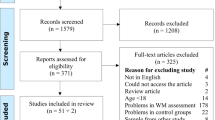
Abstract
The Mini-Mental Status Examination (MMSE) is a widely used cognitive screening measure. The MMSE is used with diverse cultures, yet multiple factors may impact test performance, interpretation, and normative statistics. The current study observes factors specific to Iranians’ that influence performances on the Persian MMSE. A literature review compiled studies of the Persian MMSE administered to both healthy and clinical groups. Out of 1008 articles found, 45 met inclusion criteria. Meta-analysis of aggregate data was used to develop global means, standard deviations, and cutoff scores for both clinical and healthy groups. Iranian MMSE normative mean and standard deviation values were 27 and 2.2, respectively. Iranian MMSE clinical mean and standard deviation values were 22 and 5.7, respectively. An MMSE cut-off score of 22.6, or any score below 23 (e.g., <23 or 22 and lower), would represent 2 standard deviations below the mean and closely resemble a clinical population. This is consistent with Ansari, et al. (2010) cut of score of 23 and Seyedian et al. (2007) cut-off score of 22. Therefore, an Iranian patient who scores below 23 would be suspected of having potential cognitive decline. Demographic adjusted normative and clinical regressions equations were also generated. However, gender and age did not show significant correlations while education showed the largest and most significant correlation in healthy samples. Therefore, higher educated Iranians cut-off score will likely be higher than 23. Clinicians may use the global normative mean and standard deviation to calculate z-scores. This helps clinician to better assess cognition in Iranian patients.

Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Not applicable.
Code Availability
Not applicable.
References
Allahyari, T., Rangi, N. H., Khalkhali, H., & Khosravi, Y. (2014). Occupational cognitive failures and safety performance in the workplace. International Journal of Occupational Safety and Ergonomics, 20(1), 175–180.
Amani, M., Barahmand, U., & Narimani, M. (2012). An examination of the effectiveness of neuropsychological and content-based training methods in the remediation of mathematics disorder. Journal of Learning Disabilities, 1(2), 6–21.
Ansari, N. N., Naghdi, S., Hasson, S., Valizadeh, L., & Jalaie, S. (2010). Validation of a mini-mental state examination (MMSE) for the Persian population: A pilot study. Applied Neuropsychology, 17(3), 190–195.
Ashrafi, F., Daemi, M., Asaadi, S., Ommi, D., Nasiri, Z., & Pakdaman, H. (2014). Frontal assessment battery in a Persian population with Parkinson's disease. International Clinical Neuroscience Journal, 1(1), 18–21.
Bahramitash, R., & Esfahani, H. S. (2014). Gender and entrepreneurship in Iran. Middle East Critique, 23(3), 293–312.
Baluch, B. (1996). Word frequency effects in naming for experienced and previously experienced adult readers of Persian. Reading and Writing, 8(5), 433–441.
Barekatain, M., Askarpour, H., Zahedian, F., Walterfang, M., Velakoulis, D., Maracy, M. R., & Jazi, M. H. (2014). The relationship between regional brain volumes and the extent of coronary artery disease in mild cognitive impairment. Journal of Research in Medical Sciences: The Official Journal of Isfahan University of Medical Sciences, 19(8), 739–745.
Barekatain, M., Walterfang, M., Behdad, M., Tavakkoli, M., Mahvari, J., Maracy, M. R., & Velakoulis, D. (2010). Validity and reliability of the Persian language version of the neuropsychiatry unit cognitive assessment tool. Dementia and Geriatric Cognitive Disorders, 29(6), 516–522.
Chabok, S. Y., Kapourchali, S. R., Saberi, A., & Mohtasham-Amiri, Z. (2012). Operative and nonoperative linguistic outcomes in brain injury patients. Journal of the Neurological Sciences, 317(1–2), 130–136.
Daneshmand, R., Mazinani, R., & Fadai, F. (2007). The effect of risperidone on cognitive symptoms of schizophrenia: A comparison with haloperidol. Journal of Mazandaran University of Medical Sciences, 17(59), 1–10.
