Abstract
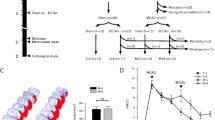
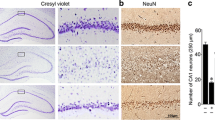
Cognitive issues in stroke arise as a result of reperfusion of a clogged artery, which is reported to exacerbate the injury in the brain leading to oxidative stress. Through the present work, we try to understand the regional variations across brain regions mainly cortex and striatum associated with the progression of ischemia-reperfusion injury (IRI). In a rat model of IRI, the influence of varying ischemia and reperfusion times on the biochemical phases across the brain regions were monitored. IRI resulted in the blood-brain barrier disruption and developed mild areas of risk. The brain’s tolerance towards IRI indicated a progressive trend in the injury and apoptosis from ischemia to reperfusion that was supported by the activities of plasma lactate dehydrogenase and tissue caspase-3. Cognitive impairment in these rats was an implication of cellular oxidative stress (higher lipid peroxidation and lower antioxidant enzyme activity) that persisted by 24-h reperfusion. The oxidative stress was prominent in the cortex than the striatum and was supported by the lower ATP level. Upregulated Mn-SOD expression leading to a preserved mitochondria in the striatum could be attributed to the regional protection. Overall, a progression of IRI was observed from striatum to cortex leading to 5-day cognitive decline.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Almeida A, Allen KL, Bates TE, Clark JB (1995) Effect of reperfusion following cerebral ischaemia on the activity of the mitochondrial respiratory chain in the gerbil brain. J Neurochem 65:1698–1703
Anselmi A, Abbate A, Girola F, Nasso G, Biondi-Zoccai GG, Possati G, Gaudino M (2004) Myocardial ischemia, stunning, inflammation, and apoptosis during cardiac surgery: A review of evidence. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg 25:304–311. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejcts.2003.12.003
Bačić G, Pavićević A, Peyrot F (2016) In vivo evaluation of different alterations of redox status by studying pharmacokinetics of nitroxides using magnetic resonance techniques. Redox Biol 8:226–242. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.redox.2015.10.007
Bai J, Lyden PD (2015) Revisiting cerebral postischemic reperfusion injury: New insights in understanding reperfusion failure, hemorrhage, and edema. Int J Stroke 10:143–152. https://doi.org/10.1111/ijs.12434
Banu SA, Ravindran S, Kurian GA (2016) Hydrogen sulfide post-conditioning preserves interfibrillar mitochondria of rat heart during ischemia reperfusion injury. Cell Stress Chaperones 21:571–582. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12192-016-0682-8
Baron J-C, Yamauchi H, Fujioka M, Endres M (2013) Selective neuronal loss in ischemic stroke and cerebrovascular disease. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 34:2–18. https://doi.org/10.1038/jcbfm.2013.188
Barrientos A, Fontanesi F, Díaz F (2009) Evaluation of the mitochondrial respiratory chain and oxidative phosphorylation system using polarography and spectrophotometric enzyme assays. Current protocols in human genetics / editorial board, Jonathan L. Haines … [et al.] CHAPTER:Unit19.3-Unit19.3. https://doi.org/10.1002/0471142905.hg1903s63
Bruin JP de, Sanchez-Santed F, Heinsbroek RP, Donker A, Postmes P (1994) A behavioural analysis of rats with damage to the medial prefrontal cortex using the Morris water maze: evidence for behavioural flexibility, but not for impaired spatial navigation. Brain Res 652:323–333
Brustovetsky N, Brustovetsky T, Purl KJ, Capano M, Crompton M, Dubinsky JM (2003) Increased susceptibility of striatal mitochondria to calcium-induced permeability transition. J Neurosci 23:4858–4867
Bulteau A-L, Lundberg KC, Ikeda-Saito M, Isaya G, Szweda LI (2004) Reversible redox-dependent modulation of mitochondrial aconitase and proteolytic activity during in vivo cardiac ischemia/reperfusion. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 102:5987–5991. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0501519102
Candelario-Jalil E, Mhadu NH, Al-Dalain SM, Martinez G, Leon OS (2001) Time course of oxidative damage in different brain regions following transient cerebral ischemia in gerbils. Neurosci Res 41:233–241
Chen B, Friedman B, Cheng Q, Tsai P, Schim E, Kleinfeld D, Lyden PD (2009) Severe Blood–Brain Barrier Disruption and Surrounding Tissue Injury. Stroke 40:e666. https://doi.org/10.1161/STROKEAHA.109.551341
