Abstract
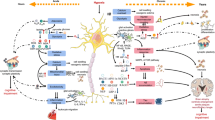
Neonatal hypoxia–ischemia brain damage is an important cause of death by affecting prognosis of neural diseases. It is difficult to find effective methods of prevention and treatment due to the complexity of its pathogenesis. N-methyl-d-aspartate (NMDA), as an excitotoxicity amino acids, has proven to play an important role in hypoxic–ischemic. However, the exact effects of the NMDA subunits, NR2A and NR2B, during hypoxic–ischemic have not been investigated in detail. Therefore, we sought to study whether the NMDA receptor antagonist could confer neuroprotective effects in a neonatal rat hypoxia–ischemia model. The effects of intraperitoneal injections of different drugs, namely MK-801 (0.5 mg/kg), NVP-AAM077 (5 mg/kg), and Ro25-6981 (5 mg/kg), on the expressions of anti-apoptotic protein Bcl-2 and apoptosis protein Bax in the subventricular zone were analyzed by immunohistochemical staining to explore the roles of NMDA subunits (NR2A and NR2B) in hypoxic–ischemic. We found that the NR2B antagonist (Ro25-6981) could inhibit hypoxic–ischemic with the increasing Bcl-2 expression. NR2A antagonists (NVP-AAM077) can increase cerebral hypoxia–ischemia in neonatal rats, promoting the expression of apoptotic protein Bax.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abend, N. S., & Licht, D. J. (2008). Predicting outcome in children with hypoxic ischemic encephalopathy. Pediatric Critical Care Medicine, 9, 32–39.
Abrous, D. N., Koehl, M., & Le Moal, M. (2005). Adult neurogenesis: From precursors to network and physiology. Physiological Reviews, 85, 523–569.
Brewer, L. D., Thibault, O., Staton, J., Thibault, V., Rogers, J. T., Garcia-Ramos, G., et al. (2007). Increased vulnerability of hippocampal neurons with age in culture: Temporal association with increases in NMDA receptor current, NR2A subunit expression and recruitment of L-type calcium channels. Brain Research, 1151, 20–31.
Chao, C. P., Zaleski, C. G., & Patton, A. C. (2006). Neonatal hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy: multimodality imaging findings. Radiographics, 26, S159–S172.
Chen, M., Lu, T. J., Chen, X. J., Zhou, Y., Chen, Q., Feng, X. Y., et al. (2008). Differential roles of NMDA receptor subtypes in ischemic neuronal cell death and ischemic tolerance. Stroke, 39, 3042–3048.
Chipuk, J. E., & Green, D. R. (2008). How do BCL-2 proteins induce mitochondrial outer membrane permeabilization? Trends in Cell Biology, 18, 157–164.
Choi, D. W. (1992). Excitotoxic cell death. Journal of Neurobiology, 23, 1261–1276.
Choi, D. W. (1995). Calcium : Still center-stage in hypoxic-ischemic neuronal death. Trends in Neurosciences, 18, 58–60.
Choi, D. W., & Koh, J. Y. (1998). Zinc and brain injury. Annual Review of Neuroscience, 21, 347–375.
Cooper, D. J. (2011). Induced hypothermia for neonatal hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy: Pathophysiology, current treatment, and nursing considerations. Neonatal. Netw., 30, 29–35.
Ghibelli, L., & Diederich, M. (2010). Multistep and multitask Bax activation. Mitochondrion, 10, 604–613.
Greer, D. M. (2006). Mechanisms of injury in hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy: Implications to therapy. Seminars in Neurology, 26, 373–379.
Kinnally, K. W., & Antonsson, B. (2007). A tale of two mitochondrial channels, MAC and PTP, in apoptosis. Apoptosis, 12, 857–868.
Lam, M., Dubyak, G., Chen, L., Nuñez, G., Miesfeld, R. L., & Distelhorst, C. W. (1994). Evidence that BCL-2 represses apoptosis by regulating endoplasmic reticulum-associated Ca2+ fluxes. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 91, 6569–6573.
Lee, J. M., Zipfel, G. J., & Choi, D. W. (1999). The changing landscape of ischaemic brain injury mechanisms. Nature, 399, A7–A14.
Levison, S. W., Rothstein, R. P., Romanko, M. J., Snyder, M. J., Meyers, R. L., & Vannucci, S. J. (2001). Hypoxia-ischemia depletes the rat perinatal subventricular zone of oligodendrocyte progenitors and neural stem cells. Devel. Neurosci., 23, 234–247.
