Abstract
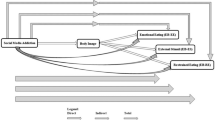
Using Objectification Theory as a guide, social media use is found to be connected to self-objectification, body satisfaction and restrained eating among young Western women and men and Chinese women. However, the relationship among young Chinese men is largely unknown. The current study aimed to examine whether these relationships exist among young Chinese men, as well as self-objectification and body satisfaction’s serial mediation effects. 335 male young Chinese participants (aged 18–35) were recruited to complete questionnaires evaluating their social media usage, self-objectification, body dissatisfaction and restrained eating. A significant correlation between using social media and restrained eating was mediated by self-objectification. However, the impact of social media use on restrained eating was not mediated by body satisfaction, as young Chinese men’s body satisfaction was not correlated with social media use, restrained eating or self-objectification. The fact that Objectification Theory is partially applicable to young Chinese men means that cultural context, especially Eastern context, is important in this framework. And in this case, young Chinese men’s self-compassion and masculinity may be able to explain the partial non-applicability.
Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The corresponding author will deliver the datasets generated during the current work upon reasonable request.
References
Cash, T. F., Fleming, E. C., Alindogan, J., Steadman, L., & Whitehead, A. (2002). Beyond body image as a trait: The development and validation of the body Image States Scale. Eating Disorders, 10(2), 103–113. https://doi.org/10.1080/10640260290081678
Chan, W. T. (1957). Transformation of Buddhism in China. Philosophy East and West, 7(3/4), 107–116. https://doi.org/10.2307/1397344
Daniels, E. A., Zurbriggen, E. L., & Monique Ward, L. (2020). Becoming an object: A review of self-objectification in girls. Body Image, 33, 278–299. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bodyim.2020.02.016
Ellison, N. B., Steinfield, C., & Lampe, C. (2007). The benefits of Facebook friends: Social Capital and College Students’ Use of Online Social Network sites. Journal of Computer-Mediated Communication, 12(4), 1143–1168. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1083-6101.2007.00367.x
Fardouly, J., & Vartanian, L. R. (2015). Negative comparisons about one’s appearance mediate the relationship between Facebook usage and body image concerns. Body Image, 12, 82–88. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bodyim.2014.10.004
Ferreira, C., Pinto-Gouveia, J., & Duarte, C. (2013). Self-compassion in the face of shame and body image dissatisfaction: Implications for eating disorders. Eating Behaviors, 14(2), 207–210. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eatbeh.2013.01.005
Fredrickson, B. L., Noll, S. M., Roberts, T. A., Quinn, D. M., & Twenge, J. M. (1998). That swimsuit becomes you: Sex differences in Self-Objectification, restrained eating, and Math Performance. Journal of Personality & Social Psychology, 75(1), 269–283. https://doi.org/10.1037/0022-3514.75.1.269
Fredrickson, B. L., & Roberts, T. A. (1997). Objectification Theory: Toward understanding women’s lived experiences and Mental Health risks [Article]. Psychology of Women Quarterly, 21(2), 173. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1471-6402.1997.tb00108.x
Fung, J., Chen, G., Kim, J., & Lo, T. (2021). The relations between Self-Compassion, Self-Coldness, and psychological functioning among North American and Hong Kong College Students. Mindfulness, 12(9), 2161–2172. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12671-021-01670-0
Goldfield, G. S., Moore, C., Henderson, K., Buchholz, A., Obeid, N., & Flament, M. F. (2010). Body dissatisfaction, Dietary Restraint, Depression, and Weight Status in adolescents. Journal of School Health, 80(4), 186–192. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1746-1561.2009.00485.x
Hao, M., Fang, Y., Yan, W., Gu, J., Hao, Y., & Wu, C. (2022). Relationship between body dissatisfaction, insufficient physical activity, and disordered eating behaviors among university students in southern China. Bmc Public Health, 22(1), 1–7. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12889-022-14515-9
Hayes, A. F. (2013). Introduction to Mediation, Moderation, and conditional process analysis: A regression-based Approach. Guilford Press.
