Abstract
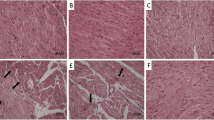
Selenium (Se) has been well recognized as an immune-enhancing agent with antioxidant and anti-tumor properties. The commonly used chemotherapy drug, cyclophosphamide (CTX), induces liver injury by increasing the reactive oxygen species (ROS) level. However, little is known about how Se alleviates CTX-induced liver injury in geese. In this study, 90 male Magang geese (3 days old) were randomly allocated into three groups (control, CTX, and Se + CTX group) with three replicates per group and ten geese per replicate. The control and CTX groups were fed a basal diet (Se content was 0.03 mg/kg). The Se + CTX group was fed a basal diet containing 0.44 mg/kg sodium selenite (Se content was 0.2 + 0.03 mg/kg). The control group was injected with 0.5 mL saline, while the CTX and Se + CTX groups were injected with CTX at 40 mg/kg body weight per day on days 21–23. The liver index, liver histology, and ultra-micromorphology detected antioxidant enzyme activity in the liver and serum. In addition, we detected the liver marker enzymes and protein levels in serum, and hepatocyte DNA damage. Se could alleviate liver development dysregulation, hepatocyte structural damage, the disturbances in antioxidant enzyme (GPx, CAT, and SOD) activity, and malondialdehyde (MDA) levels in the serum and liver. Besides, Se could alleviate the dysregulation of liver marker enzyme (ALT and AST) activity and protein (ALB and TP) levels in the serum, and DNA migration induced by CTX. In conclusion, Se may inhibit hepatocyte necrosis and DNA damage by inhibiting CTX-induced oxidative stress.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Xu D, Tian Y (2015) Selenium and polysaccharides of Atractylodes macrocephala Koidz play different roles in improving the immune response induced by heat stress in chickens. Biol Trace Elem Res 168(1):235–241
Xu D, Li W, Huang Y, He J, Tian Y (2014) The effect of selenium and polysaccharide of Atractylodes macrocephala Koidz. (PAMK) on immune response in chicken spleen under heat stress. Biol Trace Elem Res 160(2):232–237
Yao H et al (2013) Selenoprotein W serves as an antioxidant in chicken myoblasts. Biochim Biophys Acta 1830(4):3112–3120
El-Bayoumy K, Sinha R (2004) Mechanisms of mammary cancer chemoprevention by organoselenium compounds. Mutat Res Fundam Mol Mech Mutagen 551(1–2):181–197
Zheng S, Xing H, Zhang Q, Xue H, Zhu F, Xu S (2018) Pharmacokinetics of sodium selenite administered orally in blood and tissues of selenium-deficient ducklings. Biol Trace Elem Res. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-018-1567-8
Milošević M et al (2018) Role of selenium and vitamin C in mitigating oxidative stress induced by fenitrothion in rat liver. Biomed Pharmacother 106:232–238
Wang Y, Xiao X, Zhan X (2018) Antagonistic effects of different selenium sources on growth inhibition, oxidative damage, and apoptosis induced by fluorine in broilers. Poult Sci 97(9):3207–3217
Li B, Liu Y, Li W, Tian Y, Xu D, Cao N (2018) Effect of selenium on ion profiles and antioxidant defense in mice livers. Biol Trace Elem Res 184(1):127–135
Ognjanovi B et al (2012) Lipid peroxidative damage on cisplatin exposure and alterations in antioxidant defense system in rat kidneys: a possible protective effect of selenium. Int J Mol Sci 13(2):1790–1803
Wang F, Shu G, Peng X, Fang J, Chen K, Cui H, Chen Z, Zuo Z, Deng J, Geng Y, Lai W (2013) Protective effects of sodium selenite against aflatoxin B1-induced oxidative stress and apoptosis in broiler spleen. Int J Environ Res Public Health 10(7):2834–2844
Young B et al (2013) The role of cyclophosphamide in enhancing antitumor efficacy of an adenovirus oncolytic vector in subcutaneous Syrian hamster tumors. Cancer Gene Ther 20(9):521–530
Ettaya A, Dhibi S, Samout N, Elfeki A, Hfaiedh N (2016) Hepatoprotective activity of white horehound (Marrubium vulgare) extract against cyclophosphamide toxicity in male rats. Can J Physiol Pharmacol 94(4):441–447
Huang G et al (2013) Hepatoprotective effects of eburicoic acid and dehydroeburicoic acid from Antrodia camphorata in a mouse model of acute hepatic injury. Food Chem 141(3):3020–3027
