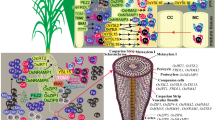
Abstract
Over three billion people suffer from various health issues due to the low supply of zinc (Zn) and iron (Fe) in their food. Low supply of micronutrients is the main cause of malnutrition and biofortification could help to solve this issue. Understanding the molecular mechanisms of biofortification is challenging. The membrane transporters are involved in the uptake, transport, storage, and redistribution of Zn and Fe in plants. These transporters are also involved in biofortification and help to load the Zn and Fe into the endosperm of the seeds. Very little knowledge is available on the role and functions of membrane transporters involved in seed biofortification. Understanding the mechanism and role of membrane transporters could be helpful to improve biofortification. In this review, we provide the details on membrane transporters involved in the uptake, transport, storage, and redistribution of Zn and Fe. We also discuss available information on transporters involved in seed biofortification. This review will help plant breeders and molecular biologists understand the importance and implications of membrane transporters for seed biofortification.





Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of Data and Materials
Not applicable to this article.
References
Lockyer S, White A, Buttriss JL (2018) Biofortified crops for tackling micronutrient deficiencies–what impact are these having in developing countries and could they be of relevance within Europe? Nutr Bull 43:319–357
Page V, Feller U (2015) Heavy metals in crop plants: transport and redistribution processes on the whole plant level. Agronomy 5:447–463
Welch RM, Norvell WA (1999) Mechanisms of cadmium uptake, translocation and deposition in plants. In: McLaughlin MJ, Singh BR (eds) Cadmium in soils and plants. Developments in Plant and Soil Sciences, vol 85. Springer, Dordrecht, 125–150
Briskin DP (1994) Membranes and transport systems in plants: an overview. Weed Sci 42:255–262
Ahmad I, Maathuis FJM (2014) Cellular and tissue distribution of potassium: physiological relevance, mechanisms and regulation. J Plant Physiol 171:708–714
Ajeesh Krishna TP, Ceasar SA, Maharajan T, Ramakrishnan M, Duraipandiyan V, Al-Dhabi NA, Ignacimuthu S (2017) Improving the zinc-use efficiency in plants: a review. SABRAO J Breed Genet 49:211–230
Ajeesh Krishna TP, Maharajan T, Victor Roch G et al (2020) Structure, function, regulation and phylogenetic relationship of ZIP family transporters of plants. Front Plant Sci. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2020.00662
Chowdhury R, Nallusamy S, Shanmugam V, et al (2022) Genome-wide understanding of evolutionary and functional relationships of rice yellow stripe-like (YSL) transporter family in comparison with other plant species. Biologia 77:39–53
Kawachi M, Nagasaki-Takeuchi N, Kato M, Maeshima M (2011) Radioisotopes: applications in bio-medical science. Nirmal S (eds) Application of radioisotopes in biochemical analyses: metal binding proteins and metal transporters. InTech 115–126
Menguer PK, Farthing E, Peaston KA et al (2013) Functional analysis of the rice vacuolar zinc transporter OsMTP1. J Exp Bot 64:2871–2883
Pinto E, Ferreira IM (2015) Cation transporters/channels in plants: tools for nutrient biofortification. J Plant Physiol 179:64–82
Tang B, Luo M, Zhang Y et al (2021) Natural variations in the P-type ATPase heavy metal transporter gene ZmHMA3 control cadmium accumulation in maize grains. J Exp Bot 72:6230–6246
