Abstract
Maternal diet during gestation can exert a long-term effect on the progeny’s health by programming their developmental scheme and metabolism. The aim of this study is to analyze the influence of maternal diet on lipid metabolism in 10- and 16-week-old rats. Pregnant dams were fed one of four diets: a normal protein and normal folic acid diet (NP-NF), a protein-restricted and normal folic acid diet (PR-NF), a protein-restricted and folic-acid-supplemented diet (PR-FS), or a normal protein and folic-acid-supplemented diet (NP-FS). We also tested whether prenatal nutrition determines the reaction of an organism to a postweaning high-fat diet. Blood biochemistry and biometrical parameters were evaluated. The expression patterns of PPARα, PPARγ, and LXRα in the liver and adipose tissue were examined by real-time PCR. In the 10-week-old, rats folic acid supplementation of the maternal diet was associated with reduced circulating glucose and total cholesterol concentrations (P < 0.01 and P < 0.001, respectively). Neither prenatal diets nor postnatal feeding affected blood insulin concentrations. In the 16-week-old rats, body weight, abdominal fat mass and central adiposity were reduced in the progeny of the folic acid–supplemented dams (P < 0.01, P < 0.001 and P < 0.01, respectively). Maternal protein restriction had no effect on biometry or blood biochemical parameters. Folic acid supplementation of the maternal diet was associated with reduced expression of PPARα, PPARγ, and LXRα in the liver (P < 0.001). Reduced protein content in the maternal diet was associated with increased PPARα mRNA level in the liver (P < 0.001) and reduced LXRα in adipose tissue (P < 0.01). PPARα and PPARγ transcription in the liver, as well as LXRα transcription in adipose tissue, was also dependent on interaction effects between prenatal and postnatal diet compositions. PPARγ transcription in the liver was correlated with the abdominal fat mass, body weight, and calorie intake, while PPARγ transcription in adipose tissue was correlated with reduced body weight and calorie intake. Total serum cholesterol concentration was correlated with LXRα transcription in the liver. Folic acid supplementation of the maternal diet may have favorable effects for lipid metabolism in the progeny, but these effects are modified by the postnatal diet and age. Furthermore, the expression of LXRα, PPARα, and PPARγ in the liver and adipose tissue largely depends on the protein and folic acid content in the maternal diet during gestation. However, the altered transcription profile of these key regulators of lipid metabolism does not straightforwardly explain the observed phenotype.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
Abnormalities in energy expenditure and lipid metabolism lead to dyslipidemia, obesity, and metabolic syndrome, all of which are major health problems in developed countries (Wild et al. 2004; Ghandehari et al. 2008; Muhlhausler and Smith 2009; Qi and Cho 2008). Lipid metabolism depends on numerous environmental and genetic factors, and one essential environmental factor is food intake. Recent studies have shown that maternal nutrition during gestation (the maternal effect) also contributes significantly to determining metabolism. This phenomenon is known as fetal programming (Chmurzynska 2010; Jones and Ozanne 2009; Heerwagen et al. 2010). One of the molecular mechanisms that underlies fetal programming is a change in epigenetic DNA modifications—mainly DNA methylation—due to altered availability of the nutrients involved in the methylation process (i.e. methionine, folates, vitamins B6 and B12, and choline) (Burdge et al. 2004, 2009a; Mathers and McKay 2009). Moreover, the metabolic state of a mother can affect the development of a fetus through the secretion of numerous hormones and cytokines (Barker 1998; McMillen and Robinson 2005; Gicquel et al. 2008; Valsamakis et al. 2010).
Different variants of a maternal diet may evoke different long-term effects, and methionine content and sulfur amino acid balance in the maternal diet has been identified as one of the most important programming factors (Langley-Evans 2000; Rees et al. 2006a, b, c). Sulfur amino acids are involved not only in methylation processes, but are also regulators of lipid metabolism (Oda 2006).The interrelation between sulfur-containing amino acids and lipid metabolism has recently been underlined (Obeid and Herrmann 2009). Since methionine and homocysteine homeostasis depend on the folate pathway (among other factors), it is not surprising that several studies have revealed a relation between folate status and lipoprotein profile (Semmler et al. 2010; Ojeda et al. 2008; Lim et al. 2008), as well as liver steatosis (Esfandiari et al. 2005; Christensen et al. 2010), but also adiposity and fat distribution (Mahabir et al. 2008). Sulfur amino acids and folic acid may therefore contribute to fetal programming in two ways—directly, by influencing fetal DNA methylation, and indirectly, by influencing maternal metabolism.
Control of lipid homeostasis is a very complex process and involves transcriptional regulation of many genes, which is achieved by the concerted action of key lipid metabolism regulators—liver X receptors (LXRs) and peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors (PPARs) (Beaven and Tontonoz 2006). LXRs operate as cholesterol sensors, protecting against cholesterol overload through decreasing the levels of intestinal absorption of cholesterol, and by stimulating cholesterol efflux to HDL, its transport to the liver, its conversion to bile acids, and biliary excretion (Wójcicka et al. 2007). PPARα is the key regulator of fatty acid oxidation and thus is a regulator of energy expenditure (Pyper et al. 2010). The biological function of PPARγ relies on the control of adipogenesis. Moreover, lipid accumulation may occur via PPARγ activation in cells other than adipocytes (Desvergne et al. 2004).
The influence of methyl donor content in the maternal diet on DNA methylation and lipid metabolism in progeny has been analyzed in several experiments (Burdge et al. 2004, 2008; Erhuma et al. 2007a, b). In most of these studies, the Southampton low-protein diet was used. This is a casein-based diet, supplemented with DL-methionine. It has been shown that a low protein diet in utero programs hypertriglyceridemia and insulin resistance in the aging rats (Erhuma et al. 2007b). On the other hand, it has been suggested that folic acid supplementation during gestation prevents an altered epigenotype caused by protein restriction (Lillycrop et al. 2005). Folic acid intake in the juvenile-pubertal period may also modify the prenatally induced metabolic phenotype (Burdge et al. 2009b). Furthermore, the effect of maternal nutrition during gestation is modified by postnatal feeding (Burdge et al. 2008; Erhuma et al. 2007a; Jones et al. 1984).