Ebady, S. A., Arami, M., & Shafigh, M. H. (2008). Investigation on the relationship between diabetes mellitus type 2 and cognitive impairment. Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice, 82(3), 305–309.
Ebrahimi, A., Talaei, A., Mokhber, N., Akbarzadeh, F., Akhlaghi, S., Nejati, R., & Talaei, A. (2014). Efficacy of addition of folic acid to sodium valproate in treatment of acute mania, a double blind clinical trial study. Medical Journal of Mashhad University of Medical Sciences, 57(1), 398–405.
Emsaki, G., Molavi, H., Chitsaz, A., Abtahi, M. M., & Asgari, K. (2011). Psychometric properties of the Montreal cognitive assessment (MoCA) in Parkinson's disease patients in Isfahan. Journal of Isfahan Medical School, 29(158), 1–10.
Folstein, M. F., Folstein, S. E., & McHugh, P. R. (1975). “Mini-mental state”: A practical method for grading the cognitive state of patients for the clinician. Journal of Psychiatric Research, 12(3), 189–198.
Foroughan, M., Jafari, Z., Shirin, B. P., Ghaem, M. F. Z., & Rahgozar, M. (2008). Validation of mini-mental state examination (MMSE) in the elderly population of Tehran. Advances in Cognitive Science, 10(2), 29–37.
Gates, N. J., & March, E. G. (2016). A neuropsychologist’s guide to undertaking a systematic review for publication: Making the most of PRISMA guidelines. Neuropsychology Review, 26(2), 109–120.
Ghanbari, A., Moaddab, F., Salari, A., Leyli, E. K., Sabet, M. S., & Paryad, E. (2013). The study of cognitive function and related factors in patients with heart failure. Nursing and Midwifery Studies, 2(3), 34–38.
Gharaeipour, M., & Andrew, M. K. (2013). Examining cognitive status of elderly Iranians: Farsi version of the modified mini-mental state examination. Applied Neuropsychology. Adult, 20(3), 215–220.
Hassani, F., Ahadi, H., Askari, P., Shariat, A., & Khuzestan, I. R. (2012). Validation of a new version for memory assessment in a group of Farsi speaking, shiraz residents. Life Science Journal, 4(9), 4353–4359.
Iranmanesh, F., Sayyadi, A., Fayegh, A., & Shafiee, Z. (2006). Surveying of estrogen and progesterone effects on electroencephalogram and mini-mental status examination (MMSE) in female patients with Alzheimer’s disease. Journal of Birjand University, 13(2), 9–15.
Jabbari, A. F., Talaei, A., Rafatpanah, H., Yousefzadeh, H., Jafari, R., Talaei, A., & Jafari, M. (2014). Association between cytokine production and disease severity in Alzheimer's disease. Iranian Journal of Allergy, Asthma, and Immunology, 13, 433–439.
Jafari, Z., & Rezaei, A. (2013). Cognitive status, lexical learning and memory in deaf adults using sign language. Bimonthly Audiology-Tehran University of Medical Sciences, 22(2), 73–82.
Jafari, Z., Toufan, R., Aghamollaei, M., Asad Malayeri, S., Rahimzadeh, S., & Esmaili, M. (2012). Impact of tinnitus on divided and selective auditory attention in workers exposed to occupational noise. Advances in Cognitive Science, 14(3), 51–62.
Javadi, P. S. H. S., Zendehbad, A., Darabi, F., Khosravifar, S., & Noroozian, M. (2015). Development and implementation of Persian test of elderly for assessment of cognition and executive function (PEACE). Electronic Physician, 7(7), 1549–1556.
Jobson, L., & Cheraghi, S. (2016). Influence of memory theme and posttraumatic stress disorder on memory specificity in British and Iranian trauma survivors. Memory, 24(8), 1015–1022.
