Abstract
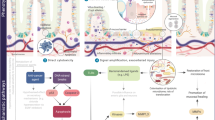
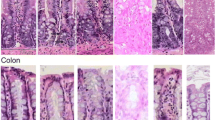
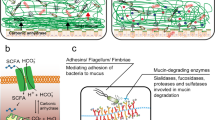
Chemotherapy for cancer causes significant gut toxicity known as mucositis. The pathogenesis of mucositis is ill defined. Recent clinical research guidelines have highlighted epithelial junctional complexes as emerging targets within mucositis research. Given the robust biological evidence linking tight junctions and matrix metalloproteinases, key mediators of mucositis, tight junction proteins have received significant attention. Despite this, the link between tight junctions, matrix metalloproteinases and mucositis development is yet to be established. This critical review therefore aims to describe the role of matrix metalloproteinases in mucositis, and how matrix metalloproteinase-dependent tight junction disruption may contribute to the pathobiology of mucositis.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Keefe D, Schubert M et al (2007) Updated clinical practice guidelines for the prevention and treatment of mucositis. Cancer 109:820–831
Sonis S (2004) The pathobiology of mucositis. Nat Rev Cancer 4:277–284
Sonis S, Shklar T et al (1990) An animal model for mucositis induced by cancer chemotherapy. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol 69:437–443
Paris F, Fuks Z et al (2001) Endothelial apoptosis as the primary lesion initiating intestinal radiation damage in mice. Science 293:293–297
Logan R, Stringer A et al (2009) Is the pathobiology of chemotherapy-induced alimentary tract mucositis influenced by the type of mucotoxic drug administered? Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 63:239–251
Stringer A, Gibson R et al (2009) Irinotecan-induced mucositis manifesting as diarrhoea corresponds with an amended intestinal flora and mucin profile. Int J Exp Pathol 90:489–499
Stringer A, Gibson R et al (2009) Chemotherapy-induced changes to microflora: evidence and implications of change. Curr Drug Metab 10:79–83
Al-Dasooqi N, Bowen J et al (2011) Irinotecan-induced alterations in intestinal cell kinetics and extracellular matrix component expression in the dark agouti rat. Int J Exp Pathol 92:357–365
Al-Dasooqi N, Gibson R et al (2010) Matrix metalloproteinases are possible mediators for the development of alimentary tract mucositis in the DA rat. Exp Biol Med 235:1244–1256
Ma T, Iwamoto G et al (2004) TNF-alpha-induced increase in intestinal epithelial tight junction permeability requires NF-kappa B activation. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 286:G367–G376
Blijlevens NM, Donnelly JP, de Pauw BE (2005) Prospective evaluation of gut mucosal barrier injury following various myeloablative regimens for haematopoietic stem cell transplant. Bone Marrow Transplant 35(7):707–711
Walsh-Reitz M, Huang E et al (2005) AMP-18 protects barrier function of colonic epithelial cells: role of tight junction proteins. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 289:G163–G171
Wardill H, Bowen J, Gibson R (2013) Chemotherapy-induced gut toxicity: are alterations to intestinal tight junctions pivotal? Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 70:627–635
Hollander D (1999) Intestinal permeability, leaky gut, and intestinal disorders. Curr Gastroenterol Rep 1:410–416
Gonzalez-Mariscal L, Tapia R, Chamorro D (2008) Crosstalk of tight junction components with signaling pathways. Biochim Biophys Acta 1778(3):729–756
Keefe D, Cummins AG et al (1997) Effect of high-dose chemotherapy on intestinal permeability in humans. Clin Sci 92:385–389
Keefe D (2000) Chemotherapy for cancer causes apoptosis that precedes hypoplasia in crypts of the small intestine in humans. Gut 47:632–637
Hamada K, Shitara Y et al (2010) Zonula Occluden-1 alterations and enhances intestinal permeability in methotrexate-treated rats. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 66:1031–1038
Nakao T, Kurita N et al (2012) Irinotecan injures tight junction and causes bacterial translocation in rat. J Surg Res 173(2):341–347
Youmba SB, Belmonte L et al (2011) Methotrexate Modulates Tight Junctions Through NF-kappaB, MEK and JNK Pathways. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr
Stringer A, Al-Dasooqi N et al (2013) Biomarkers of chemotherapy-induced diarrhoea: a clinical study of intestinal microbiome alterations, inflammation and circulating matrix metalloproteinases. Support Care Cancer. [Epub ahead of print]
Sengupta N, MacDonald T (2007) The role of matrix metalloproteinases in stromal/epithelial interactions in the gut. Physiology 22:401–409
Clark I, Swingler T et al (2008) The regulation of matrix metalloproteinases and their inhibitors. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 40:1362–1378
Manicone A, McGuire J (2008) Matrix metalloproteinases as modulators of inflammation. Semin Cell Dev Biol 19:34–41
Wolf M, Albrecht S, Marki C (2008) Proteolytic processing of Chemokines: implications in physiological and pathological conditions. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 40:1185–1198
Klein T, Bischoff R (2011) Physiology and pathophysiology of matrix metalloproteinases. Amino Acids 41:271–290
Chakraborti S, Mandal M et al (2003) Regulation of matrix metalloproteinases: an overview. Mol Cell Biochem 253:269–285
Pender S, MacDonald T (2004) Matrix metalloproteinases and the gut- new roles for old enzymes. Curr Opin Pharmacol 4:546–550
Van Wart H, Birkedal-Hansen H (1990) The cysteine switch: a principle of regulation of metalloproteinase activity with potential applicability to the entire matrix metalloproteinase gene family. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 87:5578–5582
Dhaouadi T, Sfar I et al (2007) Role of immune system, apoptosis and angiogenesis in pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis and joint destruction, a systematic review. Tunis Med 85:991–998
Sorsa T, Tjaderhane L et al (2006) Matrix metalloproteinases: contribution to pathogenesis, diagnosis and treatment of periodontal inflammation. Ann Med 38:306–321
Vandenbroucke R, Dejonckheere E, and Libert C (2011) A therapeutic role for MMP inhibitors in lung diseases? Eur Respir J [Epub ahead of print]
Parks W, Wilson C, Lopez-Boado Y (2004) Matrix metalloproteinases as modulators of inflammation and innate immunity. Nat Rev Immunol 4:617–629
Shipley J, Wesselschmidt R et al (1996) Metalloelastase is required for macrophage-mediated proteolysis and matrix invasion in mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci 93:3942–3946
Warner R, Lewis C et al (2001) The role of metalloelastase in immune complex-induced acute lung injury. Am J Pathol 158:2139–2144
Lanone S, Zheng T et al (2002) Overlapping and enzyme-specific contributions of matrix metalloproteinases-9 and -12 in IL-13-induced inflammation and remodeling. J Clin Invest 110:463–474
Itoh T, Matsuda H et al (2002) The role of matrix metalloproteinase-2 and matrix metalloproteinase-9 in antibody-induced arthritis. J Immunol 169:2643–2647
Mudgett J, Hutchinson N et al (1998) Susceptability of stromelysin-1 deficient mice to collagen-induced arthritis and cartilage destruction. Arthritis Rheum 41:110–121
Corry D, Rishi K et al (2002) Decreased allergic lung inflammatory cell egression and increased susceptability to asphyxiation in MMP2-deficiency. Nat Immunol 3:347–353
Hartzell W, Shapiro S (1999) Marcophage elastase prevents Gemella morbillorum infection and improves outcome following murine bone marrow transplantation. Chest 116:31S–32S
Burke B (2004) The role of matrix metalloproteinase 7 in innate immunity. Immunobiology 209:51–56
Page-McCaw A, Ewald A, Werb Z (2007) Matrix metalloproteinases and the regulation of tissue remodelling. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 8:221–233
Will C, Fromm M, Muller D (2008) Claudin tight junction proteins: novel aspects in paracellular transport. Perit Dial Int J Int Soc Perit Dial 28(6):577–584
Anderson JM, Balda MS, Fanning AS (1993) The structure and regulation of tight junctions. Curr Opin Cell Biol 5(5):772–778
Fanning AS, Anderson JM (2009) Zonula occludens-1 and -2 are cytosolic scaffolds that regulate the assembly of cellular junctions. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1165:113–120
Katsuno T, Umeda K et al (2008) Deficiency of zonula occludens-1 causes embryonic lethal phenotype associated with defected yolk sac angiogenesis and apoptosis of embryonic cells. Mol Biol Cell 19(6):2465–2475
Shin K, Margolis B (2006) ZOning out tight junctions. Cell 126(4):647–649
