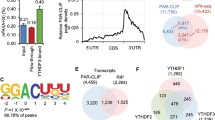
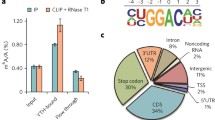
Abstract
N6-methyladenosine (m6A) is the most abundant—internal modification of eukaryotic mRNA. m6A can be installed and removed by specific enzymes. The “writer,” “eraser,” and “reader” of m6A modification have been reported. These discoveries facilitate our understanding of the functional significance of m6A. m6A plays an essential role in diverse biological processes by recruiting the corresponding YTH domain-containing proteins, as well as recruiting additional translation initiation factors. Here, we provide an update on the various aspects of YTH domain-containing proteins, including an introduction to the YTH domain, the categories, distribution in cells, and biological roles of YTH proteins. Then we focus on the mechanisms that YTH proteins recognize m6A and mediate the fate of methylated-RNAs in eukaryotic cells.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fu, Y., Dominissini, D., Rechavi, G., & He, C. (2014). Gene expression regulation mediated through reversible m6A RNA methylation. Nature Reviews Genetics, 15, 293–306.
Wu, R., Jiang, D., Wang, Y., & Wang, X. (2016). N6-methyladenosine m6A methylation in mRNA with a dynamic and reversible epigenetic modification. Molecular Biotechnology, 58, 450–459.
Adams, J. M., & Cory, S. (1975). Modified nucleosides and bizarre 5′-termini in mouse myeloma messenger-RNA. Nature, 255, 28–33.
Wei, C. M., & Moss, B. (1977). Nucleotide-sequences at N6-methyladenosine sites of HeLa-cell messenger ribonucleic-acid. Biochemistry-US, 16, 1672–1676.
Krug, R. M., Morgan, M. A., & Shatkin, A. J. (1976). Influenza viral mRNA contains internal N6-methyladenosine and 5′-terminal 7-methylguanosine in cap structures. Journal of Virology, 20, 45–53.
Jia, G. F., Fu, Y., Zhao, X., Dai, Q., et al. (2011). N6-methyladenosine in nuclear RNA is a major substrate of the obesity-associated FTO. Nature Chemical Biology, 7, 885–887.
Dominissini, D., Moshitch-Moshkovitz, S., Schwartz, S., Salmon-Divon, M., et al. (2012). Topology of the human and mouse m6A RNA methylomes revealed by m6A-sEq. Nature, 485, 201–206.
Meyer, K. D., Saletore, Y., Zumbo, P., Elemento, O., et al. (2012). Comprehensive analysis of mRNA methylation reveals enrichment in 3’ UTRs and near stop codons. Cell, 149, 1635–1646.
Roundtree, I. A., & He, C. (2016). Nuclear m6A reader YTHDC1 regulates mRNA splicing. Trends Genetics, 32, 320–321.
Cui, Q., Shi, H. L., Ye, P., Li, L., et al. (2017). m6A RNA methylation regulates the self-renewal and tumorigenesis of glioblastoma stem cells. Cell Reports, 18, 2622–2634.
Xiang, Y., Laurent, B., Hsu, C. H., Nachtergaele, S., et al. (2017). RNA m6A methylation regulates the ultraviolet-induced DNA damage response. Nature, 543, 573–576.
Lee, A. S., Kranzusch, P. J., & Cate, J. H. (2015). eIF3 targets cell-proliferation messenger RNAs for translational activation or repression. Nature, 522, 111–114.
Wang, X., Zhao, B. S., Roundtree, I. A., Lu, Z., et al. (2015). N6-methyladenosine modulates messenger RNA translation efficiency. Cell, 161, 1388–1399.
Wang, X., Lu, Z., Gomez, A., Hon, G. C., et al. (2014). N6-methyladenosine-dependent regulation of messenger RNA stability. Nature, 505, 117–120.
Desrosiers, R., Friderici, K., & Rottman, F. (1974). Identification of methylated nucleosides in messenger-RNA from Novikoff hepatoma-cells. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences USA, 71, 3971–3975.