The aim of our study is to analyze the influence of maternal diets differing in the quantities of protein and folic acid they contain on the lipid metabolism of 10- and 16-week-old progeny. We also investigated whether prenatal nutrition determines the response to high-fat feeding. In the present study, we have used casein-based, sulfur amino acid balanced diets, supplemented with l-cystine—that is, a modification of the standard AIN-93 diet for growing, pregnant, and lactating rodents.
Materials and methods
Experimental procedure
All animal studies were approved by the local ethics committee (approval no. 35/2007). Rats were housed in individual metabolic cages on a 12-h light/12-h dark cycle, at a temperature of 20°C. Twenty virgin female Wistar rats (five per group) were mated with eight male rats. After successful mating was confirmed by the presence of a vaginal plug, the female rats were assigned to one of four groups: the NP-NF group was fed the normal protein, normal folic acid diet (the AIN-93 diet; 20% casein and 2 mg folic acid/kg diet); the PR-NF group was fed a protein-restricted, normal folic acid diet (9% casein and 2 mg folic acid/kg diet); the PR-FS group was fed a protein-restricted, folic acid–supplemented diet (9% casein and 5 mg folic acid/kg diet); and the NP-FS group was fed a normal protein, folic acid–supplemented diet (20% casein and 5 mg folic acid/kg diet). All diets were supplemented with l-cystine, with the protein-restricted diets being supplemented by a quantity of l-cystine proportional to their protein content. In the protein-restricted diets, casein was replaced by wheat starch, and so the diets were isocaloric. The litters were culled to a maximum of eight pups within 3 days of delivery to minimize variation in nutrition during the suckling period. The minimal size of a litter was eight.
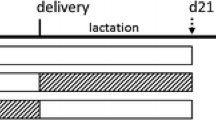
At the age of 4 weeks, the offspring of each mother group (eight per group, four males and four females) were randomly assigned to two groups that were fed the AIN-93 diet (the AIN groups), or a high-fat diet (HF groups) for 6 weeks. Since programming effects can differ depending on age, the other animals (n = 6, three males and three females) were introduced to this feeding scheme at the age of 10 weeks. The design of the study is presented in Fig. 1 and has been recently described (Chmurzynska et al. 2011). The high-fat diet was 39.5% fat by weight, which was provided by sunflower oil and lard (Table 1).
Design of the study. There were two periods in which the experimental diets were used: during pregnancy and the postweaning period. During pregnancy, the following diets were used: a normal protein, normal folic acid diet (NP-NF) (this was a modified AIN-93 diet); a protein-restricted, normal folic acid diet (PR-NF); a protein-restricted, folic acid–supplemented diet (PR-FS); and a normal protein, folic acid–supplemented diet (NP-FS). Two groups of progeny (4 and 10 weeks old) of each maternal dietary group were fed with the modified AIN-93 (NP-NF) or the HF diets for 6 weeks (the dotted lines). Each group of younger rats consisted of eight individuals (four males and four females), while the older animal groups consisted of six individuals (three males and three females)
Food intake was measured every day during pregnancy and throughout the life of the offspring. The weight gain of the mothers and of the offspring was measured weekly. Food intake was normalized for body weight (g food intake/day per 100 g body weight), and was calculated as the average calorie daily intake in kcal/day per 100 g body weight. Moreover, the feed conversion efficiency (FCE) was calculated as kcal food consumed per g weight gained.
Analysis of body composition and measurements of biochemical blood parameters
At the end of the experimental period, the animals were anesthetized by sodium thiopental injection (40 mg/kg body weight) after an overnight fast, and euthanized by cardiac puncture. Liver samples were taken and the total amount of visible fat in the abdominal cavity was removed and accurately weighed. Central adiposity was calculated as a percentage of the abdominal fat mass in the entire body weight. Plasma glucose, total cholesterol, HDL cholesterol, LDL cholesterol, and triacylglycerol (TAG) concentrations were measured by standard colorimetric assay using a Vitalab Flexor biochemical analyzer. Serum insulin concentration was measured using radioimmunological assay (Rat Insulin Radioimmunoassay Kit, Millipore Corporation, Billerica, MA, USA), according to the manufacturer’s protocol.
RNA extraction
Total RNA was extracted from the liver and visceral fat tissues using Tripure Isolation Reagent (Roche) according to the manufacturer’s protocol. In order to remove excess lipids, one additional step was introduced in which the visceral fat samples were centrifuged upon homogenization at 12,000 rpm/10 min/+4°C, and the clear solution was transferred to a fresh tube, from which point further RNA extraction steps were performed.
Reverse transcription
Approximately 1 μg RNA was taken for cDNA synthesis. Samples of RNA were incubated with a set of random hexamers (Roche, 0.25 μg/μl) and oligodT(15) (Roche, 0.25 μg/μl) at 70°C/10 min. A mixture of dNTP (5.0 mM, Roche), 1 U reverse transcriptase AMV (EURX, Poland), and 20 U Protector RNase Inhibitor (Roche) was added. After a 2-h incubation at 37°C, the AMV enzyme was inactivated at 94°C/5 min. The cDNA was then diluted 3× and stored at −20°C.