Umeda K, Ikenouchi J et al (2006) ZO-1 and ZO-2 independently determine where claudins are polymerized in tight-junction strand formation. Cell 126(4):741–754
Bertiaux-Vandaele N, Youmba SB et al (2011) The expression and the cellular distribution of the tight junction proteins are altered in irritable bowel syndrome patients with differences according to the disease subtype. Am J Gastroenterol 106(12):2165–2173
Schulzke JD, Ploeger S et al (2009) Epithelial tight junctions in intestinal inflammation. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1165:294–300
Turner J (2009) Intestinal mucosal barrier function in health and disease. Nat Rev Immunol 9:799–809
Cummins PM (2012) Occludin: one protein, many forms. Mol Cell Biol 32(2):242–250
Schulzke JD, Gitter AH et al (2005) Epithelial transport and barrier function in occludin-deficient mice. Biochim Biophys Acta 1669(1):34–42
Ulluwishewa D, Anderson RC et al (2011) Regulation of tight junction permeability by intestinal bacteria and dietary components. J Nutr 141(5):769–776
Fazeny-Dorner B, Veitl M et al (2002) Alterations in intestinal permeability following the intensified polydrug-chemotherapy IFADIC (ifosfamide, Adriamycin, dacarbazine). Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 49(4):294–298
Wardill H, Bowen J and Gibson R (2013) Irinotecan disrupts tight junction protein occludin in the rat small intestine, in Multinational Association for Supprotive Care in Cancer. J Support Care Cancer. Berlin, Germany
Bauer A, Burgers H et al (2010) Matrix metalloproteinase-9 mediates hypoxia-induced vascular leakage in the brain via tight junction rearrangement. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 30:837–848
Lischper M, Beuck S et al (2010) Metalloproteinase mediated occludin cleavage in the cerebral microcapillary endothelium under pathological conditions. Brain Res 1326:114–127
Vermeer P, Denker J et al (2009) MMP9 modulates tight junction integrity and cell viability in human airway epithelia. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 296:L751–L762
Blecharz K, Haghikia A et al (2010) Glucocorticoid effects on endothelial barrier function in the murine brain endothelial cell line cEND incubated with sera from patients with multiple sclerosis. Mult Scler 16:293–302
Liu W, Hendren J et al (2009) Normobaric hyperoxia attenuates early blood–brain barrier disruption by inhibiting MMP-9-mediated occludin degradation in focal cerebral ischemia. J Neurochem 108:811–820
Chen W, Hartman R, Ayer R, Marcantonio S, Kamper J, Tang J, Zhang JH (2009) Matrix metalloproteinases inhibition provides neuroprotection against hypoxia-ischemia in the developing brain. J Neurochem 111:726–736
Higashida T, Kreipke CW, Rafols JA, Peng C, Schafer S, Schafer P, Ding JY, Dornbos D 3rd, Li X, Guthikonda M, Rossi NF, Ding Y (2011) The role of hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha, aquaporin-4 and matrix metalloproteinase-9 in blood–brain barrier disruption and brain edema after traumatic brain injury. J Neurosurg 114:92–101
Siu M, Lee W, Cheng C (2003) The interplay of collagen IV, tumor necrosis factor-alpha, gelatinase B (matrix metalloprotease-9), and tissue inhibitor of metalloproteases-1 in the basal lamina regulates Sertoli cell-tight junction dynamics in the rat testis. Endocrinology 144:371–387
Gorodeski G (2007) Estrogen decrease in tight junction resistance involves matrix metalloproteinase-7-mediated remodeling of occludin. Endocrinology 148:218–231
Jeong S, Ledee D et al (2012) Interaction of clusterin and matrix metalloproteinase-9 and its implication for epithelial homeostasis and inflammation. Am J Pathol 180:2028–2039
Acknowledgments
Dr Noor Al-Dasooqi is a Clinical Centre of Research Excellence Post-Doctoral Research Fellow; Ms Hannah Wardill is the recipient of an Australian Post-Graduate Scholarship
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Al-Dasooqi, N., Wardill, H.R. & Gibson, R.J. Gastrointestinal Mucositis: The Role of MMP-Tight Junction Interactions in Tissue Injury. Pathol. Oncol. Res. 20, 485–491 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12253-013-9733-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12253-013-9733-y