Kamyab, S. (2015). The university entrance exam crisis in Iran. International Higher Education, 51, 22–23.
Karamshaii, A., Yarmohamadian, A., & Abedi, A. (2015). Development of executive functioning in children with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder and normal children: From preschool to the end of primary school. Transformational Psychology: Iranian psychologists, 42(11), 209–218.
Kormi-Nouri, R., Moradi, A. R., Moradi, S., Akbari-Zardkhaneh, S., & Zahedian, H. (2012). The effect of bilingualism on letter and category fluency tasks in primary school children: Advantage or disadvantage? Bilingualism: Language and Cognition, 15(2), 351–364.
Lampley-Dallas, V. T. (2001). Neuropsychological screening tests in African Americans. Journal of the National Medical Association, 93(9), 323–328.
Mahdavi, A., Haghighi, A., & Kazem Malakouti, S. (2016). Prevalence of cognitive disorders in patients with systemic lupus erythromatosus; a cross-sectional study in Rasoul-e-Akram hospital, Tehran, Iran. Archives of Iranian Medicine, 19(4), 257–261.
Malakouti, S. K., Panaghi, L., Foroughan, M., Salehi, M., & Zandi, T. (2012). Farsi version of the neuropsychiatric inventory: Validity and reliability study among Iranian elderly with dementia. International Psychogeriatrics, 24(2), 223–230.
Manavifar, L., & Karimooy, H. N. (2013). Homocysteine, cobalamin and folate status and their relations to neurocognitive and psychological markers in elderly in northeasten of Iran. Iranian Journal of Basic Medical Sciences, 16(6), 772–780.
Mani, A., Hashemi, T., Haghshenas, H., Garouci Farshi, M. T., & Sharlat, A. H. (2010). Memory process in demented and non-demented elderly patients. Iranian Red Crescent Medical Journal, 12(5), 525–528.
Mani, A., Shenavandeh, S., Sadat Sepehrtaj, S., & Javadpour, A. (2015). Memory and learning functions in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus: A neuropsychological case-control study. The Egyptian Rheumatologist, 37, S13–S17.
Mehri, A., Ghaemi, H., & Kord, N. (2009). Providing a picture verb naming test and determine its validity in Persian aphasia patients. Journal of Modern Rehabilitation, 3(1), 6–10.
Melamed, F., & Zaidel, E. (1993). Language and task effects on lateralized word recognition. Brain and Language, 45, 70–85.
Moher, D., Liberati, A., Tetzlaff, J., Altman, D. G., & Prisma Group. (2009). Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: The PRISMA statement. PLoS medicine, 6(7), e1000097.
Mooney, C. Z. (1997). Monte Carlo Simulation (Vol. 116). Sage Publications, Inc.
Moradi, A. R., Miraghaei, M. A., Parhon, H., Jabbari, H., & Jobson, L. (2013). Posttraumatic stress disorder, depression, executive functioning, and autobiographical remembering in individuals with HIV and in carers of those with HIV in Iran. AIDS Care, 25(3), 281–288.
Namazi Shabestari, A., Saeedi Moghaddam, S., Sharifi, F., Fadayevatan, R., Nabavizadeh, F., Delavari, A., & Naderimagham, S. (2014). The most prevalent causes of deaths, DALYs, and geriatric syndromes in Iranian elderly people between 1990 and 2010: Findings from the global burden of disease study 2010. Archives of Iranian Medicine, 18(8), 462–479.
Oskoei, A. S., Nejati, V., & Ajilchi, B. (2013). The effectiveness of cognitive rehabilitation on improving the selective attention in patients with mild cognitive impairment. Journal of Behavioral and Brain Science, 3(6), 474–478.
Pouretemad, H. R., Khatibi, A., Ganjavi, A., Shams, J., & Zarein, M. (2009). Validation of Addenbrooke’s cognitive examination (ACE) in a Persian-speaking population. Dementia and Geriatric Cognitive Disorders, 28, 343–347.
