Abstract
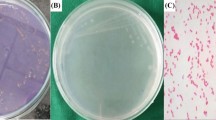
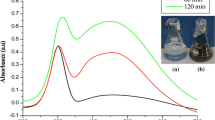
Mosquitoes transmit serious human infections and cause a number of deaths in tropical and subtropical environment countries every year. In the present work the zinc-substituted hydroxyapatite Ca5−xZnx(PO4)3OH (x = 0, 0.05, 0.2 and 1.0) was synthesized by two different methods: the hydrothermal method and the sol–gel method. The phase formation, functional group and surface morphology of Zn-HAP were authenticated using X-ray diffraction, Fourier transform infrared and scanning electron microscopy-energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy, respectively. The antimicrobial activity of the synthesized compounds was tested against different organisms such as Escherichia coli, Staphylococcus aureus and Candida albicans. Moreover, excellent antimicrobial activity was observed for hydrothermal-synthesized (Zn-HAP) compound compared to that of the sol–gel method. The synthesized Zn-HAP nanoparticles were reported for larvicidal activity against the filarial and Japanese encephalitis vector, Culex quinquefasciatus. The hydrothermal-synthesized (1.0 M Zn-HAP) compound exhibited higher larvicidal activity (93 ± 6.62) with minimum lethal concentration LC50 (33.74 mg ml−1) (to kill 50% of the care for larvae of the relevant species) and LC90 (139.92 mg ml−1) (to kill 90% of the treated larvae of the respective species) after 24 h, respectively than that of the sol–gel method.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rajakumar G and Abdul Rahuman A 2011 Acta Trop. 118 196
Kovendan K, Murugan K, Vincent S and Barnard D R 2011 Parasitol. Res. 110 195
Logeswari P, Silambarasan S and Abraham J 2013 Sci. Iran. 20 1049
Rezza G 2014 Pathog. Glob. Health 108 349
WHO 2012 Handbook for integrated vector management (Geneva: World Health Organization)
WHO 2014 Lymphatic filariasis Fact sheet N 102
Ghosh A, Chowdhury N and Chandra G 2012 Indian J. Med. Res. 135 581
Sumathi S and Buvaneswari G 2014 Appl. Surf. Sci. 303 277
Ragab H S, Ibrahim F A, Abdallah F, Al-Ghamdi A A, Tantawy F E and Yakuphanoglu F 2014 J. Pharm. Biol. Sci. 9 77
Prakasam M, Locs J, Salma-Ancane K, Loca D, Largeteau A and Berzina-Cimdina L 2015 J. Funct. Biomater. 6 1099
Galindo T G P, Kataoka T and Tagaya M 2015 J. Nanomater. 2015 1
Gunawan, Sopyan I, Suryanto and Naqshbandi A 2014 Indian J. Chem. 53A 152
Gayathri B, Muthukumarasamy N, Velauthapillai D, Santhosh S B and Asokan V 2018 Arabian J. Chem. 11 645
Ramesh S, Natasha A N, Tan C Y, Bang L T, Niakan A, Purbolaksono J et al 2015 Ceram. Int. 41 10434
Bilton M, Milne S J and Brown A P 2012 Open J. Inorg. Non-metallic Mater. 2 1
Rahuman A A, Gopalakrishnan G, Ghouse B S, Arumugam S and Himalayan B 2000 Fitoterapia 71 553
Ofudje E A, Adeogun A I, Idowu M A and Kareem S O 2019 Heliyon 5 e0176
Stanic V, Dimitrijevic S, Antic-Stankovic J, Mitric M, Jokic B, Plecas I B et al 2010 Appl. Surf. Sci. 256 6083
Acknowledgement
We would like to thank VIT management for providing all required facilities.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Valarmathi, N., Sabareeswari, K. & Sumathi, S. Antimicrobial and larvicidal activity of zinc-substituted hydroxyapatite. Bull Mater Sci 43, 218 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12034-020-02192-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12034-020-02192-6