Li, Y. Z., Lu, D. Y., Tan, W. Q., Wang, J. X., & Li, P. F. (2008). p53 initiates apoptosis by transcriptionally targeting the antiapoptoic protein ARC. Molecular and Cellular Biology, 28, 564–574.
Liu, Y., Wong, T. P., Aarts, M., Rooyakkers, A., Liu, L., Lai, T. W., et al. (2007). Nmda receptor subunits have differential roles in mediating excitotoxic neuronal death both in vitro and in vivo. Journal of Neuroscience, 27, 2846–2857.
Luo, C., Zhu, C., Jiang, J., Lu, Y., Zhang, G., Yuan, G., et al. (1999). Alterations of bcl-2, bcl-x and bax protein expression in area CA-3 of rat hippocampus following fluid percussion brain injury. Chin. J. Traumatol., 2, 101–104.
Martin, H. G., & Wang, Y. T. (2010). Blocking the deadly effects of the NMDA receptor in stroke. Cell, 140, 174–176.
Olney, J. W. (2003). Excitotoxicity, apoptosis and neuropsychiatric disorders. Current Opinion in Pharmacology, 3, 101–109.
Racay, P., Tatarkova, Z., Chomova, M., Hatok, J., Kaplan, P., & Dobrota, D. (2009). Mitochondrial calcium transport and mitochondrial dysfunction after global brain ischemia in rat hippocampus. Neurochemical Research, 34, 1469–1478.
Rothman, S. M., & Olney, J. W. (1995). Excitotoxicity and the NMDA receptor-still lethal after eight years. Trends in Neurosciences, 18, 57–58.
Savignon, T., Costa, E., Tenorio, F., Manhães, A. C., & Barradas, P. C. (2012). Prenatal hypoxic-ischemic insult changes the distribution and number of NADPH-diaphorase cells in the cerebellum. PLoS ONE, 7(4), e35786.
Scott, I., & Youle, R. J. (2010). Mitochondrial fission and fusion. essays. Biochem., 47, 85–98.
Sheng, M., & Kim, M. J. (2002). Postsynaptic signaling and plasticity mechanisms. Science, 298, 776–780.
Siesjo, B. K. (1989). Calcium and cell death. Magnesium, 8, 223–237.
Vannucci, R. C. (2000). Hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy. American Journal of Perinatology, 17, 112–113.
Vannucci, R. C., & Vannucci, S. J. (2005). Perinatal hypoxic-ischemic brain damage: Evolution of an animal model. Developmental Neuroscience, 27, 81–86.
Walls, K. C., Ghosh, A. P., Ballestas, M. E., Klocke, B. J., & Roth, K. A. (2009). Bcl-2/Adenovirus E1B19-kd interacting protein 3(BNIP3) regulates hypoxia-induced neural precursor cell death. Journal of Neuropathology and Experimental Neurology, 68, 1326–1338.
Wiswedel, I., Gardemann, A., Storch, A., Peter, D., & Schild, L. (2010). Degradation of phospholipids by oxidative stress-exceptional significance of cardiolipin. Free. Radic. Res., 44, 135–145.
Zarch, A. V., Toroudi, H. P., Soleimani, M., Bakhtiarian, A., Katebi, M., & Djahanguiri, B. (2009). Neuroprotective effects of diazoxide and its antagonism by glibenclamide in pyramidal neurons of rat hippocampus subjected to ischemia-reperfusion-induced injury. International Journal of Neuroscience, 119(9), 1346–1361.
Zhang, M. Y., Fan, S. J., Li, L. P., Wu, B. Y., & Wang, Y. (2011). The anti-injury effect of breviscapine injection on the hypoxic ischemic brain damage of neonatal rats and the expression of Bcl-2 and Bax. Chinese Journal of Applied Physiology, 27, 196–200.
Zhang, R., Xue, Y. Y., Lu, S. D., Wang, Y., Zhang, L. M., Huang, Y. L., et al. (2006). Bcl-2 enhances neurogenesis and inhibits apoptosis of newborn neurons in adult rat brain following a transient middle cerebral artery occlusion. Neurobio. Dis., 24, 345–356.
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81171141 to Tiejun Xu); this project was funded by the Priority Academic Program Development (PAPD) of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Hongbin Fan and Xiaoquan Li contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fan, H., Li, X., Wang, W. et al. Effects of NMDA-Receptor Antagonist on the Expressions of Bcl-2 and Bax in the Subventricular Zone of Neonatal Rats with Hypoxia–Ischemia Brain Damage. Cell Biochem Biophys 73, 323–330 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12013-015-0586-8
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12013-015-0586-8