Batista, P. J., Molinie, B., Wang, J., Qu, K., et al. (2014). m6A RNA modification controls cell fate transition in mammalian embryonic stem cells. Cell Stem Cell, 15, 707–719.
Molinie, B., Wang, J., Lim, K. S., Hillebrand, R., et al. (2016). m6A-LAIC-seq reveals the census and complexity of the m6A epitranscriptome. Nature Methods, 13, 692–698.
Liu, J., Yue, Y., Han, D., Wang, X., et al. (2014). A METTL3-METTL14 complex mediates mammalian nuclear RNA N6-adenosine methylation. Nature Chemical Biology, 10, 93–95.
Ping, X. L., Sun, B. F., Wang, L., Xiao, W., et al. (2014). Mammalian WTAP is a regulatory subunit of the RNA N6-methyladenosine methyltransferase. Cell Research, 24, 177–189.
Zheng, G. Q., Dahl, J. A., Niu, Y. M., Fedorcsak, P., et al. (2013). ALKBH5 Is a mammalian RNA demethylase that impacts RNA metabolism and mouse fertility. Molecular Cell, 49, 18–29.
Narayan, P., & Rottman, F. M. (1988). An in vitro system for accurate methylation of internal adenosine residues in messenger RNA. Science, 242, 1159–1162.
Bokar, J. A., Rath-Shambaugh, M. E., Ludwiczak, R., Narayan, P., et al. (1994). Characterization and partial purification of mRNA N6-adenosine methyltransferase from HeLa cell nuclei. Internal mRNA methylation requires a multisubunit complex. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 269, 17697–17704.
Bokar, J. A., Shambaugh, M. E., Polayes, D., Matera, A. G., et al. (1997). Purification and cDNA cloning of the AdoMet-binding subunit of the human mRNA (N6-adenosine)-methyltransferase. RNA, 3, 1233–1247.
Wang, X., Feng, J., Xue, Y., Guan, Z., et al. (2017). Corrigendum: Structural basis of N6-adenosine methylation by the METTL3-METTL14 complex. Nature, 542, 260.
Wang, P., Doxtader, K. A., & Nam, Y. (2016). Basis for Cooperative function of Mettl3 and Mettl14 methyltransferases. Molecular Cell, 63, 306–317. Structural.
Wang, Y., Li, Y., Toth, J. I., Petroski, M. D., et al. (2014). N6-methyladenosine modification destabilizes developmental regulators in embryonic stem cells. Nature Cell Biology, 16, 191–198.
Geula, S., Moshitch-Moshkovitz, S., Dominissini, D., Mansour, A. A., et al. (2015). m6A mRNA methylation facilitates resolution of naive pluripotency toward differentiation. Science, 347, 1002–1006.
Gerken, T., Girard, C. A., Tung, Y. C., Webby, C. J., et al. (2007). The obesity-associated FTO gene encodes a 2-oxoglutarate-dependent nucleic acid demethylase. Science, 318, 1469–1472.
Frayling, T. M., Timpson, N. J., Weedon, M. N., Zeggini, E., et al. (2007). A common variant in the FTO gene is associated with body mass index and predisposes to childhood and adult obesity. Science, 316, 889–894.
Scuteri, A., Sanna, S., Chen, W. M., Uda, M., et al. (2010). Genome-wide association scan shows genetic variants in the FTO gene are associated with obesity-related traits. PLoS Genetics. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pgen.0030115.
Thomson, J. A., Itskovitz-Eldor, J., Shapiro, S. S., Waknitz, M. A., et al. (1998). Embryonic stem cell lines derived from human blastocysts. Science, 282, 1145–1147.
Jaffrey, S. R., & Kharas, M. G. (2017). Emerging links between m6A and misregulated mRNA methylation in cancer. Genome Medicine, 9, 2.
Wang, S. W., Sun, C. X., Li, J. H., Zhang, E. B., et al. (2017). Roles of RNA methylation by means of N6-methyladenosine in human cancers. Cancer Letters, 408, 112–120.
