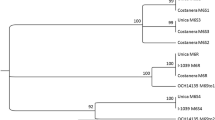
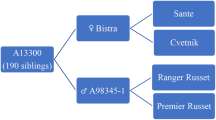
Abstract
Potato virus Y (PVY) impacts potato production worldwide by reducing potato yield, tuber quality, and successful certification of seed. Extreme resistance to PVY is conferred by three genes (Ryadg, Rysto, and Rychc) which have been introgressed from wild species into cultivated varieties. Both Rysto and Ryadg are used in many breeding programs worldwide, but Rychc is found in only a limited number of varieties and previously had been absent in varieties and germplasm representative of the russet market class that is widely grown in North America. Five russet breeding clones were identified as having the molecular marker associated with Rychc. Confirmation of the presence of Rychc was established following field and greenhouse screening of the clones for resistance to PVY with no infection by the virus being observed. These clones also have been characterized as having resistance to late blight and cold-induced sweetening of tubers and all are male-fertile as well. The unique assemblage of resistances in this russet germplasm will be of value to the potato breeding community in the development of russet potato varieties, especially with respect to Rychc which previously has not been reported as being present in this potato market class.
Resumen
El virus Y de la papa (PVY) impacta la producción de papa en todo el mundo al reducir el rendimiento de la papa, la calidad del tubérculo y la certificación exitosa de la semilla. La resistencia extrema al PVY es conferida por tres genes (Ry adg, Ry sto y Ry chc) que han sido incorporados de especies silvestres a variedades cultivadas. Tanto Ry sto como Ry adg se utilizan en muchos programas de mejoramiento en el mundo, pero Ry chc se encuentra solo en un número limitado de variedades y anteriormente había estado ausente en variedades y germoplasma representativos de la clase de mercado tipo russet que se cultiva ampliamente en América del Norte. Se identificaron cinco clones avanzados de tipo russet que tenían el marcador molecular asociado con Ry chc. Se estableció la confirmación de la presencia de Ry chc después de la evaluación de campo e invernadero de los clones para detectar resistencia a PVY sin que se observara infección por el virus. Estos clones también se han caracterizado por tener resistencia al tizón tardío y al endulzamiento de los tubérculos inducido por el frío y todos machos fertiles también. El ensamblaje único de resistencias en este germoplasma tipo russet será de valor para la comunidad de mejoramiento de papa en el desarrollo de variedades de papa tipo russet, especialmente con respecto a Ry chc que anteriormente no se ha reportado previamente como presente en esta clase de papa en el mercado.


taken from 6–7 representative tubers after harvest in 2020

Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
16 November 2021
A Correction to this paper has been published: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12230-021-09854-z
References
Asama, K., I. H, M. N, and I. T. 1982. New potato variety “Konafubuki”. Bull Hokkaido Pref Agr Exp Stn 48:75-84.
Clark, M.F., and A.N. Adams. 1977. Characteristics of the microplate method of enzyme linked immunosorbent assay for the detection of plant viruses. Journal of General Virology 34: 475–483.
Corsini, D., J. Pavek, and J. Davis. 1988. Verticillium wilt resistance in noncultivated tuber-bearing Solanum species. Plant Disease 72: 148–151.
Corsini, D.L., J.J. Pavek, M.W. Martin, and C.R. Brown. 1994. Potato germplasm with combined resistance to leafroll virus and viruses X and Y. American Potato Journal 71: 377–385.
Elison, G.L., D.G. Hall, R.G. Novy, and J.L. Whitworth. 2020. Development and application of a multiplex marker assay to detect PVY resistance genes in solanum tuberosum. American Journal of Potato Research 97: 289–296.
Flis, B., J. Hennig, D. Strzelczyk-Żyta, C. Gebhardt, and W. Marczewski. 2005. The Ry-f sto gene from Solanum stoloniferum for extreme resistant to Potato virus Y maps to potato chromosome XII and is diagnosed by PCR marker GP122 718 in PVY resistant potato cultivars. Molecular Breeding 15: 95–101.
Fujimatsu, M., H. Hashizume, T. Fudan, Y. Koma, R. Sanetomo, S. Ono, and K. Hosaka. 2018. Harimaru: A new potato variety for a local specialty. Breeding Science 68: 284–288.
Fulladolsa, A.C., A. Charkowski, X. Cai, J. Whitworth, S. Gray, and S. Jansky. 2019. Germplasm with Resistance to Potato virus Y Derived from Solanum chacoense: Clones M19 (39–7) and M20 (XD3). American Journal of Potato Research 96: 390–395.
Halbert, S.E., D.L. Corsini, and M.A. Wiebe. 2003. Potato virus Y transmission efficiency for some common aphids in Idaho. American Journal of Potato Research 80: 87–91.
Hosaka, K. Collections. http://univ.obihiro.ac.jp/~Potato/collections/home.html. Accessed 23 September 2021
Hosaka, K., Y. Hosaka, M. Mori, T. Maida, and H. Matsunaga. 2001. Detection of a simplex RAPD marker linked to resistance to potato virus Y in a tetraploid potato. American Journal of Potato Research 78: 191–196.
Karasev, A.V., and S.M. Gray. 2013. Continuous and emerging challenges of potato virus y in potato. Pages 571–586 in: Annual Review of Phytopathology.
