Abstract
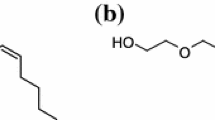
We report on the physical properties of swollen solutions of the amphiphilic molecules of cetylpyridinium chloride and hexanol in brine. A remarkable characteristic of this system is the existence of a crossover between dilute and less dilute solutions, in the lamellar phase and the sponge phase, with some interesting consequences for the theory of membranes.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
I Nastishin, E Lambert and P Boltenhagen, Comptes-Rendus. Acad. Sci. Paris IIb. 321, 205 (1995)
P Boltenhagen, O D Lavrentovich and M Kleman, J. Phys. II France 1, 1233 (1991)
P Boltenhagen, M Kleman and O D Lavrentovich, J. Phys. II France 4, 1439 (1994)
G Friedel, Ann. Phys. France 2, 273 (1922)
C Meyer, S Asnacios, C Bourgaux and M Kleman, ILCC 17, Strasbourg 1998, in press
O Diat and D Roux, J. Phys. II France 3, 9 (1993)
T Gulik-Krzywicki, J C Dedieu, D Roux C Degert and R Laversanne, Langmuir 12, 4668 (1996)
H F Mahjoub, K M McGrath and M Kleman, Langmuir 12, 3131 (1996)
H F Mahjoub, C Bourgaux, K McGrath J F Tassin and M Kleman, Mat. Res. Soc. Symp. Proc. 464, 145 (1997)
H F Mahjoub, C Bourgaux, P Sergot and M Kleman, Phys. Rev. Lett. 81, 2076 (1998)
C Bourgaux, private communication
For a review on fluctuations see e.g. Statistical Mechanics of Membranes and Surfaces, edited by D Nelson et al (World Scientific, Singapore, 1989). The main results of the renormalization group approach in the calculation of κ and \(\bar \kappa \) have recently been challenged by Helfrich, Eur. Phys. J. B1, 481 (1998)
P Boltenhagen, O D Lavrentovich and M Kleman, Phys. Rev. A46, R1743 (1992)
P Snabre and G Porte, Europhys. Lett. 13, 642 (1990)
O Diat and D Roux Langmuir 11, 1392 (1995)
H Hoffmann, S Hoffmann, A Rauscher and J Kalus, Progr. Coll. Polym. Sci. 84, 24 (1991)
J Yamamoto and H Tanaka, Phys. Rev. Lett. 77, 4390 (1996)
H F Mahjoub, J F Tassin and M Kleman, in preparation
The results which follow belong to H F Mahjoub, PhD Thesis (Universite Paris 6, 1998) (see ref. [14])
G Porte, M Delsanti, I Billard, M Skouri, J Appell, J Marignan, and F J Debeauvais, J. Phys. II France 1, 1101 (1991)
G Waton and G Porte, J. Phys. II France 4, 5152 (1993)
S T Milner, M E Cates and D Roux, J. Phys. (France) 51, 2629 (1990)
L Golubovic, Phys. Rev. E50, 2419 (1994)
D C Morse, Phys. Rev. E50, 2423 (1994)
G Porte, J Appell, P Bassereau and J J Marignan, J Phys. (France) 50, 285 (1989)
S P Timoshenko, Theory of Elastic Stability (McGraw- Hill Book Cy, New York, 1961)
We adopt the notation used by liquid crystals people, viz. ξ⊥ for lengths measured parallel the surface of the membrane, ξ‖ for lengths measured perpendicular to the membrane.
W Helfrich and R M Servuss, Il Nuovo Cimento. 3D, 137 (1984)
B D Coleman and M Kleman, in preparation
Also called the projected area, because this theoretical approach is valid for quasi-planar surfaces
P G De Gennes and C Taupin J. Phys. Chem. 86, 2294 (1982)
W Helfrich, Z Natur. 33A, 305 (1978)
L Peliti and S Leibler, Phys. Rev. Lett. 54, 1690 (1985)
L Golubovic and T C Lubensky, Phys. Rev. A41, 4343 (1990)
F David, in Statistical Mechanics of Membranes and Surfaces edited by D Nelson et al. (World Scientific, Singapore, 1989) p. 157
P Boltenhagen, M Kleman and O D Lavrentovich, in Soft Order in Physical Systems edited by Y Rabin and R Bruinsma (Plenum Press, New York, 1994) p. 5
C Blanc, private communication
M Kleman, Philos. Mag. 34, 79 (1976)
M E Cates, D Roux, D Andelman, S T Milner and S A Safran, Europhys. Lett. 5, 733 (1988)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kleman, M. The lamellar and sponge phases of dilute surfactant systems: Structures and defects at equilibrium and under shear. Pramana - J Phys 53, 107–119 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12043-999-0143-3
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12043-999-0143-3