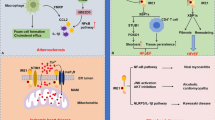
Abstract
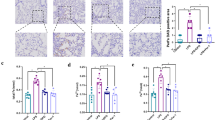
Arsenic is a common environmental pollutant and poses a serious threat to human and animal health. In this study, we used the ducks to mimic arsenic trioxide (ATO) exposure and investigated the mechanism of cardiac toxicity. The results indicated that ATO inhibited the body and organ growth of ducks, led to an increase in LDH content, and caused obvious deformity, ischemia infarction. It is found that ATO exacerbated the swell of mitochondrial and the contraction of cell nuclei in the heart of ducks through transmission electron microscopy (TEM). ATO also induced an increase in MDA content; inhibited the activation of the Nrf 2 pathway; downregulated the expression of mRNA and protein of Nrf 2, HO-1, and SOD-1; and upregulated the expression of mRNA and protein of Keap 1. At the same time, ATO induced apoptosis which not only upregulated the expression levels of mRNA and proteins (Caspase 3, Cyt-C, P53, Bax) but also decreased the mRNA and protein expression level of Bcl-2. These results indicated that ATO can lead to oxidative stress and apoptosis in the heart of ducks. In general, our research shows that ATO triggers mitochondrial dysfunction, oxidative stress, and apoptosis via Nrf 2/Caspase 3 signaling pathway in the heart of ducks.
Graphical abstract







Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
All relevant data and materials are available from the authors upon reasonable request.
Code Availability
Not applicable.
Change history
07 May 2022
A Correction to this paper has been published: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-022-03267-7
References
Vineetha VP, Raghu KG (2019) An overview on arsenic trioxide-induced cardiotoxicity. Cardiovasc Toxicol 19(2):105–119. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12012-018-09504-7
Hughes MF, Beck BD, Chen Y, Lewis AS, Thomas DJ (2011) Arsenic exposure and toxicology: a historical perspective. Toxicol Sci 123(2):305–332. https://doi.org/10.1093/toxsci/kfr184
Cervantes C, Ji G, Ramirez JL, Silver S (1994) Resistance to arsenic compounds in microorganisms. Fems Microbiol Rev 15(4):355–367. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1574-6976.1994.tb00145.x
Kang Y, Liu G, Chou CL, Wong MH, Zheng L, Ding R (2011) Arsenic in Chinese coals: distribution, modes of occurrence, and environmental effects. Sci Total Environ 412–413:1–13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2011.10.026
Leaphart JC, Oldenkamp RE, Bryan AL, Kennamer RA, Beasley JC (2020) Patterns of trace element accumulation in waterfowl restricted to impoundments holding coal combustion waste. Environ Toxicol Chem 39(5):1052–1059. https://doi.org/10.1002/etc.4697
Fu Z, Xi S (2020) The effects of heavy metals on human metabolism. Toxicol Mech Method 30(3):167–176. https://doi.org/10.1080/15376516.2019.1701594
Wu S, Yu W, Jiang X, Huang R, Zhang X, Lan J, Zhong G, Wan F, Tang Z, Hu L (2021) Protective effects of curcumin on ATO-induced nephrotoxicity in ducks in relation to suppressed autophagy, apoptosis and dyslipidemia by regulating oxidative stress. Ecotox Environ Safe 219:112350. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2021.112350
Li SW, Sun X, He Y, Guo Y, Zhao HJ, Hou ZJ, Xing MW (2017) Assessment of arsenic trioxide in the heart of Gallus gallus: alterations of oxidative damage parameters, inflammatory cytokines, and cardiac enzymes. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 24(6):5781–5790. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-8223-7
Jomova K, Jenisova Z, Feszterova M, Baros S, Liska J, Hudecova D, Rhodes CJ, Valko M (2011) Arsenic: toxicity, oxidative stress and human disease. J Appl Toxicol 31(2):95–107. https://doi.org/10.1002/jat.1649
Yang HY, Lee TH (2015) Antioxidant enzymes as redox-based biomarkers: a brief review. Bmb Rep 48(4):200–208. https://doi.org/10.5483/bmbrep.2015.48.4.274