Kasai, K., Y. Morikawa, V.A. Sorri, J.P.T. Valkonen, C. Gebhardt, and K.N. Watanabe. 2000. Development of SCAR markers to the PVY resistance gene RY(adg) based on a common feature of plant disease resistance genes. Genome 43: 1–8.
Mori, K., N. Mukojima, T. Nakao, S. Tamiya, Y. Sakamoto, N. Sohbaru, K. Hayashi, H. Watanuki, K. Nara, K. Yamazaki, T. Ishii, and K. Hosaka. 2012. Germplasm Release: Saikai 35, a Male and Female Fertile Breeding Line Carrying Solanum Phureja-Derived Cytoplasm and Potato Cyst Nematode Resistance (H1) and Potato Virus Y Resistance (Ry chc) Genes. American Journal of Potato Research 89: 63–72.
Mosley, A.R., S. Yilma, D.C. Hane, S. James, K.A. Rykbost, C.C. Shock, B. Charlton, E. Eldredge, and L. Leroux. 2003. Oregon. National Potato Germplasm Evaluation and Enhancement Report:369–388.
Munoz, F.J., R.L. Plaisted, and H.D. Thurston. 1975. Resistance to potato virus Y inSolanum tuberosum spp.andigena. American Potato Journal 52: 107–115.
Novy, R.G., J.L. Whitworth, J.C. Stark, B.L. Schneider, N.R. Knowles, M.J. Pavek, L.O. Knowles, B.A. Charlton, V. Sathuvalli, S. Yilma, C.R. Brown, M. Thornton, T.L. Brandt, and N. Olsen. 2017. Payette Russet: A Dual-Purpose Potato Cultivar with Cold-Sweetening Resistance, Low Acrylamide Formation, and Resistance to Late Blight and Potato Virus Y. American Journal of Potato Research 94: 38–53.
Novy, R.G., S.L. Love, D.L. Corsini, J.J. Pavek, J.L. Whitworth, A.R. Mosley, S.R. James, D.C. Hane, C.C. Shock, K.A. Rykbost, C.R. Brown, R.E. Thornton, N.R. Knowles, M.J. Pavek, N. Olsen, and D.A. Inglis. 2006. Defender: A high-yielding, processing potato cultivar with foliar and tuber resistance to late blight. American Journal of Potato Research 83: 9–19.
Novy, R.G., J.L. Whitworth, J.C. Stark, B.A. Charlton, S. Yilma, N.R. Knowles, M.J. Pavek, T.L. Brandt, S. Gupta, N. Olsen, M. Thornton, C.R. Brown, D.L. Corsini, J.J. Pavek, S.R. James, D.C. Hane, H. Lozoya-Saldana, and M.I. Vales. 2012. Palisade Russet: A Late Blight Resistant Potato Cultivar Having a Low Incidence of Sugar Ends and High Specific Gravity. American Journal of Potato Research 89: 89–101.
Plaisted, R.L., D.E. Halseth, B.B. Brodie, S.A. Slack, J.B. Sieczka, B.J. Christ, K.M. Paddock, and M.W. Peck. 2001. Eva: A midseason golden nematode- and virus-resistant variety for use as tablestock or chipstock. American Journal of Potato Research 78: 65–68.
Ross, H. 1958. Inheritance of extreme resistance to potato virus Y in Solanum stoloniferum and its hybrids with Solanum tuberosum. Proc Third Conf Potato Virus Diseases:204–211.
Sato, M., K. Nishikawa, K. Komura, and K. Hosaka. 2006. Potato virus Y resistance gene, Rychc, mapped to the distal end of potato chromosome 9. Euphytica 149: 367–372.
Slater, A.T., L. Schultz, M. Lombardi, B.C. Rodoni, C. Bottcher, N.O.I. Cogan, and J.W. Forster. 2020. Screening for Resistance to PVY in Australian Potato Germplasm. Genes 11.
Solomon-Blackburn, R.M., and H. Barker. 2001. Breeding virus resistant potatoes (Solanum tuberosum): A review of traditional and molecular approaches. Heredity 86: 17–35.
Świeżyński, K.M. 1994. Inheritance of resistance to viruses. Pages 339–363. CAB INTERNATIONAL, Wallingford.
Valkonen, J.P.T. 1994. Natural Genes and Mechanisms for Resistance to Viruses in Cultivated and Wild Potato Species (Solanum spp.). Plant Breeding 112: 1–16.
Xu, Y., and S.M. Gray. 2020. Aphids and their transmitted potato viruses: A continuous challenges in potato crops. Journal of Integrative Agriculture 19: 367–375.
Funding
This work was partially funded by USDA-NIFA Specialty Crop Research Initiative award no. 2014-51181-22373 and by USDA-NIFA Specialty Crop Research Initiative award no. 2020-51181-32136.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Elison, G.L., Novy, R.G. & Whitworth, J.L. Russet Potato Breeding Clones with Extreme Resistance to Potato Virus Y Conferred by Rychc as well as Resistance to Late Blight and Cold-Induced Sweetening. Am. J. Potato Res. 98, 411–419 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12230-021-09852-1
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12230-021-09852-1