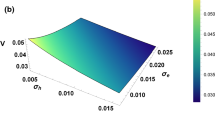
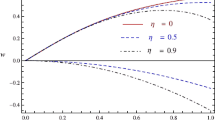
Abstract
The existence of the large-amplitude dust inertial Alfvén waves (DIAWs) has been presented in an electron-depleted, two-fluid dust-ion plasma. Linear analysis shows that the DIAWs travel slower than the dust Alfvén waves. DIAWs are the obliquely (with respect to the external magnetic field) propagating oscillations of dust density, having the characteristics of a solitary wave. In order to observe the nonlinear behaviour of the DIAWs, the Sagdeev pseudopotential method has been used to derive the energy balance equation and from the expression of the Sagdeev pseudopotential, the existence conditions for the DIAWs have also been determined. It is observed that density rarefactions travelling at sub- and super-Alfvénic speeds are associated with DIAWs.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
H Alfvén, Nature 150, 405 (1942)
W H Bostick and M A Levine, Phys. Rev. Lett. 87, 671 (1952)
N F Cramer, The physics of Alfvén waves (Wiley-VCH Press, 2005)
C K Goertz and R W Boswell, J. Geophys. Res. 84, 7239 (2014)
D J Wu and J K Chao, J. Geophys. Res. 109, A06211 (2004)
C K Goertz, Rev. Geophys. 27, 271 (1989)
M Horanyi and D A Mendis, Astrophys. J. 307, 800 (1989)
A A Samarian, B W James, S V Vladimirov and N F Cramer, Phys. Rev. E 64, 025402 (2001)
N C Adhikary, H Bailung, A R Pal, J Chutia and Y Nakamura, Phys. Plasmas 14, 103705 (2007)
M M Hossen, M S Alam, S Sultana and A A Mamun, Eur. Phys. J. D 70, 252 (2016)
K Singh, P Sethi and N Saini, Phys. Plasmas 25, 033705 (2018)
K Singh, Y Ghai, N Kaur and N S Saini, Eur. Phys. J. D 72, 160 (2018)
Y Ghai, N Kaur, K Singh and N S Saini, Plasma Sci. Technol. 20, 74005 (2018)
K Singh and N S Saini, Phys. Plasmas 26, 113702 (2019)
R K Shikha, N A Chowdhury, A Mannan and A A Mamun, Eur. Phys. J. D 73, 177 (2019)
K Singh and N S Saini, Front. Phys. 8, 602229 (2020)
R K Shikha, N A Chowdhury, A Mannan and A A Mamun, Contributions to plasma physics, https://doi.org/10.1002/ctpp.202000117 (2020)
J Akter, N A Chowdhury, A Mannan and A A Mamun, Indian J. Phys., https://doi.org/10.1007/s12648-020-01927-9 (2021)
S Mahmood, H Ur-Rehman, M Z Ali and A Basit, Contrib. Plasma Phys., https://doi.org/10.1002/ctpp.202000211 (2021)
P K Shukla and A A Mamun, Introduction to dusty plasma physics (Institute of Physics, Bristol, 2002), pp. 3-4.
C Yinhua, L Wei and M Y Yu, Phys. Rev. E 61(1), 809 (2000)
A M Mirza, M A Mahmood and G Murtaza, New. J. Phys. 5, 116 (2003)
S Mahmood and H Saleem, Phys. Lett. A 338, 345 (2005)
N S Saini, B Kaur, M Singh and A S Bains, Phys. Plasmas 24, 073701 (2017)
M Salimullah and M Rosenberg, Phys. Lett. A 254, 347 (1999)
M A Mahmood, A M Mirza, P H Sakanaka and G Murtaza, Phys. Plasmas 9, 3794 (2002)
M Singh, N Kaur and N S Saini, Phys. Plasmas 25, 023705 (2018)
B B Kadomtsev, Plasma turbulence (Academic Press, New York, 1965) p. 82.
P K Shukla, H Ur-Rahman and R P Sharma, J. Plasma Phys. 28, 125 (1982)
M K Kalita and B C Kalita, J. Plasma Phys. 35, 267 (1986)
N Kaur and N S Saini, Astrophys. Space Sci. 361, 331 (2016)
A Hasegawa and C Uberoi, The Alfven wave (Technical Information Center, U.S. Department of Energy, Washington, 1982)
E Thomas, Jr, R L Merlino and M Rosenberg, Plasma Phys. Controlled Fusion 54, 124034 (2012)
E F El-Shamy, Phys. Rev. E 91, 033105 (2015)
Acknowledgements
NSS gratefully acknowledges the support for this research work from Department of Science and Technology, Govt. of India, New Delhi under DST-SERB project No. CRG/2019/003988.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Appendix A. Linearisation and derivation of dispersion relation
Appendix A. Linearisation and derivation of dispersion relation
The linearisation of eqs (10)–(17) is performed by assuming the following linearisation scheme: \(n_{i}=n_{i0}+n_{i1}\), \(n_{d}=n_{d0}+n_{d1}\), \(v_{iz}=v_{iz1}\), \(v_{dx}=v_{dx1}\), \(v_{dz}=v_{dz1}\), \(\phi _{\perp }=\phi _{\perp 1}\) and \(\psi _{\parallel }=\psi _{\parallel 1}\). In this linearisation scheme, the quantities with the index ‘0’ represent the unperturbed value of that quantity, while the quantities with the index ‘1’ represent its first-order fluctuation. Thus, after the linearisation of eqs (10)–(14) and assuming all the first-order fluctuations to be of the form \(A=A\mathrm {e}^{i(k_\perp x+k_\parallel z-\omega t)}\), we obtain the following set of equations respectively:
and
Combining eqs (15) and (16), and linearising it, we obtain
The linearisation of eq. (17) yields
From eqs (A.1) and (A.2), we get
Similarly, from eqs (A.3)–(A.5), we get
Now, using eqs (A.8) and (A.9) in eq. (A.7), we get
Using eqs (A.5), (A.8) and (A.10) in eq. (A.6), we get the required dispersion relation of the dust inertial Alfvén waves
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Singh, M., Singh, K. & Saini, N.S. Large-amplitude dust inertial Alfvén waves in an electron-depleted dusty plasma. Pramana - J Phys 95, 197 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12043-021-02226-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12043-021-02226-6