Chen W, Sun Y, Liu K, Sun X (2014) Autophagy: a double-edged sword for neuronal survival after cerebral ischemia. Neural Regen Res 9:1210–1216. https://doi.org/10.4103/1673-5374.135329
Chinopoulos C, Zhang SF, Thomas B, Ten V, Starkov AA (2011) Isolation and functional assessment of mitochondria from small amounts of mouse brain tissue. Methods Mol Biol 793:311–324. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-61779-328-8_20
Davis M, Whitely T, Turnbull DM, Mendelow AD (1997) Selective impairments of mitochondrial respiratory chain activity during aging and ischemic brain damage. Acta Neurochir Suppl 70:56–58
Erecińska M, Silver IA (2001) Tissue oxygen tension and brain sensitivity to hypoxia. Respir Physiol 128:263–276. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0034-5687(01)00306-1
Fontaine E, Eriksson O, Ichas F, Bernardi P (1998) Regulation of THE permeability transition pore in skeletal muscle mitochondria: modulation by electron flow through the respiratory chain complex I. J Biol Chem 273:12662–12668. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.273.20.12662
Friberg H, Connern C, Halestrap AP, Wieloch T (1999) Differences in the activation of the mitochondrial permeability transition among brain regions in the rat correlate with selective vulnerability. J Neurochem 72:2488–2497
Friberg H, Wieloch T, Castilho RF (2002) Mitochondrial oxidative stress after global brain ischemia in rats. Neurosci Lett 334:111–114
Garbarino VR, Orr ME, Rodriguez KA, Buffenstein R (2015) Mechanisms of Oxidative Stress Resistance in The Brain: Lessons Learned From Hypoxia Tolerant Extremophilic Vertebrates. Arch Biochem Biophys 576:8–16. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.abb.2015.01.029
Gehring TV, Luksys G, Sandi C, Vasilaki E (2015) Detailed classification of swimming paths in the Morris water maze: multiple strategies within one trial. Sci Rep 5:14562. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep14562
Gilbert K, Godbout R, Rousseau G (2016) Caspase-3 Activity in the Rat Amygdala Measured by Spectrofluorometry After Myocardial Infarction. J Vis Exp 53207. https://doi.org/10.3791/53207
Granger DN, Kvietys PR (2015) Reperfusion injury and reactive oxygen species: the evolution of a concept. Redox Biol 6:524–551. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.redox.2015.08.020
Hebert-Chatelain E, Desprez T, Serrat R, Bellocchio L, Soria-Gomez E, Busquets-Garcia A, Pagano Zottola AC, Delamarre A, Cannich A, Vincent P, Varilh M, Robin LM, Terral G, García-Fernández MD, Colavita M, Mazier W, Drago F, Puente N, Reguero L, Elezgarai I, Dupuy J-W, Cota D, Lopez-Rodriguez M-L, Barreda-Gómez G, Massa F, Grandes P, Bénard G, Marsicano G (2016) A cannabinoid link between mitochondria and memory. Nature 539:555 EP–555559. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature20127
Homi HM, Freitas JJS, Curi R, Velasco IT, Junior BAS (2002) Changes in superoxide dismutase and catalase activities of rat brain regions during early global transient ischemia/reperfusion. Neurosci Lett 333:37–40
Hu Y, Deng H, Xu S, Zhang J (2015) MicroRNAs regulate mitochondrial function in cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury. Int J Mol Sci 16:24895–24917. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms161024895
Jonas EA, Mnatsakanyan N, Miranda P, Park H-A, Chen R, Licznerski P, Weinert M, Smith PJ, Chavez A, Zukin RS, Gribkoff VK, Alavian KN (2017) Mitochondria and memory: bioenergetics, synaptic plasticity and neurodegeneration. Biophys J 112:180a. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bpj.2016.11.996
Kahl A, Stepanova A, Konrad C, Anderson C, Manfredi G, Zhou P, Iadecola C, Galkin A (2018) Critical role of flavin and glutathione in complex I-mediated bioenergetic failure in brain ischemia/reperfusion injury. Stroke 49:1223–1231. https://doi.org/10.1161/STROKEAHA.117.019687
Kalogeris T, Baines CP, Krenz M, Korthuis RJ (2012) Cell Biology of Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury. Int Rev Cell Mol Biol 298:229–317. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-394309-5.00006-7
Kobayashi T, Kuroda S, Tada M, Houkin K, Iwasaki Y, Abe H (2003) Calcium-induced mitochondrial swelling and cytochrome c release in the brain: its biochemical characteristics and implication in ischemic neuronal injury. Brain Res 960:62–70
Kumar R, Bukowski MJ, Wider JM, Reynolds CA, Calo L, Lepore B, Tousignant R, Jones M, Przyklenk K, Sanderson TH (2016) Mitochondrial dynamics following global cerebral ischemia. Mol Cell Neurosci 76:68–75. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mcn.2016.08.010