Fustin, J. M., Doi, M., Yamaguchi, Y., Hida, H., et al. (2013). RNA-methylation-dependent RNA processing controls the speed of the circadian clock. Cell, 155, 793–806.
Akhtar, R. A., Reddy, A. B., Maywood, E. S., Clayton, J. D., et al. (2002). Circadian cycling of the mouse liver transcriptome, as revealed by cDNA microarray, is driven by the suprachiasmatic nucleus. Current Biology, 12, 540–550.
Koike, N., Yoo, S. H., Huang, H. C., Kumar, V., et al. (2012). Transcriptional architecture and chromatin landscape of the core circadian clock in mammals. Science, 338, 349–354.
Kennedy, E. M., Bogerd, H. P., Kornepati, A. V. R., Kang, D., et al. (2017). Posttranscriptional m6A editing of HIV-1 mRNAs enhances viral gene expression (vol 19, pg 675, 2016). Cell Host & Microbe, 22, 830–830.
Brocard, M., Ruggieri, A., & Locker, N. (2017). m6A RNA methylation, a new hallmark in virus-host interactions. Journal of General Virology, 98, 2207–2214.
Li, H. B., Tong, J. Y., Zhu, S., Batista, P. J., et al. (2017). m6A mRNA methylation controls T cell homeostasis by targeting the IL-7/STAT5/SOCS pathways. Nature, 548, 338–342.
Li, L. J., Fan, Y. G., Leng, R. X., Pan, H. F., et al. (2018). Potential link between m6A modification and systemic lupus erythematosus. Molecular Immunology, 93, 55–63.
Kan, L., Grozhik, A. V., Vedanayagam, J., Patil, D. P., et al. (2017). The m6A pathway facilitates sex determination in Drosophila. Nature Communications, 8, 15737.
Haussmann, I. U., Bodi, Z., Sanchez-Moran, E., Mongan, N. P., et al. (2016). m6A potentiates Sxl alternative pre-mRNA splicing for robust Drosophila sex determination. Nature, 540, 301–304.
Roost, C., Lynch, S. R., Batista, P. J., Qu, K., et al. (2015). Correction to “structure and thermodynamics of N6-methyladenosine in RNA: A spring-loaded base modification”. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 137, 8308.
Imai, Y., Matsuo, N., Ogawa, S., Tohyama, M., et al. (1998). Cloning of a gene, YT521, for a novel RNA splicing-related protein induced by hypoxia/reoxygenation. Molecular Brain Research, 53, 33–40.
Hartmann, A. M., Nayler, O., Schwaiger, F. W., Obermeier, A., et al. (1999). The interaction and colocalization of Sam68 with the splicing-associated factor YT521-B in nuclear dots is regulated by the Src family kinase p59(fyn). Molecular Biology of the Cell, 10, 3909–3926.
Xu, C., Wang, X., Liu, K., Roundtree, I. A., et al. (2015). Structural basis for selective binding of m6A RNA by the YTHDC1 YTH domain (vol 10, pg 927, 2014). Nature Chemical Biology, 11, 815.
Altschul, S. F., Madden, T. L., Schaffer, A. A., Zhang, J., et al. (1997). Gapped BLAST and PSI-BLAST: A new generation of protein database search programs. Nucleic Acids Research, 25, 3389–3402.
Stoilov, P., Rafalska, I., & Stamm, S. (2002). YTH: A new domain in nuclear proteins. Trends in Biochemical Sciences, 27, 495–497.
Hoffman, D. W., Query, C. C., Golden, B. L., White, S. W., et al. (1991). RNA-binding domain of the A protein component of the U1 small nuclear ribonucleoprotein analyzed by NMR spectroscopy is structurally similar to ribosomal proteins. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences USA, 88, 2495–2499.
Luo, S. K., & Tong, L. (2014). Molecular basis for the recognition of methylated adenines in RNA by the eukaryotic YTH domain. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences USA, 111, 13834–13839.
Zhu, T., Roundtree, I. A., Wang, P., Wang, X., et al. (2014). Crystal structure of the YTH domain of YTHDF2 reveals mechanism for recognition of N6-methyladenosine. Cell Research, 24, 1493–1496.
