through anti-inflammation in rats. J Surg Res. 2016;201(2):340–7.
Wang Z, Ni S, Zhang H, Fan Y, Xia L, Li N. Silencing SGK1 alleviates osteoarthritis through epigenetic regulation of CREB1 and ABCA1 expression. Life Sci. 2021;268:118733.
Liu J, He Q. Ca(2+)/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase IV attenuates inflammation and mitochondrial dysfunction under insulin resistance in C2C12 cells. Arch Physiol Biochem 2020;1–10
Li K, Yang J, Lei XF, Li SL, Yang HL, Xu CQ, et al. EZH2 inhibition promotes ANGPTL4/CREB1 to suppress the progression of ulcerative colitis. Life Sci. 2020;250:117553.
Chen J, Ding Q, Jiao X, Wang B, Sun Z, Zhang Y, et al. Dexmedetomidine attenuates hippocampal neuroinflammation in postoperative neurocognitive disorders by inhibiting microRNA-329-3p and activating the CREB1/IL1RA axis. Psychopharmacology. 2022;239(7):2171–86.
Bombeli T, Karsan A, Tait JF, Harlan JM. Apoptotic vascular endothelial cells become procoagulant. Blood. 1997;89(7):2429–42.
Matsuzaki S, Pouly JL, Canis M. Effects of U0126 and MK2206 on cell growth and re-growth of endometriotic stromal cells grown on substrates of varying stiffness. Sci Rep. 2017;7:42939.
Santulli P, Marcellin L, Chouzenoux S, Boulard V, Just PA, Nicco C, et al. Role of the protein kinase BRAF in the pathogenesis of endometriosis. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2016;20(8):1017–29.
Feng Y, Tan BZ. LncRNA MALAT1 inhibits apoptosis of endometrial stromal cells through miR-126-5p-CREB1 axis by activating PI3K-AKT pathway. Mol Cell Biochem. 2020;475(1–2):185–94.
Yang J, Liu S, Wang H, Liu Y, Liu Y. miR-134-5p inhibition reduces infarct-induced cardiomyocyte apoptosis via Creb1 upregulation. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis : the official journal of National Stroke Association. 2020;29(8):104850.
Zhang T, Ge J. Mechanism of CREB1 in cardiac function of rats with heart failure via regulating the microRNA-376a-3p/TRAF6 axis. Mammalian Genome : official journal of the International Mammalian Genome Society. 2022;33(3):490–501.
Hassan FM, Alsultan A, Alzehrani F, Albuali W, Bubshait D, Abass E, et al. Genetic Variants of RPL5 and RPL9 Genes among Saudi Patients Diagnosed with Thrombosis. Med Arch (Sarajevo, Bosnia and Herzegovina). 2021;75(3):188–93.
Wang G, Zhao W, Yang Y, Yang G, Wei Z, Guo J. Identification of biomarkers of venous thromboembolism by bioinformatics analyses. Medicine. 2018;97(14):e0152.
Watanabe M, Toyomura T, Wake H, Nishinaka T, Hatipoglu OF, Takahashi H, et al. Identification of ribosomal protein L9 as a novel regulator of proinflammatory damage-associated molecular pattern molecules. Mol Biol Rep. 2022;49(4):2831–8.
Huang T, Jiang C, Yang M, Xiao H, Huang X, Wu L, et al. Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium inhibits the innate immune response and promotes apoptosis in a ribosomal/TRP53-dependent manner in swine neutrophils. Vet Res. 2020;51(1):105.
Iosef C, Alastalo TP, Hou Y, Chen C, Adams ES, Lyu SC, et al. Inhibiting NF-κB in the developing lung disrupts angiogenesis and alveolarization. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2012;302(10):L1023–36.
Ma J, Li X, Wang Y, Yang Z, Luo J. Rivaroxaban attenuates thrombosis by targeting the NF-κB signaling pathway in a rat model of deep venous thrombus. Int J Mol Med. 2017;40(6):1869–80.
Lu Z, Ye Y, Liu Y, Yang X, Ding Q, Wang Y, et al. Aqueous extract of Paeoniae Radix Rubra prevents deep vein thrombosis by ameliorating inflammation through inhibiting GSK3β activity. Phytomed : international journal of phytotherapy and phytopharmacology. 2021;92:153767.
Funding
The work was supported by Youth Science Fund of National Natural Science Foundation of China (approval number: 81900143), Health Commission of Hubei Province Scientific Research Project (approval number: WJ2019H354), Wuhan Health Research Fund (approval number: WX19Q07) and Hubei Natural Science Foundation (approval number: 2021CFB264).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Xiaorong Jian conceived and designed the experiments. Dehua Yang, Li Wang Xiaorong Jian and Hongxiang Wang carried out the experiments. Xiaorong Jian analyzed the data. Xiaorong Jian drafted the manuscript. All authors have read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethical Statement
All experiments involving animals were approved by the Animal Ethics Committee of The Central Hospital of Wuhan, Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, and all experimental protocols strictly followed the Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals published by the National Institutes of Health (NIH publication no.85–23, revised 1996).
Competing Interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Associate Editor Junjie Xiao oversaw the review of this article
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Jian, X., Yang, D., Wang, L. et al. CREB1 Silencing Protects Against Inflammatory Response in Rats with Deep Vein Thrombosis Through Reducing RPL9 Expression and Blocking NF-κB Signaling. J. of Cardiovasc. Trans. Res. (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12265-023-10450-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12265-023-10450-1