Kumari Naga K, Panigrahi M, Prakash Babu P (2007) Changes in endogenous antioxidant enzymes during cerebral ischemia and reperfusion. Neurol Res 29:877–883. https://doi.org/10.1179/016164107X181842
Lai JC, Walsh JM, Dennis SC, Clark JB (1977) Synaptic and non-synaptic mitochondria from rat brain: isolation and characterization. J Neurochem 28:625–631
Lee J-M, Grabb MC, Zipfel GJ, Choi DW (2000) Brain tissue responses to ischemia. J Clin Invest 106:723–731
Li Y, Schellhorn HE (2007) Rapid kinetic microassay for catalase activity. J Biomol Tech 18:185–187
Li P-A, Liu G-J, He QP, Floyd RA, Siesjö BK (1999) Production of hydroxyl free radical by brain tissues in hyperglycemic rats subjected to transient forebrain ischemia. Free Radic Biol Med 27:1033–1040. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0891-5849(99)00152-5
Lim CC, Bryan NS, Jain M, Garcia-Saura MF, Fernandez BO, Sawyer DB, Handy DE, Loscalzo J, Feelisch M, Liao R (2009) Glutathione peroxidase deficiency exacerbates ischemia-reperfusion injury in male but not female myocardium: insights into antioxidant compensatory mechanisms. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 297:H2144–H2153. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpheart.00673.2009
Liu F, Lu J, Manaenko A, Tang J, Hu Q (2018) Mitochondria in ischemic stroke: new insight and implications. Aging Dis 9:924–937. https://doi.org/10.14336/AD.2017.1126
Lunnon K, Keohane A, Pidsley R, Newhouse S, Riddoch-Contreras J, Thubron EB, Devall M, Soininen H, Kloszewska I, Mecocci P, Tsolaki M, Vellas B, Schalkwyk L, Dobson R, Malik AN, Powell J, Lovestone S, Hodges A (2017) Mitochondrial genes are altered in blood early in Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol Aging 53:36–47. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2016.12.029
Mak TW, Yeh W-C (2002) Signaling for survival and apoptosis in the immune system. Arthritis Res 4(Suppl 3):S243–S252. https://doi.org/10.1186/ar569
Margaritescu O, Mogoanta L, Pirici I, Pirici D, Cernea D, Margaritescu C (2009) Histopathological changes in acute ischemic stroke. Romanian J Morphol Embryol 50:327–339
Martin LJ (2012) Biology of mitochondria in neurodegenerative diseases. Prog Mol Biol Transl Sci 107:355–415. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-385883-2.00005-9
Martins IVA, Rivers-Auty J, Allan SM, Lawrence CB (2017) Mitochondrial abnormalities and synaptic loss underlie memory deficits seen in mouse models of obesity and Alzheimer’s disease. J Alzheimers Dis 55:915–932. https://doi.org/10.3233/JAD-160640
Matire H, Harry M, Kathryn M, Mark W (2000) Ethnicity and equity: missing the point. Stroke 31:2517–2527. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.STR.31.10.2517
Nandi A, Chatterjee IB (1988) Assay of superoxide dismutase activity in animal tissues. J Biosci 13:305–315. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02712155
Nishizawa Y (2001) Glutamate release and neuronal damage in ischemia. Life Sci 69:369–381
Ohkawa H, Ohishi N, Yagi K (1979) Assay for lipid peroxides in animal tissues by thiobarbituric acid reaction. Anal Biochem 95:351–358. https://doi.org/10.1016/0003-2697(79)90738-3
Ordy JM, Wengenack TM, Bialobok P, Coleman PD, Rodier P, Baggs RB, Dunlap WP, Kates B (1993) Selective vulnerability and early progression of hippocampal CA1 pyramidal cell degeneration and GFAP-positive astrocyte reactivity in the rat four-vessel occlusion model of transient global ischemia. Exp Neurol 119:128–139. https://doi.org/10.1006/exnr.1993.1014
Petschner P, Gonda X, Baksa D, Eszlari N, Trivaks M, Juhasz G, Bagdy G (2018) Genes linking mitochondrial function, cognitive impairment and depression are associated with endophenotypes serving precision medicine. Neuroscience 370:207–217. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2017.09.049
Piantadosi CA, Zhang J (1996) Mitochondrial generation of reactive oxygen species after brain ischemia in the rat. Stroke 27:327–331 discussion 332
Picard M, McEwen BS (2014) Mitochondria impact brain function and cognition. Proc Natl Acad Sci 111:7–8. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1321881111
Pulli B, Ali M, Forghani R, Schob S, Hsieh KLC, Wojtkiewicz G, Linnoila JJ, Chen JW, Johnson R (2013) Measuring Myeloperoxidase Activity in Biological Samples. PLoS ONE 8:e67976. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0067976