Real-time PCR
The real-time PCRs were performed on a Light Cycler 2.0 (Roche) based on the SYBR Green detection system (Roche). 18S ribosomal RNA (18S rRNA) and β-actin (ACTB) genes were used as references for the normalization of data. Each 10-μl reaction mixture consisted of 3 μl cDNA, 0.5 μl LightCycler Fast Start DNA Master SYBR Green I® kit (Roche), 20 μM MgCl2 (PPARγ and 18S rRNA), 30 μM MgCl2 (PPARα), 40 μM MgCl2 (LXRα) or 50 μM MgCl2 (ACTB), and 0.3 μM forward and reverse primers. The primers used are presented in Table 2. The real-time PCR cycling involved predenaturation at 95°C for 10 min, followed by 45 cycles of denaturation at 95°C for 10 s, annealing at 62°C for 2 s (67°C for LXRα), and elongation at 72°C for 8 s (7 s for LXRα). The amplified fragment specificity was confirmed by the melting curve and product length analysis on 1.6% agarose gel. The relative quantification of the mRNA level was performed in duplicates based on a Second Derivative Maximum Method (Roche). Standard curves were designed as tenfold dilutions of the appropriate PCR product in the range of 10–0.0001 aM. The abundance of PPARα, PPARγ, and LXRα gene transcripts was then normalized to a geometric mean of two reference genes (18S rRNA and ACTB) (Vandesompele et al. 2002).
Statistical analysis
Values are presented as group means with standard errors. Statistical analysis was carried out using STATISTICA 8 for Windows. The effects of prenatal and postnatal diets were assessed using a fixed model ANOVA (fixed effects: maternal protein intake, maternal folic acid intake, fat content in the postnatal diet, and offspring sex), followed by a post hoc Scheffé’s test. The initial ANOVA model included sex as a factor. In analyses where sex showed significance, males and females were analyzed separately, otherwise male and female data were considered together. P < 0.05 was accepted as statistically significant. Effect strengths were estimated by partial eta squared (partial ε2). For all presented results, power analysis showed a power of 0.8–1.0, with α = 0.05.
Results
Food intake
The diet consumption of mothers was normalized for body weight, and no significant differences were found between dam groups (NP-NF 5.8 ± 0.32; PR-NF 6.06 ± 0.09; PR-FS 6.59 ± 0.27; NP-FS 6.05 ± 0.35 g/day per 100 g body weight). However, overall weight gain was dependent on the protein content in the diet. Protein restriction was associated with a lower weight gain in pregnant dams (86.1 ± 3.7 g vs. 98.2 ± 2.3 g; P < 0.05).
In the 10-week-old rats, higher intake was observed in the male sex. Moreover, food intake was higher in the animals fed with the AIN-93 diet than in those fed with the HF diet (P < 0.05). The calorie intake (kcal/day per 100 g body weight) was not affected by the maternal diet or by the postnatal feeding scheme. However, in the 16-week-old rats, higher calorie intake was observed in the male rats (P < 0.001). There was also an interaction effect of protein and folic acid content in the maternal diet on calorie intake in the progeny (P < 0.01), and the highest calorie intake was observed in the progeny of NP-NF dams.
In the 10-week-old rats, sex was a factor which influenced the FCE (P < 0.001), and this reached a higher level in the female rats. The higher fat content in the postweaning diet was associated with a lower FCE (P < 0.001). There was also an interaction effect of protein and folic acid content (P < 0.001), and the highest FCE was found in the progeny of the NP-FS dams. Similarly, in the 16-week-old rats, the FCE was affected by sex (P < 0.001), being higher in the females. An interaction effect of protein content in the maternal diet and sex was also detected (P < 0.01), with the FCE being 20% higher in the female progeny of protein-restricted dams, compared with the female progeny of dams fed with the normal-protein diet, while there was no such association in the male rats.
Biometry
Body weight in the 10-week-old rats was not affected by prenatal or postnatal nutritional factors. In the 16-week-old animals, however, lower body weight was observed in the progeny of the folic acid–supplemented dams (320 ± 19 g) than in the progeny of the non-supplemented dams (353 ± 22 g; P < 0.01)—see Fig. 2. Moreover, body weight was influenced by fat content in the postweaning diet (P < 0.01). Body weight was also affected by sex in both the younger and older rats, with higher values in the male rats (P < 0.001 for both associations).
In the 10-week-old rats, the high-fat diet stimulated abdominal fat accumulation (12.43 ± 0.76 g vs. 17.17 ± 0.89 g, P < 0.001) and resulted in increased central adiposity. Abdominal fat mass was also affected by sex (P < 0.001), and was higher in the males—see Fig. 3a. The effects of prenatal nutrition on abdominal fat mass were only observed in the 16-week-old rats. The progeny of dams fed with the normal folic acid diet had significantly higher abdominal fat mass than the progeny of folic acid–supplemented dams (29.43 ± 2.77 g vs. 21.53 ± 1.71 g, P < 0.001), and high-fat feeding produced a similar effect (30.50 ± 2.90 g vs. 20.82 ± 1.41 g, P < 0.001).There was also an interaction effect of folic acid and sex (P < 0.05), as shown in Fig. 3b. Abdominal fat mass was positively correlated with body weight (r = 0.66 and r = 0.79; P < 0.05 in 10- and 16-week-old rats, respectively) and with serum insulin concentration (r = 0.27; P < 0.05 in 10-week-old rats).
The main effect of sex on abdominal fat weight in the 10-week-old rats (multi-way ANOVA, P < 0.001). The abdominal fat weight was higher in the males, irrespective of prenatal folic acid supplementation (a). In the 16-week-old rats, there was an interaction effect of folic acid content in the maternal diet and sex on abdominal fat weight (multi-way ANOVA, P < 0.001 (b). Bars without a common superscript are significantly different
In 16-week-old rats folic acid supplementation of the maternal diet was followed by decreases in central adiposity of almost 20% (P < 0.01). There was a tendency toward increased central adiposity in animals prenatally fed with the normal folic acid diet and postnatally fed with the high-fat diet. Moreover, an interaction effect of folic acid and age was detected, and 16-week-old progeny of folic acid–supplemented dams had over 30% increased central adiposity compared with other groups (P < 0.05).