Theler, D., Dominguez, C., Blatter, M., Boudet, J., et al. (2014). Solution structure of the YTH domain in complex with N6-methyladenosine RNA: A reader of methylated RNA. Nucleic Acids Research, 42, 13911–13919.
Li, F., Zhao, D., Wu, J., & Shi, Y. (2014). Structure of the YTH domain of human YTHDF2 in complex with an m6A mononucleotide reveals an aromatic cage for m6A recognition. Cell Research, 24, 1490–1492.
Yang, X., Li, H., Huang, Y., & Liu, S. (2013). The dataset for protein-RNA binding affinity. Protein Sci, 22, 1808–1811.
Mauer, J., Luo, X., Blanjoie, A., Jiao, X., et al. (2017). Reversible methylation of m6Am in the 5′ cap controls mRNA stability. Nature, 541, 371–375.
Wei, C. M., & Moss, B. (1975). Methylated nucleotides block 5′-terminus of vaccinia virus messenger RNA. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences USA, 72, 318–322.
Patil, D. P., Chen, C. K., Pickering, B. F., Chow, A., et al. (2016). m6A RNA methylation promotes XIST-mediated transcriptional repression. Nature, 537, 369–373.
Dai, X. X., Wang, T. L., Gonzalez, G., & Wang, Y. S. (2018). Identification of YTH domain-containing proteins as the readers for N1-methyladenosine in RNA. Analytical Chemistry, 90, 6380–6384.
Safra, M., Sas-Chen, A., Nir, R., Winkler, R., et al. (2017). The m1A landscape on cytosolic and mitochondrial mRNA at single-base resolution. Nature, 551, 251.
Dominissini, D., Nachtergaele, S., Moshitch-Moshkovitz, S., Peer, E., et al. (2016). The dynamic N1-methyladenosine methylome in eukaryotic messenger RNA. Nature, 530, 441.
Oates, M. E., Romero, P., Ishida, T., Ghalwash, M., et al. (2013). (DP2)-P-2: Database of disordered protein predictions. Nucleic Acids Research, 41, D508–D516.
Du, H., Zhao, Y., He, J. Q., Zhang, Y., et al. (2016). YTHDF2 destabilizes m6A-containing RNA through direct recruitment of the CCR4-NOT deadenylase complex. Nature Communications, 7, 12626.
Lichinchi, G., Gao, S., Saletore, Y., Gonzalez, G. M., et al. (2016). Dynamics of the human and viral m6A RNA methylomes during HIV-1 infection of T cells. Nature Microbiology, 1, 16011.
Tanabe, A., Tanikawa, K., Tsunetomi, M., Takai, K., et al. (2016). RNA helicase YTHDC2 promotes cancer metastasis via the enhancement of the efficiency by which HIF-1 alpha mRNA is translated. Cancer Letter, 376, 34–42.
Meyer, K. D., Patil, D. P., Zhou, J., Zinoviev, A., et al. (2015). 5′ UTR m6A promotes cap-independent translation. Cell, 163, 999–1010.
Alarcon, C. R., Goodarzi, H., Lee, H., Liu, X. H., et al. (2015). HNRNPA2B1 is a mediator of m6A-dependent nuclear RNA processing events. Cell, 162, 1299–1308.
Chen, K., Lu, Z., Wang, X., Fu, Y., et al. (2015). High-resolution N6-methyladenosine map using photo-crosslinking-assisted m6A sequencing. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 54, 1587–1590.
Wu, B. X., Su, S. C., Patil, D. P., Liu, H. H., et al. (2018). Molecular basis for the specific and multivariant recognitions of RNA substrates by human hnRNP A2/B1. Nature Communications, 9, 420
Huang, H., Weng, H., Sun, W., Qin, X., et al., (2018). Author Correction: Recognition of RNA N6-methyladenosine by IGF2BP proteins enhances mRNA stability and translation. Nature Cell Biology, 20, 285–295.
