Abstract
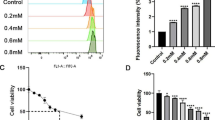
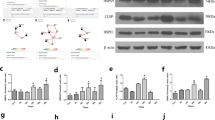
Parkinson's disease (PD) is the second most common neurodegenerative disease in humans. The effect of Krüppel-like factor (KLF) 4 in PD is unknown. In this study, KLF4 was found to be increased in both a time-dependent manner and a dose-dependent manner in response to the incubation with 1-methyl-4-phenylpyridinium (MPP+) in human dopamine neuroblastoma M17 cells, suggesting a potential role in MPP + −induced neurotoxicity. Following experiments showed that overexpression of KLF4 in M17 cells promoted MPP + −induced oxidative stress, embodied by exacerbated reactive oxygen species, 4-hydroxy-2-nonenal, and protein carbonyls. Furthermore, overexpression of KLF4 slowed cell proliferation and promoted lactate dehydrogenase release. Conversely, inhibition of KLF4 in M17 cells attenuated MPP + −induced neurotoxicity. The expression of superoxide dismutase (SOD) 1 in both mRNA and protein levels was found to be decreased by overexpressing KLF4, while increased by knockdown of KLF4. Moreover, promoter luciferase experiments showed that transcriptional activity on SOD1 was inhibited by KLF4. All the results indicated that KLF4 promoted the neurotoxicity of MPP + via inhibiting the transcription of SOD1, suggesting a potential mechanism of increased oxidative stress and cell death in Parkinson’s disease.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barc S, Page G, Barrier L, Piriou A, Fauconneau B (2001) Impairment of the neuronal dopamine transporter activity in MPP + −treated rat was not prevented by treatments with nitric oxide synthase or poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase inhibitors. Neurosci Lett 314:82–86
Bieker JJ (2001) Kruppel-like factors: three fingers in many pies. J Biol Chem 276:34355–34358
Chen ZY, Shie J, Tseng C (2000) Up-regulation of gut-enriched Krüppel-like factor by interferon-gamma in human colon carcinoma cells. FEBS Lett 477:67–72
Cookson MR (2009) Alpha-synuclein and neuronal cell death. Mol Neurodegener 4:9
Dauer W, Przedborski S (2003) Parkinson's disease: mechanisms and models. Neuron 39:889–909
Dawson TM, Dawson VL (2003) Molecular pathways of neurodegeneration in Parkinson’s disease. Science 302:819–822
Dekker RJ, van Thienen JV, Rohlena J et al (2005) Endothelial KLF2 links local arterial shear stress levels to the expression of vascular tone-regulating genes. Am J Pathol 167(2):609–618
Ghaleb AM, Nandan MO, Chanchevalap S, Dalton WB, Hisamuddin IM, Yang VW (2005) Kruppel-like factors 4 and 5: the yin and yang regulators of cellular proliferation. Cell Res 15(2):92–96
Goedert M, Spillantini MG, Del Tredici K, Braak H (2012) 100 years of Lewy pathology. Nat Rev Neurol 10:242
He Y, Zhou H, Tang H, Luo Y (2006) Deficiency of disulfide bonds facilitating fibrillogenesis of endostatin. J Biol Chem 281(2):1048–1057
Kaushik DK, Mukhopadhyay R, Kumawat KL, Gupta M, Basu A (2012) Therapeutic targeting of Krüppel-like factor 4 abrogates microglial activation. J Neuroinflammation 9:57
Kitao Y, Matsuyama T, Takano K et al (2007) Does ORP150/HSP12A protect dopaminergic neurons against MPTP/MPP(+)-induced neurotoxicity? Antioxid Redox Signal 9:589–595
Li QL, Ito K, Sakakura C et al (2002) Causal relationship between the loss of RUNX3 expression and gastric cancer. Cell 109:113–124
Li Z, Zhao J, Li Q et al (2010) KLF4 promotes hydrogen-peroxide-induced apoptosis of chronic myeloid leukemia cells involving the bcl-2/bax pathway. Cell Stress Chaperones 15(6):905–912