Blood parameters
In the 10-week-old rats, a main effect of folic acid content in the maternal diet on glucose concentration was found (Table 3), and higher folic acid content was associated with lower plasma glucose concentrations—7.51 ± 0.14 mmol/l versus 6.76 ± 0.24 mmol/l, P < 0.01. Folic acid supplementation of the maternal diet was associated with about 20% lower cholesterol concentration in both the 10- and 16-week-old rats (P < 0.001). In the 16-week-old rats, an association was found between prenatal nutrition and the ratio of HDL cholesterol to total cholesterol: lower protein content or higher folic acid content in the maternal diet was associated with an increased value of this ratio (P < 0.01 and P < 0.05, respectively). The ratio of HDL cholesterol to total cholesterol was also influenced by the protein content × age and folic acid content × age effects (P < 0.01 and P < 0.05 respectively). The highest values were detected in the protein-restricted 16-week-old rats and in the folic acid–supplemented 16-week-old rats. There was no effect of prenatal nutrition on the LDL cholesterol and TAG concentrations in the 10-week-old rats (Table 3). In the 16-week-old animals, higher folic acid content in the maternal diet was associated with a lower TAG concentration in the progeny (0.31 ± 0.03 mmol/l vs. 0.45 ± 0.04 mmol/l, P < 0.01). The TAG concentration was also influenced by the folic acid content × age effect (P < 0.01), and the reduced TAG level was associated with older age and folic acid supplementation of the maternal diet.
There was no significant effect of prenatal or postnatal nutrition on serum insulin concentrations in 10-week-old rats. The group means are presented in Table 3. Insulin concentration correlated positively with body weight, abdominal fat mass, and calorie intake (r = 0.32, r = 0.27 and r = 0.33; P < 0.05, respectively).
Gene expression—liver
The expression of LXRα, PPARα, and PPARγ was analyzed in the liver of the 10-week-old rats. The level of folic acid in the maternal diet had a very significant effect on the expression level of the LXRα gene (P < 0.001; partial eta ε2 = 0.42). In the progeny of mothers fed with the normal folic acid diet, the mRNA level was twice as high as in the progeny of supplemented dams. There was also an interaction effect of the protein and folic acid content in the maternal diet (P < 0.001; partial ε2 = 0.39), with expression being lowered in all groups compared with the NP-NF groups—Fig. 4a. Postnatal feeding did not affect LXRα gene expression.
Quantification of mRNA levels of LXRα (a), PPARγ (b), and PPARα (c) in the livers of rats belonging to different maternal dietary groups. The results are presented as group means with standard errors. The significant effects of protein content × folic acid and content × fat content are shown in b and c (multi-way ANOVA, P < 0.01 for both associations). Bars with the same superscript are not significantly different from each other (n = 8)
The increased PPARγ gene expression was associated with lower folic acid content in the maternal diet (0.0080 ± 0.001 vs. 0.0045 ± 0.001, P < 0.01; partial ε2 = 0.14) and higher fat intake during postnatal life (0.0079 ± 0.001 vs. 0.0046 ± 0.001, P < 0.01; partial ε2 = 0.13). An interaction effect between the protein and folic acid content in the maternal diet, and the fat content in the postweaning diet, was observed (P < 0.05; partial ε2 = 0.11). The highest transcription level of the PPARγ gene was detected in the PR-NF HF animals—Fig. 4b. In males, PPARγ expression was twice as high as in females (P < 0.001).
The protein restriction or normal folic acid content in the maternal diet was reflected by a higher PPARα gene expression level (P < 0.001 and P < 0.01, respectively; partial eta squared 0.29 and 0.15, respectively). In the progeny of mothers belonging to the protein-restricted group, expression was twice as high as in the other animals. Folic acid supplementation of the dams’ diet resulted in about a 40% decrease in PPARα transcription in the offspring. Moreover, there was an interaction effect between the protein and folic acid content in the maternal diet, with the result that 7–8 times lower level of PPARα transcription was found in the progeny of NP-FS dams (P < 0.001; partial ε2 = 0.22). A significant difference was observed between animals fed with the high-fat diet, but exposed to different folic acid levels in utero (non-supplemented and high-fat diet rats: 0.0183 ± 0.002b; non-supplemented and low-fat diet rats: 0.0143 ± 0.002a,b; supplemented and high-fat diet rats: 0.0077 ± 0.002a; and supplemented and low-fat diet rats: 0.0127 ± 0.003a,b; P < 0.05; partial ε2 = 0.08). An interaction effect was also found for protein and folic acid content in the maternal diet and the fat content in the postweaning diet (P < 0.01; partial ε2 = 0.17)—Fig. 4c.
There was a positive correlation between PPARα and PPARγ (r = 0.36; P < 0.05), and between PPARγ and LXRα mRNA levels (r = 0.31; P < 0.05). Moreover, the PPARγ transcription level was positively correlated with abdominal fat mass, body weight, weight gain, and calorie intake, with correlation coefficients 0.30, 0.42, 0.46, and 0.37, respectively (P < 0.05). The LXRα mRNA level correlated with cholesterol concentration (r = 0.35; P < 0.05).
Gene expression—adipose tissue
Exposure to protein restriction was reflected by lowered LXRα gene expression—0.039 ± 0.004 versus 0.058 ± 0.005, P < 0.01. An interaction effect of protein and folic acid content in the maternal diet also occurred (P < 0.05). The progeny of the NP-NF dams differed significantly from other maternal dietary groups, in which approximately a twofold higher transcription level was noticed. Furthermore, a protein × fat content effect was found in the diets (P < 0.05). The highest level of LXRα expression was thus associated with normal folic acid content in the dams’ diet, and low fat in the postnatal diet. Prenatal and postnatal factors did not alter PPARγ gene expression in adipose tissue, but expression was influenced by sex (P < 0.01). The relative levels of expression of LXRα and PPARγ in adipose tissue in all maternal dietary groups are presented in Fig. 5a, b. There was a significant positive correlation between PPARγ and LXRα transcription (r = 0.43; P < 0.05). LXRα transcription correlated with serum glucose concentration (r = 0.25; P < 0.05). Moreover, the PPARγ transcription level was negatively correlated with body weight, weight gain, and calorie intake (P < 0.05), and the correlation coefficients were −0.33, −0.35, and −0.26, respectively.