Li, D. Y., Zhang, H. J., Hong, Y. B., Huang, L., et al. (2014). Genome-wide identification, biochemical characterization, and expression analyses of the YTH domain-containing RNA-binding protein family in Arabidopsis and rice. Plant Molecular Biology Reporter, 32, 1169–1186.
Reichel, M., Liao, Y., Rettel, M., Ragan, C., et al. (2016). In planta determination of the mRNA-binding proteome of Arabidopsis etiolated seedlings. The Plant Cell, 28, 2435–2452.
Arribas-Hernandez, L., Bressendorff, S., Hansen, M. H., Poulsen, C., et al. (2018). An m6A-YTH module controls developmental timing and morphogenesis in Arabidopsis. The Plant Cell, 30, 952–967.
Tirumuru, N., Zhao, B. S., Lu, W. X., Lu, Z. K., et al., (2016). N6-methyladenosine of HIV-1 RNA regulates viral infection and HIV-1 Gag protein expression. Elife, 5, e15528.
Nguyen, T. T., Ma, L. N., Slovak, M. L., Bangs, C. D., et al. (2006). Identification of novel Runx1 (AML1) translocation partner genes SH3D19, YTHDF2, and ZNF687 in acute myeloid leukemia. Genes Chromosomes Cancer, 45, 918–932.
Zhou, J., Wan, J., Gao, X., Zhang, X., et al. (2015). Dynamic m6A mRNA methylation directs translational control of heat shock response. Nature, 526, 591–594.
Wang, X., Sun, B., Jiang, Q. (2018). mRNA m6A plays opposite role in regulating UCP2 and PNPLA2 protein expression in adipocytes. International Journal of Obesity, 42, 1912–1924.
Wu, R., Yao, Y., Jiang, Q., Cai, M., et al. (2018). Epigallocatechin gallate targets FTO and inhibits adipogenesis in an mRNA m6A-YTHDF2-dependent manner. International Journal of Obesity (London), 42, 1378–1388.
Zhao, B. S., Wang, X., Beadell, A. V., Lu, Z., et al. (2017). m6A-dependent maternal mRNA clearance facilitates zebrafish maternal-to-zygotic transition. Nature, 542, 475–478.
Wei, L. H., Song, P. Z., Wang, Y., Lu, Z. K., et al. (2018). The m6A reader ECT2 controls trichome morphology by affecting mRNA stability in Arabidopsis. The Plant Cell, 30, 968–985.
Scutenaire, J., Deragon, J. M., Jean, V., Benhamed, M., et al. (2018). The YTH domain protein ECT2 is an m6A reader required for normal trichome branching in Arabidopsis. The Plant Cell, 30, 986–1005.
Hsu, P. J., Zhu, Y. F., Ma, H. H., Guo, Y. H., et al. (2017). YTHDC2 is an N6-methyladenosine binding protein that regulates mammalian spermatogenesis. Cell Research, 27, 1115–1127.
Jain, D., Puno, M. R., Meydan, C., Lailler, N., et al. (2018). ketu mutant mice uncover an essential meiotic function for the ancient RNA helicase YTHDC2. Elife, 7, e30919.
Drayman, N., Karin, O., Mayo, A., Danon, T., et al. (2017). Dynamic proteomics of herpes simplex virus infection. MBio. https://doi.org/10.1128/mBio.01612-17.
Ma, S., Menon, R., Poulos, R. C., & Wong, J. W. H. (2017). Proteogenomic analysis prioritises functional single nucleotide variants in cancer samples. Oncotarget, 8, 95841–95852.
Shichino, Y., Otsubo, Y., Kimori, Y., Yamamoto, M., et al. (2018). YTH-RNA-binding protein prevents deleterious expression of meiotic proteins by tethering their mRNAs to nuclear foci. Elife. https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.32155.001.
Shi, H. L., Wang, X., Lu, Z. K., Zhao, B. X. S., et al. (2017). YTHDF3 facilitates translation and decay of N6-methyladenosine-modified RNA. Cell Research, 27, 315–328.
Hubstenberger, A., Courel, M., Benard, M., Souquere, S., et al. (2017). P-body purification reveals the condensation of repressed mRNA regulons. Molecular Cell, 68, 144–157 e5.
