Abstract
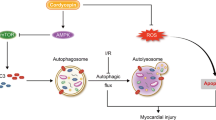
Autophagy plays various roles at different stages of ischemia reperfusion (I/R) injury in cardiomyocytes. It has been reported that tissue factor pathway inhibitor (TFPI) has a protective effect on I/R injury. This study aimed to determine the roles of TFPI in autophagy during the I/R injury process in cardiomyocytes and the possible mechanisms. An isolated hypoxia/reoxygenation (H/R) pattern of cardiomyocytes was established by the MIC101 system. The cell viability and oxidative stress of cardiomyocytes were detected by an MTT assay and ROS assay, respectively. The autophagy level was measured by Ad-mCherry-GFP-LC3B and MDC. We detected the expression levels of autophagy-related proteins by western blotting. After 2 h of hypoxia and 12 h of reoxygenation, the cardiomyocyte viability in the H/R group was significantly lower than that in the control group (p < 0.05) than in the H/R group. According to intracellular ROS production, the fluorescence intensity in the H/R group was enhanced compared with that in the negative control group, and it was weaker in the H/R + rTFPI group compared with the H/R group. The level of autophagy and the expression levels of autophagy-related proteins (LC3-II/LC3-I, Beclin-1 and PI3K) were markedly increased in the H/R group compared to the control group (p < 0.05) whereas the levels were markedly decreased in the H/R + rTFPI group compared to the H/R group (p < 0.05). TFPI could relieve cardiomyocyte injury by inhibiting the Class III PI3K/Beclin-1 pathway and oxidative stress; thus, TFPI decreased autophagy and protected cardiomyocytes induced by H/R injury. In conclusion, TFPI may be a new direction for the prevention of myocardial I/R injury.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data generated or analyzed during the research are all included in this published manuscript.
References
Caccioppo, A., Franchin, L., Grosso, A., Angelini, F., D’Ascenzo, F., & Brizzi, M. F. (2019). Ischemia reperfusion injury: Mechanisms of damage/protection and novel strategies for cardiac recovery/regeneration. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 20(20), 5024
Tommasino, C., Marconi, M., Ciarlo, L., Matarrese, P., & Malorni, W. (2015). Autophagic flux and autophagosome morphogenesis require the participation of sphingolipids. Apoptosis, 20(5), 645–657
Hu, C., Zhao, L., Wu, D., & Li, L. (2019). Modulating autophagy in mesenchymal stem cells effectively protects against hypoxia- or ischemia-induced injury. Stem Cell Research & Therapy, 10(1), 120
Wood, J. P., Ellery, P. E., Maroney, S. A., & Mast, A. E. (2014). Biology of tissue factor pathway inhibitor. Blood, 123(19), 2934–2943
Kahraman, S., Erdim, R., Helvacioglu, F., Dogan, A., Sozer, V., Gunay, D., Aytekin, S., & Aytekin, V. (2018). The impact of TFPI on coronary atherosclerotic burden. Bratislavske Lekarske Listy, 119(6), 385–390
Yin, X., Fu, Y., Yutani, C., Ikeda, Y., Enjyoji, K., & Kato, H. (2009). HVJ-AVE liposome-mediated tissue factor pathway inhibitor (TFPI) gene transfer with recombinant TFPI (rTFPI) irrigation attenuates restenosis in atherosclerotic arteries. International Journal of Cardiology, 119(6), 385–390
Ushigome, H., Sano, H., Okamoto, M., Kadotani, Y., Nakamura, K., Akioka, K., Yoshimura, R., Ohmori, Y., & Yoshimura, N. (2002). The role of tissue factor in renal ischemic reperfusion injury of the rat. Journal of Surgical Research, 102(2), 102–109
Zhang, C., Liang, R., Gan, X., Yang, X., Chen, L., & Jian, J. (2019). MicroRNA-384-5p/Beclin-1 as potential indicators for epigallocatechin gallate against cardiomyocytes ischemia reperfusion injury by inhibiting autophagy via PI3K/Akt pathway. Drug Design Development and Therapy, 13, 3607–3623
Zhao, Y., Fu, Y., Hu, J., Liu, Y., & Yin, X. (2013). The effect of tissue factor pathway inhibitor on the expression of monocyte chemotactic protein-3 and IκB-α stimulated by tumour necrosis factor-α in cultured vascular smooth muscle cells. Archives of Cardiovascular Diseases, 106(1), 4–11
Fu, Y., Ma, D., Liu, Y., Li, H., Chi, J., Liu, W., Lin, F., Hu, J., Zhang, X., Zhu, M., Zhao, Y., & Yin, X. (2015). Tissue factor pathway inhibitor gene transfer prevents vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation by interfering with the MCP-3/CCR2 pathway. Laboratory Investigation, 95(11), 1246–1257
Fu, Y., Zhao, Y., Liu, Y., Zhu, Y., Chi, J., Hu, J., Zhang, X., & Yin, X. (2012). Adenovirus-mediated tissue factor pathway inhibitor gene transfer induces apoptosis by blocking the phosphorylation of JAK-2/STAT-3 pathway in vascular smooth muscle cells. Cell Signaling, 24(10), 1909–1917
Eltzschig, H. K., & Eckle, T. (2011). Ischemia and reperfusion-from mechanism to translation. Nature Medicine, 17(11), 1391–1401
Wang, Z., Wang, Y., Ye, J., Lu, X., Cheng, Y., Xiang, L., Chen, L., Feng, W., Shi, H., Yu, X., Lin, L., Zhang, H., Xiao, J., & Li, X. (2015). BFGF attenuates endoplasmic reticulum stress and mitochondrial injury on myocardial ischaemia/reperfusion via activation of PI3K/Akt/ERK1/2 pathway. Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine, 19(3), 595–607