Discussion
The present study shows that different amounts of protein and folic acid in the maternal diet during gestation may induce widespread changes in lipid metabolism of the 10- and 16-week-old progeny.
Programming of lipid metabolism
The influence of prenatal nutrition on body weight was only observed in the 16-week-old rats, and the progeny of folic acid–supplemented dams had lower body weights compared with the progeny of dams fed with the normal folic acid diet (P < 0.01). The maternal diet also determined the adiposity of the rats, and in the 16-week-old rats the abdominal fat mass and central adiposity were much higher in the offspring of dams not supplemented with folic acid, especially in combination with high-fat postweaning feeding. The differences in abdominal fat mass with respect to folic acid content in the maternal diet were also dependent on sex, and were more pronounced in the male rats. Folic acid supplementation of the maternal diet was associated with over 30% reduction in abdominal fat mass in the male rats, while in the females the reduction was only about 15%. In the 10-week-old rats, the lowest fat mass was observed in the AIN NP-FS group, but the differences did not reach a significant level. In the study of Burdge et al. (2008), where the Southampton low protein diet was used, the protein-restricted diet with additional folic acid caused reduced weight gain, but no effect on adiposity was reported. In the present study, as in the studies of Rees et al. (2006b), there was no effect of protein content in the maternal diet on fat accretion in the offspring. On the contrary, in female offspring of dams fed during gestation with the protein-restricted Hope Farm diet, a lower weight of endometrial fat pads was observed (Rees et al. 2006c). Most likely, the profound differences in the effect of protein restriction or folic acid supplementation on adipose tissue development are the results of the different formulas of the diets. Our study indicates for the first time that when the diet is sulfur amino acid balanced, folic acid supplementation of the maternal diet can have a significant effect on body weight and abdominal fat accumulation in the offspring. This effect is independent of protein content but may change with age.
PPARs have been considered to be proteins involved in fetal adaptations to maternal diet, and candidate genes responsible for the programmed phenotype (Rees et al. 2008). In our study, the hepatic expression of the PPARγ gene was determined by either protein or folic acid content in the maternal diet. We detected lower PPARγ mRNA levels in the progeny of normal protein diet–fed dams or folic acid–supplemented dams. Erhuma et al. (2007b) also observed the induction of PPARγ expression by prenatal protein restriction, but only in aging rats. Interestingly, in our study, the enhanced expression of PPARγ in the liver was correlated with increased abdominal fat mass, body weight, and calorie intake, while the abundance of PPARγ in adipose tissue correlated negatively with these parameters. The consequences of altered PPARγ expression for lipid metabolism have been studied in several experiments. The expression of PPARγ in the liver is found at a very low level, and its activation leads to lipid accumulation and stimulation of several adipogenic target genes in hepatocytes (Schadinger et al. 2005). However, adenoviral overexpression of PPARγ in the liver and adipose tissue attenuated steatohepatitis by redistributing of fatty acids from the liver to adipose tissue (Wu et al. 2010). On the other hand, adenoviral hepatic overexpression of PPARγ results in adipogenic differentiation and accumulation of fat in the liver in PPARα−/− mice (Yu et al. 2003). Liver PPARγ also affects the accumulation of fat in other tissues. Mice without hepatic PPARγ develop relative fat intolerance, increased adiposity, hyperlipidemia, and insulin resistance (Gavrilova et al. 2003). Decreased expression of PPARγ in the liver and adipose tissue leads to reduced body weight, reduced total fat mass, and dyslipidemia (Tsai et al. 2009). Furthermore, PPARγ is also involved in food intake control (Cecil et al. 2006). PPARγ agonists increase food intake resulting in an accumulation of subcutaneous body fat (Larsen et al. 2003), possibly by favoring lipid deposition in subcutaneous depots (Laplante et al. 2006). Correlations between PPARγ transcription and abdominal fat mass observed in the present study may therefore be a consequence of reduced food intake, as a correlation between PPARγ and calorie intake was also revealed. This hypothesis is also supported by the observation that there was a correlation between the expression of PPARγ and the leptin gene in adipose tissue (r = 0.57, P < 0.05; data not shown; results concerning leptin gene expression have been described previously Chmurzynska et al. 2011). Taken together, it can be concluded that food intake and lipid metabolism is regulated not only by PPARγ expression in the adipose tissue but also in the liver, and fat distribution may depend on the interplay between the expression of PPARγ in the liver and in adipose tissue.
The altered lipid metabolism programmed by maternal nutrition during gestation was also reflected by biochemical blood parameters. A reduced blood glucose concentration was associated with protein restriction or a higher level of folic acid in the maternal diet. In the progeny of dams fed with the folic acid–supplemented diet, total cholesterol content was lowered by approximately 20%. In the 16-week-old rats, the ratio of HDL cholesterol to total cholesterol was larger in those animals whose mothers were fed the diet with a normal level of protein or a diet supplemented with folic acid. Folic acid supplementation in the maternal diet was associated with a reduction of blood TAG level in the older animals, while in the 10-week-old rats, this parameter was unaffected by maternal nutrition. On the contrary, folic acid supplementation of the maternal diet has been shown to be associated with increased TAG concentration in male rat progeny (Burdge et al. 2008). Increased plasma glucose and TAG concentrations following prenatal protein restriction have also been demonstrated (Burdge et al. 2004, 2008), but we did not observe such associations. Erhuma et al. (2007a) observed that prenatal protein restriction did not affect plasma lipid metabolism in the adult rats, but at the age of 18 months, the protein-restricted animals exhibited hypertriglyceridemia, insulin resistance, and hepatic steatosis. These discrepancies can be explained by the differences in the formula of the experimental diets. In addition, the age of the studied animals seems to be an important factor confounding the results, as the favorable effect of folic acid supplementation in the maternal diet on TAG concentration in the progeny was only observed in 16-week-old rats.
