Abstract
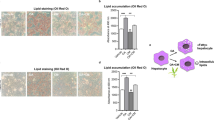
Obesity is a chronic disease associated with increased morbidity and mortality. The rapidly increasing prevalence of obesity makes it a global health problem, while treatment options remain limited. Given the potential of boron in the treatment of obesity, the aim of this study is to investigate the anti-adipogenic activity of the newly synthesised boron glycine monoester compound (BGM) using 3T3-L1 adipocytes by analysing lipid accumulation, CTRP3 and PPARy gene expression, oxidative stress and apoptotic effects. 3T3-L1 fibroblast cells (ATCC® CL-173) were transformed into adipocyte cells in vitro. Fat accumulation in the 3T3-L1 adipocyte cells was detected by Oil Red O staining. Gene expression levels were determined with qPCR. Biochemical analyzes were performed using spectrophotometric method (CAT, ALP and ACP) and ELISA kit (TAS, TOS, NADP-IDH). Apoptosis studies were performed on the muse cell nalyser using the Muse Annexin V & Dead Cell Assay Kit. When BGM-treated cells were compared to control adipocyte cells, lipid accumulation decreased in a dose-dependent manner. BGM-treated adipocyte cells had higher CTRP3 expression levels and lower PPAR-γ gene expression levels compared to control adipocyte cells (p < 0.001). While BGM application increased the TAS level, it showed an antioxidant effect by regulating the activity of oxidative metabolism enzymes (p < 0.001). BGM application increased total apoptosis by 1.5-fold. These results show that BGM is a potential therapeutic agent for obesity by regulating the expression of genes related to adipogenesis and lipogenesis in adipocyte cells and by affecting the activity of enzymes of oxidative metabolism and apoptosis.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Not applicable.
Code Availability
Not applicable.
References
Koldemir-Gündüz M, Çevik M, Çağatay P, Süsleyici B (2019) The effects of oral antidiabetics on adipogenesis related gene expressions in 3T3-L1, AML12 cell lines and their co-cultures. Eurasian J Bio Chem Sci 2:29–37
te Velde SJ, van Nassau F, Uijtdewilligen L, van Stralen MM, Cardon G, De Craemer M, Manios Y, Brug J, Chinapaw MJM (2012) Energy balance-related behaviours associated with overweight and obesity in preschool children: a systematic review of prospective studies. Obes Rev 13:56–74. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-789X.2011.00960
World Health Organization (2011) Global status report on noncommunicable diseases.
Bohula EA, Wiviott SD, McGuire DK, Inzucchi SE, Kuder J et al (2018) Cardiovascular Safety of Lorcaserin in Overweight or Obese Patients. N Engl J Med 379:1107–1117. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1808721
Abdik H, Cumbul A, Hayal TB, Abdik EA, Taşlı PN, Kırbaş OK, Baban D, Şahin F (2021) Sodium pentaborate pentahydrate ameliorates lipid accumulation and pathological damage caused by high fat diet induced obesity in BALB/c mice. J Trace Elem Med Biol 66:126736. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtemb.2021.126736
Bei G, Tongtian Z, Feng X, Xiao L, Fuxingzi L, Su-Kang S, Feng W, Jia-Yu Z, Yi W, Ming-Hui Z, Qiu-Shuang X, Ullah MHE, Ling-Qing Y (2020) New ınsights ınto ımplications of CTRP3 in obesity, metabolic dysfunction, and cardiovascular diseases: potential of therapeutic ınterventions. Front Physiol 3:570270. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphys.2020.570270
JungUJ CMS (2014) Obesity and itsmetabolic complications: the role of adipokines and the relationship between obesity, inflammation, insulin resistance, dyslipidemia and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Int J Mol Sci 15:6184–6223. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms15046184
Shao X, Wang M, Wei X, Deng S, Fu N, Peng Q, Jiang Y, Ye L, Xie J, Lin Y (2016) Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-γ: master regulator of adipogenesis and obesity. Curr Stem Cell Res Ther 11:282–289. https://doi.org/10.2174/1574888x10666150528144905
Schaffler A, Weigert J, Neumeier M, Scholmerich J, Buechler C (2007) Regulation and function of collagenous repeat containing sequence of 26-kDa protein gene product “cartonectin.” Obesity 15:303–313. https://doi.org/10.1038/oby.2007.566