Waters BM, Chu H-H, DiDonato RJ et al (2006) Mutations in Arabidopsis yellow stripe-like1 and yellow stripe-like3 reveal their roles in metal ion homeostasis and loading of metal ions in seeds. Plant Physiol 141:1446–1458
Zou W, Chen J, Meng L et al (2021) The rice cation/H+ exchanger family involved in Cd tolerance and transport. Int J Mol Sci 22:8186
Conte SS, Walker EL (2011) Transporters contributing to iron trafficking in plants. Mol Plant 4:464–476
Kobae Y, Uemura T, Sato MH et al (2004) Zinc transporter of Arabidopsis thaliana AtMTP1 is localized to vacuolar membranes and implicated in zinc homeostasis. Plant Cell Physiol 45:1749–1758
Milner MJ, Seamon J, Craft E, Kochian LV (2013) Transport properties of members of the ZIP family in plants and their role in Zn and Mn homeostasis. J Exp Bot 64:369–381
Nevo Y, Nelson N (2006) The NRAMP family of metal-ion transporters. Biochim Biophys Acta (BBA)-Molecular Cell Res 1763:609–620
Sanz A, Pike S, Khan MA et al (2019) Copper uptake mechanism of Arabidopsis thaliana high-affinity COPT transporters. Protoplasma 256:161–170
Shigaki T, Hirschi KD (2006) Diverse functions and molecular properties emerging for CAX cation/H+ exchangers in plants. Plant Biol 8:419–429
Williams LE, Mills RF (2005) P1B-ATPases–an ancient family of transition metal pumps with diverse functions in plants. Trends Plant Sci 10:491–502
Buturi CV, Mauro RP, Fogliano V et al (2021) Mineral biofortification of vegetables as a tool to improve human diet. Foods 10:223
Viana VE, Maltzahn LE, Costa de Oliveira A, Pegoraro C (2021) Genetic approaches for iron and zinc biofortification and arsenic decrease in Oryza sativa L. grains. Biol Trace Elem Res 11:1–19
Huang S, Wang P, Yamaji N, Ma JF (2020) Plant nutrition for human nutrition: hints from rice research and future perspectives. Mol Plant 13:825–835
Ishimaru Y, Suzuki M, Kobayashi T et al (2005) OsZIP4, a novel zinc-regulated zinc transporter in rice. J Exp Bot 56:3207–3214
Lee S, An G (2009) Over-expression of OsIRT1 leads to increased iron and zinc accumulations in rice. Plant Cell Environ 32:408–416
Wu T-Y, Gruissem W, Bhullar NK (2018) Facilitated citrate-dependent iron translocation increases rice endosperm iron and zinc concentrations. Plant Sci 270:13–22
Inoue H, Kobayashi T, Nozoye T et al (2009) Rice OsYSL15 is an iron-regulated iron (III)-deoxymugineic acid transporter expressed in the roots and is essential for iron uptake in early growth of the seedlings. J Biol Chem 284:3470–3479
Evens NP, Buchner P, Williams LE, Hawkesford MJ (2017) The role of ZIP transporters and group F bZIP transcription factors in the Zn-deficiency response of wheat (Triticum aestivum). Plant J 92:291–304
Connorton JM, Jones ER, Rodríguez-Ramiro I et al (2017) Wheat vacuolar iron transporter TaVIT2 transports Fe and Mn and is effective for biofortification. Plant Physiol 174:2434–2444
Gupta OP, Pandey V, Saini R et al (2021) Comparative physiological, biochemical and transcriptomic analysis of hexaploid wheat (T. aestivum L.) roots and shoots identifies potential pathways and their molecular regulatory network during Fe and Zn starvation. Genomics 113:3357–3372
Li S, Zhou X, Huang Y et al (2013) Identification and characterization of the zinc-regulated transporters, iron-regulated transporter-like protein (ZIP) gene family in maize. BMC Plant Biol 13:1–14
Han J, Song X, Li P et al (2009) Maize ZmFDR3 localized in chloroplasts is involved in iron transport. Sci China Ser C Life Sci 52:864–871
Li S, Zhou X, Li H et al (2015) Overexpression of ZmIRT1 and ZmZIP3 enhances iron and zinc accumulation in transgenic Arabidopsis. PLoS One 10:e0136647