In the present study, total cholesterol and HDL cholesterol concentrations correlated positively with the hepatic LXRα expression, and glucose concentration correlated with the LXRα transcription level in adipose tissue. A twofold decrease in the hepatic expression of LXRα in the progeny of folic acid supplemented dams was observed (P < 0.001). Moreover, there was an interaction effect of protein × folic acid content in the maternal diet. In comparison with the progeny of the NP-NF dams, the expression of LXRα was decreased by approximately 40% in the PR-NF and PR-FS groups, and by 77% in the NP-FS group. Prenatal protein restriction induced downregulation of LXRα in adipose tissue. There was also an interaction effect between protein and folic acid content in the maternal diet, leading to a reduced level of LXRα mRNA in all maternal dietary groups, compared with the progeny of the NP-NF dams. Interestingly, transcription of this gene was sex dependent only in adipose tissue. LXRα has been shown to regulate hepatic fatty acid synthesis by upregulating sterol regulatory element binding protein-1c (SREBP-1c), which enhances the expression of lipogenic enzymes and thereby leads to an increased circulating TAG concentration (Baranowski 2008). LXRα regulates also cholesterol synthesis by influencing SREBP-2 (Wójcicka et al. 2007). LXRα-null mice exhibited higher expressions of SREBP-2 and its target genes, which suggests that LXRα inhibits cholesterol synthesis (Peet et al. 1998). The function of LXRα in adipose tissue has not yet been well described, but it has been shown that LXR agonists modulate lipid metabolism in adipocytes (Stulnig et al. 2002; Hummasti et al. 2004). Our results show that prenatal nutrition determines LXRα expression in the liver and adipose tissue, but the consequences of the altered expression profile for the observed phenotype are not straightforward.
Programming of the response to a high-fat diet
It has been postulated that negative consequences of fetal programming can be observed when there is a mismatch between prenatal and postnatal nutritional environment (Gluckman and Hanson 2008). Jones et al. (1984) found that the detrimental effect of improper maternal diet (specifically, a 50% food restriction) can be exacerbated by a nutritional challenge (a high-fat diet) in postnatal life. Protein and folic acid content in the maternal diet has been shown to influence TAG and glucose concentrations, but the effect was modified by fat intake after weaning (Burdge et al. 2008). In our study, the altered response to the high-fat diet programmed by maternal nutrition during pregnancy was detected as changed gene expression in the 10-week-old rats and central adiposity in the 16-week-old rats. Hepatic PPARγ transcription in response to the high-fat diet was dependent on maternal nutrition. Similarly, activation of PPARα gene by high-fat feeding was dependent on prenatal nutrition. The highest PPARα mRNA level following the high-fat diet was detected in the progeny of normal folic acid dams, where it was 237% of those in the progeny of folic acid–supplemented dams. Enhanced expression of the PPARα gene has an anti-obesity effect which is achieved by the activation of target genes responsible for lipid metabolism. It is also capable of decreasing the dyslipidemia associated with metabolic syndrome (Yoon 2009). We can therefore speculate that decreased PPARα expression may have an adverse effect on health, yet no such correlation was found. However, it cannot be ruled out that this effect may be detectable only after long-term high-fat feeding. An altered response to high-fat feeding programmed by maternal protein restriction, mediated by hepatic SREBP-1c expression, was previously described by Erhuma et al. (2007a).
Final remarks
The genes examined here are the key regulators of lipid metabolism which, in response to nutritional stimuli, regulate several biochemical processes and adjust their intensity to nutrient availability. Interestingly, in our model, the expression of LXRα, PPARα, and PPARγ genes in the liver and adipose tissue depended mainly on the maternal diet, but the postnatal diet modified the expression profile. However, the altered transcription profile of these genes does not straightforwardly explain the changes in biometry or biochemical parameters observed on the dietary manipulations used in our study.
Changed gene expression may result from its altered methylation profile, and previous studies have shown that maternal protein restriction during gestation is associated with reduced methylation of PPARα in the liver of progeny (Lillycrop et al. 2005, 2008). The LXRα promoter was hypermethylated in the fetal liver upon maternal protein restriction (van Straten et al. 2010). On the other hand, dietary manipulations did not alter the methylation of PPARγ (Lillycrop et al. 2005). In our studies, however, we did not measure methylation of the genes.
We confirmed that folic acid and protein content in the maternal diet has a programming effect on the progeny’s lipid metabolism, but this effect also depends on fat content in the postnatal diet and on the age of the animals. It should, however, be underlined that the observed effects are not caused by a single nutrient, but by the overall composition of the diets. The most significant novelty in our findings is that folic acid supplementation of the maternal diet may improve lipid metabolism by reducing abdominal fat accumulation, and by reducing serum cholesterol and TAG concentrations. As mentioned, an interrelation between folate and lipid metabolism has already been observed (Obeid and Herrmann 2009). In case of folate deficiency or hyperhomocysteinemia, associated lipid metabolism disturbances have also been noted (Obeid and Herrmann 2009) and, on the other hand, high folate levels are associated with favorable blood lipid profiles (Semmler et al. 2010; Lim et al. 2008). Our results resemble the situations described in these studies. This may suggest that higher folate availability during fetal life programs the development of the body and leads to better folate absorption or usage in the postnatal period. However, the underlying mechanism remains unknown.