Li, A., Chen, Y. S., Ping, X. L., Yang, X., et al. (2017). Cytoplasmic m6A reader YTHDF3 promotes mRNA translation. Cell Research, 27, 444–447.
Zhang, Z. Y., Theler, D., Kaminska, K. H., Hiller, M., et al. (2010). The YTH domain is a novel RNA binding domain. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 285, 14701–14710.
Ke, S. D., Pandya-Jones, A., Saito, Y., Fak, J. J., et al. (2017). m6A mRNA modifications are deposited in nascent pre-mRNA and are not required for splicing but do specify cytoplasmic turnover. Genes & Development, 31, 990–1006.
Engreitz, J. M., Pandya-Jones, A., McDonel, P., Shishkin, A., et al. (2013). The Xist lncRNA exploits three-dimensional genome architecture to spread across the X chromosome. Science, 341,1237973.
Kretschmer, J., Rao, H., Hackert, P., Sloan, K. E., et al. (2018). The m6A reader protein YTHDC2 interacts with the small ribosomal subunit and the 5′-3′ exoribonuclease XRN1. RNA, 24, 1339–1350.
Tanabe, A., Konno, J., Tanikawa, K., & Sahara, H. (2014). Transcriptional machinery of TNF-alpha-inducible YTH domain containing 2 (YTHDC2) gene. Gene, 535, 24–32.
Hornbeck, P. V., Zhang, B., Murray, B., Kornhauser, J. M., et al. (2015). PhosphoSitePlus, 2014: mutations, PTMs and recalibrations. Nucleic Acids Research, 43, D512–D520.
Kato, M., Han, T. N. W., Xie, S. H., Shi, K., et al. (2012). Cell-free formation of RNA granules: low complexity sequence domains form dynamic fibers within hydrogels. Cell, 149, 753–767.
Thinon, E., Serwa, R. A., Broncel, M., Brannigan, J. A., et al. (2014). Global profiling of co- and post-translationally N-myristoylated proteomes in human cells. Nature Communications, 5, 4919.
Lichinchi, G., Zhao, B. S., Wu, Y. A., Lu, Z. K., et al. (2016). Dynamics of human and viral RNA methylation during zika virus infection. Cell Host & Microbe, 20, 666–673.
Gokhale, N. S., McIntyre, A. B. R., McFadden, M. J., Roder, A. E., et al. (2016). N6-methyladenosine in flaviviridae viral RNA genomes regulates infection. Cell Host & Microbe, 20, 654–665.
Dixit, D., Xie, Q., Rich, J. N., & Zhao, J. C. (2017). Messenger rna methylation regulates glioblastoma tumorigenesis. Cancer Cell, 31, 474–475.
Zhang, S. C., Zhao, B. S., Zhou, A. D., Lin, K. Y., et al. (2017). m6A demethylase ALKBH5 maintains tumorigenicity of glioblastoma stem-like cells by sustaining FOXM1 expression and cell proliferation program. Cancer Cell, 31, 591–606.
Kwok, C. T., Marshall, A. D., Rasko, J. E. J., & Wong, J. J. L. (2017). Genetic alterations of m6A regulators predict poorer survival in acute myeloid leukemia (vol 10, 39, 2017). Journal of Hematology & Oncology, 10, 39.
Canaani, D., Kahana, C., Lavi, S., & Groner, Y. (1979). Identification and mapping of N6-methyladenosine containing sequences in Simian Virus-40 RNA. Nucleic Acids Research, 6, 2879–2899.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 31572413), the Natural Science Foundation of Zhejiang Province (No. LZ17C170001), the State Key Program of National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 3163000269), and the Special Fund for Cultivation and Breeding of New Transgenic Organism (No. 2014ZX0800949B).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, Y.L., Liu, Y.H., Wu, R.F. et al. Understanding m6A Function Through Uncovering the Diversity Roles of YTH Domain-Containing Proteins. Mol Biotechnol 61, 355–364 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12033-018-00149-z
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12033-018-00149-z