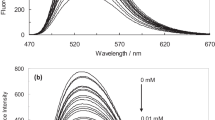
Abstract
The inhibition of the cytotoxicity of NK cells by microgravity in space is of serious concern to the health of astronauts. However, there remains a lack of in-depth research into the mechanisms of action of this suppression. In the present study, the effects of simulated microgravity (SMG) on the morphology, survival rate and the ability of NK cells to kill were studied initially and then the mechanism of SMG in the inhibition of NK cytotoxicity was preliminarily investigated from the perspectives of stimulatory and inhibitory receptor expression. Further, the present study attempted to reveal the molecular mechanisms of SMG inhibition of the stimulatory receptor NKG2D from the perspective of DNA methylation and the expression of its adaptor protein DAP10. The results demonstrated that down-regulation of stimulatory receptor NKG2D expression and significantly up-regulated expression of inhibitory receptor CD158a may be important in explaining for the inhibition of NK cell cytotoxicity by SMG. The down-regulation of DAP10 expression, and not its DNA methylation, that is the possible cause of the down-regulation of NKG2D expression by SMG and the subsequent suppression of NK cell activity. However, inhibition of DAP10 expression by SMG was also not achieved by influencing methylation, and so additional analysis of the mechanism is required. The results of the present study lay the foundations for finally elucidating the molecular mechanisms by which microgravity leads to a decline in NK cell activity and contributes important evidence for interpreting the regulatory mechanisms of NK cell cytotoxicity.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baba, Y., Watanabe, M., Baba, H.: A review of the alterations in DNA methylation in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Surg. Today. 43(12), 1355–1364 (2013)
Bigley, A.B., Agha, N.H., Baker, F.L., Spielmann, G., Kunz, H.E., Mylabathula, P.L., Rooney, B., Laughlin, M.S., Mehta, S.K., Pierson, D.L., Crucian, B.E., Simpson, R.J.: NK-cell function is impaired during long-duration spaceflight. J. Appl. Physiol. 126(4), 842–853 (2019)
Brown, R., Klaus, D., Todd, P.: Effects of space flight, clinorotation, and centrifugation on the substrate utilization efficiency of E. coli. Microgravity Sci. Technol. 13(4), 24–29 (2002)
Burgess, S.J., Marusina, A.I., Pathmanathan, I., Borrego, F., Coligan, J.E.: IL-21 down-regulates NKG2D/DAP10 expression on human NK and CD8+ T cells. J. Immunol. 176(3), 1490–1497 (2006)
Crucian, B.E., Alexander, C., Simpson, R.J., Satish, M., Gailen, M., Smith, S.M., Zwart, S.R., Martina, H., Sergey, P., Alexandra, W.: Immune system Dysregulation during spaceflight: potential countermeasures for deep space exploration missions. Front. Immunol. 9, 1437 (2018)
Fernándezsánchez, A., Baragaño, R.A., Carvajal, P.R., Sanz, A.B., Ortiz, A., Ortega, F., Suárezálvarez, B., Lópezlarrea, C.: DNA demethylation and histone H3K9 acetylation determine the active transcription of the NKG2D gene in human CD8+ T and NK cells. Epigenetics. 8(1), 66–78 (2013)
Gilfillan, S., Ho, E.L., Cella, M., Yokoyama, W.M., Colonna, M.: NKG2D recruits two distinct adapters to trigger NK cell activation and costimulation. Nat. Immunol. 3(12), 1150–1155 (2002)
Huang, Q.S., Li, Q., Huang, Y., Shang, P., Zhang, M.J.: Expansion of human natural killer cells ex vivo. Chin. J. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 24(12), 1167–1173 (2008)
Huyan, T., Li, Q., Yang, H., Jin, M.L., Zhang, M.J., Ye, L.J., Li, J., Huang, Q.S., Yin, D.C.: Protective effect of polysaccharides on simulated microgravity-induced functional inhibition of human NK cells. Carbohydr. Polym. 101(1), 819–827 (2014)
Klaus, D.M., Howard, H.N.: Antibiotic efficacy and microbial virulence during space flight. Trends Biotechnol. 24(3), 131–136 (2006)
Konjevic, G., Martinovic, K.M., Jurisic, V., Babovic, N., Spuzic, I.: Biomarkers of suppressed natural killer (NK) cell function in metastatic melanoma: decreased NKG2D and increased CD 158a receptors on CD3-CD16+NK cells. Biomarkers. 14(4), 258–270 (2009)
Konjevic, G., Vuletic, A., Mirjacic Martinovic, K., Colovic, N., Colovic, M., Jurisic, V.: Decreased CD161 activating and increased CD158a inhibitory receptor expression on NK cells underlies impaired NK cell cytotoxicity in patients with multiple myeloma. J. Clin. Pathol. 69, 1009–1016 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1136/jclinpath-2016-203614
Konstantinova, I.V., Sonnenfeld, G., Lesnyak, A.T., Shaffar, L., Mandel, A., Rykova, M.P., Antropova, E.N., Ferrua, B.: Cellular immunity and lymphokine production during spaceflights. Physiologist. 34(1 Suppl), S52–S56 (1991)
Konstantinova, I.V., Rykova, M., Meshkov, D., Peres, C., Husson, D., Schmitt, D.A.: Natural killer cells after ALTAIR mission. Acta Astronaut. 36(8–12), 713–718 (1995)