References
Baranowski M (2008) Biological role of liver X receptors. J Physiol Pharmacol 59(Suppl 7):31–55
Barker DJ (1998) In utero programming of chronic disease. Clin Sci (Lond) 95(2):115–128
Beaven SW, Tontonoz P (2006) Nuclear receptors in lipid metabolism: targeting the heart of dyslipidemia. Annu Rev Med 57:313–329
Burdge GC, Phillips ES, Dunn RL, Jackson AA, Lillycrop KA (2004) Effect of reduced maternal protein consumption during pregnancy in the rat on plasma lipid concentrations and expression of peroxisomal proliferator-activated receptors in the liver and adipose tissue of the offspring. Nutr Res 24:639–646
Burdge GC, Lillycrop KA, Jackson AA, Gluckman PD, Hanson MA (2008) The nature of the growth pattern and of the metabolic response to fasting in the rat are dependent upon the dietary protein and folic acid intakes of their pregnant dams and post-weaning fat consumption. Br J Nutr 99(3):540–549
Burdge GC, Lillycrop KA, Jackson AA (2009a) Nutrition in early life, and risk of cancer and metabolic disease: alternative endings in an epigenetic tale? Br J Nutr 101:619–630
Burdge GC, Lillycrop KA, Phillips ES, Slater-Jefferies JL, Jackson AA, Hanson MA (2009b) Folic acid supplementation during the juvenile-pubertal period in rats modifies the phenotype and epigenotype induced by prenatal nutrition. J Nutr 139(6):1054–1060
Cecil JE, Watt P, Palmer CN, Hetherington M (2006) Energy balance and food intake: the role of PPAR gamma gene polymorphisms. PhysiolBehav 88(3):227–233
Chmurzynska A (2010) Fetal programming: link between early nutrition, DNA methylation, and complex diseases. Nutr Rev 68(2):87–98
Chmurzynska A, Stachowiak M, Pruszynska-Oszmalek E (2011) Maternal protein and folic acid intake during gestation does not program leptin transcription or serum concentration in juvenile rat progeny. Genes Nutr. doi:10.1007/s12263-011-0239-5
Christensen KE, Wu Q, Wang X, Deng L, Caudill MA, Rozen R (2010) Steatosis in mice is associated with gender, folate intake, and expression of genes of one-carbon metabolism. J Nutr 140(10):1736–1741
Desvergne B, Michalik L, Wahli W (2004) Be fit or be sick: peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors are down the road. Mol Endocrinol 18(6):1321–1332
Erhuma A, Bellinger L, Langley-Evans SC, Bennett AJ (2007a) Prenatal exposure to undernutrition and programming of responses to high-fat feeding in the rat. Br J Nutr 98(3):517–524
Erhuma A, Salter AM, Sculley DV, Langley-Evans SC, Bennett AJ (2007b) Prenatal exposure to a low-protein diet programs disordered regulation of lipid metabolism in the aging rat. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 292(6):E1702–E1714
Esfandiari F, Villanueva JA, Wong DH, French SW, Halsted CH (2005) Chronic ethanol feeding and folate deficiency activate hepatic endoplasmic reticulum stress pathway in micropigs. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 289(1):G54–G63
Gavrilova O, Haluzik M, Matsusue K, Cutson JJ, Johnson L, Dietz KR, Nicol CJ, Vinson C, Gonzalez FJ, Reitman ML (2003) Liver peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma contributes to hepatic steatosis, triglyceride clearance, and regulation of body fat mass. J Biol Chem 278(36):34268–34276
Ghandehari H, Kamal-Bahl S, Wong ND (2008) Prevalence and extent of dyslipidemia and recommended lipid levels in US adults with and without cardiovascular comorbidities: the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2003–2004. Am Heart J 156(1):112–119
Gicquel C, El-Osta A, Le Bouc Y (2008) Epigenetic regulation and fetal programming. Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metab 22(1):1–16
Gluckman PD, Hanson MA (2008) Developmental and epigenetic pathways to obesity: an evolutionary-developmental perspective. Int J Obes (Lond) 32:S62–S71
Heerwagen MJ, Miller MR, Barbour LA, Friedman JE (2010) Maternal obesity and fetal metabolic programming: a fertile epigenetic soil. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 299(3):R711–R722
Hummasti S, Laffitte BA, Watson MA, Galardi C, Chao LC, Ramamurthy L, Moore JT, Tontonoz P (2004) Liver X receptors are regulators of adipocyte gene expression but not differentiation: identification of apoD as a direct target. J Lipid Res 45(4):616–625
Jones RH, Ozanne SE (2009) Fetal programming of glucose-insulin metabolism. Mol Cell Endocrinol 297(1–2):4–9
Jones AP, Simson EL, Friedman MI (1984) Gestational undernutrition and the development of obesity in rats. J Nutr 114(8):1484–1492
Langley-Evans SC (2000) Critical differences between two low protein diet protocols in the programming of hypertension in the rat. Int J Food Sci Nutr 51:11–17
Laplante M, Festuccia WT, Soucy G, Gélinas Y, Lalonde J, Berger JP, Deshaies Y (2006) Mechanisms of the depot specificity of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma action on adipose tissue metabolism. Diabetes 55(10):2771–2778
Larsen PJ, Jensen PB, Sørensen RV, Larsen LK, Vrang N, Wulff EM, Wassermann K (2003) Differential influences of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors gamma and -alpha on food intake and energy homeostasis. Diabetes 52(9):2249–2259
Lillycrop KA, Phillips ES, Jackson AA, Hanson MA, Burdge GC (2005) Dietary protein restriction of pregnant rats induces and folic acid supplementation prevents epigenetic modification of hepatic gene expression in the offspring. J Nutr 135(6):1382–1386
Lillycrop KA, Phillips ES, Torrens C, Hanson MA, Jackson AA, Burdge GC (2008) Feeding pregnant rats a protein-restricted diet persistently alters the methylation of specific cytosines in the hepatic PPAR alpha promoter of the offspring. Br J Nutr 100(2):278–282
Lim HJ, Choi YM, Choue R (2008) Dietary intervention with emphasis on folate intake reduces serum lipids but not plasma homocysteine levels in hyperlipidemic patients. Nutr Res 28(11):767–774