Mythili Y, Sudharsan PT, Selvakumar E, Varalakshmi P (2004) Protective effect of DL-alpha-lipoic acid on cyclophosphamide induced oxidative cardiac injury. Chem Biol Interact 151(1):13–19
Zhao X, Wang Y, Yan P, Cheng G, Wang C, Geng N, Wang X, Liu J (2017) Effects of polysaccharides from platycodon grandiflorum on immunity-enhancing activity in vitro. Molecules 22(11):1918. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22111918
Sanchez-Valle V, C. Chavez-Tapia N, Uribe M, Mendez-Sanchez N (2012) Role of oxidative stress and molecular changes in liver fibrosis: a review. Curr Med Chem 19(28):4850–4860
Wang Y, Zhao H, Guo M, Shao Y, Liu J, Jiang G, Xing M (2018) Arsenite renal apoptotic effects in chickens co-aggravated by oxidative stress and inflammatory response. Metallomics 10(12):1805–1813
Zhao H, Wang Y, Shao Y, Liu J, Wang S, Xing M (2018) Oxidative stress-induced skeletal muscle injury involves in NF-kappaB/p53-activated immunosuppression and apoptosis response in copper (II) or/and arsenite-exposed chicken. Chemosphere 210:76–84
Li A et al (2014) Resources and biological activities of natural polyphenols. Nutrients 6(12):6020–6047
Gunes S, Sahinturk V, Karasati P, Sahin IK, Ayhanci A (2017) Cardioprotective effect of selenium against cyclophosphamide-induced cardiotoxicity in rats. Biol Trace Elem Res 177(1):107–114
Gunes S, Sahinturk V, Uslu S, Ayhanci A, Kacar S, Uyar R (2018) Protective effects of selenium on cyclophosphamide-induced oxidative stress and kidney injury. Biol Trace Elem Res 185(1):116–123
Bhattacharjee A, Basu A, Biswas J, Bhattacharya S (2015) Nano-Se attenuates cyclophosphamide-induced pulmonary injury through modulation of oxidative stress and DNA damage in Swiss albino mice. Mol Cell Biochem 405(1–2):243–256
Li W, Guo S, Xu D, Li B, Cao N, Tian Y, Jiang Q (2018) Polysaccharide of Atractylodes macrocephala Koidz (PAMK) relieves immunosuppression in cyclophosphamide-treated geese by maintaining a humoral and cellular immune balance. Molecules 23(4):E932. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23040932
Wang W, Chen M, Jin X, Li X, Yang Z, Lin H, Xu S (2018) H2S induces Th1/Th2 imbalance with triggered NF-κB pathway to exacerbate LPS-induce chicken pneumonia response. Chemosphere 208:241–246
Zheng S, Jin X, Chen M, Shi Q, Zhang H, Xu S (2019) Hydrogen sulfide exposure induces jejunum injury via CYP450s/ROS pathway in broilers. Chemosphere 214:25–34
Singh C, Prakash C, Tiwari KN, Mishra SK, Kumar V (2018) Premna integrifolia ameliorates cyclophosphamide-induced hepatotoxicity by modulation of oxidative stress and apoptosis. Biomed Pharmacother 107:634–643
Fouad A, Qutub H, Al-Melhim W (2016) Punicalagin alleviates hepatotoxicity in rats challenged with cyclophosphamide. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 45:158–162
Kamel E et al (2016) A phytochemical and computational study on flavonoids isolated from Trifolium resupinatum L. and their novel hepatoprotective activity. Food Funct 7(4):2094–2106
Ahmadi A, Hosseinimehr SJ, Naghshvar F, Hajir E, Ghahremani M (2008) Chemoprotective effects of hesperidin against genotoxicity induced by cyclophosphamide in mice bone marrow cells. Arch Pharm Res 31(6):794–797
Jiang W, Liu J, Li P, Lu Q, Pei X, Sun Y, Wang G, Hao K (2017) Magnesium isoglycyrrhizinate shows hepatoprotective effects in a cyclophosphamide-induced model of hepatic injury. Oncotarget 8(20):33252–33264
Wang Y, Zhao H, Shao Y, Liu J, Li J, Luo L, Xing M (2018) Copper (II) and/or arsenite-induced oxidative stress cascades apoptosis and autophagy in the skeletal muscles of chicken. Chemosphere 206:597–605
Elshater A et al (2018) Fullerene C 60 nanoparticles ameliorated cyclophosphamide-induced acute hepatotoxicity in rats. Biomed Pharmacother 97:53–59
Selvakumar E, Prahalathan C, Mythili Y, Varalakshmi P (2005) Beneficial effects of dl-alpha-lipoic acid on cyclophosphamide-induced oxidative stress in mitochondrial fractions of rat testis. Chem Biol Interact 152(1):59–66
Jin X, Jia T, Liu R, Xu S (2018) The antagonistic effect of selenium on cadmium-induced apoptosis via PPAR-γ/PI3K/Akt pathway in chicken pancreas. J Hazard Mater 357:355–362
Yao H et al (2013) Gene expression of endoplasmic reticulum resident selenoproteins correlates with apoptosis in various muscles of Se-deficient chicks. J Nutr 143(5):613–619