Gustin JL, Zanis MJ, Salt DE (2011) Structure and evolution of the plant cation diffusion facilitator family of ion transporters. BMC Evol Biol 11:1–13
Kolaj-Robin O, Russell D, Hayes KA et al (2015) Cation diffusion facilitator family: structure and function. FEBS Lett 589:1283–1295
Guerinot ML (2000) The ZIP family of metal transporters. Biochim Biophys Acta (BBA)-Biomembranes 1465:190–198
Martins V, Carneiro F, Conde C et al (2017) The grapevine VvCAX3 is a cation/H+ exchanger involved in vacuolar Ca 2+ homeostasis. Planta 246:1083–1096
Neeraj J, Rajani N, Shigaki T (2009) Mining cation (CAX) transporter diversity for nutrition-enhanced crops and phytoremediation. Int J Integr Biol 7:22–25
Choe M, Choe W, Cha S, Lee I (2018) Changes of cationic transport in AtCAX5 transformant yeast by electromagnetic field environments. J Biol Phys 44:433–448
Møller J V, Juul B, le Maire M (1996) Structural organization, ion transport, and energy transduction of P-type ATPases. Biochim Biophys Acta (BBA)-Reviews Biomembr 1286:1–51
Ram H, Sardar S, Gandass N (2021) Vacuolar iron transporter (like) proteins: regulators of cellular iron accumulation in plants. Physiol Plant 171:823–832
Yang M, Li Y, Liu Z et al (2020) A high activity zinc transporter OsZIP9 mediates zinc uptake in rice. Plant J 103:1695–1709
Zhang Y, Xu Y, Yi H, Gong J (2012) Vacuolar membrane transporters OsVIT1 and OsVIT2 modulate iron translocation between flag leaves and seeds in rice. Plant J 72:400–410
Grotz N, Fox T, Connolly E et al (1998) Identification of a family of zinc transporter genes from Arabidopsis that respond to zinc deficiency. Proc Natl Acad Sci 95:7220–7224
Huang S, Sasaki A, Yamaji N et al (2020) The ZIP transporter family member OsZIP9 contributes to root zinc uptake in rice under zinc-limited conditions. Plant Physiol 183:1224–1234
Watts-Williams SJ, Wege S, Ramesh SA, et al (2020) Identification of a unique ZIP transporter involved in zinc uptake via the arbuscular mycorrhizal fungal pathway. BioRxiv
Cai H, Huang S, Che J et al (2019) The tonoplast-localized transporter OsHMA3 plays an important role in maintaining Zn homeostasis in rice. J Exp Bot 70:2717–2725
Che J, Yamaji N, Ma JF (2021) Role of a vacuolar iron transporter OsVIT2 in the distribution of iron to rice grains. New Phytol 230:1049–1062
Cao Y, Zhao X, Liu Y, et al (2019) Genome-wide identification of ZmHMAs and association of natural variation in ZmHMA2 and ZmHMA3 with leaf cadmium accumulation in maize. PeerJ 7:e7877
Li S, Liu X, Zhou X et al (2019) Improving zinc and iron accumulation in maize grains using the zinc and iron transporter ZmZIP5. Plant Cell Physiol 60:2077–2085. https://doi.org/10.1093/pcp/pcz104
Zang J, Huo Y, Liu J et al (2020) Maize YSL2 is required for iron distribution and development in kernels. J Exp Bot 71:5896–5910
Gupta OP, Pandey V, Saini R et al (2020) Identifying transcripts associated with efficient transport and accumulation of Fe and Zn in hexaploid wheat (T. aestivum L.). J Biotechnol 316:46–55
Vatansever R, Filiz E, Eroglu S (2017) Genome-wide exploration of metal tolerance protein (MTP) genes in common wheat (Triticum aestivum): insights into metal homeostasis and biofortification. Biometals 30:217–235
Menguer PK, Vincent T, Miller AJ et al (2018) Improving zinc accumulation in cereal endosperm using Hv MTP 1, a transition metal transporter. Plant Biotechnol J 16:63–71
Takahashi M, Nozoye T, Kitajima N et al (2009) In vivo analysis of metal distribution and expression of metal transporters in rice seed during germination process by microarray and X-ray fluorescence imaging of Fe, Zn, Mn, and Cu. Plant Soil 325:39–51
