Abstract
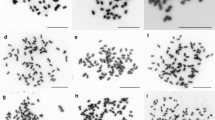
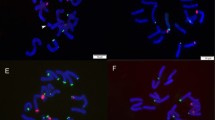
Amorphophallus, a perennial herb belongs to the family Araceae, and is widely distributed in Asia and Africa. As an agricultural crop, it has been cultivated and consumed for ~2000 years in China. Previous studies have found that there are chromosome number and ploidy changes in this genus, but there are a few reports on the evolution of different karyotypes. For this study, we collected 37 samples of a wild population of Amorphophallus muelleri from Myanmar and analysed their karyotypes. The karyotype analysis showed that it is a population with mixed chromosome numbers and ploidy, with four karyotypes of 2n = 24, 26, 28 and 39. Combining the results of this study with previous literature, we speculate that karyotypes with 2n = 26 may be the common ancestor, and further the other three karyotypes were evolved from this by various ways. As far as we know, this is the first attempt to put forward the hypothesis of the evolution of those four karyotypes together. On the other hand, by using inter-simple sequence repeat marker-based unweighted pair group method with arithmetic mean cluster analysis, we found that these individuals of four karyotypes can be divided into four corresponding categories, indicating that they have been differentiated at the genome, providing a theoretical basis for future use of these wild germplasm resources.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anil S. R., Beevy S. S. and Siril E. A. 2014 Cytotaxonomic investigations to assess diversity and evolution in Amorphophallus Blume ex Decne. (Araceae). Nucleus 57, 189–201.
Arano H. and Nakamura T. 1964 Cytological studies in subfamily Carduoideae (Compositae) of Japan XV. Bot Mag Tokyo. 77, 54–58.
Brandham P. E. and Chauhan K. P. S. 1985 Chromosome and DNA variation in Amorphophallus (Araceae). Kew Bull. 40, 745–758.
Camin J. H. and Sokal R. R. 1965 A method for deducing branching sequences in phylogeny. Evolution 19, 311–326.
Chen X., Yuan L. Q., Li L. J., Lv Y., Chen P. F. and Pan L. 2017 Suppression of gastric cancer by extract from the tuber of amorphophallus konjac via induction of apoptosis and autophagy. Oncol. Rep. 38, 1051–1058.
Devaraj R. D., Reddy C. K. and Xu B. 2019 Health-promoting effects of konjac glucomannan and its practical applications: A critical review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 126, 273–281.
Dey Y. N., Wanjari M. M., Kumar D., Lomash V. and Jadhav A. D. 2016 Curative effect of Amorphophallus paeoniifolius tuber on experimental hemorrhoids in rats. J. Ethnopharmacol. 192, 183–191.
Eichler E. E. and Sankoff D. 2003 Structural dynamics of eukaryotic chromosome evolution. Science 301, 793–797.
Felix L. P. and Guerra M. 2010 Variation in chromosome number and the basic number of subfamily Epidendroideae (Orchidaceae). Bot. J. Linn. Soc. 163, 234–278.
Gao Y., Yin S., Yang H., Wu L. and Yan Y. 2018 Genetic diversity and phylogenetic relationships of seven Amorphophallus species in southwestern China revealed by chloroplast DNA sequences. Mitochondrial DNA A DNA Mapp. Seq. Anal. 29, 679–686.
Gholave A. R., Pawar K. D., Yadav S. R., Bapat V. A. and Jadhav J. P. 2017 Reconstruction of molecular phylogeny of closely related Amorphophallus species of India using plastid DNA marker and fingerprinting approaches. Physiol. Mol. Biol. Plant 23, 155–167.
Gholave A. R., Lekhak M. M. and Yadav S. R. 2020 Comparative karyological analysis of Indian Amorphophallus (Araceae). Plant Biosyst. 154, 806–813.
Harmayani E., Aprilia V. and Marsono Y. 2014 Characterization of glucomannan from Amorphophallus oncophyllus and its prebiotic activity in vivo. Carbohydr. Polym. 112, 475–479.
Hashizume T., Shimamoto I. and Hiral M. 2003 Construction of a linkage map and QTL analysis of horticultural traits for watermelon [Citrullus lanatus (THUNB.) MATSUM & NAKAI] using RAPD, RFLP and ISSR markers. Theor. Appl. Genet. 106, 779–785.
Hetterscheid W. and Bogner J. 1999 Notes on the genus Amorphophallus (Araceae) 10. Revision of the endemic Amorphophallus species of Madagascar. Bot. Jahrbücher. 121, 1–17.
Jian W., Siu K. C. and Wu J. Y. 2015 Effects of pH and temperature on colloidal properties and molecular characteristics of Konjac glucomannan. Carbohydr. Polym. 134, 285–292.
Kite G. C. and Hetterscheid W. L. A. 2017 Phylogenetic trends in the evolution of inflorescence odours in Amorphophallus. Phytochemistry 142, 126–142.
Kolar F., Certner M., Suda J., Schonswetter P. and Husband B. C. 2017 Mixed-ploidy species: progress and opportunities in polyploid research. Trends Plant Sci. 22, 1041–1055.