Wang Y, Zhan XA, Yuan D, Zhang XW, Wu RJ (2011) Influence of dietary selenomethionine supplementation on performance and selenium status of broiler breeders and their subsequent progeny. Biol Trace Elem Res 143(3):1497–1507
Talas Z et al (2009) Antioxidative effects of novel synthetic organoselenium compound in rat lung and kidney. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 72(3):916–921
Godoy P, Hewitt NJ, Albrecht U, Andersen ME, Ansari N, Bhattacharya S, Bode JG, Bolleyn J, Borner C, Böttger J, Braeuning A, Budinsky RA, Burkhardt B, Cameron NR, Camussi G, Cho CS, Choi YJ, Craig Rowlands J, Dahmen U, Damm G, Dirsch O, Donato MT, Dong J, Dooley S, Drasdo D, Eakins R, Ferreira KS, Fonsato V, Fraczek J, Gebhardt R, Gibson A, Glanemann M, Goldring CEP, Gómez-Lechón MJ, Groothuis GMM, Gustavsson L, Guyot C, Hallifax D, Hammad S, Hayward A, Häussinger D, Hellerbrand C, Hewitt P, Hoehme S, Holzhütter HG, Houston JB, Hrach J, Ito K, Jaeschke H, Keitel V, Kelm JM, Kevin Park B, Kordes C, Kullak-Ublick GA, LeCluyse EL, Lu P, Luebke-Wheeler J, Lutz A, Maltman DJ, Matz-Soja M, McMullen P, Merfort I, Messner S, Meyer C, Mwinyi J, Naisbitt DJ, Nussler AK, Olinga P, Pampaloni F, Pi J, Pluta L, Przyborski SA, Ramachandran A, Rogiers V, Rowe C, Schelcher C, Schmich K, Schwarz M, Singh B, Stelzer EHK, Stieger B, Stöber R, Sugiyama Y, Tetta C, Thasler WE, Vanhaecke T, Vinken M, Weiss TS, Widera A, Woods CG, Xu JJ, Yarborough KM, Hengstler JG (2013) Recent advances in 2D and 3D in vitro systems using primary hepatocytes, alternative hepatocyte sources and non-parenchymal liver cells and their use in investigating mechanisms of hepatotoxicity, cell signaling and ADME. Arch Toxicol 87(8):1315–1530
Dalia A et al (2017) The effect of dietary bacterial organic selenium on growth performance, antioxidant capacity, and selenoproteins gene expression in broiler chickens. BMC Vet Res 13(1):254. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12917-017-1159-4
Sefi M, Ben Amara I, Troudi A, Soudani N, Hakim A, Zeghal KM, Boudawara T, Zeghal N (2012) Effect of selenium on methimazole-induced liver damage and oxidative stress in adult rats and their offspring. Toxicol Ind Health 30(7):653–669
Senthilkumar S, Devaki T, Manohar BM, Babu MS (2006) Effect of squalene on cyclophosphamide-induced toxicity. Clin Chim Acta 364(1–2):335–342
Al-Jafari A et al (2011) Human platelet acetylcholinesterase inhibition by cyclophosphamide: a combined experimental and computational approach. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets 10(8):928–935
Amara I et al (2012) Dimethoate induced oxidative damage and histopathological changes in lung of adult rats: modulatory effects of selenium and/or vitamin E. Biomed Environ Sci 25(3):340–351
Dechsupa S, Yingsakmongkol W, Limthongkul W, Singhatanadgige W, Honsawek S (2018) Relative telomere length and oxidative DNA damage in hypertrophic ligamentum flavum of lumbar spinal stenosis. PeerJ 6:e5381. https://doi.org/10.7717/peerj.5381
Abd El-Moneim O, Abd El-Rahim A, Hafiz N (2018) Evaluation of selenium nanoparticles and doxorubicin effect against hepatocellular carcinoma rat model cytogenetic toxicity and DNA damage. Toxicol Rep 5:771–776
Bhattacharjee A et al (2013) Protective effect of selenium nanoparticle against cyclophosphamide induced hepatotoxicity and genotoxicity in Swiss albino mice. J Biomater Appl 29(2):303–317
Acknowledgements
We appreciate the support of Guangdong Province Key Laboratory of Waterfowl Healthy Breeding, Guangzhou 510225, China.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Key Technologies R&D Program of China (No. 2016YFD0501605), Major Research Project in Universities of Guangdong Province (No. 2017KZDXM046), Inter-governmental S & T Exchanges Project between China and Belarus (No. CB01-13), and Science & Technology Planning Project of Guangzhou (No. 201604020061).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, B., Li, W., Tian, Y. et al. Selenium-Alleviated Hepatocyte Necrosis and DNA Damage in Cyclophosphamide-Treated Geese by Mitigating Oxidative Stress. Biol Trace Elem Res 193, 508–516 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-019-01717-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-019-01717-3