Díaz-Benito P, Banakar R, Rodríguez-Menéndez S et al (2018) Iron and zinc in the embryo and endosperm of rice (Oryza sativa L.) seeds in contrasting 2′-deoxymugineic acid/nicotianamine scenarios. Front Plant Sci 9:1190
Stephens BW, Cook DR, Grusak MA (2011) Characterization of zinc transport by divalent metal transporters of the ZIP family from the model legume Medicago truncatula. Biometals 24:51–58
Hall J, áL, Williams LE, (2003) Transition metal transporters in plants. J Exp Bot 54:2601–2613
Kumar L, Meena NL, Singh U (2016) Zinc transporter: mechanism for improving Zn availability. In: Singh U, Praharaj C, Singh S, Singh N (eds) Biofortification of food crops. Springer, New Delhi, 129–146
Cohen CK, Garvin DF, Kochian LV (2004) Kinetic properties of a micronutrient transporter from Pisum sativum indicate a primary function in Fe uptake from the soil. Planta 218:784–792
Gupta N, Ram H, Kumar B (2016) Mechanism of zinc absorption in plants: uptake, transport, translocation and accumulation. Rev Environ Sci Bio/Technology 15:89–109
Bashir K, Ishimaru Y, Nishizawa NK (2012) Molecular mechanisms of zinc uptake and translocation in rice. Plant Soil 361:189–201
Zhang X, Zhang D, Sun W, Wang T (2019) The adaptive mechanism of plants to iron deficiency via iron uptake, transport, and homeostasis. Int J Mol Sci 20:2424
Kim SA, Lou GM (2007) Mining iron: iron uptake and transport in plants. FEBS Lett 581:2273–2280
Kobayashi T, Nozoye T, Nishizawa NK (2019) Iron transport and its regulation in plants. Free Radic Biol Med 133:11–20
Bashir K, Seki M, Nishizawa NK (2019) The transport of essential micronutrients in rice. Mol Breed 39:1–17
Tan L, Zhu Y, Fan T et al (2019) OsZIP7 functions in xylem loading in roots and inter-vascular transfer in nodes to deliver Zn/Cd to grain in rice. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 512:112–118
Liu XS, Feng SJ, Zhang BQ et al (2019) OsZIP1 functions as a metal efflux transporter limiting excess zinc, copper and cadmium accumulation in rice. BMC Plant Biol 19:1–16
Meng L, Sun L, Tan L (2018) Progress in ZIP transporter gene family in rice. Yi Chuan= Hered 40:33–43
Lee S, Kim SA, Lee J et al (2010) Zinc deficiency-inducible OsZIP8 encodes a plasma membrane-localized zinc transporter in rice. Mol Cells 29:551–558
Ricachenevsky FK, Punshon T, Lee S et al (2018) Elemental profiling of rice FOX lines leads to characterization of a new Zn plasma membrane transporter, OsZIP7. Front Plant Sci 9:865
Ramesh SA, Shin R, Eide DJ, Schachtman DP (2003) Differential metal selectivity and gene expression of two zinc transporters from rice. Plant Physiol 133:126–134
Ishimaru Y, Masuda H, Suzuki M et al (2007) Overexpression of the OsZIP4 zinc transporter confers disarrangement of zinc distribution in rice plants. J Exp Bot 58:2909–2915
Yang X, Huang J, Jiang Y, Zhang H-S (2009) Cloning and functional identification of two members of the ZIP (Zrt, Irt-like protein) gene family in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Mol Biol Rep 36:281–287
Mondal TK, Ganie SA, Rana MK, Sharma TR (2014) Genome-wide analysis of zinc transporter genes of maize (Zea mays). Plant Mol Biol Report 32:605–616
Lilay GH, Persson DP, Castro PH et al (2021) Arabidopsis bZIP19 and bZIP23 act as zinc sensors to control plant zinc status. Nat Plants 7:137–143
Clemens S, Deinlein U, Ahmadi H et al (2013) Nicotianamine is a major player in plant Zn homeostasis. Biometals 26:623–632
Verret F, Gravot A, Auroy P et al (2005) Heavy metal transport by AtHMA4 involves the N-terminal degenerated metal binding domain and the C-terminal His11 stretch. FEBS Lett 579:1515–1522