Prince, M. J., Acosta, D., Castro-Costa, E., Jackson, J., & Shaji, K. S. (2009). Packages of care for dementia in low-and middle-income countries. PLoS medicine, 6(11), e1000176.
Rahmandoust, M., Ahmadian, S., & Shah, I. M. (2011). Iranian entrepreneurs in Malaysia: Reasons for their migration. World Applied Sciences Journal, 13(9), 2075–2081.
Rashedi, V., Rezaei, M., & Gharib, M. (2014). Prevalence of cognitive impairment in community-dwelling older adults. Basic and Clinical Neuroscience, 5(1), 28–30.
Rostami-Povey, E. (2016). The women’s movement in its historical context. In T. Povey & E. Rostami-Povey (Eds.), Women, Power and Politics in 21st Century Iran (pp. 33–50). Routledge.
Salehi, H., Nezakatolhoseini, M., & Azadian, A. (2014). Attention deficit during dual-task performance in Alzheimer’s disease patients. Salmand, 9(2), 88–96.
Seyedian, M., Fallah, M., Norouzian, M., Nejat, S., Delavar, A., & Ghasemzadeh, H. (2007). Validity of the Farsi version of mini-mental state examination. Journal of Medical Council of Islamic Republic of Iran, 25(4), 408–414.
Seyfaddini, R. (2006). Ti: Cognitive function in diabetes mellitus patients. American Journal of Applied Sciences, 3(1), 1682–1684.
Thorell, L. B., Veleiro, A., Siu, A. F., & Mohammadi, H. (2013). Examining the relation between ratings of executive functioning and academic achievement: Findings from a cross-cultural study. Child Neuropsychology, 19(6), 630–638.
Wimo, A., & Prince, M. (2010) World Alzheimer report 2010: The global economic impact of dementia. Alzheimer’s disease international. Retrieved June 4, 2021, from https://www.alz.org/documents/national/world_alzheimer_report_2010.pdf
Zeng, X., Zhang, Y., Kwong, J. S., Zhang, C., Li, S., Sun, F., & Du, L. (2015). The methodological quality assessment tools for preclinical and clinical studies, systematic review and meta-analysis, and clinical practice guideline: A systematic review. Journal of Evidence-Based Medicine, 8(1), 2–10.
Funding
There was no funding or any financial support on this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of Interest
Not applicable.
We declare that this is an original work and there is no conflict of interest in this research. The field of study can be considered cross-cultural psychiatry research.
First author declares that he has no conflict of interest.
Second author declares that he has no conflict of interest.
Third author declares that she has no conflict of interest.
Fourth author declares that he has no conflict of interest.
Fifth author declares that she has no conflict of interest.
Ethical Approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Appendix
Appendix
Article Excluded:
-
1.
Rashedi et al., 2014;
-
2.
Hassani et al., 2012;
-
3.
Oskoei et al., 2013;
-
4.
Chabok et al., 2012;
-
5.
Emsaki et al., 2011;
-
6.
Mehri et al., 2009;
-
7.
Seyfaddini, 2006;
-
8.
Moradi et al., 2013;
-
9.
Manavifar & Karimooy, 2013;
-
10.
Kormi-Nouri et al., 2012;
-
11.
Baluch, 1996;
-
12.
Allahyari et al., 2014;
-
13.
Jobson & Cheraghi, 2016;
-
14.
Thorell et al., 2013;
-
15.
Amani et al., 2012;
-
16.
Salehi et al., 2014;
-
17.
Karamshaii et al., 2015
-
18.
Gharaeipour & Andrew, 2013
Modified MMSE Versions Excluded
-
1.
Modified MMSE
-
2.
3 MMSE,
-
3.
Farsi Version of 3MS or F-3MS
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ramezani, A., Alvani, S.R., Saleh, M.I. et al. Healthy and clinical meta-data and aggregated mini-mental status exam scores for the Persian speaking population. Curr Psychol 42, 7135–7148 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12144-021-01998-9
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12144-021-01998-9