Abstract
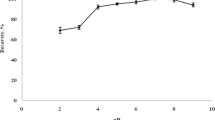
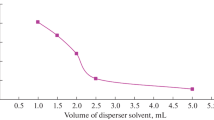
A novel ultrasound-assisted dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction (UA-DLLME) based on melting of the donor phase for the determination of Cd, Cu, and Fe in margarine samples using high-resolution continuum source electrothermal atomic absorption spectrometry (HR-CS ET AAS) is proposed. Considering that margarine is in the solid phase at room temperature, requiring heat for melting, the microextraction process was assisted by an ultrasonic bath to ensure the melting point of the samples and to increase the extraction efficiency of the analytes by UA-DLLME. After the extraction procedure, the aqueous phase was collected and directly introduced into a graphite furnace. The procedure was applied for extraction and multi-element determination, exploring the strategy of simultaneous and sequential determination of analytes by HR-CS ET AAS. A low volume of nitric acid solution in the presence of ethanol and hydrogen peroxide allowed the metals to be separated from the sample in an aqueous phase with subsequent determination by HR-CS ETAAS. In the extraction procedure, 5.0 g of each margarine sample was sonicated under heating in the presence of 100 μL of a solution containing HNO3 0.1 mol L−1, ethanol (95.1%, v v−1), and H2O2 3% (v v−1) in a volume proportion of 2:1:1. The influences of the time of extraction, temperature of extraction, and amplitude of sonication were examined, and the proposed conditions were as follows: extraction time, 10 min; temperature, 60 °C; and amplitude, 100%. Using 5 g of margarine sample, limits of detection of 0.03, 0.52, and 224 ng g−1 were obtained for Cd, Cu, and Fe, respectively. Recovery tests were performed, and the results ranged from 87 to 108% for Cd, 91 to 115% for Cu, and 85 to 112% for Fe. The results obtained by the proposed extraction procedure agreed with those obtained after wet digestion of the sample and determination by inductively coupled plasma optical emission spectrometry (ICP OES).





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Almeida JS, Anunciação TA, Brandão GC, Dantas AF, Lemos VA, Teixeira LSG (2015) Ultrasound-assisted single-drop microextraction for the determination of cadmium in vegetable oils using high-resolution continuum source electrothermal atomic absorption spectrometry. Spectrochim Acta, Part B 107:159–163. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sab.2015.03.002
Almeida JS, Brandão GC, dos Santos GL, Teixeira LSG (2016) Fast sequential determination of manganese and chromium in vegetable oil and biodiesel samples by high-resolution continuum source graphite furnace atomic absorption spectrometry. Anal Methods 8:3249–3254. https://doi.org/10.1039/C6AY00165C
Almeida JS, Souza OCCO, Teixeira LSG (2018) Determination of Pb, Cu and Fe in ethanol fuel samples by high-resolution continuum source electrothermal atomic absorption spectrometry by exploring a combination of sequential and simultaneous strategies. Microchem J 137:22–26. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.microc.2017.09.012
Almeida JS, Santos GL, Brandão GC, Korn MGA, Teixeira LSG (2019) Multivariate optimization of ultrasound-assisted extraction using Doehlert matrix for simultaneous determination of Fe and Ni in vegetable oils by high-resolution continuum source graphite furnace atomic absorption spectrometry. Food Chem 273:130–135. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2018.01.112
Anwar F, Kazi TG, Saleem R, Bhanger MI (2004) Rapid determination of some trace metals in several oils and fats. Grasas Aceites 55:160–168
Bakircioglu D, Topraksever N, Kurtulus YB (2015) Separation/preconcentration system based on emulsion-induced breaking procedure for determination of cadmium in edible oil samples by flow injection-flame atomic absorption spectrometry. Food Anal Methods 8:2178–2184. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12161-015-0112-z
Baran EK, Yasar SB (2010) Copper and iron determination with [N,N’-Bis(salicylidene)-2,2′-dimethyl-1,3-propanediaminato] in edible oils without digestion. J Am Oil Chem Soc 87:1389–1395. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11746-010-1633-7
Benzo Z, Marcano E, Gómez C, Ruiz F, Salas J, Quintal M, Garaboto A, Murillo M (2002) Simultaneous determination of nickel, iron, and copper in margarine by inductively coupled plasma-atomic emission spectroscopy after sample emulsification. J AOAC Int 85:967–970. https://doi.org/10.1093/jaoac/85.4.967
Boschetti W, Orlando M, Dullius M, Dessuy MB, Vale MGR, Welz B, de Andrade JB (2016) Sequential and simultaneous determination of four elements in soil samples using high-resolution continuum source grafite furnace atomic and molecular absorption spectrometry. J Anal At Spectrom 31:1269–1277. https://doi.org/10.1039/C6JA00031B
Cabrera C, Lloris F, Gimenez R, Olalla M, Lopez C (2003) Mineral content in legumes and nuts: contribution to the Spanish dietary intake. Sci Total Environ 308:1–14. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0048-9697(02)00611-3