Hussain D, Haydon MJ, Wang Y et al (2004) P-type ATPase heavy metal transporters with roles in essential zinc homeostasis in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 16:1327–1339
Verret F, Gravot A, Auroy P et al (2004) Overexpression of AtHMA4 enhances root-to-shoot translocation of zinc and cadmium and plant metal tolerance. FEBS Lett 576:306–312
Takahashi R, Bashir K, Ishimaru Y et al (2012) The role of heavy-metal ATPases, HMAs, in zinc and cadmium transport in rice. Plant Signal Behav 7:1605–1607
Sasaki A, Yamaji N, Ma JF (2014) Overexpression of OsHMA3 enhances Cd tolerance and expression of Zn transporter genes in rice. J Exp Bot 65:6013–6021
Satoh-Nagasawa N, Mori M, Nakazawa N et al (2012) Mutations in rice (Oryza sativa) heavy metal ATPase 2 (OsHMA2) restrict the translocation of zinc and cadmium. Plant Cell Physiol 53:213–224
Takahashi R, Ishimaru Y, Shimo H et al (2012) The OsHMA2 transporter is involved in root-to-shoot translocation of Zn and Cd in rice. Plant Cell Environ 35:1948–1957
Tan J, Wang J, Chai T et al (2013) Functional analyses of T a HMA 2, a P1B-type ATPase in wheat. Plant Biotechnol J 11:420–431
Moradi K, Abdollahi Mandoulakani B (2020) Expression pattern of HMA1, HMA2 and HMA9 genes under Zn deficiency conditions in bread wheat cultivars with different Zn uptake efficiency. Cereal Res 9:347–357
Zhiguo E, Tingting LI, Chen C, Lei W (2018) Genome-wide survey and expression analysis of P1B-ATPases in rice, maize and sorghum. Rice Sci 25:208–217
Song W-Y, Choi KS, Kim DY et al (2010) Arabidopsis PCR2 is a zinc exporter involved in both zinc extrusion and long-distance zinc transport. Plant Cell 22:2237–2252. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.109.070185
Ramesh SA, Choimes S, Schachtman DP (2004) Over-expression of an Arabidopsis zinc transporter in Hordeum vulgare increases short-term zinc uptake after zinc deprivation and seed zinc content. Plant Mol Biol 54:373–385
Ramegowda Y, Venkategowda R, Jagadish P et al (2013) Expression of a rice Zn transporter, OsZIP1, increases Zn concentration in tobacco and finger millet transgenic plants. Plant Biotechnol Rep 7:309–319
Bughio N, Yamaguchi H, Nishizawa NK et al (2002) Cloning an iron-regulated metal transporter from rice. J Exp Bot 53:1677–1682
Ishimaru Y, Suzuki M, Tsukamoto T, Suzuki K, Nakazono M, Kobayashi T, Wada Y, Watanabe S, Matsuhashi S, Takahashi M, Nakanishi H (2006) Rice plants take up iron as an Fe3+-phytosiderophore and as Fe2+. Plant J 45:335–346
Wang W, Ye J, Ma Y et al (2020) OsIRO3 plays an essential role in iron deficiency responses and regulates iron homeostasis in rice. Plants 9:1095
Chen WR, Feng Y, Chao YE (2008) Genomic analysis and expression pattern of OsZIP1, OsZIP3, and OsZIP4 in two rice (Oryza sativa L.) genotypes with different zinc efficiency. Russ J Plant Physiol 55:400–409
Lee S, Jeong HJ, Kim SA et al (2010) OsZIP5 is a plasma membrane zinc transporter in rice. Plant Mol Biol 73:507–517
Koike S, Inoue H, Mizuno D et al (2004) OsYSL2 is a rice metal-nicotianamine transporter that is regulated by iron and expressed in the phloem. Plant J 39:415–424
Senoura T, Sakashita E, Kobayashi T et al (2017) The iron-chelate transporter OsYSL9 plays a role in iron distribution in developing rice grains. Plant Mol Biol 95:375–387
Lee S, Kim Y-Y, Lee Y, An G (2007) Rice P1B-type heavy-metal ATPase, OsHMA9, is a metal efflux protein. Plant Physiol 145:831–842. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.107.102236