Koldemir-Gündüz M, Bolat M, Kaymak G, Berikten D, Köse DA (2022) Therapeutic effects of newly synthesized boron compounds (BGM and BGD) on hepatocellular carcinoma. Biol Trace Elem Res 200:134–146. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-021-02647-9
Kuru R, Yilmaz S, Balan G, Tuzuner BA, Tasli PN, Akyuz S, YenerOzturk F, Altuntas Y, Yarata A, Sahin F (2019) Boron-rich diet may regulate blood lipid profile and prevent obesity: a nondrug and self-controlled clinical trial. J Trace Elem Med Biol 54:191–198. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtemb.2019.04.021
Aşkar TK, Er H, Demirdöğen RE (2018) The effects of boron on bone metabolism as a nutraceutical. Journal of Eurasian Health Sciences 1:7–12
Nielsen FH (2002) The nutritional ımportance and pharmacological potential of boron for higher animals and human In Boron in Plant and Animal Nutrition, Boston, MA: Springer, US 37–49https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4615-0607-2_4
Bakken NA, Hunt CD (2003) Dietary boron decreases peak pancreatic ın situ ınsulin release in chicks and plasma ınsulin concentrations in rats regardless of vitamin D or magnesium status. J Nutr 133:3577–3583. https://doi.org/10.1093/jn/133.11.3577
Demirdogen RE (2020) Relationship among blood boron level, diabetes mellitus, lipid metabolism, bone metabolism and obesity: can boron be an efficient ındicator for metabolic dissesases? Health Sci J 14:1. https://doi.org/10.36648/1791-809X.14.1.689
Koldemir-Gündüz M, Aydin HE, Berikten D, Kaymak G, Köse DA, Arslantaş A (2021) Synthesis of new boron derived compounds; anticancer, antioxidant and antimicrobial effect in vitro glioblastoma tumor model. Journal of Korean Neurosurgical Society 64:864. https://doi.org/10.3340/jkns.2021.0032
Köse DA, Zumreoglu-Karan B, Hökelek T (2011) A comparative examination of mono- and bis-chelate salicylatoborate complexes and the crystal structure of layered magnesium bis-salicylatoborate. Inorg Chim Acta 375:236–241. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ica.2011.05.012
Köse DA, Zümreoglu-Karan B (2012) Mixed ligand complexes of boric acid with organic biomolecules. Chem Pap 66:54–60. https://doi.org/10.2478/s11696-011-0108-0
Zumreoglu-Karan B, Kose DA (2015) Boric acid: a simple molecule of physiologic, therapeutic and prebiotic significance. Pure Appl Chem 87(2015):155–162. https://doi.org/10.1515/pac-2014-0909
Miggiano GA, Gagliardi L (2005) Diet, nutrition and bone health. Clin Ter 156:47–56. https://doi.org/10.4103/jmsr.jmsr4118
Miwa K, Fujiwara T (2010) Boron transport in plants: co-ordinated regulation of transporters. Ann Bot 105:1103–1108. https://doi.org/10.1093/aob/mcq044
Park M, Li Q, Shcheynikov N, Muallem S, Zeng W (2005) Borate transport and cell growth and proliferation: not only in plants. Cell Cycle 4:24–26. https://doi.org/10.4161/cc.4.1.1394
Zhang W, Ogando DG, Bonanno JA, Obukhov AG (2015) Human SLC4A11 is a novel NH3:H+ co-transporter. J Biol Chem 290:16894–16905. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M114.627455
Zhang W, Ogando DG, Kim ET, Choi MJ, Li H, Tenessen JM, Bonanno JA (2017) Conditionally immortal Slc4a11-/- mouse corneal endothelial cell line recapitulates disrupted glutaminolysis seen in Slc4a11-/- mouse model. Investig Opthalmology Vis Sci 58:3723–3731. https://doi.org/10.1167/iovs.17-21781
Scorei IR, Popa R (2013) Sugar-borate esters – potential chemical agents in prostate cancer chemoprevention. Anticancer Agents Med Chem 13:901–909
Miard S, Dombrowski L, Carter S, Boivin L, Picard F (2009) Aging alters PPARgamma in rodent and human adipose tissue by modulating the balance in steroid receptor coactivator-1. Aging Cell 8:449–459. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1474-9726.2009.00490.x
Lillie RD, Ashburn LL (1943) Supersaturated solutions of fat stains in dilute isopropanol for demonstration of acute fatty degeneration not shown by Herxheimer’s technique. Archs Path 36:432
Yerlikaya A, Okur E, Şeker S, Erin N (2010) Combined effects of the proteasome inhibitor bortezomib and Hsp70 inhibitors on the B16F10 melanoma cell line. Mol Med Rep 3: 333–339. https://doi.org/10.3892/mmr00000262
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Analytical Biochemistry 72: 248–254. https://doi.org/10.1006/abio.1976.9999
Aebi H (1974) Catalase invitro. In: Bergmeyer HU (ed) 2 nd ed, FLMethods of enzymatic analysis 121–126.