Dohnalova L, Bucek P, Vobornik P, Dohnal V (2017) Determination of nickel in hydrogenated fats and selected chocolate bars in Czech Republic. Food Chem 217:456–460. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2016.08.066
El-Shahawi MS, Al-Saidi HM (2013) Dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction for chemical speciation and determination of ultra-trace concentrations of metal ions. TrAC Trends Anal Chem 44:12–24. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trac.2012.10.011
Endo Y (2018) Analytical methods to evaluate the quality of edible fats and oils: the JOCS standard methods for analysis of fats, oils and related materials (2013) and advanced methods. J Oleo Sci 67:1–10. https://doi.org/10.5650/jos.ess17130
Gharehbaghi M, Shemirani F, Baghdadi M (2008) Dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction and spectrophotometric determination of cobalt in water samples. Int J Environ Anal Chem 88:513–523. https://doi.org/10.1080/03067310701809128
Hartwig CA, Pereira RM, Novo DLR, Oliveira DTT, Mesko MF (2017) Green and efficient sample preparation method for the determination of catalyst residues in margarine by ICP-MS. Talanta 174:394–400. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2017.06.037
Ieggli CVS, Bohrer D, Do Nascimento PC, De Carvalho LM (2011) Flame and graphite furnace atomic absorption spectrometry for trace element determination in vegetable oils, margarine and butter after sample emulsification. Food Addit Contam, Part A 28:640–648. https://doi.org/10.1080/19440049.2011.555843
Iskander FY (1993) Determination of seventeen elements in edible oils and margarine by instrumental neutron activation analysis. J Am Oil Chem Soc 70:803–805. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02542605
Kalschne DL, Canan C, Barin JS, Picoloto RS, Leite OD, Flores ELM (2020a) Reversed-phase dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction (RP-DLLME) as a green sample preparation method for multielement determination in fish oil by ICP-OES. Food Anal Methods 13:230–237. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12161-019-01606-4
Kalschne DL, Canan C, Beato MO, Leite OD, Flores ELM (2020b) A new and feasible analytical method using reversed-phase dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction (RP-DLLME) for further determination of nickel in hydrogenated vegetable fat. Talanta 208:120409. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2019.120409
Krebs B (1987) Direct determination of nickel in margarine. Fresenius' Z Anal Chem 328:388–389. https://doi.org/10.1007/PL00020627
Lepri FG, Chaves ES, Vieira MA, Ribeiro AS, Curtius AJ, De Oliveira LCC, De Campos RC (2011) Determination of trace elements in vegetable oils and biodiesel by atomic spectrometric techniques—a review. Appl Spectrosc Rev 46:175–206. https://doi.org/10.1080/05704928.2010.529628
Lodyga-Chruscinska E, Sykula-Zajac A, Olejnik D (2012) Determination of nickel in Polish brands of margarines. Food Addit Contam, Part B 5:251–254. https://doi.org/10.1080/19393210.2012.702287
López-García I, Vicente-Martínez Y, Hernández-Córdoba M (2013) Nonchromatographic speciation of selenium in edible oils using dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction and electrothermal atomic absorption spectrometry. J Agric Food Chem 61:9356–9361. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf4027537
López-García I, Vicente-Martínez Y, Hernández-Córdoba M (2014) Determination of cadmium and lead in edible oils by electrothermal atomic absorption spectrometry after reverse dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction. Talanta 124:106–110. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2014.02.011
López-García I, Briceño M, Vicente-Martínez Y, Hernández-Córdoba M (2015) Rapid screening of water soluble arsenic species in edible oils using dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction. Food Chem 167:396–401. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2014.06.121
Lourenço EC, Eyng E, Bittencourt PRS, Duarte FA, Picoloto RS, Flores ELM (2019) A simple, rapid and low cost reversed-phase dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction for the determination of Na, K, Ca and Mg in biodiesel. Talanta 199:1–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2019.02.054
Martí-Cid R, Llobet JM, Castell V, Domingo JL (2008) Dietary intake of arsenic, cadmium, mercury, and lead by the population of Catalonia, Spain. Biol Trace Elem Res 125:120–132. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-008-8162-3
Mendil D, Uluözlü OD, Tüzen M, Soylak M (2009) Investigation of the levels of some element in edible oil samples produced in Turkey by atomic absorption spectrometry. J Hazard Mater 165:724–728. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2008.10.046
Nash AM, Mounts TL, Kwolek WF (1983) Determination of ultratrace metals in hydrogenated vegetable oils and fats. J Am Oil Chem Soc 60:811–814. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02787433
Neto MCV, Silva TBC, Araújo VE, Souza SVC (2019) Lead contamination in food consumed and produced in Brazil: systematic review and meta-analysis. Food Res Int 126:108671. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodres.2019.108671