Ishimaru Y, Takahashi R, Bashir K et al (2012) Characterizing the role of rice NRAMP5 in manganese, iron and cadmium transport. Sci Rep 2:1–8
Takahashi R, Ishimaru Y, Nakanishi H, Nishizawa NK (2011) Role of the iron transporter OsNRAMP1 in cadmium uptake and accumulation in rice. Plant Signal Behav 6:1813–1816
Kakei Y, Ishimaru Y, Kobayashi T et al (2012) OsYSL16 plays a role in the allocation of iron. Plant Mol Biol 79:583–594
Singh SP, Keller B, Gruissem W, Bhullar NK (2017) Rice nicotianamine synthase 2 expression improves dietary iron and zinc levels in wheat. Theor Appl Genet 130:283–292
Ueno D, Yamaji N, Ma JF (2009) Further characterization of ferric—phytosiderophore transporters ZmYS1 and HvYS1 in maize and barley. J Exp Bot 60:3513–3520
Curie C, Panaviene Z, Loulergue C et al (2001) Maize yellow stripe1 encodes a membrane protein directly involved in Fe (III) uptake. Nature 409:346–349
Deshpande P, Dapkekar A, Oak M et al (2018) Nanocarrier-mediated foliar zinc fertilization influences expression of metal homeostasis related genes in flag leaves and enhances gluten content in durum wheat. PLoS One 13:e0191035
Sharma S, Kaur G, Kumar A et al (2020) Gene expression pattern of vacuolar-iron transporter-like (VTL) genes in hexaploid wheat during metal stress. Plants 9:229
Durmaz E, Coruh C, Dinler G et al (2011) Expression and cellular localization of ZIP1 transporter under zinc deficiency in wild emmer wheat. Plant Mol Biol Report 29:582–596
Carey-Fung O, Beasley JT (2021) Johnson AAT (2021) Annotation and molecular characterisation of the TaIRO3 and TaHRZ iron homeostasis genes in bread wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Genes 12:653
Eide D, Broderius M, Fett J, Lou GM (1996) A novel iron-regulated metal transporter from plants identified by functional expression in yeast. Proc Natl Acad Sci 93:5624–5628
Krausko M, Labajová M, Peterková D, Jásik J (2021) Specific expression of AtIRT1 in phloem companion cells suggests its role in iron translocation in aboveground plant organs. Plant Signal Behav 16:1–11
Vert G, Grotz N, Dédaldéchamp F et al (2002) IRT1, an Arabidopsis transporter essential for iron uptake from the soil and for plant growth. Plant Cell 14:1223–1233
Nakanishi H, Ogawa I, Ishimaru Y et al (2006) Iron deficiency enhances cadmium uptake and translocation mediated by the Fe2+ transporters OsIRT1 and OsIRT2 in rice. Soil Sci Plant Nutr 52:464–469
Jiang Y, Chen X, Chai S et al (2021) TpIRT1 from Polish wheat (Triticum polonicum L.) enhances the accumulation of Fe, Mn Co, and Cd in Arabidopsis. Plant Sci 312:111058
Xiong H, Kobayashi T, Kakei Y et al (2012) AhNRAMP1 iron transporter is involved in iron acquisition in peanut. J Exp Bot 63:4437–4446
Connolly EL, Campbell NH, Grotz N et al (2003) Overexpression of the FRO2 ferric chelate reductase confers tolerance to growth on low iron and uncovers posttranscriptional control. Plant Physiol 133:1102–1110
Durrett TP, Gassmann W, Rogers EE (2007) The FRD3-mediated efflux of citrate into the root vasculature is necessary for efficient iron translocation. Plant Physiol 144:197–205
Roschzttardtz H, Séguéla-Arnaud M, Briat J-F et al (2011) The FRD3 citrate effluxer promotes iron nutrition between symplastically disconnected tissues throughout Arabidopsis development. Plant Cell 23:2725–2737
Yokosho K, Yamaji N, Ueno D et al (2009) OsFRDL1 is a citrate transporter required for efficient translocation of iron in rice. Plant Physiol 149:297–305
Morrissey J, Baxter IR, Lee J et al (2009) The ferroportin metal efflux proteins function in iron and cobalt homeostasis in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 21:3326–3338. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.109.069401