Walter K, Schült C (1974) Acid and alkaline phosphatase in serum (two point method). In: Bergmeyer HU (ed) 2nd ed, FLMethods of Enzymatic Analysis, 856–886
Erel O (2005) A new automated colorimetric method for measuring total oxidantstatus. Clin Biochem 38(1103):11
Atmaca H, İlhan S, Batır MB, Pulat ÇÇ, Güner A, Bektaş H (2020) Novel benzimidazole derivatives: synthesis, in vitro cytotoxicity, apoptosis and cell cycle studies. Chem Biol Interact 327:109163. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbi.2020.109163
Abdik EA, Abdik H, Taşlı PN, Deniz AAH, Şahin F (2019) Suppressive role of boron on adipogenic differentiation and fat deposition in human mesenchymal stem cells. Biol Trace Elem Res 188:384–392. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-018-1428-5
Doğan A, Demirci S, Apdik H, Bayrak OF, Gulluoglu S, Tuysuz EC, Gusev O, Rizvanov AA, Nikerel E, Şahin F (2017) A new hope for obesity management: Boron inhibits adipogenesis in progenitor cells through the Wnt/β-catenin pathway. Metabolism 69:130–142. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.metabol.2017.01.021
Li X, Jiang L, Yang M, Wu YW, Sun JZ (2018) Impact of weight cycling on CTRP3 expression, adipose tissue inflammation and insulin sensitivity in C57BL/6J mice. Exp Ther Med 16:2052–2059. https://doi.org/10.3892/etm.2018.6399
Jr. Keaney JF, (2003) Obesity and systemic oxidative stress: clinical correlates of oxidative stress in the Framingham Study. Atheroscler Thromb Vasc Biol 23:434–439. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.ATV.0000058402.34138.11
Furukawa S, Fujita T, Shimabukuro M, Iwaki M, Yamada Y, Nakajima N, Nakayama O, Makishima M, Matsuda M, Shimomura I (2004) Increased oxidative stress in obesity and its impact on metabolic syndrome. J Clin Invest 114:1752–17061. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI21625
Karimkhani H, Mervenur K, Ülfer G, Yiğitbası T, Emekli N (2019) Evaluation level of total antioxidant status (TAS), total oxidant status (TOS) and thiol disulfide between non-obese and obese ındividuals. Conference: Iranian Journal of Basic Medical Sciences, Isfahan University of Medical Sciences, Isfahan, IranVolume: Volume 22, Supplement 1 (The 15th Iranian National Congress of Biochemistry & 6th International Congress of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology), Page 128.
Cruz-Mejía S, Durán-López HH, Navarro-Meza M, Xochihua-Rosas I, De la Peña S, Arroyo-Helguera OE (2018) Body mass index is associated with interleukin-1, adiponectin, oxidative stress and ioduria levels in healthy adults. Nutr Hosp 2:841–846. https://doi.org/10.20960/nh.1614
Kayhan FE, EsmerDuruel HE, Kızılkaya Ş, Dinç SK, Kaymak G, Akbulut C, YönErtuğ N (2020) Toxic effects of herbicide tribenuron-methyl on liver tissue of zebrafish (Danio Rerio). Fresenius Environ Bull 29:11175–11179
Pandey S, Parvez S, Sayeed I, Haque R, Bin-Hafeez B, Raisuddin S (2003) Biomarkers of oxidative stress: a comparative study of River Yamuna fish Wallago attu (Bl. & Schn.). The Science of The Total Environment 309:105–115. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0048-9697(03)00006-8
Dominguez-Perez M, Nuno-Lambarri N, Clavijo-Cornejo D, Luna-López A, Souza V, Bucio L, Miranda RU, Munoz L, Gomez-Quiroz LE, Uribe-Carvajal S, Gutiérrez-Ruiz MC (2016) Hepatocyte growth factor reduces free cholesterol-mediated lipotoxicity in primary hepatocytes by countering oxidative stress. Oxid Med Cell Longev. https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/7960386
Koh HJ, Lee BG, Lee SH, Ryoo ZY, Chang KT, Park JW, Park DC, Song BJ, Veech RL, Song H, Huh TL (2004) Cytosolic NADP+-dependent isocitrate dehydrogenase plays a key role in lipid metabolism. J Biol Chem 279:39968–39974. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M402260200
Brazhnikova DA, Popova TN, Kryl’skii ED, Shulgin KK, Matasova LV, Shikhaliev HS, Popov SS, (2020) The effect of 6-hydroxy-2, 2, 4-trimethyl-1, 2-dihydroquinoline on the ıntensity of free radical processes and activity of oxidative metabolism enzymes in rats with toxic liver ınjury. Biochemistry (Moscow). Supplement Series B: Biomedical Chemistry 14:70–77. https://doi.org/10.1134/S1990750820010060
Acknowledgements
I would like to thank Prof. Dr. Dursun Ali KÖSE and the National Boron Institute (BOREN, 2020-30-06-30-002) for the synthesis of boron glycine mono ester used in the study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
MK-G: conceptualization; data curation; formal analysis; investigation; methodology; resources; supervision; visualisation; writing — original draft; writing — review and editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics Approval
Not applicable.
Conflict of Interest
The author declares no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Koldemir Gündüz, M. BGM, a Newly Synthesised Boron Compound, Induces Apoptosis and Reduces Oxidative Stress by Inhibiting Lipogenesis in 3T3-L1 Adipocytes via PPARγ and CTRP3. Biol Trace Elem Res 200, 4807–4816 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-022-03261-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-022-03261-z