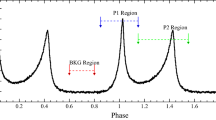
Abstract
In the first 3.5 years of operations, Fermi detected several sources whose flaring activity brought them to exceed daily fluxes brighter than F(E > 100MeV) > 10−6 ph cm−2 s−1. These episodes were promptly reported to the scientific community by the Fermi collaboration by means of astronomer telegrams (ATels). We focus our attention on the sample composed by these flaring sources, most of which are blazars, known to be extremely variable over the whole electromagnetic spectrum, from radio to γ-ray energies. We study properties of the selected sample and compare them to general characteristics of the Fermi source catalogue.




Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
More information regarding the ‘gammamw’ mailing list are available at: http://fermi.gsfc.nasa.gov/ssc/library/newsletter/.
These templates are publicly available and can be found at the web address: http://fermi.gsfc.nasa.gov/ssc/data/access/lat/BackgroundModels.html
The square root of TS in the case of two degree of freedom is distributed as χ 2, therefore TS=25 roughly corresponds to 4.6 sigma.
AGU refers to sources without a good optical spectrum or without an optical spectrum at all, whereas AGN refers to sources that are neither confirmed blazars nor blazar candidates. For more details, we address the reader to Ackermann et al. (2011).
References
Ackermann, M. et al. 2012, Astrophys. J. Suppl., 203, 4.
Ackermann, M. et al. 2011, Astrophys. J., 743, 171.
Atwood, W. B. et al. 2009, Astrophys. J., 697, 1071.
Ciprini, S. and the Fermi-LAT Collaboration, 2012, American Inst. Phys. Conf. Ser., 1595, 697.
Kerr, M. 2011, Ph.D. in physics (New York: University of Washington).
Mattox, J. R. 1996, Astrophys. J., 461, 396.
Nolan, P. L. et al. 2012, Astrophys. J. Suppl., 199, 31.
Thompson, D. J. et al. 1993, Astrophys. J. Suppl., 86, 629.
Acknowledgements
Fermi LAT Collaboration acknowledges support from a number of agencies and institutes for both development and operation of the LAT as well as scientific data analysis. These include NASA and DOE in United States, CEA/Irfu and IN2P3/CNRS in France, ASI and INFN in Italy, MEXT, KEK and JAXA in Japan, and K. A. Wallenberg Foundation, the Swedish Research Council and the National Space Board in Sweden. Additional support from INAF in Italy and CNES in France, for science analysis during the operations phase is also gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Consortia
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Buson, S., Bastieri, D., D’Ammando, F. et al. Fermi LAT View of a Sample of Flaring γ-Ray AGNs. J Astrophys Astron 35, 373–378 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12036-014-9233-9
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12036-014-9233-9