Herman, C. P., & Mack, D. (1975). Restrained and unrestrained eating. Journal of Personality, 43(4), 647–660. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-6494.1975.tb00727.x
Holland, G., Tiggemann, M. J. B., & i. (2016). A systematic review of the impact of the use of social networking sites on body image and disordered eating outcomes. Body Image, 17(17), 100–110. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bodyim.2016.02.008
Liu, F. (2014). From degendering to (re)gendering the self: Chinese youth negotiating modern womanhood. Gender and Education, 26, 18–34. https://doi.org/10.1080/09540253.2013.860432
Louie, K. (2014). Chinese Masculinities in a Globalizing World (1st ed.). Routledge. https://doi.org/10.4324/9781315884646
Martins, Y., Tiggemann, M., & Kirkbride, A. (2007). Those speedos become them: The role of self-objectification in gay and heterosexual men’s body image. Personality & Social Psychology Bulletin, 33(5), 634–647. https://doi.org/10.1177/0146167206297403
Modica, C. A. (2020). The Associations Between Instagram Use, Selfie Activities, Appearance Comparison, and Body Dissatisfaction in Adult Men. Cyberpsychology, behavior and social networking, 23(2), 90-99. https://doi.org/10.1089/cyber.2019.0434
Moradi, B., & Yu-Ping, H. (2008). Objectification Theory and psychology of women: A decade of advances and future directions. Psychology of Women Quarterly, 32(4), 377–398. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1471-6402.2008.00452.x
Neff, K. D. (2003). The Development and Validation of a scale to measure Self-Compassion. Self & Identity, 2(3), 223. https://doi.org/10.1080/15298860309027
Neff, K. D., Pisitsungkagarn, K., & Hsieh, Y. P. (2008). Self-Compassion and Self-Construal in the United States, Thailand, and Taiwan. Journal of Cross-Cultural Psychology, 39(3), 267–285. https://doi.org/10.1177/0022022108314544
Niu, G., Sun, L., Liu, Q., Chai, H., Sun, X., & Zhou, Z. (2020). Selfie-posting and young adult women’s restrained eating: The role of Commentary on Appearance and Self-Objectification. Sex Roles, 82(3/4), 232–240. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11199-019-01045-9
Noll, S. M., & Frederickson, B. L. (1998). A mediational model linking self-objectification, body shame, and disordered eating. Psychology of Women Quarterly, 22(4), 623. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1471-6402.1998.tb00181.x
O’Gorman, B., Sheffield, J. K., Clarke, R., & Griffiths, S. J. C. P. (2020). Guys don’t talk about their bodies: A qualitative investigation of male body dissatisfaction and sociocultural influences in a sample of 40 Australian males. Clinical Psychologist, 24(2), 123–132. https://doi.org/10.1111/cp.12198
Oliveira, N., Coelho, G. M. O., Cabral, M. C., Bezerra, F. F., Faerstein, E., & Canella, D. S. (2020). Association of body image (dis)satisfaction and perception with food consumption according to the NOVA classification: Pró-Saúde Study. Appetite, 144, 104464. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.appet.2019.104464
Podsakoff, P. M., MacKenzie, S. B., Jeong-Yeon, L., & Podsakoff, N. P. (2003). Common Method Biases in Behavioral Research: A Critical Review of the Literature and Recommended Remedies. Journal of Applied Psychology, 88(5), 879. https://doi.org/10.1037/0021-9010.88.5.879
Pope, H. G., Phillips, K. A., & Olivardia, R. (2000). The Adonis Complex: The Secret Crisis of male body obsession. Simon and Schuster.
Seekis, V., Bradley, G. L., & Duffy, A. L. (2020). Appearance-related social networking sites and Body Image in Young women: Testing an objectification-social comparison model. Psychology of Women Quarterly, 44(3), 377–392. https://doi.org/10.1177/0361684320920826
Seekis, V., Bradley, G. L., & Duffy, A. L. (2021). Social networking sites and men’s drive for muscularity: Testing a revised objectification model. Psychology of Men & Masculinities, 22(1), 189–200. https://doi.org/10.1037/men0000265
Shanghai University of Sport, Shanghai Sen Rong Network Technology Co., L., & Weber Shandwick (2021). 2021 China Fitness Industry Data Report. https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/HJh10fWMOmisnlYB4uHzRw
Song, G., & Hird, D. (2013). Men and masculinities in Contemporary China. Brill.
