Abstract
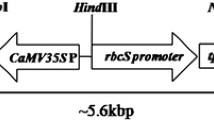
Nucleotide sequence encoding the truncated insecticidal Cry1Ca1 protein from Bacillus thuringiensis was extensively modified based on the codon usage of rice genes. The overall G + C contents of the synthetic cry1Ca1 coding sequence were raised to 65% with an additional bias of enriching for G and C ending codons as preferred by monocots. The synthetic gene was introduced into the Chinese japonica variety, Xiushui 11, by Agrobacterium-mediated transformation. Transgenic rice plants harboring this gene were highly resistant to Chilo suppressalis and Spodoptera litura larvae as revealed by insect bioassays. High levels of Cry1Ca1 protein were obtained in the leaves of transgenic rice, which were effective in achieving 100% mortality of S. litura and C. suppressalis larvae. The levels of Cry1Ca1 expression in the leaves of these transgenic plants were up to 0.34% of the total soluble proteins. The larvae of C. suppressalis and S. litura could consume a maximum of 1.89 and 4.89 mm2 of transgenic leaf area whereas the consumption of non-transgenic leaves by these larvae was significantly higher; 58.33 and 61.22 mm2, respectively. Analysis of R1 transgenic plants indicated that the cry1Ca1 was inherited by the progeny plants and provided complete protection against C. suppressalis and S. litura larvae.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lee, M. K., Aguda, R. M., Cohen, M. B., Gould, F. L., & Dean, D. H. (1997). Determination of binding of Bacillus thuringiensis delta-endotoxin receptors to rice stem borer midguts. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 63, 1453–1459.
Wang, Z. G., Shu, Q. Y., Ye, G. Y., Cui, H. R., Wu, D. X., Altosaar, I., et al. (2002). Genetic analysis of resistance of Bt rice to stripe stem borer (Chilo suppressalis). Euphytica, 123, 379–386.
Sudhir, K. S., Biswas, R., Garg, D. K., Gyawali, B. K., Haque, N. M. M., Ijaj, P., et al. (2004). Management of stem borers of rice and wheat in rice-wheat system of Pakistan, Nepal, India and Bangladesh. Rice-Wheat Consortium for the Indo-Gangetic Plains (p. 204). Rice-Wheat Consortium Paper Series 17. New Delhi, India.
Muralidharan, K., & Pasalu, I. C. (2006). Assessments of crop losses in rice ecosystems due to stem borer damage (Lepidoptera: Pyralidae). Crop Protection, 25, 409–417.
Breitler, J. C., Vassal, J. M., Catala, M. D., Meynard, D., Marfa, V., Mele, E., et al. (2004). Bt rice harbouring cry genes controlled by a constitutive or wound-inducible promoter: protection and transgene expression under Mediterranean field conditions. Plant Biotechnology Journal, 2, 417–430.
Rao, G. V. R., Wightman, J. A., & Ranga Rao, D. V. (1993). World review of the natural enemies and diseases of Spodoptera litura (F.) (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). Insect Science and its Application, 14, 273–284.
Dale, D. (1994). Insect pests of the rice plant: Their biology and ecology. In E. A. Heinrichs (Ed.), Biology and management of rice insects. New Delhi, India: Wiley Eastern Limited, New Age International Limited.
Alcantara, E. P., Aguda, R. M., Curtiss, A., Dean, D. H., & Cohen, M. B. (2004). Bacillus thuringiensis-endotoxin binding to brush border membrane vesicles of rice stem borers. Archives of Insect Biochemistry and Physiology, 55, 169–177.
Hofte, H., & Whiteley, H. R. (1989). Insecticidal crystal proteins of Bacillus thuringiensis. Microbiological Reviews, 53, 242–255.
Visser, B., Munsterman, E., Stoker, A., & Dirkse, W. G. (1990). A novel Bacillus thuringiensis gene encoding a Spodoptera-exigua-specific crystal protein. Journal of Bacteriology, 172, 6783–6788.
Crickmore, N., Zeigler, D. R., Feitelson, J., Schnepf, E., Van Rie, J., Lereclus, D., et al. (1998). Revision of the nomenclature for the Bacillus thuringiensis pesticidal crystal proteins. Microbiology and Molecular Biology Reviews, 62, 807–813.