Kreiner J. M., Kron P. and Husband B. C. 2017 Frequency and maintenance of unreduced gametes in natural plant populations: associations with reproductive mode, life history and genome size. New Phytol. 214, 879–889.
Krishnan R., Magoon M. L. and Bai K. V. 2011 Karyological studies in Amorphophallus campanulatus. Genome 12, 187–196.
Leven A. 1964 Nomenclature for centromeric position on chromosomes. Hereditas 52, 201–220.
Li M. and Chen R. 1985 A suggestion on the standardization of karyotype analysis in plants. J. Wuhan Bot. Res. 3, 297–302.
Liu E., Yang C., Liu J., Jin S., Harijati N., Hu Z. et al. 2019 Comparative analysis of complete chloroplast genome sequences of four major Amorphophallus species. Sci. Rep-UK. 9, 809.
Liu L., Ma X., Wei J., Qin J. and Mo C. 2011 The first genetic linkage map of Luohanguo (Siraitia grosvenorii) based on ISSR and SRAP markers. Genome 54, 19–25.
Marchant C. J. 1971 Chromosome variation in Araceae III: Philodendreae to Pythonieae. Kew Bull. 25, 323–329.
Marchant C. J. and Brighton C. A. 1974 Cytological diversity and triploid frequency in a complex population of Ranunculus ficaria L. Ann. Bot. 38, 7–15.
Niu Y. 2005 The germplasm resources of Amorphophallus rivieri Durieu: a review. Southwest Hort. 27, 634–638.
Niu Y., Zhang S., Wang Z. and Liu P. 2005 Amorphophallus resources in China. Southwest Hort. 33, 22–24.
Paniel S., Marhold K., Filová B. and Zozomová-Lihová J. 2011 Genetic and morphological variation in the diploid–polyploid Alyssum montanum in Central Europe: taxonomic and evolutionary considerations. Plant Syst. Evol. 294, 1–25.
Passamonti M., Mantovani B. and Scali V. 2004 Phylogeny and karyotype evolution of the Iberian Leptynia attenuata species complex (Insecta Phasmatodea). Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 30, 87–96.
Qiao W., Jian W. and Geng Z. 2011 Characteristics of Konjac Glucomannan (KGM) in A. bulbifer compared with that in A. rivieri and A. albus. Adv. Mater. Res. 236–238, 2045–2052.
Ramachandran K. 1977 Karyological studies on four South Indian species of Amorphophallus. Cytologia. 42, 645–652.
Ramsey J. 2007 Unreduced gametes and neopolyploids in natural populations of Achillea borealis (Asteraceae). Heredity (Edinb). 98, 143–150.
Sabara H. A., Kron P. and Husband B. C. 2013 Cytotype coexistence leads to triploid hybrid production in a diploid–tetraploid contact zone of Chamerion angustifolium (Onagraceae). Am. J. Bot. 100, 962–970.
Shete C. C., Wadkar S. S., Gaikwad N. B. and Paul K. S. 2015 Cytological studies in some members of Amorphophallus from western ghats of Maharashtra. J. Cytol. Genet. 16, 17–24.
Stebbins G. L. 1971 Chromosomal evolution in higher plants. Edward Arnold Publisher, London.
Subramanian D. and Munian M. 1988 Cytotaxonomical studies in South Indian Araceae. Cytologia 53, 59–66.
Tester R. F. and Al-Ghazzewi F. H. 2016 Beneficial health characteristics of native and hydrolysed konjac (Amorphophallus konjac) glucomannan. J. Sci. Food Agric. 96, 3283–3291.
Thompson J. D. and Lumaret R. 1992 The evolutionary dynamics of polyploid plants: origins, establishment and persistence. Trends Ecol. Evol. 7, 302–307.
Tracy L. B. and Brian C. H. 2001 Fecundity and offspring ploidy in matings among diploid, triploid and tetraploid Chamerion angustifolium (Onagraceae): consequences for tetraploid establishment. Heredity 87, 573–583.
Travenzoli N. M., Cardoso D. C., Werneck H. A., Fernandes-Salomao T. M., Tavares M. G. and Lopes D. M. 2019 The evolution of haploid chromosome numbers in Meliponini. PLoS One 14, e0224463.
Xu L., Wang L., Gong Y., Dai W., Wang Y., Zhu X. et al. 2012 Genetic linkage map construction and QTL mapping of cadmium accumulation in radish (Raphanus sativus L.). Theor. Appl. Genet. 125, 659–670.
Zalewski B. M., Chmielewska A. and Szajewska H. 2015 The effect of glucomannan on body weight in overweight or obese children and adults: a systematic review of randomized controlled trials. Nutrition 31, 437–442.
Zhang F. 2014 Karyotype study and ISSR analysis of genetic relationship of Amorphophallus tuberosus. Southwest University.
Zhu F. 2018 Modifications of konjac glucomannan for diverse applications. Food Chem. 256, 419–426.
Acknowledgements
Authors thank Hubei Agricultural Science and Technology Innovation Action Project for their support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Corresponding editor: H. A. Ranganath
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, C., She, X., Liu, E. et al. A mixed ploidy natural population of Amorphophallus muelleri provides an opportunity to trace the evolution of Amorphophallus karyotype. J Genet 100, 10 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12041-020-01255-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12041-020-01255-1