Stice, E. J. P. (2002). Risk and maintenance factors for eating pathology: A meta-analytic review. Psychological Bulletin, 128 5, 825–848. https://doi.org/10.1037//0033-2909.128.5.825
Strien, T., Frijters, J. E. R., Bergers, G. P. A., Defares, P. B., &, J. I. J. G. I. S. (1986). The Dutch eating Behavior Questionnaire (DEBQ) for assessment of restrained, emotional, and external eating behavior. International Journal of Eating Disorders, 5(2), 295–315. https://doi.org/10.1002/1098-108X%28198602%295:2%3C295::AID-EAT2260050209%3E3.0.CO;2-T
Terán, L., Yan, K., & Aubrey, J. S. (2020). But first let me take a selfie: U.S. adolescent girls’ selfie activities, self-objectification, imaginary audience beliefs, and appearance concerns. Journal of Children & Media, 14(3), 343–360. https://doi.org/10.1080/17482798.2019.1697319
Wang, W., Chen, Z., & Ding, X. (2022). Cyberbullying victimization and disordered eating behaviors: The mediating roles of self-compassion and self-objectification. Appetite, 178, 106267. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.appet.2022.106267
We Are Social (2023). Digital 2023: China. https://wearesocial.com/cn/blog/2023/01/digital-2023/
Wollast, R., Riemer, A. R., Bernard, P., Leys, C., Kotsou, I., & Klein, O. (2019). How self-compassion moderates the effect of body surveillance on subjective happiness and depression among women [Article]. Scandinavian Journal of Psychology, 60(5), 464–472. https://doi.org/10.1111/sjop.12553
Xinhua (2017). China unveils 10-year plan for youth development. The State Council, the People’s Republic of China. http://english.www.gov.cn/policies/latest_releases/2017/04/14/content_281475626290850.htm
Yanover, T., & Thompson, J. K. (2010). Perceptions of health and attractiveness: The effects of body fat, muscularity, gender, and ethnicity. Journal of Health Psychology, 15(7), 1039–1048. https://doi.org/10.1177/1359105309360426
Zarychta, K., Chan, C. K. Y., Kruk, M., & Luszczynska, A. (2020). Body satisfaction and body weight in under- and healthy-weight adolescents: Mediating effects of restrictive dieting, healthy and unhealthy food intake. Eating and Weight Disorders: EWD, 25(1), 41–50. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40519-018-0496-z
Zhang, J., Wang, Y., Li, Q., & Wu, C. (2021). The relationship between SNS usage and disordered eating behaviors: A Meta-analysis. Frontiers in Psychology, 12, 641919. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2021.641919
Zhao, T., Liang, X., & Guo, X. (2020). The impact of short-video use on depression of female undergraduate: A chain mediating model of self-objectification and body satisfaction. Journal of Psychological Science, 5, 1220–1226. https://doi.org/10.16719/j.cnki.1671-6981.20200527
Zhu, Z. (2023). Social Media Use and Young Chinese Men’s Restrained Eating: The Roles of Self-objectification and Body Satisfaction. Shanghai International Studies University. China National Knowledge Infrastructure.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
We certify that we do not have any competing interests.
Informed consent
The individuals taking part in this research manifested their informed permission.
Ethical Statement
This article is original, we certify, and neither it has been published anywhere nor is it presently being considered for publication elsewhere. This study is not the outcome of a single study that was divided into multiple parts in order to enhance the number of submissions made over time to one publication or to several. The findings are provided in a straightforward, truthful manner without embellishment, falsification, or improper data manipulation.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhu, Z., Chi, R. Social media use and young Chinese men’s restrained eating: the mediating roles of self-objectification and body satisfaction. Curr Psychol 43, 11642–11650 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12144-023-05306-5
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12144-023-05306-5