Liao J, Yang F, Chen H, Yu W, Han Q, Li Y, Hu L, Guo J, Pan J, Liang Z, Tang Z (2019) Effects of copper on oxidative stress and autophagy in hypothalamus of broilers. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 185:109710. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2019.109710
Wasik U, Milkiewicz M, Kempinska-Podhorodecka A, Milkiewicz P (2017) Protection against oxidative stress mediated by the Nrf2/Keap1 axis is impaired in Primary Biliary Cholangitis. Sci Rep-Uk 7(1):44769. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep44769
Ashino T, Yamamoto M, Numazawa S (2016) Nrf2/Keap1 system regulates vascular smooth muscle cell apoptosis for vascular homeostasis: role in neointimal formation after vascular injury. Sci Rep-Uk 6(1):26291. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep26291
Taguchi K, Motohashi H, Yamamoto M (2011) Molecular mechanisms of the Keap1-Nrf2 pathway in stress response and cancer evolution. Genes Cells 16(2):123–140. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2443.2010.01473.x
You L, Yang C, Du Y, Liu Y, Chen G, Sai N, Dong X, Yin X, Ni J (2019) Matrine exerts hepatotoxic effects via the ROS-dependent mitochondrial apoptosis pathway and inhibition of Nrf2-mediated antioxidant response. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2019:1–15. https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/1045345
Wang C, Nie G, Yang F, Chen J, Zhuang Y, Dai X, Liao Z, Yang Z, Cao H, Xing C, Hu G, Zhang C (2020) Molybdenum and cadmium co-induce oxidative stress and apoptosis through mitochondria-mediated pathway in duck renal tubular epithelial cells. J Hazard Mater 383:121157. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.121157
Müller LUW, Milsom MD, Harris CE, Vyas R, Brumme KM, Parmar K, Moreau LA, Schambach A, Park I, London WB, Strait K, Schlaeger T, Devine AL, Grassman E, D’Andrea A, Daley GQ, Williams DA (2012) Overcoming reprogramming resistance of Fanconi anemia cells. Blood 119(23):5449–5457. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2012-02-408674
Jabbour AM, Daunt CP, Green BD, Vogel S, Gordon L, Lee RS, Silke N, Pearson RB, Vandenberg CJ, Kelly PN, Nutt SL, Strasser A, Borner C, Ekert PG (2010) Myeloid progenitor cells lacking p53 exhibit delayed up-regulation of Puma and prolonged survival after cytokine deprivation. Blood 115(2):344–352. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2009-07-230730
Ge X, Pan M, Wang L, Li W, Jiang C, He J, Abouzid K, Liu L, Shi Z, Jiang B (2018) Hypoxia-mediated mitochondria apoptosis inhibition induces temozolomide treatment resistance through miR-26a/Bad/Bax axis. Cell Death Dis 9(11):1128. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41419-018-1176-7
Rao VK, Oliveira JB (2011) How I treat autoimmune lymphoproliferative syndrome. Blood 118(22):5741–5751. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2011-07-325217
Cui T, Jiang W, Yang F, Luo J, Hu R, Cao H, Hu G, Zhang C (2021) Molybdenum and cadmium co-induce hypothalamus toxicity in ducks via disturbing Nrf2-mediated defense response and triggering mitophagy. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 228:113022. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2021.113022
Wu S, Rao G, Wang R, Pang Q, Zhang X, Huang R, Li T, Tang Z, Hu L (2021) The neuroprotective effect of curcumin against ATO triggered neurotoxicity through Nrf2 and NF-kappaB signaling pathway in the brain of ducks. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 228:112965. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2021.112965
Wu S, Zhong G, Wan F, Jiang X, Tang Z, Hu T, Rao G, Lan J, Hussain R, Tang L, Zhang H, Huang R, Hu L (2021) Evaluation of toxic effects induced by arsenic trioxide or/and antimony on autophagy and apoptosis in testis of adult mice. Environ Sci Pollut R 28(39):54647–54660. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-14486-1