Liu, D. Q., Chen, S. P., Sun, J., Wang, X. M., Chen, N., Zhou, Y. Q., Tian, Y. K., & Ye, D. W. (2019). Berberine protects against ischemia-reperfusion injury: A review of evidence from animal models and clinical studies. Pharmacological Research, 148, 104385
Billah, M., Ridiandries, A., Allahwala, U. K., Mudaliar, H., Dona, A., Hunyor, S., Khachigian, L. M., & Bhindi, R. (2020). Remote ischemic preconditioning induces cardioprotective autophagy and signals through the IL-6-dependent JAK-STAT pathway. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 21(5), 1692
Yao, L., Chen, H., Wu, Q., & Xie, K. (2019). Hydrogen-rich saline alleviates inflammation and apoptosis in myocardial I/R injury via PINK-mediated autophagy. International Journal of Molecular Medicine, 44(3), 1048–1062
Zeng, M., Wei, X., Wu, Z. Y., Li, W. W., Li, B., Fei, Y., He, Y. L., Chen, J. X., Wang, P., & Liu, X. J. (2014). Reactive oxygen species contribute to simulated ischemia/reperfusion-induced autophagic cell death in human umbilical vein endothelial cells. Medical Science Monitor, 20, 1017–1023
Ma, S., Wang, Y., Chen, Y., & Cao, F. (2015). The role of the autophagy in myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta, 1852(2), 271–276
Lwaleed, B. A., & Bass, P. (2006). Tissue factor pathway inhibitor: Structure, biology and involvement in disease. Journal of Pathology, 208(3), 327–339
Lai, Y. H., He, R. Y., Chou, J. L., Chan, M. W., Li, Y. F., & Tai, C. K. (2014). Promoter hypermethylation and silencing of tissue factor pathway inhibitor-2 in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Journal of Translational Medicine, 12, 237
Kato, H. (2002). Regulation of functions of vascular wall cells by tissue pathway inhibitor. Arteriosclerosis, Thrombosis, and Vascular Biology, 22(4), 539–548
Yuan, H. Q., Hao, Y. M., Ren, Z., Gu, H. F., Liu, F. T., Yan, B. J., Qu, S. L., Tang, Z. H., Liu, L. S., Chen, D. X., & Jiang, Z. S. (2019). Tissue factor pathway inhibitor in atherosclerosis. Clinica Chimica Acta, 491, 97–102
Yoshimura, N., Kobayashi, Y., Nakamura, K., Yamagishi, H., & Oka, T. (1999). The effect of tissue factor pathway inhibitor on hepatic ischemic reperfusion injury of the rat. Transplantation, 67(1), 45–53
Niiro, M., Nagayama, T., Yunoue, S., Obara, S., & Hirano, H. (2008). Changes in tissue factor and the effects of tissue factor pathway inhibitor on transient focal cerebral ischemia in rats. Thrombosis Research, 122(2), 247–255
Dong, Y., Chen, H., Gao, J., Liu, Y., Li, J., & Wang, J. (2019). Molecular machinery and interplay of apoptosis and autophagy in coronary heart disease. Journal of Molecular and Cellular Cardiology, 136, 27–41
He, C., & Klionsky, D. J. (2009). Regulation mechanisms and signaling pathways of autophagy. Annual Review of Genetics, 43, 67–93
Guo, Q. Q., Wang, S. S., Zhang, S. S., Xu, H. D., Li, X. M., Guan, Y., Yi, F., Zhou, T. T., Jiang, B., Bai, N., Ma, M. T., Wang, Z., Feng, Y. L., Guo, W. D., Wu, X., Zhao, G. F., Fan, G. J., Zhang, S. P., Wang, C. G., Cao, L. Y., O’Rourke, B. P., Liu, S. H., Wang, P. Y., Han, S., Song, X. Y., & Cao, L. (2020). ATM-CHK2-Beclin 1 axis promotes autophagy to maintain ROS homeostasis under oxidative stress. The EMBO Journal, 39(10), e103111
Heusch, G. (2007). Critical issues for the translation of cardioprotection. Circulation Research, 120(9), 1477–1486
Heusch, G. (2018). Cardioprotection research must leave its comfort zone. European Heart Journal, 39(36), 3393–3395
Hausenloy, D. J., Botker, H. E., Engstrom, T., Erlinge, D., Heusch, G., Ibanez, B., Kloner, R. A., Ovize, M., Yellon, D. M., & Garcia-Dorado, D. (2017). Targeting reperfusion injury in patients with ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction: Trials and tribulations. European Heart Journal, 38(13), 935–941
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 81200143, 81200235, 82170513); Natural Science Fund of Heilongjiang projects (No. QC2012C015); Provincial youth science fund of Heilongjiang (No. QC2017104); Heilongjiang Traditional Chinese Medicine Scientific Research Project (ZHY12-W035) and the Foundation of the First Affiliated Hospital of Harbin Medical University (2015B002, 2014B08).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All the authors contributed to the study conception and design. R.Y., R.X., Q.C., and L.S. performed the investigation. W.G. and W.C. validated the data and carried on statistical analysis. Y.Z. and W.G. wrote the original manuscript, Y.F. and Y.Z. edited and revised the manuscript. All the authors had read the full manuscript and approved the publication of this manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Yan, R., Gao, W., Chen, W. et al. rTFPI Protects Cardiomyocytes from Hypoxia/Reoxygenation Injury through Inhibiting Autophagy and the Class III PI3K/Beclin-1 Pathway. Cell Biochem Biophys 81, 97–104 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12013-022-01113-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12013-022-01113-0