Raval AP, Liu C, Hu BR (2009) Rat model of global cerebral ischemia: the two-vessel occlusion (2VO) model of forebrain ischemia. In: Chen J, Xu ZC, Xu X-M, Zhang JH (eds) Animal models of acute neurological injuries. Humana Press, Totowa, NJ, pp 77–86
Sancheti JS, Shaikh MF, Khatwani PF, Kulkarni SR, Sathaye S (2013) Development and validation of a HPTLC method for simultaneous estimation of L-glutamic acid and γ-aminobutyric acid in mice brain. Indian J Pharm Sci 75:716–721
Sanderson TH, Reynolds CA, Kumar R, Przyklenk K, Hüttemann M (2012) Molecular mechanisms of ischemia-reperfusion injury in brain: pivotal role of the mitochondrial membrane potential in reactive oxygen species generation. Mol Neurobiol 47:9–23. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-012-8344-z
Scaduto RC, Grotyohann LW (1999) Measurement of mitochondrial membrane potential using fluorescent rhodamine derivatives. Biophys J 76:469–477
Scarpulla RC (2011) Metabolic control of mitochondrial biogenesis through the PGC-1 family regulatory network. Biochim Biophys Acta 1813:1269–1278. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbamcr.2010.09.019
Schaar KL, Brenneman MM, Savitz SI (2010) Functional assessments in the rodent stroke model. Exp Transl Stroke Med 2:13. https://doi.org/10.1186/2040-7378-2-13
Schimidt HL, Vieira A, Altermann C, Martins A, Sosa P, Santos FW, Mello-Carpes PB, Izquierdo I, Carpes FP (2014) Memory deficits and oxidative stress in cerebral ischemia–reperfusion: neuroprotective role of physical exercise and green tea supplementation. Neurobiol Learn Mem 114:242–250. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nlm.2014.07.005
Sedlak J, Lindsay RH (1968) Estimation of total, protein-bound, and nonprotein sulfhydryl groups in tissue with Ellman’s reagent. Anal Biochem 25:192–205. https://doi.org/10.1016/0003-2697(68)90092-4
Selakovic V, Korenic A, Radenovic L (2011) Spatial and temporal patterns of oxidative stress in the brain of gerbils submitted to different duration of global cerebral ischemia. Int J Dev Neurosci 29:645–654. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijdevneu.2011.02.009
Shaik IH, Mehvar R (2006) Rapid determination of reduced and oxidized glutathione levels using a new thiol-masking reagent and the enzymatic recycling method: application to the rat liver and bile samples. Anal Bioanal Chem 385:105–113. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-006-0375-8
Sims NR (1992) Energy metabolism and selective neuronal vulnerability following global cerebral ischemia. Neurochem Res 17:923–931
Tachibana M, Ago T, Wakisaka Y, Kuroda J, Shijo M, Yoshikawa Y, Komori M, Nishimura A, Makihara N, Nakamura K, Kitazono T (2017) Early Reperfusion After Brain Ischemia Has Beneficial Effects Beyond Rescuing Neurons. Stroke 48:2222–2230. https://doi.org/10.1161/STROKEAHA.117.016689
Wang X, Michaelis EK (2010) Selective neuronal vulnerability to oxidative stress in the brain. Front Aging Neurosci 2:12. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnagi.2010.00012
Yen LF, Wei VC, Kuo EY, Lai TW (2013) Distinct Patterns of Cerebral Extravasation by Evans Blue and Sodium Fluorescein in Rats. PLoS ONE 8:e68595. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0068595
Zhou Y, Lian S, Zhang J, Lin D, Huang C, Liu L, Chen Z (2018) Mitochondrial perturbation contributing to cognitive decline in streptozotocin-induced type 1 diabetic rats. Cell Physiol Biochem 46:1668–1682. https://doi.org/10.1159/000489243
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to acknowledge the Honorable Vice-Chancellor Dr. Vaidhyasubramniyam S. and SASTRA Deemed University for providing an excellent facility for the conduct of this research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Gino Kurian designed the study and interpreted the data. Sriram Ravindran conducted the surgery, behavioral studies, biochemical experiments, and statistical analysis. Both the authors were involved in writing and thorough review of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(PDF 277 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ravindran, S., Kurian, G.A. Eventual analysis of global cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury in rat brain: a paradigm of a shift in stress and its influence on cognitive functions. Cell Stress and Chaperones 24, 581–594 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12192-019-00990-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12192-019-00990-4