Mahabir S, Ettinger S, Johnson L, Baer DJ, Clevidence BA, Hartman TJ, Taylor PR (2008) Measures of adiposity and body fat distribution in relation to serum folate levels in postmenopausal women in a feeding study. Eur J Clin Nutr 62(5):644–650
Mathers JC, McKay JA (2009) Epigenetics—potential contribution to fetal programming. Adv Exp Med Biol 646:119–123
McMillen IC, Robinson JS (2005) Developmental origins of the metabolic syndrome: prediction, plasticity, and programming. Physiol Rev 85(2):571–633
Muhlhausler B, Smith SR (2009) Early-life origins of metabolic dysfunction: role of the adipocyte. Trends Endocrinol Metab 20(2):51–57
Obeid R, Herrmann W (2009) Homocysteine and lipids: S-adenosyl methionine as a key intermediate. FEBS Lett 583(8):1215–1225
Oda H (2006) Functions of sulfur-containing amino acids in lipid metabolism. J Nutr 136(6 Suppl):1666S–1669S
Ojeda ML, Delgado-Villa MJ, Llopis R, Murillo ML, Carreras O (2008) Lipid metabolism in ethanol-treated rat pups and adults: effects of folic Acid. Alcohol Alcohol 43(5):544–550
Peet DJ, Turley SD, Ma W, Janowski BA, Lobaccaro JM, Hammer RE, Mangelsdorf DJ (1998) Cholesterol and bile acid metabolism are impaired in mice lacking the nuclear oxysterol receptor LXR alpha. Cell 93(5):693–704
Pyper SR, Viswakarma N, Yu S, Reddy JK (2010) PPAR alpha: energy combustion, hypolipidemia, inflammation and cancer. Nucl Recept Signal 8:e002
Qi L, Cho YA (2008) Gene-environment interaction and obesity. Nutr Rev 66(12):684–694
Rees WD, Wilson FA, Maloney CA (2006a) Sulfur amino acid metabolism in pregnancy: the impact of methionine in the maternal diet. J Nutr 136(6 Suppl):1701S–1705S
Rees WD, Hay SM, Cruickshank M (2006b) An imbalance in the methionine content of the maternal diet reduces postnatal growth in the rat. Metabolism 55:763–770
Rees WD, Hay SM, Cruickshank M, Reusens B, Remacle C, Antipatis C, Grant G (2006c) Maternal protein intake in the pregnant rat programs the insulin axis and body composition in the offspring. Metabolism 55(5):642–649
Rees WD, McNeil CJ, Maloney CA (2008) The roles of PPARs in the fetal origins of metabolic health and disease. PPAR Res 2008:459030
Schadinger SE, Bucher NL, Schreiber BM, Farmer SR (2005) PPARgamma2 regulates lipogenesis and lipid accumulation in steatotichepatocytes. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 288(6):E1195–E1205
Semmler A, Moskau S, Grigull A, Farmand S, Klockgether T, Smulders Y, Blom H, Zur B, Stoffel-Wagner B, Linnebank M (2010) Plasma folate levels are associated with the lipoprotein profile: a retrospective database analysis. Nutr J 9:31
Stulnig TM, Steffensen KR, Gao H, Reimers M, Dahlman-Wright K, Schuster GU, Gustafsson JA (2002) Novel roles of liver X receptors exposed by gene expression profiling in liver and adipose tissue. Mol Pharmacol 62(6):1299–1305
Tsai YS, Tsai PJ, Jiang MJ, Chou TY, Pendse A, Kim HS, Maeda N (2009) Decreased PPAR gamma expression compromises perigonadal-specific fat deposition and insulin sensitivity. Mol Endocrinol 23(11):1787–1798
Valsamakis G, Kumar S, Creatsas G, Mastorakos G (2010) The effects of adipose tissue and adipocytokines in human pregnancy. Ann N Y AcadSci 1205:76–81
van Straten EM, Bloks VW, Huijkman NC, Baller JF, van Meer H, Lütjohann D, Kuipers F, Plösch T (2010) The liver X-receptor gene promoter is hypermethylated in a mouse model of prenatal protein restriction. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 298(2):R275–R282
Vandesompele J, De Preter K, Pattyn F, Poppe B, Van Roy N, De Paepe A, Spelman F (2002) Accurate normalization of real-time quantitative RT-PCR data by geometric averaging of multiple internal control genes. Genome Biol 3:1–12
Wild S, Roglic G, Green A, Sicree R, King H (2004) Global prevalence of diabetes: estimates for the year 2000 and projections for 2030. Diabetes Care 27(5):1047–1053
Wójcicka G, Jamroz-Wiśniewska A, Horoszewicz K, Bełtowski J (2007) Liver X receptors (LXRs). Part I: structure, function, regulation of activity, and role in lipid metabolism. Postepy Hig Med Dosw (Online) 61:736–759
Wu CW, Chu ES, Lam CN, Cheng AS, Lee CW, Wong VW, Sung JJ, Yu J (2010) PPARgamma is essential for protection against nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Gene Ther 17(6):790–798
Yoon M (2009) The role of PPAR alpha in lipid metabolism and obesity: focusing on the effects of estrogen on PPAR alpha actions. Pharmacol Res 60(3):151–159
Yu S, Matsusue K, Kashireddy P, Cao WQ, Yeldandi V, Yeldandi AV, Rao MS, Gonzalez FJ, Reddy JK (2003) Adipocyte-specific gene expression and adipogenicsteatosis in the mouse liver due to peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma1 (PPARgamma1) overexpression. J BiolChem 278(1):498–505
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the Polish Ministry of Education and Science, grant No N312 151034.
Open Access
This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Noncommercial License which permits any noncommercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author(s) and source are credited.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
Open Access This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Noncommercial License (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/2.0), which permits any noncommercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author(s) and source are credited.
About this article
Cite this article
Chmurzynska, A., Stachowiak, M., Gawecki, J. et al. Protein and folic acid content in the maternal diet determine lipid metabolism and response to high-fat feeding in rat progeny in an age-dependent manner. Genes Nutr 7, 223–234 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12263-011-0253-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12263-011-0253-7