Zhong G, Wan F, Wu S, Jiang X, Tang Z, Zhang X, Huang R, Hu L (2021) Arsenic or/and antimony induced mitophagy and apoptosis associated with metabolic abnormalities and oxidative stress in the liver of mice. Sci Total Environ 777:146082. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.146082
Zhong G, Wan F, Lan J, Jiang X, Wu S, Pan J, Tang Z, Hu L (2021) Arsenic exposure induces intestinal barrier damage and consequent activation of gut-liver axis leading to inflammation and pyroptosis of liver in ducks. Sci Total Environ 788:147780. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.147780
Wu S, Yu W, Jiang X, Huang R, Zhang X, Lan J, Zhong G, Wan F, Tang Z, Hu L (2021) Protective effects of curcumin on ATO-induced nephrotoxicity in ducks in relation to suppressed autophagy, apoptosis and dyslipidemia by regulating oxidative stress. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 219:112350. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2021.112350
Flora SJ (2011) Arsenic-induced oxidative stress and its reversibility. Free Radic Biol Med 51(2):257–281. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2011.04.008
Li X, Yi H, Wang H (2018) Sulphur dioxide and arsenic affect male reproduction via interfering with spermatogenesis in mice. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 165:164–173. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2018.08.109
Meng P, Zhang S, Jiang X, Cheng S, Zhang J, Cao X, Qin X, Zou Z, Chen C (2020) Arsenite induces testicular oxidative stress in vivo and in vitro leading to ferroptosis. Ecotox Environ Safe 194:110360. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2020.110360
Xie Z, Shen G, Wang Y, Wu C (2019) Curcumin supplementation regulates lipid metabolism in broiler chickens. Poultry Sci 98(1):422–429. https://doi.org/10.3382/ps/pey315
Zhang Y, Ma X, Zhang T, Qin M, Sun B, Li Q, Hu D, Ren L (2019) Protective effects of Apocynum venetum against Pirarubicin-induced cardiotoxicity. Am J Chin Med 47(05):1075–1097. https://doi.org/10.1142/S0192415X19500551
Sun TL, Liu Z, Qi ZJ, Huang YP, Gao XQ, Zhang YY (2016) (-)-Epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG) attenuates arsenic-induced cardiotoxicity in rats. Food Chem Toxicol 93:102–110. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fct.2016.05.004
Li S, Sun X, He Y, Guo Y, Zhao H, Hou Z, Xing M (2017) Assessment of arsenic trioxide in the heart of Gallus gallus: alterations of oxidative damage parameters, inflammatory cytokines, and cardiac enzymes. Environ Sci Pollut R 24(6):5781–5790. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-8223-7
Liguori I, Russo G, Curcio F, Bulli G, Aran L, Della-Morte D, Gargiulo G, Testa G, Cacciatore F, Bonaduce D, Abete P (2018) Oxidative stress, aging, and diseases. Clin Interv Aging 13:757–772. https://doi.org/10.2147/CIA.S158513
Gao S, Duan X, Wang X, Dong D, Liu D, Li X, Sun G, Li B (2013) Curcumin attenuates arsenic-induced hepatic injuries and oxidative stress in experimental mice through activation of Nrf2 pathway, promotion of arsenic methylation and urinary excretion. Food Chem Toxicol 59:739–747. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fct.2013.07.032
Hirano S, Cui X, Li S, Kanno S, Kobayashi Y, Hayakawa T, Shraim A (2003) Difference in uptake and toxicity of trivalent and pentavalent inorganic arsenic in rat heart microvessel endothelial cells. Arch Toxicol 77(6):305–312. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-003-0447-x
Li N, Sun Y, He L, Huang L, Li T, Wang T, Tang L (2020) Amelioration by Idesia polycarpa Maxim. var. vestita Diels. of oleic acid-induced nonalcoholic fatty liver in HepG2 cells through antioxidant and modulation of lipid metabolism. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2020:1–13. https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/1208726