Lam, V.C., Lanier, L.L.: NK cells in host responses to viral infections. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 44, 43–51 (2017)
Lanier, L.L.: NK cell recognition. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 23(1), 225–274 (2005)
Li, Q., Mei, Q., Huyan, T., Xie, L., Che, S., Yang, H., Zhang, M., Huang, Q.: Effects of simulated microgravity on primary human NK cells. Astrobiology. 13(8), 703–714 (2013)
Lopez-Larrea, C., Suarez-Alvarez, B., Lopez-Soto, A., Lopez-Vazquez, A., Gonzalez, S.: The NKG2D receptor: sensing stressed cells. Trends Mol. Med. 14(4), 179–189 (2008)
Martinez, E.M., Yoshida, M.C., Candelario, T.L., Hughes-Fulford, M.: Spaceflight and simulated microgravity cause a significant reduction of key gene expression in early T-cell activation. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 308(6), R480–R488 (2015)
Moore, L.D., Le, T., Fan, G.: DNA methylation and its basic function. Neuropsychopharmacol. 38(1), 23–38 (2013)
Moretta, L., Bottino, C., Pende, D., Castriconi, R., Mingari, M.C., Moretta, A.: Surface NK receptors and their ligands on tumor cells. Semin. Immunol. 18(3), 151–158 (2006)
Mylabathula, P.L., Bigley, A.B., Li, L., Crucian, B.E., Pierson, D.L., Mehta, S.K., Rezvani, K., Simpson, R.J.: Simulated microgravity ‘disarms’ human natural killer cells and suppresses cytotoxic activity against tumor target cells. Brain Behav. Immun. 66, e31 (2017)
Mylabathula, P.L., Li, L., Bigley, A.B., Markofski, M.M., Crucian, B.E., Mehta, S.K., Pierson, D.L., Laughlin, M.S., Rezvani, K., Simpson, R.J.: Simulated microgravity disarms human NK-cells and inhibits anti-tumor cytotoxicity in vitro. Acta Astronaut. 174, 32–40 (2020)
Ogasawara, K., Benjamin, J., Takaki, R., Phillips, J.H., Lanier, L.L.: Function of NKG2D in natural killer cell-mediated rejection of mouse bone marrow grafts. Nat. Immunol. 6(9), 938–945 (2005)
Park, Y.P., Choi, S.C., Kiesler, P., Gil-Krzewska, A., Coligan, J.E.: Complex regulation of human NKG2D-DAP10 cell surface expression: opposing roles of the γ c cytokines and TGF-β1. Blood. 118(11), 3019–3027 (2011)
Shao, D., Yao, L., Riaz, M.S., Zhu, J., Shi, J., Jin, M., Huang, Q., Yang, H.: Simulated microgravity affects some biological characteristics of Lactobacillus acidophilus. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 101(8), 1–11 (2017)
Simpson, R. J., Bigley, A. B., Spielmann, G., Kunz, H. E., Agha, N., Baker, F., Rooney, B., Mylabathula, P. L., Graff, R. M., Crucian, B. E.: Long duration spaceflight impairs NK-cell function in astronauts: 338 board #175 june 1, 9. Med. Sci. Sport. Exer. 48, 87 (2016)
Singh, K.P., Kumari, R., DuMond, J.W.: Simulated microgravity-induced epigenetic changes in human lymphocytes. J. Cell. Biochem. 111(1), 123–129 (2010)
Smyth, M.J., Cretney, E., Kelly, J.M., Westwood, J.A., Street, S.E., Yagita, H., Takeda, K., van Dommelen, S.L., Degliesposti, M.A., Hayakawa, Y.: Activation of NK cell cytotoxicity. Mol. Immunol. 42(4), 501–510 (2005)
Suárez-Alvarez, B., López-Vázquez, A., Baltar, J.M., Ortega, F., López-Larrea, C.: Potential role of NKG2D and its ligands in organ transplantation: new target for Immunointervention. Am. J. Transplant. 9(2), 251–257 (2009)
Talas, M., Batkai, L., Stoger, I., Nagy, L., Hiros, L., Konstantinova, I., Rykova, M., Mozgovaya, I., Guseva, O., Kozharinov, V.: Results of space experiment program “Interferon”. I. Production of interferon in vitro by human lymphocytes aboard space laboratory Solyut-6 (“Interferon I”) and infl uence of space fl ight on lymphocyte functions of cosmonauts (“Interferon III”). Acta Microbiol. Hung. 30(1), 53–61 (1983)
Upshaw, J. L., Leibson, P. J.: NKG2D-Mediated Activation of Cytotoxic Lymphocytes: Unique Signaling Pathways and Distinct Functional Outcomes. Semin Immunol. 18(3), 167–175 (2006)
Vivier, E., Nunès, J.A., Vély, F.: Natural killer cell signaling pathways. Science. 306(5701), 1517–1519 (2004)
Wu, J., Song, Y., Bakker, A.B., Bauer, S., Spies, T., Lanier, L.L., Phillips, J.H.: An activating immunoreceptor complex formed by NKG2D and DAP10. Science. 285(5428), 730–732 (1999)
Xie, X., Lei, D., Zhang, Q., Wang, Y., Wen, L., Ye, Z., Ud Din, A., Jia, D., Apicella, A., Wang, G.: Effect of simulated microgravity induced PI3K-nos2b signalling on zebrafish cardiovascular plexus network formation. J. Biomech. 87, 83–92 (2019)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shao, D., Ye, L., Zhu, B. et al. Mechanisms of the Effect of Simulated Microgravity on the Cytotoxicity of NK Cells Following the DNA Methylation of NKG2D and the Expression of DAP10. Microgravity Sci. Technol. 33, 6 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12217-020-09863-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12217-020-09863-3