Thomine S and Vert G (2013) Iron transport in plants: better be safe than sorry. Curr Opin Plant Biol 16:322–327
Lanquar V, Lelièvre F, Bolte S et al (2005) Mobilization of vacuolar iron by AtNRAMP3 and AtNRAMP4 is essential for seed germination on low iron. EMBO J 24:4041–4051
Desbrosses-Fonrouge A-G, Voigt K, Schröder A et al (2005) Arabidopsis thaliana MTP1 is a Zn transporter in the vacuolar membrane which mediates Zn detoxification and drives leaf Zn accumulation. FEBS Lett 579:4165–4174
Arrivault S, Senger T, Krämer U (2006) The Arabidopsis metal tolerance protein AtMTP3 maintains metal homeostasis by mediating Zn exclusion from the shoot under Fe deficiency and Zn oversupply. Plant J 46:861–879
Morel M, Crouzet J, Gravot A, Auroy P, Leonhardt N, Vavasseur A, Richaud P (2009) AtHMA3, a P1B-ATPase allowing Cd/Zn/co/Pb vacuolar storage in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 149:894–904
Chu H-H, Conte SS, Chan Rodriguez D et al (2013) Arabidopsis thaliana Yellow Stripe1-Like4 and Yellow Stripe1-Like6 localize to internal cellular membranes and are involved in metal ion homeostasis. Front Plant Sci 4:283
Lee S, Lee J, Ricachenevsky FK, et al (2021) Redundant roles of four ZIP family members in zinc homeostasis and seed development in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J
Gaitán-Solís E, Taylor NJ, Siritunga D et al (2015) Overexpression of the transporters AtZIP1 and AtMTP1 in cassava changes zinc accumulation and partitioning. Front Plant Sci 6:492
Tan L, Qu M, Zhu Y, Peng C, Wang J, Gao D, Chen C (2020) zinc transporter5 and zinc transporter9 function synergistically in zinc/cadmium uptake. Plant Physiol 183:1235–1249
Tan S, Han R, Li P et al (2015) Over-expression of the MxIRT1 gene increases iron and zinc content in rice seeds. Transgenic Res 24:109–122
Xiong H, Guo X, Kobayashi T et al (2014) Expression of peanut iron regulated transporter 1 in tobacco and rice plants confers improved iron nutrition. Plant Physiol Biochem 80:83–89
Masuda H, Usuda K, Kobayashi T et al (2009) Overexpression of the barley nicotianamine synthase gene HvNAS1 increases iron and zinc concentrations in rice grains. Rice 2:155–166
Nozoye T, Otani M, Senoura T et al (2017) Overexpression of barley nicotianamine synthase 1 confers tolerance in the sweet potato to iron deficiency in calcareous soil. Plant Soil 418:75–88
Barabasz A, Krämer U, Hanikenne M et al (2010) Metal accumulation in tobacco expressing Arabidopsis halleri metal hyperaccumulation gene depends on external supply. J Exp Bot 61:3057–3067
Narayanan N, Beyene G, Chauhan RD et al (2015) Overexpression of Arabidopsis VIT1 increases accumulation of iron in cassava roots and stems. Plant Sci 240:170–181
Gao F, Robe K, Gaymard F et al (2019) The transcriptional control of iron homeostasis in plants: a tale of bHLH transcription factors? Front Plant Sci 10:6
Wang N, Cui Y, Liu Y et al (2013) Requirement and functional redundancy of Ib subgroup bHLH proteins for iron deficiency responses and uptake in Arabidopsis thaliana. Mol Plant 6:503–513
Yuan Y, Wu H, Wang N et al (2008) FIT interacts with AtbHLH38 and AtbHLH39 in regulating iron uptake gene expression for iron homeostasis in Arabidopsis. Cell Res 18:385–397
Yuan YX, Zhang J, Wang DW, Ling HQ (2005) AtbHLH29 of Arabidopsis thaliana is a functional ortholog of tomato FER involved in controlling iron acquisition in strategy I plants. Cell Res 15:613–621