Yuan S, Yang Y, Li J, Tan X, Cao Y, Li S, Hong H, Liu L, Zhang Q (2020) Ganoderma lucidum Rhodiola compound preparation prevent d-galactose-induced immune impairment and oxidative stress in aging rat model. Sci Rep-Uk 10(1):19244. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-76249-1
Pan L, Zhao Y, Farouk MH, Bao N, Wang T, Qin G (2018) Integrins were involved in soybean agglutinin induced cell apoptosis in IPEC-J2. Int J Mol Sci 19(2):587. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19020587
Rahaman MS, Banik S, Akter M, Rahman MM, Sikder MT, Hosokawa T, Saito T, Kurasaki M (2020) Curcumin alleviates arsenic-induced toxicity in PC12 cells via modulating autophagy/apoptosis. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 200:110756. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2020.110756
Shi M, Zhou L, Zhao L, Shang M, He T, Tang Z, Sun H, Ren P, Lin Z, Chen T, Yu J, Xu J, Yu X, Huang Y (2017) Csseverin inhibits apoptosis through mitochondria-mediated pathways triggered by Ca2 + dyshomeostasis in hepatocarcinoma PLC cells. PLoS Negl Trop Dis 11(11):e6074. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pntd.0006074
Savulescu D, Feng J, Ping YS, Mai O, Boehm U, He B, O’Malley BW, Melamed P (2013) Gonadotropin-releasing hormone-regulated prohibitin mediates apoptosis of the gonadotrope cells. Mol Endocrinol 27(11):1856–1870. https://doi.org/10.1210/me.2013-1210
Sakurai T, Ochiai M, Kojima C, Ohta T, Sakurai MH, Takada NO, Qu W, Waalkes MP, Himeno S, Fujiwara K (2005) Preventive mechanism of cellular glutathione in monomethylarsonic acid-induced cytolethality. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 206(1):54–65. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.taap.2004.11.008
Mi X, Hou J, Wang Z, Han Y, Ren S, Hu J, Chen C, Li W (2018) The protective effects of maltol on cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity through the AMPK-mediated PI3K/Akt and p53 signaling pathways. Sci Rep-Uk 8(1):15922. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-34156-6
Liu Y, Huang J, Zheng X, Yang X, Ding Y, Fang T, Zhang Y, Wang S, Zhang X, Luo X, Guo A, Newell KA, Yu Y, Huang X (2017) Luteolin, a natural flavonoid, inhibits methylglyoxal induced apoptosis via the mTOR/4E-BP1 signaling pathway. Sci Rep-Uk 7(1):7877. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-08204-6
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (#31402264), the Guangzhou Science and Technology Program key projects (#201803020003), and Program of Department of Natural Resources of Guangdong Province (Nos. GDME2018C014 and GDNRC [2020]038).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization: Gan Rao; methodology: Gan Rao, Gaolong Zhong, Shaofeng Wu; formal analysis and investigation: Gan Rao, Gaolong Zhong; writing-original draft preparation: Gan Rao; writing — review and editing: Jiajia Tan, Lianmei Hu; funding acquisition: Lianmei Hu; resources: Lianmei Hu; supervision: Xiaoyong Zhang, Riming Huang, Zhaoxin Tang, Lianmei Hu.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics Declarations
All animal procedures and experimental methods in this research were authorized by the Ethics Committee of South China Agricultural University. The treatment of animals in all experiments conforms to the ethical standards of experimental animals.
Consent to Participate
Not applicable.
Consent for Publication
All authors agree for publication.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
The original version of this article was revised to correct Figures 5 and 6.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rao, G., Zhong, G., Hu, T. et al. Arsenic Trioxide Triggers Mitochondrial Dysfunction, Oxidative Stress, and Apoptosis via Nrf 2/Caspase 3 Signaling Pathway in Heart of Ducks. Biol Trace Elem Res 201, 1407–1417 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-022-03219-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-022-03219-1