Zhao, J. Z., Cao, J., Li, Y., Collins, H. L., Roush, R. T., Earle, E. D., et al. (2003). Transgenic plants expressing two Bacillus thuringiensis toxins delay insect resistance evolution. Nature Biotechnology, 21, 1493–1497.
Sardana, R., Dukiandjiev, S., Giband, M., Cheng, X. Y., Cowan, K., Sauder, C., et al. (1996). Construction and rapid testing of synthetic and modified toxin gene sequences CryIA (b&c) by expression in maize endosperm culture. Plant Cell Reports, 15, 677–681.
Gutierrez, R. A., MacIntosh, G. C., & Green, P. J. (1999). Current perspectives on mRNA stability in plants: Multiple levels and mechanisms of control. Trends in Plant Science, 4, 429–438.
Culbertson, M. R., & Leeds, P. F. (2003). Looking at mRNA decay pathways through the window of molecular evolution. Current Opinion in Genetics and Development, 13, 207–214.
Datla, R. S. S., Bekkaoui, F., Hammerlindl, J. K., Pilate, G., Dunstan, D. I., & Crosby, W. L. (1993). Improved high-level constitutive foreign gene-expression in plants using an AMV RNA4 untranslated leader sequence. Plant Science, 94, 139–149.
Sambrook, J., & Russell, D. W. (2001). Molecular cloning: A laboratory manual. Cold Spring Harbor, NY: Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory.
Holsters, M., Silva, B., Vanvliet, F., Hernalsteens, J. P., Genetello, C., VanMontagu, M., et al. (1978). In vivo transfer of Ti-plasmid of Agrobacterium tumefaciens to Escherichia coli. Molecular and General Genetics, 163, 335–338.
Martinez-Trujillo, M., Cabrera-Ponce, J. L., & Herrera-Estrella, L. (2003). Improvement of rice transformation using bombardment of scutellum-derived calli. Plant Molecular Biology Reporter, 21, 429–437.
Zaidi, M. A., Mohammadi, M., Postel, S., Masson, L., & Altosaar, I. (2005). The Bt gene cry2Aa2 driven by a tissue specific ST-LS1 promoter from potato effectively controls Heliothis virescens. Transgenic Research, 14, 289–298.
Ge, A. Z., Pfister, R. M., & Dean, D. H. (1990). Hyperexpression of a Bacillus thuringiensis δ-endotoxin encoding gene in Escherichia coli: Properties of the product. Gene, 93, 49–54.
Ye, G. Y., Shu, Q. Y., Cui, H. R., Hu, C., Gao, M. W., Xia, Y. W., et al. (2000). A leaf-section bioassay for evaluating rice stem borer resistance in transgenic rice containing a synthetic cry1Ab gene from Bacillus thuringiensis Berliner. Bulletin of Entomological Research, 90, 179–182.
Tang, Q. Y., & Feng, M. G. (2002). DPS © data processing system: Experimental design, statistical analysis and data mining. Beijing, China: Science Press.
Leroy, T., Henry, A. M., Royer, M., Altosaar, I., Frutos, R., Duris, D., et al. (2000). Genetically modified coffee plants expressing the Bacillus thuringiensis cry1Ac gene for resistance to leaf miner. Plant Cell Reports, 19, 382–389.
High, S. M., Cohen, M. B., Shu, Q. Y., & Altosaar, I. (2004). Achieving successful deployment of Bt rice. Trends in Plant Science, 9, 286–292.
Bashir, K., Husnain, T., Fatima, T., Riaz, N., Makhdoom, R., & Riazuddin, S. (2005). Novel indica basmati line (B-370) expressing two unrelated genes of Bacillus thuringiensis is highly resistant to two lepidopteran insects in the field. Crop Protection, 24, 870–879.
Christou, P., Capell, T., Kohli, A., Gatehouse, J. A., & Gatehouse, A. M. R. (2006). Recent developments and future prospects in insect pest control in transgenic crops. Trends in Plant Science, 11, 302–308.
Zaidi, M. A., Cheng, X., Xu, H., & Altosaar, I. (2006). Ex situ application of foliar-produced lepidoptericides from transgenic rice to control Pieris rapae and Cry1Ab stability in vivo. Crop Protection, 25, 748–752.
Valderrama, A. M., Velásquez, N., Rodríguez, E., Zapata, A., Zaidi, M. A., & Altosaar, I. (2007). Resistance to the Guatemalan potato moth, Tecia solanivora Povolny in three transgenic Andean potato varieties expressing Cry1Ac protein. Journal of Economic Entomology, 100, 172–179.