Colangelo EP, Lou GM (2004) The essential basic helix-loop-helix protein FIT1 is required for the iron deficiency response. Plant Cell 16:3400–3412
Jakoby M, Wang H-Y, Reidt W et al (2004) FRU (BHLH029) is required for induction of iron mobilization genes in Arabidopsis thaliana. FEBS Lett 577:528–534
Bauer P, Ling H-Q, Lou GM (2007) FIT, the FER-like iron deficiency induced transcription factor in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol Biochem 45:260–261
Kim Y-C, Kang Y, Yang E-Y, et al (2021) Applications and major achievements of genome editing in vegetable crops: a review. Front Plant Sci 12:
Ahmed T, Noman M, Shahid M et al (2021) Potential application of CRISPR/Cas9 system to engineer abiotic stress tolerance in plants. Protein Pept Lett 28:861–877
Qin Y, Park T-S, Cho YS, Lim M-H (2021) TALEN-mediated bar-knockout rice production and transcriptome profiling. Plant Breed Biotechnol 9:32–44
Ceasar SA, Rajan V, Prykhozhij SV et al (2016) Insert, remove or replace: a highly advanced genome editing system using CRISPR/Cas9. Biochim Biophys Acta - Mol Cell Res 1863:2333–2344. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbamcr.2016.06.009
Hillary VE, Ceasar SA (2019) Application of CRISPR/Cas9 genome editing system in cereal crops. Open Biotechnol J 13:
Zhang D, Zhang Z, Unver T, Zhang B (2021) CRISPR/Cas: a powerful tool for gene function study and crop improvement. J Adv Res 29:207–221
Tan L, Qu M, Zhu Y et al (2020) Zinc transporter5 and zinc transporter9 function synergistically in zinc/cadmium uptake1. Plant Physiol 183:1235–1249. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.19.01569
Inaba S, Kurata R, Kobayashi M et al (2015) Identification of putative target genes of bZIP19, a transcription factor essential for Arabidopsis adaptation to Zn deficiency in roots. Plant J 84:323–334
Zhang D, Zhang Z, Unver T, Zhang B (2020) CRISPR/Cas: a powerful tool for gene function study and crop improvement. J Adv Res
Fiaz S, Ahmad S, Noor MA et al (2019) Applications of the CRISPR/Cas9 system for rice grain quality improvement: perspectives and opportunities. Int J Mol Sci 20:888
Gindri RG, Navarro BB, da Cruz Dias PV et al (2020) Physiological responses of rice (Oryza sativa L.) oszip7 loss-of-function plants exposed to varying Zn concentrations. Physiol Mol Biol Plants 26:1349–1359
Wang Y, Yang J, Miao R, et al (2021) A novel zinc transporter essential for Arabidopsis zinc and iron-dependent growth. J Plant Physiol 256:153296
Gu D, Zhou X, Ma Y, et al (2021) Expression of a Brassica napus metal transport protein (BnMTP3) in Arabidopsis thaliana confers tolerance to Zn and Mn. Plant Sci 304:110754
Acknowledgements
We sincerely thank Rajagiri College of Social Sciences, Kochi, Kerala, for providing the research facilities and support.
Funding
This work was financially supported by Rajagiri College of Social Sciences (Autonomous), Kerala, India, under Seed Money for Faculty Minor Research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
TPAK, TM, and SAC conceptualized and wrote the manuscript. SAC critically revised the manuscript for publication.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics Approval and Consent to Participate
Not applicable.
Consent for Publication
All authors have agreed for publication.
Competing Interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Krishna, T.P.A., Maharajan, T. & Ceasar, S.A. The Role of Membrane Transporters in the Biofortification of Zinc and Iron in Plants. Biol Trace Elem Res 201, 464–478 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-022-03159-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-022-03159-w