Onianwa PC, Adeyemo AO, Idowu OE, Ogabiela EE (2001) Copper and zinc contents of Nigerian foods and estimates of the adult dietary intakes. Food Chem 72:89–95. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0308-8146(00)00214-4
Pires LN, Almeida JS, Dias FS, Teixeira LSG (2020) Sequential and simultaneous determination of chlorine, iron, and silicon in beer samples by high-resolution continuum source graphite furnace molecular and atomic absorption spectrometry. Food Anal Methods 13:1746–1754. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12161-020-01787-3
Resano M, Rello L, Flórez M, Belarra MA (2011) On the possibilities of high-resolution continuum source graphite furnace atomic absorption spectrometry for the simultaneous or sequential monitoring of multiple atomic lines. Spectrochim Acta, Part B 66:321–328. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sab.2011.03.008
Resano M, Flórez MR, García-Ruiz E (2013) High-resolution continuum source atomic absorption spectrometry for the simultaneous or sequential monitoring of multiple lines. A critical review of current possibilities. Spectrochim Acta, Part B 88:85–97. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sab.2013.06.004
Schümann K (2001) Safety aspects of iron in food. Ann Nutr Metab 45:91–101. https://doi.org/10.1159/000046713
Shi Z, Lee HK (2010) Dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction coupled with dispersive μ-solid-phase extraction for the fast determination of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in environmental water samples. Anal Chem 82:1540–1545. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac9023632
Sleeter RT (1981) Effects of processing on quality of soybean oil. J Am Oil Chem Soc 58:239–247. https://doi.org/10.1007/bf02582349
Souza RM, Mathias BM, Silveira CLP, Aucelio RQ (2005) Inductively coupled plasma optical emission spectrometry for trace multi-element determination in vegetable oils, margarine and butter after stabilization with propan-1-ol and water. Spectrochim Acta, Part B 60:711–715. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sab.2005.02.025
Swanson CA (2003) Iron intake and regulation: implications for iron deficiency and iron overload. Alcohol 30:99–102. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0741-8329(03)00103-4
Szłyk E, Szydłowska-Czerniak A (2004) Determination of cadmium, lead, and copper in margarines and butters by galvanostatic stripping chronopotentiometry. J Agric Food Chem 52:4064–4071. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf040032w
Taylor AA, Tsuji JS, Garry MR, McArdle ME, Goodfellow WL Jr, Adams WJ, Menzie CA (2020) Critical review of exposure and effects: implications for setting regulatory health criteria for ingested copper. Environ Manag 65:131–159. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00267-019-01234-y
Tuzen M, Uluozlu OD, Mendil D, Soylak M, Machado LOR, Dos Santos WNL, Ferreira SLC (2018) A simple, rapid and green ultrasound assisted and ionic liquid dispersive microextraction procedure for the determination of tin in foods employing ETAAS. Food Chem 245:380–384. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2017.10.115
Viñas P, Campillo N, López-García I, Hernández-Córdoba M (2013) Dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction in food analysis. A critical review. Anal Bioanal Chem 406:2067–2099. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-013-7344-9
Zgoła-Grześkowiak A, Grześkowiak T (2011) Dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction. TrAC Trends Anal Chem 30:1382–1399. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trac.2011.04.014
Acknowledgments
This study was financed in part by the Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior - Brasil (CAPES) - Finance Code 001. The authors are also grateful to Fundação de Amparo a Pesquisa do Estado da Bahia (FAPESB) and Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico (CNPq) for providing grants, fellowships, and financial support.
Funding
This study was funded by Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado da Bahia (FAPESB), Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico (CNPq), and Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior (CAPES).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
Jorge S. Almeida declares that he has no conflict of interest. Lucilia A. Meira declares that she has no conflict of interest. Ana D. S. Nascimento declares that she has no conflict of interest. Gabriel L. Santos declares that he has no conflict of interest. Valfredo A. Lemos declares that he has no conflict of interest. Leonardo Sena G. Teixeira declares that he has no conflict of interest.
Ethical Approval
This article does not contain any studies involving human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Informed Consent
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Almeida, J.S., Meira, L.A., Nascimento, A.D.S. et al. Ultrasound-Assisted Dispersive Liquid-Liquid Microextraction Based on Melting of the Donor Phase: a New Approach for the Determination of Trace Elements in Solid Samples. Food Anal. Methods 14, 596–605 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12161-020-01897-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12161-020-01897-y