Liu MD, Liu Y, Liu JW, Zhang HL, Xiao XZ (2007) Effect of Kruppel-like factor 4 overexpression on heat stress-induced apoptosis of Raw264.7 macrophages. Zhong Nan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban 32:1002–1006
Lo YC, Shih YT, Tseng YT, Hsu HT (2012) Neuroprotective effects of San-Huang-Xie-Xin-Tang in the MPP(+)/MPTP models of Parkinson's disease in vitro and in vivo. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med 2012:501032
Marco B, Elisa G, Dragan M et al (2010) Alpha-synuclein overexpression increases dopamine toxicity in BE2-M17 cells. BMC Neurosci 11:41
Minc E, de Coppet P, Masson P et al (1999) The human copper-zinc superoxide dismutase gene (SOD1) proximal promoter is regulated by Sp1, Egr-1, and WT1 via non-canonical binding sites. J Biol Chem 274(1):503–509
Moore DL, Blackmore MG, Hu Y et al (2009) KLF family members regulate intrinsic axon regeneration ability. Science 326:298–301
Niemann HH, Jäger V, Butler PJ et al (2007) Structure of the human receptor tyrosine kinase Met in complex with the Listeria invasion protein lnlB. Cell 130(2):235–246
Obata T (2006) Nitric oxide and MPP + −induced hydroxyl radical generation. J Neural Transm 113(9):1131–1144
Ohnishi S, Ohnami S, Laub F et al (2003) Downregulation and growth inhibitory effect of epithelial-type Kruppel-like transcription factor KLF4, but not KLF5, in bladder cancer. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 308(2):251–256
Rowland BD, Bernards R, Peeper DS (2005) The KLF4 tumour suppressor is a transcriptional repressor of p53 that acts as a context-dependent oncogene. Nat Cell Biol 7:1074–1082
Sheng B, Gong K, Niu Y et al (2009a) Inhibition of gamma-secretase activity reduces Abeta production, reduces oxidative stress, increases mitochondrial activity and leads to reduced vulnerability to apoptosis: implications for the treatment of Alzheimer's disease. Free Radic Biol Med 46(10):1362–1375
Sheng B, Song B, Zheng Z et al (2009b) Abnormal cleavage of APP impairs its functions in cell adhesion and migration. Neurosci Lett 450(3):327–331
Sheng B, Wang X, Su B et al (2012) Impaired mitochondrial biogenesis contributes to mitochondrial dysfunction in Alzheimer's disease. J Neurochem 120(3):419–429
Shie JL, Chen ZY, Fu M, Pestell RG, Tseng CC (2000) Gut-enriched Krüppel-like factor represses cyclin D1 promoter activity through Sp1 motif. Nucleic Acids Res 28:2969–2976
Shields JM, Christy RJ, Yang VW (1996) Identification and characterization of a gene encoding a gut-enriched Kruppel-like factor expressed during growth arrest. J Biol Chem 271:20009–200017
Wassmann S, Wassmann K, Jung A et al (2007) Induction of p53 by GKLF is essential for inhibition of proliferation of vascular smooth muscle cells. J Mol Cell Cardiol 43:301–307
Wu J, Lingrel JB (2004) KLF2 inhibits Jurkat T leukemia cell growth via upregulation of cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p21WAF1/CIP1. Oncogene 23:8088–8096
Xi J, Zhang B, Luo F, Liu J, Yang T (2012) Quercetin protects neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y cells against oxidative stress by inhibiting expression of Krüppel-like factor 4. Neurosci Lett 527(2):115–120
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, J., Wang, X., Yi, X. et al. Induction of KLF4 Contributes to the Neurotoxicity of MPP + in M17 Cells: A New Implication in Parkinson’s Disease. J Mol Neurosci 51, 109–117 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-013-9961-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-013-9961-3