Kim, S., Kim, C., Li, W., Kim, T., Li, Y., Zaidi, M. A., et al. (2008). Inheritance and field performance of transgenic Korean Bt rice lines resistant to rice yellow stem borer. Euphytica, 164, 829–839.
Gulbitti-Onarici, S., Zaidi, M. A., Taga, I., Ozcan, S., & Altosaar, I. (2009). Expression of Cry1Ac in transgenic tobacco plants under the control of a wound-inducible promoter (AoPR1) isolated from Asparagus officinalis to control Heliothis virescens and Manduca sexta. Molecular Biotechnology, 42, 341–349.
Perlak, F. J., Fuchs, R. L., Dean, D. A., Mcpherson, S. L., & Fischhoff, D. A. (1991). Modification of the coding sequence enhances plant expression of insect control protein genes. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 88, 3324–3328.
King, G. J. (2002). Through a genome, darkly: Comparative analysis of plant chromosomal DNA. Plant Molecular Biology, 48, 5–20.
Kawabe, A., & Miyashita, N. T. (2003). Patterns of codon usage bias in three dicot and four monocot plant species. Genes & Genetic Systems, 78, 343–352.
Cheng, X. Y., Sardana, R., Kaplan, H., & Altosaar, I. (1998). Agrobacterium-transformed rice plants expressing synthetic cryIA(b) and cryIA(c) genes are highly toxic to striped stem borer and yellow stem borer. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 95, 2767–2772.
Maqbool, S. B., Husnain, T., Riazuddin, S., Masson, L., & Christou, P. (1998). Effective control of yellow stem borer and rice leaf folder in transgenic rice indica varieties Bas 370 and M7 using the novel δ-endotoxin cryIIA Bacillus thuringiensis gene. Molecular Breeding, 6, 1–7.
Butaye, K. M. J., Cammue, B. P. A., Delaure, S. L., & De Bolle, M. F. C. (2005). Approaches to minimize variation of transgene expression in plants. Molecular Breeding, 16, 79–91.
Zaidi, M. A., Cheng, X. Y., & Altosaar, I. (2007). Characterization of left-border flanking sequences of T-DNA integration in transgenic rice (Oryza sativa L.) expressing cry1Ab. Cereal Research Communications, 35(137), 5–1383.
Cao, J., Tang, J. D., Strizhov, N., Shelton, A. M., & Earle, E. D. (1999). Transgenic broccoli with high levels of Bacillus thuringiensis Cry1C protein control diamondback moth larvae resistant to Cry1A or Cry1C. Molecular Breeding, 5, 131–141.
Tang, W., Chen, H., Xu, C. G., Li, X. H., Lin, Y. J., & Zhang, Q. F. (2006). Development of insect-resistant transgenic indica rice with a synthetic cry1C* gene. Molecular Breeding, 18, 1–10.
Ferré, J., & Van Rie, J. (2002). Biochemistry and genetics of insect resistance to Bacillus thuringiensis. Annual Review of Entomology, 47, 501–533.
van der Salm, T., Bosch, D., Honee, G., Feng, L., Munsteman, E., Bakker, P., et al. (1994). Insect resistance of transgenic plants that express modified Bacillus thuringiensis cryIA(b) and cryIC genes: A resistance management strategy. Plant Molecular Biology, 26, 51–59.
Kaur, S. (2006). Molecular approaches for identification and construction of novel insecticidal genes for crop protection. World Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology, 22, 233–253.
Acknowledgments
This study was funded by The Rockefeller Foundation International Rice Biotechnology Program, Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada, and the National Basic Research Program of China (No. 2007CB109202). MAZ is grateful for a UNESCO fellowship. Greatly appreciated is the expertise of Nicola Adams who helped prepare the plasmids for repair mutagenesis. We are thankful to the Bacillus Genetic Stock Center, USA, for providing us the wild-type cry1Ca1 clone in E. coli (ECE125).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zaidi, M.A., Ye, G., Yao, H. et al. Transgenic Rice Plants Expressing a Modified cry1Ca1 Gene are Resistant to Spodoptera litura and Chilo suppressalis . Mol Biotechnol 43, 232–242 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12033-009-9201-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12033-009-9201-9